Issue Archive
Table of Contents
EDITORIAL
Introduction to a review series on follicular lymphoma: solved or insoluble problem?
Although there have been many therapeutic advances in follicular lymphoma (FL) in recent years, important questions remain about how best to integrate emerging biologic insights with evolving treatment options. To address these challenges, Associate Editor Philippe Armand has assembled a comprehensive review series. Araujo-Ayala and Béguelin highlight recent advances in the biological understanding of FL, including its evolutionary pathways and therapeutic vulnerabilities. Bachy and Linton examine the challenges of designing and conducting frontline clinical trials and propose strategies to overcome them. Casulo and Sehn outline a personalized approach to managing relapsed or refractory FL. Mulvey et al explore the promise of novel assays and treatments that may shape the next era of FL care. Di et al consider key issues in trial design, particularly given the prolonged benefit seen with many current therapies. Parry and Okosun review the biology of histologic transformation and its clinical management, which is still one of the most difficult aspects of FL treatment.
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
High-dose busulfan-melphalan vs melphalan and reinforced VRD for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: a phase 3 GEM trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
While retrospective studies suggest a potential advantage of busulfan-melphalan (BUMEL) over standard high-dose melphalan (MEL200) conditioning for transplant-eligible newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, the benefit remains uncertain. Lahuerta et al report results of the phase 3 GEM12 trial directly comparing BUMEL with MEL200 in the context of an intensified bortezomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone–based first-line approach. Both deliver excellent progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival; a longer PFS was seen with BUMEL in patients with International Staging System (ISS) stage II-III disease and in those with high-risk cytogenetics [del(1p) or t(14;16)], whereas MEL200 was superior in ISS stage I disease. Despite the rapid evolution of frontline myeloma therapy, this well-conducted study suggests a possible role for intensified consolidation with BUMEL for selected patients.
REVIEW SERIES
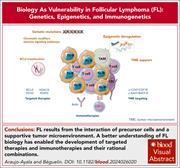
Biology as vulnerability in follicular lymphoma: genetics, epigenetics, and immunogenetics
Although there have been many therapeutic advances in follicular lymphoma (FL) in recent years, important questions remain about how best to integrate emerging biologic insights with evolving treatment options. To address these challenges, Associate Editor Philippe Armand has assembled a comprehensive review series. Araujo-Ayala and Béguelin highlight recent advances in the biological understanding of FL, including its evolutionary pathways and therapeutic vulnerabilities. Bachy and Linton examine the challenges of designing and conducting frontline clinical trials and propose strategies to overcome them. Casulo and Sehn outline a personalized approach to managing relapsed or refractory FL. Mulvey et al explore the promise of novel assays and treatments that may shape the next era of FL care. Di et al consider key issues in trial design, particularly given the prolonged benefit seen with many current therapies. Parry and Okosun review the biology of histologic transformation and its clinical management, which is still one of the most difficult aspects of FL treatment.
Frontline treatment of follicular lymphoma: what will it take to change current practice?
Although there have been many therapeutic advances in follicular lymphoma (FL) in recent years, important questions remain about how best to integrate emerging biologic insights with evolving treatment options. To address these challenges, Associate Editor Philippe Armand has assembled a comprehensive review series. Araujo-Ayala and Béguelin highlight recent advances in the biological understanding of FL, including its evolutionary pathways and therapeutic vulnerabilities. Bachy and Linton examine the challenges of designing and conducting frontline clinical trials and propose strategies to overcome them. Casulo and Sehn outline a personalized approach to managing relapsed or refractory FL. Mulvey et al explore the promise of novel assays and treatments that may shape the next era of FL care. Di et al consider key issues in trial design, particularly given the prolonged benefit seen with many current therapies. Parry and Okosun review the biology of histologic transformation and its clinical management, which is still one of the most difficult aspects of FL treatment.
Treatment of relapsed and refractory follicular lymphoma: which treatment for which patient for which line of therapy?
Clinical Trials & Observations
Although there have been many therapeutic advances in follicular lymphoma (FL) in recent years, important questions remain about how best to integrate emerging biologic insights with evolving treatment options. To address these challenges, Associate Editor Philippe Armand has assembled a comprehensive review series. Araujo-Ayala and Béguelin highlight recent advances in the biological understanding of FL, including its evolutionary pathways and therapeutic vulnerabilities. Bachy and Linton examine the challenges of designing and conducting frontline clinical trials and propose strategies to overcome them. Casulo and Sehn outline a personalized approach to managing relapsed or refractory FL. Mulvey et al explore the promise of novel assays and treatments that may shape the next era of FL care. Di et al consider key issues in trial design, particularly given the prolonged benefit seen with many current therapies. Parry and Okosun review the biology of histologic transformation and its clinical management, which is still one of the most difficult aspects of FL treatment.
