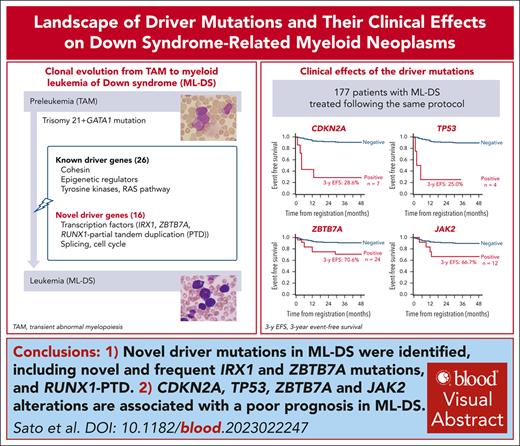
Key Points
This study provides an overall picture of driver mutations in ML-DS, including novel and frequent IRX1 and ZBTB7A mutations, and RUNX1-PTD.
CDKN2A and TP53 deletions and/or mutations are associated with a poor prognosis in ML-DS.
Visual Abstract
Transient abnormal myelopoiesis (TAM) is a common complication in newborns with Down syndrome (DS). It commonly progresses to myeloid leukemia (ML-DS) after spontaneous regression. In contrast to the favorable prognosis of primary ML-DS, patients with refractory/relapsed ML-DS have poor outcomes. However, the molecular basis for refractoriness and relapse and the full spectrum of driver mutations in ML-DS remain largely unknown. We conducted a genomic profiling study of 143 TAM, 204 ML-DS, and 34 non-DS acute megakaryoblastic leukemia cases, including 39 ML-DS cases analyzed by exome sequencing. Sixteen novel mutational targets were identified in ML-DS samples. Of these, inactivations of IRX1 (16.2%) and ZBTB7A (13.2%) were commonly implicated in the upregulation of the MYC pathway and were potential targets for ML-DS treatment with bromodomain-containing protein 4 inhibitors. Partial tandem duplications of RUNX1 on chromosome 21 were also found, specifically in ML-DS samples (13.7%), presenting its essential role in DS leukemia progression. Finally, in 177 patients with ML-DS treated following the same ML-DS protocol (the Japanese Pediatric Leukemia and Lymphoma Study Group acute myeloid leukemia -D05/D11), CDKN2A, TP53, ZBTB7A, and JAK2 alterations were associated with a poor prognosis. Patients with CDKN2A deletions (n = 7) or TP53 mutations (n = 4) had substantially lower 3-year event-free survival (28.6% vs 90.5%; P < .001; 25.0% vs 89.5%; P < .001) than those without these mutations. These findings considerably change the mutational landscape of ML-DS, provide new insights into the mechanisms of progression from TAM to ML-DS, and help identify new therapeutic targets and strategies for ML-DS.
Introduction
Transient abnormal myelopoiesis (TAM) develops in ∼5% to 10% of neonates with Down syndrome (DS; trisomy 21), and it is characterized by the rapid proliferation of abnormal blast cells that express erythrocyte- and megakaryocyte-specific genes.1 In most cases, TAM resolves spontaneously within 3 months. However, within the first 4 years of life, myeloid leukemia of DS (ML-DS) develops in ∼20% of patients.2
Nearly all TAM and ML-DS cases have mutations in GATA1 encoding erythroid and megakaryocytic transcription factor (TF) GATA1, leading to the production of an N-terminal–truncated GATA1 (GATA1s).3-7 Nonsilent mutations in TAM blasts are largely confined to GATA1. By contrast, ML-DS blasts carry a higher burden of mutations that commonly affect cohesin components, epigenetic regulators, and signal-transducing molecules, suggesting that ML-DS evolves from a TAM clone with a GATA1 mutation through the acquisition of additional mutations.8,9 However, the discovery samples analyzed with whole-exome sequencing (WES) consisted only of 14 ML-DS cases,8 which is not sufficient to clarify the entire picture of driver mutations in ML-DS.
ML-DS is associated with good responses to chemotherapy and a favorable prognosis. By contrast, patients with refractory/relapsed ML-DS have dismal clinical outcomes, even in those receiving hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.10-12 Recent studies have shown that minimal residual disease by flow cytometry or a GATA1 mutation is a risk factor for predicting relapse in patients with ML-DS.11,13 However, the molecular basis for relapse or mechanisms of resistance to chemotherapy are largely unknown.
This study investigated the genetic lesions involved in the progression of TAM to ML-DS in a large cohort. Then, mutational analyses were performed on 143 TAM, 204 ML-DS, and 34 non-DS acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (non-DS-AMKL) samples, including 39 ML-DS samples analyzed using WES. This study provides an overall picture of the genetic mutations involved in the pathogenesis of ML-DS, dramatically changing its mutational landscape. Finally, to our knowledge, this study presents the first set of gene alterations associated with poor prognosis in ML-DS.
Methods
Patients and samples
Genomic DNA from 347 individuals with DS-related myeloid neoplasms (143 TAM and 204 ML-DS) and 34 individuals with non-DS-AMKL was analyzed by WES and/or targeted deep sequencing. A total of 51 and 74 patients with ML-DS were enrolled in the Japanese Pediatric Leukemia and Lymphoma Study Group (JPLSG) acute myeloid leukemia-D05 (AML-D05)14 and AML-D1113 clinical trials, respectively. Most patients with non-DS-AMKL were enrolled in the JPLSG AML-0515 clinical trial. Most patients with TAM were prospectively registered in the JPLSG TAM-1016 study. Before sample collection, written informed consent was obtained from the parents of each participant. This study was approved by the ethics committees of Hirosaki University and Kyoto University according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
WES
At diagnosis, tumor DNA was extracted from the bone marrow– or peripheral blood–derived mononuclear cells. Genomic DNA samples from the peripheral blood of the patients in remission were used as germ line controls. Exome capture was performed using the SureSelect Human All Exon V5 (Agilent Technologies). Enriched exome fragments were subjected to massive parallel sequencing using a HiSeq 2500 platform (Illumina).
Pooled analysis of associations between somatic mutations and prognosis
Participants in the JPLSG AML-D05 and AML-D11 clinical trials received identical treatment. A pooled analysis of the 3 cohorts, namely AML-D05,14 AML-D11,13 and a retrospective cohort of patients who did not participate in the clinical trials but received the same treatment, was conducted to explore the associations between somatic mutations and outcomes. Details of the study designs and outcomes of these clinical trials are reported in previous studies.13,14 Briefly, these trials registered patients with untreated DS diagnosed with ML irrespective of blast percentage who were aged 4 months to 18 years at the time of diagnosis. Patients received a single course of induction therapy with cytarabine, etoposide, and pirarubicin (THP-adriamycin), designated as CET therapy. After risk stratification based on M1 marrow status, patients at standard risk received less intensive CET therapy, whereas those at high risk received a salvage regimen with more intensive use of cytarabine.
The outcomes of the pooled analysis were event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS). EFS was defined as the time from registration to failure to achieve remission, relapse, secondary malignancy, or death from any cause, whichever occurred first. OS was defined as the time from registration to death from any cause. The time-to-event in patients who did not experience such an event was censored as of the date of the last follow-up. EFS and OS were also analyzed as binary outcomes.
Univariable and multivariable Cox regression analyses were performed to determine the associations between somatic mutations and time-to-event outcomes. Multivariable logistic regression and the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator were used to determine the associations between somatic mutations and binary outcomes.
Additional methods
More detailed descriptions of the procedures, including WES, detection of somatic mutations, targeted deep sequencing, definition of driver genes, tailed amplicon sequencing, digital droplet polymerase chain reaction (PCR), cell culture, cell viability assay, retrovirus vector production and cell proliferation assay, bromodeoxyuridine cell cycle analysis, reporter gene assays, subcellular localization, chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) analysis, ChIP-quantitative PCR, RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis, nanopore long-read sequencing, immunoblotting, flow cytometric analysis, functional analysis using zebrafish, and statistical methods for the pooled analysis are provided in the supplemental Methods, available on the Blood website.
