Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
HOW I TREAT
How I use next-generation sequencing–MRD to plan approach and prevent relapse after HCT for children and adults with ALL
Muffly et al describe their algorithm for using next-generation sequencing (NGS) detection of MRD in the assessment of patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) before and after hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT). Using a patient case review, the authors discuss how NGS-MRD improves pre-HCT risk classification and post-HCT monitoring and can inform alternative approaches to prevent relapse.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
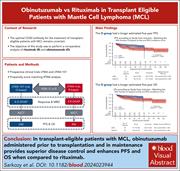
Obinutuzumab vs rituximab for transplant-eligible patients with mantle cell lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
The efficacy of obinutuzumab (O) vs rituximab (R) in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) has not been studied in a prospective randomized trial. Sarkozy et al report long-term outcomes of the LyMa-101 trial of O plus chemotherapy (CMT) before autologous transplant (Auto) for newly diagnosed patients with MCL. The authors performed a propensity score–matching analysis comparing these outcomes to those of the LyMa study using R plus CMT. Treatment with O resulted in improved estimated progression-free and overall survival, with improved MRD negativity at the end of induction compared to R. Since a randomized trial is unlikely to occur, this evidence could support O as the CD20 inhibitor of choice to combine with CMT before Auto for MCL.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Acalabrutinib, venetoclax, and obinutuzumab in relapsed/refractory CLL: final efficacy and ctDNA analysis of the CLL2-BAAG trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Fürstenau and colleagues report on the final analysis of the phase 2 CLL2-BAAG trial of measurable residual disease (MRD)–guided therapy with acalabrutinib, venetoclax, and obinutuzumab in 45 patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). At a median follow-up of 3 years, undetectable MRD was achieved in over 90% of patients, including those with TP53 abnormalities. Progression-free and overall survival rates were 85% and 93.8%, respectively. These findings support this triplet as an excellent choice for treating R/R CLL.
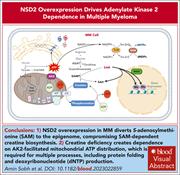
NSD2 drives t(4;14) myeloma cell dependence on adenylate kinase 2 by diverting one-carbon metabolism to the epigenome
Sobh and colleagues probed the molecular pathogenesis of the poor-prognosis subset of multiple myeloma (MM) bearing the chromosomal translocation t(4;14), which has been shown to drive overexpression of the histone methyltransferase nuclear receptor-binding SET domain protein 2 (NSD2). In a CRISPR screen, the authors identified adenylate kinase 2 (AK2) as an NSD2-driven vulnerability of t(4;14) MM cells. AK2 suppression decreased nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, leading to replication stress, DNA damage, and apoptosis, identifying a novel metabolic vulnerability in t(4;14) MM, driven by aberrant epigenomic carbon transfer.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
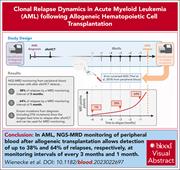
Clonal relapse dynamics in acute myeloid leukemia following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation
Relapse of acute myeloid leukemia portends a poor outcome, and it is hoped that early detection of molecular relapse will allow earlier intervention and better prognosis. Wienecke et al report on sequential MRD detection in 74 patients relapsing after allogeneic transplant to determine the predictive value of MRD monitoring. The authors provide a framework for MRD monitoring, suggesting that monthly assessment will detect 64% of relapses. However, even with monthly testing, one-third of relapses were not preceded by detectible MRD, emphasizing the complexity of early prediction of molecular relapse in time for preemptive therapy.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
Gasdermin D drives focal crystalline thrombotic microangiopathy by accelerating immunothrombosis and necroinflammation
Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) is a heterogeneous syndrome associated with microangiopathic thrombosis and life-threatening organ failure, sometimes caused by cholesterol embolization, which leads to focal, organ-specific manifestation. Watanabe-Kusunoki et al report on a role for gasdermin D (GSDMD), a pore-forming protein downstream of the pyroptosis/interleukin-1 beta pathway that amplifies neutrophil maturation and necrosis. Gsdmd deficiency or the GSDMD inhibitor disulfiram ameliorates immunothrombosis, tissue injury, and organ failure, thereby identifying a novel potential therapeutic target for amelioration of crystalline TMA.
TRANSPLANTATION
Alternative donor transplantation for severe aplastic anemia: a comparative study of the SAAWP EBMT
CME
Clinical Trials & Observations
In this month’s CME article, Montoro and colleagues compare outcomes in patients with severe aplastic anemia transplanted from alternative donors from the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) database (2012-2021), including matched unrelated donors (MUD), mismatched unrelated donors (MMUD), and haploidentical donors with posttransplant cyclophosphamide (Haplo). Based on this analysis, MUD is preferred, with lower rates of graft failure, graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), and nonrelapse mortality and better overall survival and GVHD- and relapse-free survival. The selection between MMUD and Haplo donors is uncertain and requires more study.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Efficacy of CAR T-cell therapy is not impaired by previous bispecific antibody treatment in large B-cell lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Crochet et al performed a retrospective analysis of the efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) following prior treatment of bispecific antibodies targeting different antigens, demonstrating equivalent efficacy and long-term outcomes in patients without prior exposure. This observation is important given the increasing use of bispecific antibodies at earlier stages of treatment in DLBCL.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATA
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Immunofluorescent image of intravascular neutrophil extracellular traps in a wild-type mouse kidney with thrombotic microangiopathy, stained with citrullinated histone 3 (green), Ly6G (cyan), alpha smooth muscle actin (red), and DAPI (4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; blue). See the article by Watanabe-Kusunoki et al on page 308.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals