Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
BLOOD SPOTLIGHT
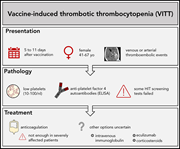
Vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia: what we know and do not know
In this timely Blood Spotlight, Arepally and Ortel discuss the latest information about VITT and highlight key “knowns” as well as pertinent “unknowns.” They also review appropriate treatments for this rare, but important complication of adenoviral COVID-19 vaccines.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
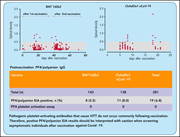
Frequency of positive anti-PF4/polyanion antibody tests after COVID-19 vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Given the emerging data on VITT and the pathogenic role played by anti-PF4 antibodies, a critical question becomes, How frequently can anti-PF4 antibodies be detected and how frequently are they pathogenic? Thiele et al studied 281 healthy vaccinees and report positive enzyme immunoassay (EIA) tests for anti-PF4 antibodies in a low percentage (6.8%), with similar frequencies for adenoviral ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine recipients and those who received the mRNA-based BNT162b2 vaccine. They conclude that low-titer EIA positives are common while pathogenic platelet-activating antibodies are rare, cautioning against overinterpretation in the absence of clinical indicators.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
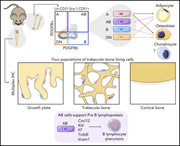
The characterization of distinct populations of murine skeletal cells that have different roles in B lymphopoiesis
Green et al dissected the bone marrow microenvironmental niche, focusing on skeletal cells and their role in hematopoiesis. They demonstrate that flow cytometry can identify 4 subpopulations, each with a distinct function. The Sca1-CD51+ cells coexpressing platelet-derived growth factor receptor α (PDGFRα) and PDGFRβ are key supporters of B-cell lymphopoiesis in the marrow.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
CD70-specific CAR T cells have potent activity against acute myeloid leukemia without HSC toxicity
CD70 is a promising target in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) due to its expression on AML blasts and leukemia stem cells and lack of expression on normal hematopoietic stem cells. CD27 is the ligand for CD70 and can be used in chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) constructs. Sauer and colleagues show that CD27z CAR T cells can effectively eliminate AML cells in vitro and in vivo without affecting normal hematopoiesis in model systems, providing preclinical support for clinical trials.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
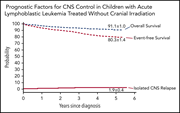
Prognostic factors for CNS control in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated without cranial irradiation
Clinical Trials & Observations
Prevention of central nervous system (CNS) relapse is critical for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) regimens, and identification of high-risk patients is necessary to develop nonmorbid strategies to reduce its incidence. Tang and colleagues report a very large comprehensive multicenter trial that identifies novel prognostic and treatment factors related to CNS control in a radiation-free backbone for childhood ALL. Among other factors, use of flow cytometry to evaluate diagnostic cerebrospinal fluid is important for reducing CNS relapse.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
SARS-CoV-2 infection induces the activation of tissue factor–mediated coagulation via activation of acid sphingomyelinase
Brief Report
In a significant contribution to our understanding of the coagulopathy of severe COVID-19, Wang and colleagues report that a phospholipid-degrading enzyme, acid sphingomyelinase (ASMase), translocates from lysosomes to the plasma membrane of macrophages upon infection with SARS-CoV-2. This enhances tissue factor (TF) procoagulant activity and release of TF-positive extracellular vesicles. These data reveal a new mechanism of TF activation and have potential therapeutic implications.
Prothrombotic immune thrombocytopenia after COVID-19 vaccination
Brief Report
Tiede and colleagues report 5 cases of patients experiencing the triad of thromboembolism, thrombocytopenia, and anti–platelet factor 4 (PF4) antibodies after vaccination with the Oxford-AstraZeneca adenoviral vector COVID-19 vaccine (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19). They highlight the unusual thrombotic presentation and distinct laboratory features. They further describe treatment for this novel syndrome, now most commonly referred to as vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT).
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection activates acid sphingomyelinase (ASMase). Macrophages infected with SARSCoV-2 spike pseudovirus were immunostained for ASMase (red). The plasma membrane was stained with PKH67 (green) and nuclei with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). The yellow color patches on the plasma membrane depict the translocation of ASMase to the outer leaflet. See the article by Wang et al on page 344.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






Understanding VITT(ual) reality
Clinical Trials & Observations