Results
Genomic landscape of DS-related myeloid neoplasms
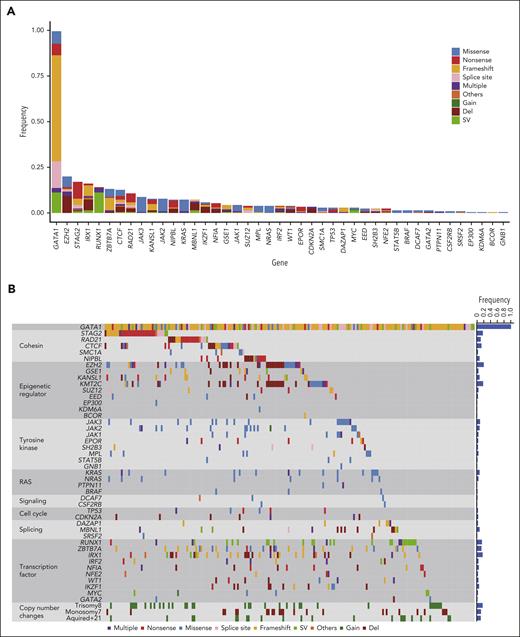
We conducted a genomic profiling study of 143 TAM, 204 ML-DS, and 34 non-DS-AMKL cases, including 39 ML-DS cases analyzed by WES (supplemental Figure 1). The mean number of nonsilent somatic mutations identified by WES in ML-DS samples (n = 39) was 6.7 (range, 1-17; supplemental Tables 1-2), which was comparable with that in the previous cohort.8 A predominant mutational signature (Sig_1) was found using the pmsignature.17 Sig_1 was characterized by age-related C > T transitions at CpG sites (supplemental Figure 2A). Combined with our previous cohort (n = 14), ML-DS driver mutations were analyzed based on positive selection using the dN/dS method.18 In total, 20 genes were significantly positively selected with dN/dS >1 (supplemental Figure 2B), including 6 novel driver genes in ML-DS, namely ZBTB7A, IRF2, NFE2, MBNL1, IRX1, and NFIA. Recurrent targets of copy-number alterations were also identified using WES, including focal deletions affecting CDKN2A and WT1 (supplemental Figure 3A). Thus, WES of 53 discovery samples revealed comprehensive mutational profiling in ML-DS.
Then, we investigated the frequency of novel driver genes in an extended cohort of ML-DS and related myeloid neoplasms using targeted deep sequencing of 343 genes, including genes with common driver mutations implicated in myeloid neoplasms, 20 newly identified driver genes, and other genes that were recurrently mutated in the 39 ML-DS samples as identified by WES (supplemental Table 3). Together with the 39 discovery samples, the extended cohort consisted of 347 myeloid malignancies related to ML-DS, including 204 ML-DS and 143 TAM, and 34 non-DS-AMKL cases (supplemental Tables 1 and 4). Intronic sequences and single-nucleotide polymorphisms have also been used to identify driver structural variants (SVs) related to AML. These included RUNX1::RUNX1T1 rearrangements and copy-number alterations (supplemental Tables 5-6).
In ML-DS samples, we confirmed frequent mutations in cohesin and related proteins (43.6%), epigenetic regulators (39.2%), and common signaling molecules such as tyrosine kinases (25.5%) and multiple RAS pathway genes (11.8%) (Figure 1A-B; supplemental Tables 7-8).8,9 In addition to the driver genes identified by WES, targeted sequencing revealed 23 putative driver genes (supplemental Table 9), including 13 genes with hot spot or gain-of-function mutations and 10 with recurrent loss-of-function mutations/SVs/deletions. Sequencing-based copy-number analysis using CNACS19 revealed recurrent focal deletions involving tumor suppressor genes (supplemental Figure 3B; supplemental Table 10). Novel putative driver genes included RUNX1, IKZF1, GSE1, EPOR, CDKN2A, DAZAP1, STAT5B, BRAF, GATA2, and PTPN11.