The future of follicular lymphoma management: strategies on the horizon
Although there have been many therapeutic advances in follicular lymphoma (FL) in recent years, important questions remain about how best to integrate emerging biologic insights with evolving treatment options. To address these challenges, Associate Editor Philippe Armand has assembled a comprehensive review series. Araujo-Ayala and Béguelin highlight recent advances in the biological understanding of FL, including its evolutionary pathways and therapeutic vulnerabilities. Bachy and Linton examine the challenges of designing and conducting frontline clinical trials and propose strategies to overcome them. Casulo and Sehn outline a personalized approach to managing relapsed or refractory FL. Mulvey et al explore the promise of novel assays and treatments that may shape the next era of FL care. Di et al consider key issues in trial design, particularly given the prolonged benefit seen with many current therapies. Parry and Okosun review the biology of histologic transformation and its clinical management, which is still one of the most difficult aspects of FL treatment.
End points and outcomes in follicular lymphoma: what should we measure, how, and why?
Clinical Trials & Observations
Although there have been many therapeutic advances in follicular lymphoma (FL) in recent years, important questions remain about how best to integrate emerging biologic insights with evolving treatment options. To address these challenges, Associate Editor Philippe Armand has assembled a comprehensive review series. Araujo-Ayala and Béguelin highlight recent advances in the biological understanding of FL, including its evolutionary pathways and therapeutic vulnerabilities. Bachy and Linton examine the challenges of designing and conducting frontline clinical trials and propose strategies to overcome them. Casulo and Sehn outline a personalized approach to managing relapsed or refractory FL. Mulvey et al explore the promise of novel assays and treatments that may shape the next era of FL care. Di et al consider key issues in trial design, particularly given the prolonged benefit seen with many current therapies. Parry and Okosun review the biology of histologic transformation and its clinical management, which is still one of the most difficult aspects of FL treatment.
An updated understanding of follicular lymphoma transformation
Although there have been many therapeutic advances in follicular lymphoma (FL) in recent years, important questions remain about how best to integrate emerging biologic insights with evolving treatment options. To address these challenges, Associate Editor Philippe Armand has assembled a comprehensive review series. Araujo-Ayala and Béguelin highlight recent advances in the biological understanding of FL, including its evolutionary pathways and therapeutic vulnerabilities. Bachy and Linton examine the challenges of designing and conducting frontline clinical trials and propose strategies to overcome them. Casulo and Sehn outline a personalized approach to managing relapsed or refractory FL. Mulvey et al explore the promise of novel assays and treatments that may shape the next era of FL care. Di et al consider key issues in trial design, particularly given the prolonged benefit seen with many current therapies. Parry and Okosun review the biology of histologic transformation and its clinical management, which is still one of the most difficult aspects of FL treatment.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
Preclinical advances in glofitamab combinations: a new frontier for non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) that simultaneously bind a tumor-associated antigen (such as CD20) and the CD3 ε subunit on T cells have demonstrated strong activity in relapsed B-cell lymphoma and are now being evaluated earlier in the treatment course and in combination strategies. Sam et al leveraged humanized mouse models to investigate the efficacy of glofitamab, a CD20×CD3 BsAb, in combination with multiple therapeutic modalities and demonstrated that glofitamab combined with chemotherapy or antibody-drug conjugates produces marked synergy. These findings provide a rational framework for the design of clinical trial combinations with BsAbs.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
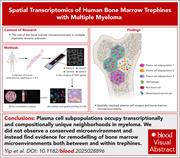
Profiling the spatial architecture of multiple myeloma in human bone marrow trephine biopsy specimens with spatial transcriptomics
While the bone marrow (BM) microenvironment influences multiple myeloma (MM) biology, the precise nature of these interactions remains poorly understood. Yip et al applied spatial transcriptomics to BM trephine biopsies from patients with precursor plasma cell dyscrasias and newly diagnosed MM to investigate the interplay between plasma cell subpopulations and their surrounding microenvironment. They did not observe a conserved tumor microenvironment (TME), finding that differences in cellular composition between distinct intratumoral neighborhoods are more pronounced than those observed between precursor stages and MM, and there were no consistent TME changes across disease stages. These findings challenge the prevailing assumption that broad, BM-wide microenvironmental changes are the primary drivers of progression in plasma cell disorders.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
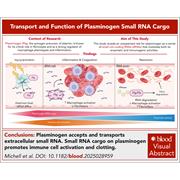
Plasminogen as a ribonucleoprotein: regulatory small RNA cargo modulates fibrinolysis and inflammation
Plasminogen (Plg), the zymogen precursor of plasmin, is well known for its central role in fibrinolysis and its ability to regulate macrophage phenotypes and inflammation. Michell et al identified an unexpected function of Plg as a carrier of small noncoding RNAs (sRNAs) that promote both immune cell activation and clotting. This discovery positions Plg-sRNA interactions as promising therapeutic targets for the treatment of thrombotic and inflammatory diseases.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Induction chemotherapy and molecular MRD influence outcomes in KMT2A-rearranged AML
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Single-cell transcriptomics of a human bone marrow trephine biopsy specimen from a lymphoma patient with no marrow involvement. Cell types are color coded using Factor Inference of Cartographic Transcriptome at Ultra-high REsolution (FICTURE) based on reference single-cell sequencing data. See the article by Yip et al on page 1837.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals










Mel200 or BuMel conditioning in myeloma: is there a winner?
Clinical Trials & Observations