Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
We didn’t start the fire, MDSC inflammasome signaling in GVHD
Danger-associated extracellular ATP counters MDSC therapeutic efficacy in acute GVHD
These studies demonstrate how activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway influences the function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in the setting of acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD).
BLOOD SPOTLIGHT
Duvelisib for CLL/SLL and follicular non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
In this Blood Spotlight, the authors review the appropriate clinical background, mechanism of action, and detailed therapeutic data about duvelisib in chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) and follicular lymphoma.
REVIEW ARTICLE
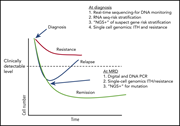
New approaches to molecular monitoring in CML (and other diseases)
In a review article, the authors discuss the present and future of molecular testing in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) as a paradigm of the evolution of technologies assisting in better diagnosis, risk stratification, and response monitoring of leukemia and other cancers.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
γ-Secretase inhibition increases efficacy of BCMA-specific chimeric antigen receptor T cells in multiple myeloma
Despite notably high response rates to B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells in multiple myeloma, few patients have a sustained, very good partial or complete response. This article presents a novel strategy to increase the efficacy of BCMA-directed CAR T-cell therapy and shows that γ-secretase inhibitors improve the efficacy of BCMA CAR T cells by increasing BCMA expression and reducing soluble BCMA.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
The whole-genome landscape of Burkitt lymphoma subtypes
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
Measurable residual disease monitoring in acute myeloid leukemia with t(8;21)(q22;q22.1): results from the AML Study Group
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
Chromatin occupancy and epigenetic analysis reveal new insights into the function of the GATA1 N terminus in erythropoiesis
GATA1 has a foundational role in erythropoiesis. The investigators compare the function of 2 forms (the full-length protein and a shorter form) of the transcription factor GATA1 and show that the N-terminal domain of GATA1 is critical to red cell differentiation.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
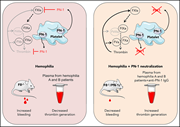
Targeting protease nexin-1, a natural anticoagulant serpin, to control bleeding and improve hemostasis in hemophilia
Targeting natural anticoagulant proteins as a means to rebalance the hemostatic system is an emerging trend in the development of innovative therapeutic strategies for hemophilia. These 2 articles develop these concepts in the areas of hemostasis and contact activation. In the study by Aymonnier and colleagues, simple amino acid substitutions converted a serpin elastase inhibitor, α1-antitrypsin (α1AT), into a potent antithrombin, activated protein C inhibitor, or anti-PKa/FXIIa inhibitor. In the study by de Maat and colleagues, redesign of α1AT strongly altered its inhibitory behavior and enables it to be used for the treatment of contact system–mediated thrombosis and inflammation.
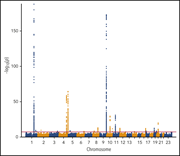
Genomic and transcriptomic association studies identify 16 novel susceptibility loci for venous thromboembolism
In this work related to familial aggregation of familial venous thromboembolism, the investigators report genomic and transcriptomic association of 16 novel susceptibility loci for venous thromboembolism.
Design and characterization of α1-antitrypsin variants for treatment of contact system–driven thromboinflammation
Targeting natural anticoagulant proteins as a means to rebalance the hemostatic system is an emerging trend in the development of innovative therapeutic strategies for hemophilia. These 2 articles develop these concepts in the areas of hemostasis and contact activation. In the study by Aymonnier and colleagues, simple amino acid substitutions converted a serpin elastase inhibitor, α1-antitrypsin (α1AT), into a potent antithrombin, activated protein C inhibitor, or anti-PKa/FXIIa inhibitor. In the study by de Maat and colleagues, redesign of α1AT strongly altered its inhibitory behavior and enables it to be used for the treatment of contact system–mediated thrombosis and inflammation.
TRANSPLANTATION
Danger-associated extracellular ATP counters MDSC therapeutic efficacy in acute GVHD
These studies demonstrate how activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway influences the function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in the setting of acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD).
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Benzidine-stained burst-forming unit–erythroid (BFU-E) colony derived from Gata1s mutant mice that are haploinsufficient for Gata2. The deficiency in erythropoiesis in Gata1s embryos can be rescued by reducing the levels of GATA2. See the article by Ling et al on page 1619.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon AdvertisingAdvertising
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






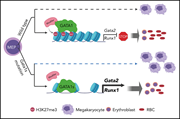


Chromatin occupancy and epigenetic analysis reveal new insights into the function of the GATA1 N terminus in erythropoiesis
GATA1 has a foundational role in erythropoiesis. The investigators compare the function of 2 forms (the full-length protein and a shorter form) of the transcription factor GATA1 and show that the N-terminal domain of GATA1 is critical to red cell differentiation.