Driver mutations in ML-DS. (A) Frequency and type of driver mutations in 204 ML-DS samples, which were identified by targeted deep sequencing. (B) Landscape of somatic mutations in 204 ML-DS samples. The types of mutations are distinguished by the indicated colors. Del, deletion; Multiple, multiple mutations.
Driver mutations in ML-DS. (A) Frequency and type of driver mutations in 204 ML-DS samples, which were identified by targeted deep sequencing. (B) Landscape of somatic mutations in 204 ML-DS samples. The types of mutations are distinguished by the indicated colors. Del, deletion; Multiple, multiple mutations.
In agreement with previous reports,8,9 mutations were rare in TAM samples, except for GATA1 (supplemental Figure 4). These findings support the widely accepted model that ML-DS evolves from a preexisting TAM clone with GATA1 mutation through the acquisition of additional mutations. This study included 20 patients with paired and sequential TAM/ML-DS. We found recurrent non-GATA1 mutations in 15 of 20 ML-DS samples, but none in the remaining 5 samples. Tailed amplicon sequencing and digital droplet PCR of the driver mutations found in ML-DS samples were performed in their corresponding TAM samples. Consistent with a recent report,9 no additional driver mutations were detected in the TAM phase in most cases, except for STAG2 mutations found in the 2 TAM cases (supplemental Table 11). These results suggest a critical role of additional mutations in disease progression to ML-DS, although it is unclear whether these mutations were already present in a small cell population during the TAM phase or were newly acquired after spontaneous remission.
In contrast to ML-DS, pediatric non-DS-AMKL is frequently associated with a poor prognosis. Non-DS-AMKL is a heterogeneous malignancy that is divided into various subgroups with distinct outcomes according to genetic alterations,20 including CBFA2T3::GLIS2, HOX fusions, NUP98::KDM5A, and GATA1 mutations, which were found in 20.6%, 8.9%, 5.9%, and 17.6% of 34 non-DS-AMKL cases, respectively (supplemental Figure 5A; supplemental Tables 12-13). In contrast to CBFA2T3::GLIS2 fusion (+) cases (n = 7), which carried few additional mutations, those with GATA1 mutations (n = 6) frequently showed mutations in various pathways that are commonly dysregulated in ML-DS (supplemental Figure 5B) and trisomy 21 (66.7%) (supplemental Tables 4 and 12), suggesting that this subgroup may be genetically related to ML-DS.
Novel mutational targets frequently observed in ML-DS
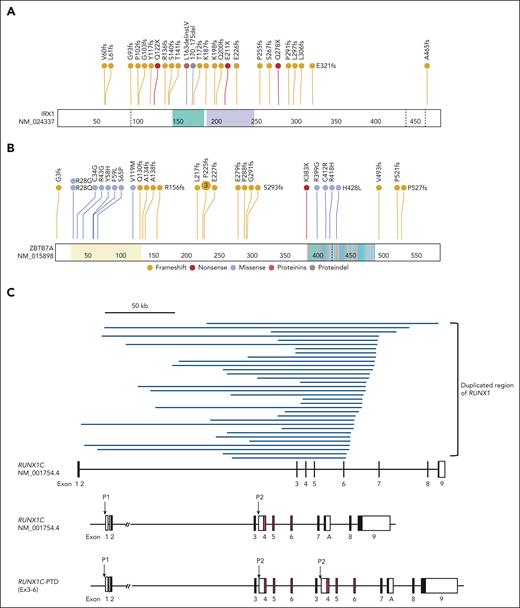
IRX1 is a novel recurrent mutational target in human cancers and encodes a member of the Iroquois homeobox protein family. Despite its involvement in embryonic pattern formation,21 its function in the hematopoietic system remains largely unknown. Deletions, mutations, or SVs involving IRX1 were found in 33 (16.2%) ML-DS and 5 (3.5%) TAM cases and 1 in non-DS-AMKL samples (Figure 1A-B; supplemental Figures 4 and 5A). Most changes were nonsense or frameshift mutations, suggesting that these mutations resulted in the loss of function (Figure 2A).
