Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
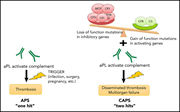
Complement activity and complement regulatory gene mutations are associated with thrombosis in APS and CAPS
Clinical Trials & Observations
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), with its often-lethal catastrophic subset (CAPS), is an acquired thrombophilia that leads to thrombosis and pregnancy loss. In a Plenary Paper, Chaturvedi and colleagues provide seminal new insights into the role of complement activation in APS pathophysiology and report a high prevalence of complement-regulatory gene mutations in patients with CAPS.
BLOOD SPOTLIGHT
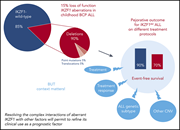
IKZF1 deletions in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: still a poor prognostic marker?
Clinical Trials & Observations
The great strides in improving survival in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) have increased focus on prognostic features predicting relapse. In a Blood Spotlight, the authors highlight the current understanding of the negative prognosis associated with IKZF1 deletions and how recent findings have elucidated the complexities of its role in ALL.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
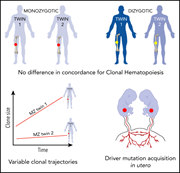
Clonal hematopoiesis in elderly twins: concordance, discordance, and mortality
Two papers examining the heritability of clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) yield highly concordant results. In independent studies of elderly monozygotic and dizygotic twins totaling over 350 pairs, Hansen et al and Fabre et al demonstrate that CHIP has a limited heritable basis, suggesting that environmental exposures are the leading contributors to clonal hematopoiesis.
Concordance for clonal hematopoiesis is limited in elderly twins
Brief Report
Two papers examining the heritability of clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) yield highly concordant results. In independent studies of elderly monozygotic and dizygotic twins totaling over 350 pairs, Hansen et al and Fabre et al demonstrate that CHIP has a limited heritable basis, suggesting that environmental exposures are the leading contributors to clonal hematopoiesis.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
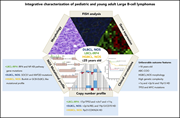
Distinct molecular profile of IRF4-rearranged large B-cell lymphoma
The authors present an integrated analysis of targeted sequencing, copy number arrays, and gene expression profiling to elucidate the molecular heterogeneity of pediatric and young adult large B-cell lymphoma.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
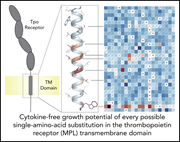
Novel drivers and modifiers of MPL-dependent oncogenic transformation identified by deep mutational scanning
Brief Report
Mutations in the transmembrane domain of the TPO receptor, encoded by exon 10 of the MPL gene, are drivers of a subset of JAK2-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs). Bridgford et al used saturation mutagenesis to identify changes in exon 10 associated with cytokine-independent growth, identifying canonical, novel, and cooperating mutations, many of which were subsequently identified in patients with MPNs.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Nonlymphoplasmacytic lymphomas associated with light-chain amyloidosis
Clinical Trials & Observations
The authors report on the subset of AL amyloidosis patients with nonlymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, emphasizing a predominance of marginal zone lymphoma, frequent delay in diagnosis, and a generally poor prognosis.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Highly proliferative germinal centers highlighted with Ki-67 (brown) in an IRF4-rearranged large B-cell lymphoma in contrast to nonproliferating cells (blue). Brown dots indicate proliferating cells, and blue dots indicate that the immunohistochemical stain is negative and thus the cells are nonproliferating. See the article by Ramis-Zaldivar et al on page 274.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals




Taken the wrong way, a complement becomes catastrophic