Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPERS
Single-cell analysis of ploidy and the transcriptome reveals functional and spatial divergency in murine megakaryopoiesis
Recent data indicate that lung megakaryocytes (MKs) can have functions beyond platelet production, with some lung MKs exhibiting phagocytosis and antigen presentation. In this Plenary Paper, Sun and colleagues discuss the use of single-cell transcriptomics, spatial discrimination, and functional assays to demonstrate the presence of 3 distinct functional subsets of MKs in murine and human bone marrow: platelet-producing, stem cell niche–supporting, and immune MKs. This paper raises new questions about this multifunctional lineage and provides cutting-edge techniques to begin answering them.
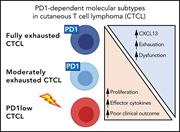
Integrated genomic analyses of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas reveal the molecular bases for disease heterogeneity
Park et al report a comprehensive analysis of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (CTCLs), including whole-exome and -genome sequencing, RNA sequencing, mass cytometry, functional assays, and murine modeling. They lay out the genetic landscape of mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome, suggest a new stage-specific molecular classification, and identify PD1 as a putative contributor to CTCL pathogenesis. This Plenary Paper will further shape our thinking about CTCL classification and therapy selection.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
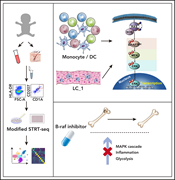
Transcriptomic landscape of circulating mononuclear phagocytes in Langerhans cell histiocytosis at the single-cell level
Shi and colleagues utilized immunophenotyping and single-cell RNA sequencing to identify differentially expressed genes in populations of circulating mononuclear cells from pediatric patients with Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH). They report universal mitogen-activated protein kinase activation, both related and unrelated to activating BRAF mutations, and a decreased frequency of circulating plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Their observations help explain how the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib may ameliorate inflammatory aspects of the disease.
PHAGOCYTES, GRANULOCYTES, AND MYELOPOIESIS
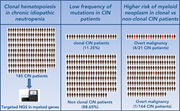
Incidence and prognosis of clonal hematopoiesis in patients with chronic idiopathic neutropenia
Clinical Trials & Observations
Chronic idiopathic neutropenia (CIN) is isolated neutropenia without a known cause that occurs from late childhood, primarily affects women, and typically runs a benign course. Tsaknakis et al used targeted next-generation sequencing to determine the frequency and clinical significance of clonal hematopoiesis (CH) in a cohort of 185 patients. They report that CH is less common than reported for other forms of isolated cytopenias of undetermined significance but that if CH is detected, it is associated with a higher risk of developing a myeloid neoplasm.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
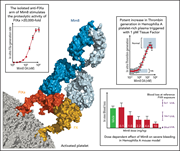
A factor VIIIa–mimetic bispecific antibody, Mim8, ameliorates bleeding upon severe vascular challenge in hemophilia A mice
Østergaard and colleagues report the development of a potent bispecific antibody, Mim8, which binds both activated factor IX and factor X, mimicking the propagation of coagulation by activated factor VIII. They detail biophysical, in vitro, and in vivo preclinical data supporting its potential as a treatment for bleeding in hemophilia A.
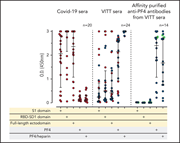
Anti–platelet factor 4 antibodies causing VITT do not cross-react with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
Greinacher et al addressed the important question of whether vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) involves anti–platelet factor 4 (PF4) antibodies that cross-react with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)–encoded spike protein, the antigen presented by COVID-19 vaccines. They report that immune responses to PF4 and to the spike protein are independent of one another and that antibodies from patients with VITT do not cross-react with the spike protein. These data confirm that SARS-CoV-2 spike protein antigen remains an appropriate target for ongoing COVID-19 vaccination strategies.
LETTER TO BLOOD
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
In situ immunostaining of platelet-generating megakaryocytes (MKs), which were defined by expression of ARNTL (green) and costained with CD41 (red), in murine bone marrow. Platelet-generating MKs, shown as yellow cells in the merged picture, were physically close to CD105+ blood vessels (violet). See the article by Sun et al on page 1211.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals


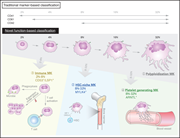

The megakaryocyte: a cell with 3 faces as a mythic god?