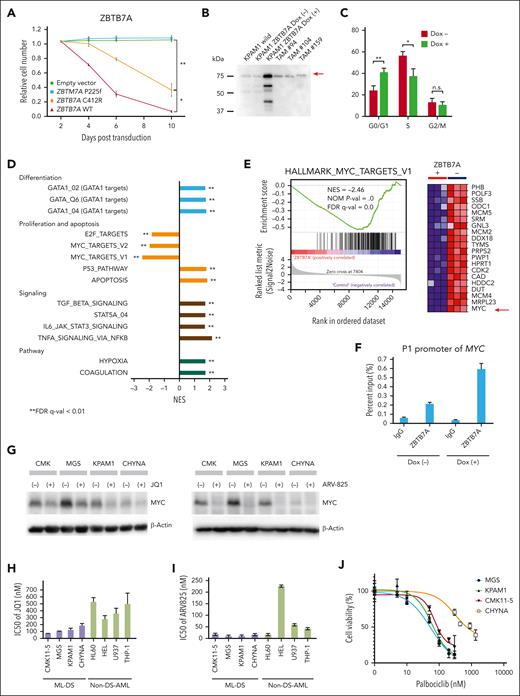
Distribution of driver mutations. (A-B) Distribution of IRX1 (A) and ZBTB7A alterations (B). Frameshift and nonsense mutations are shown in red and orange, respectively, and missense mutations are shown in blue. (C) The 33 regions of the partial tandem duplication of RUNX1 (RUNX1-PTD) found in 28 ML-DS samples (top) and a schematic representation of the RUNX1-PTD structure (bottom). The most common SVs result from the duplication of a genomic region encompassing RUNX1 exons 3 to 6 (RUNX1C-PTD [Ex3-6]). The variant was annotated as RUNX1C (NM_001754.4). Filled squares indicate coding exons and orange squares indicate runt-homology domains (RHD). P1: distal promoter; P2: proximal promoter; A: RUNX1A isoform-specific last exon. (D) Schematic presentation of RUNX1 isoforms produced from RUNX1-PTD. Only RUNX1C-PTD is expressed from the P1 promoter, whereas RUNX1A and RUNX1B and their PTD isoforms are expressed from the duplicated P2 promoters. (E) Paired associations among somatic mutations and cytogenetic abnormalities observed in at least 3% of patients with ML-DS. Significantly co-occurring and mutually exclusive mutations are indicated by red and blue circles, respectively. Odds ratios and associated q-values are indicated by the color gradient and size of the circles, respectively. Proteindel, protein in-frame deletion; Proteinins, protein in-frame insertion. Lollipop plots were generated using ProteinPaint (https://pecan.stjude.cloud/proteinpaint).
