Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
HOW I TREAT
How I treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia after venetoclax
Venetoclax therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) yields high remission rates with durable disease control. However, in patients with relapsed or refractory disease, progression is frequent. Lew et al discuss mechanisms of venetoclax resistance and use a series of 5 illustrative cases to outline their approach to the treatment of patients with CLL who relapse after time-limited or continuous venetoclax therapy.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
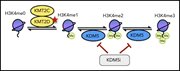
KDM5 inhibition offers a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of KMT2D mutant lymphomas
Loss-of-function mutations in the histone-methyltransferase KMT2D occur in a subset of lymphomas and are associated with decreased H3K4 methylation and changes in gene expression that are not easily targeted directly. Heward and colleagues demonstrate that inhibition of KDM5 demethylase increases H3K4 methylation and decreases proliferation of KMT2D-mutated lymphomas in vitro and in xenografts, suggesting a potential therapeutic strategy for KMT2D-mutant lymphoma.
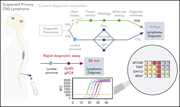
A rapid genotyping panel for detection of primary central nervous system lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Diagnosing primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) frequently requires a brain biopsy because radiographic findings are nonspecific and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) histology is positive in only 10% to 15% of cases. Gupta et al used archived specimens from PCNSL cases to confirm that a rapid genotyping assay of CSF was 57.6% sensitive and 100% specific for the diagnosis, suggesting that use of this assay would speed diagnosis and avoid neurosurgical sampling for some patients.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
Multisite 11-year experience of less-intensive vs intensive therapies in acute myeloid leukemia
Clinical Trials & Observations
Sorror et al examine the outcomes of less-intensive vs intensive therapy for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in a retrospective cohort and a prospective observational cohort to assess the validity of opting for less-intensive therapy for older patients and use an AML-composite model (AML-CM) to assign risk scores to correlate with outcomes. Less-intensive therapy is not associated with benefit for survival or quality of life, but did result in less time in hospital. The lack of definitive answers argues for a randomized clinical trial of treatment of elderly patients with AML.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
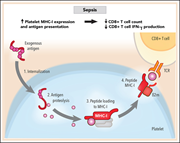
Platelet MHC class I mediates CD8+ T-cell suppression during sepsis
Guo et al report on another novel role for platelets outside the realm of hemostasis. They demonstrate that in the setting of sepsis, platelets internalize, proteolyze, and present antigens to downregulate CD8+ T-cell number and function.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Vitamin K antagonists did not increase the risk of myelodysplastic syndrome in a large-scale cohort study
Clinical Trials & Observations
It has recently been reported that vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) impair the bone marrow microenvironment and may predispose to myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). In a study of the French national health care database, Neumann et al examined data on this issue for more than 120 000 individuals on oral anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation, confirming that there is no increase in MDS in patients treated with VKAs in comparison with those treated with direct oral anticoagulants.
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Isolated platelets from a patient with sepsis costained for CD41 (white) and major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I; orange) proteins and imaged by immunocytochemistry. The antibody used for MHC-I detects all 3 human HLAs corresponding to MHC-I (HLA-A,HLA-B, and HLA-C). See the article by Guo et al on page 401.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





Epigenetic balance in DLBCL