Distribution of driver mutations. (A-B) Distribution of IRX1 (A) and ZBTB7A alterations (B). Frameshift and nonsense mutations are shown in red and orange, respectively, and missense mutations are shown in blue. (C) The 33 regions of the partial tandem duplication of RUNX1 (RUNX1-PTD) found in 28 ML-DS samples (top) and a schematic representation of the RUNX1-PTD structure (bottom). The most common SVs result from the duplication of a genomic region encompassing RUNX1 exons 3 to 6 (RUNX1C-PTD [Ex3-6]). The variant was annotated as RUNX1C (NM_001754.4). Filled squares indicate coding exons and orange squares indicate runt-homology domains (RHD). P1: distal promoter; P2: proximal promoter; A: RUNX1A isoform-specific last exon. (D) Schematic presentation of RUNX1 isoforms produced from RUNX1-PTD. Only RUNX1C-PTD is expressed from the P1 promoter, whereas RUNX1A and RUNX1B and their PTD isoforms are expressed from the duplicated P2 promoters. (E) Paired associations among somatic mutations and cytogenetic abnormalities observed in at least 3% of patients with ML-DS. Significantly co-occurring and mutually exclusive mutations are indicated by red and blue circles, respectively. Odds ratios and associated q-values are indicated by the color gradient and size of the circles, respectively. Proteindel, protein in-frame deletion; Proteinins, protein in-frame insertion. Lollipop plots were generated using ProteinPaint (https://pecan.stjude.cloud/proteinpaint).
ZBTB7A is a member of the POK (POZ/BTB and Kruppel) TF family with crucial roles in cellular differentiation and oncogenesis, is a direct target of GATA1, and plays an essential antiapoptotic role during terminal erythroid differentiation.22 Inactivating ZBTB7A mutations were reported in up to 23% of AML cases with RUNX1::RUNX1T1 fusion.23 We found mutations, SVs, and a deletion in ZBTB7A in 27 (13.2%) ML-DS and 1 non-DS-AMKL cases (Figure 1A-B; supplemental Figure 5A), most of which were loss-of-function mutations (Figure 2B).
Moreover, 106 SVs in TAM and ML-DS were identified using targeted sequencing, of which the second most frequently observed SVs of GATA1 were those affecting RUNX1. RUNX1-involving SVs were exclusively found in 28 patients with ML-DS (13.7%), except for 1 patient with TAM with RUNX1 deletion (supplemental Table 8). Surprisingly, all 33 RUNX1-involving SVs found in the 28 ML-DS samples showed partial tandem duplication (RUNX1-PTD). In most cases, a single RUNX1-PTD was identified, and copy-number analysis suggested acquisition of 1 extra copy of RUNX1. However, in 5 cases with 2 RUNX1-PTDs, low frequency of leukemic cells made it difficult to distinguish whether 2 subclones with different RUNX1-PTDs coexisted or whether RUNX1-PTD mutations occurred in 2 alleles. All RUNX1-PTDs detected by targeted sequencing were confirmed by sequencing the PCR product amplified from the genomic DNA of each patient, using primer sets specifically designed for the detection of individual SVs (supplemental Figure 6; supplemental Table 14). RUNX1-PTDs were mostly caused by the duplication of a genomic region that encompassed RUNX1 exons 3 to 6, which was inserted into intron 2 of the full-length RUNX1 gene (Figure 2C). As a result, an in-frame fusion RNA between exon 6 and the duplicated exon 3 was transcribed from the distal (P1) promoter of RUNX1,24 resulting in the production of the mutant protein (RUNX1C-PTD) with elongated runt domain (Figure 2D). RUNX1-PTD had the duplicated proximal (P2) promoters and RUNX1A and RUNX1B, in addition to RUNX1A-PTD and RUNX1B-PTD isoforms, were transcribed from the P2 promoters. Expression of RUNX1A-PTD, RUNX1B-PTD, and RUNX1C-PTD was confirmed by nanopore long-read sequencing of PCR products from samples from patients with ML-DS with RUNX1-PTD (supplemental Figure 7). Interestingly, analysis of the comutational pattern of the most frequent somatic mutations and cytogenetic abnormalities revealed a significant co-occurrence of RUNX1-PTD and acquired +21 in the ML-DS samples (Figure 2E). Chromosomal data were available for 192 of 204 cases; the remaining cases were RUNX1-PTD negative. The number of cases with acquired +21 was 10 of 28 (35.7%) with RUNX1-PTD and 7 of 164 (4.3%) without RUNX1-PTD (supplemental Tables 1, 4, and 8).
IRX1 expression induces erythroid and megakaryocytic differentiation of ML-DS cells
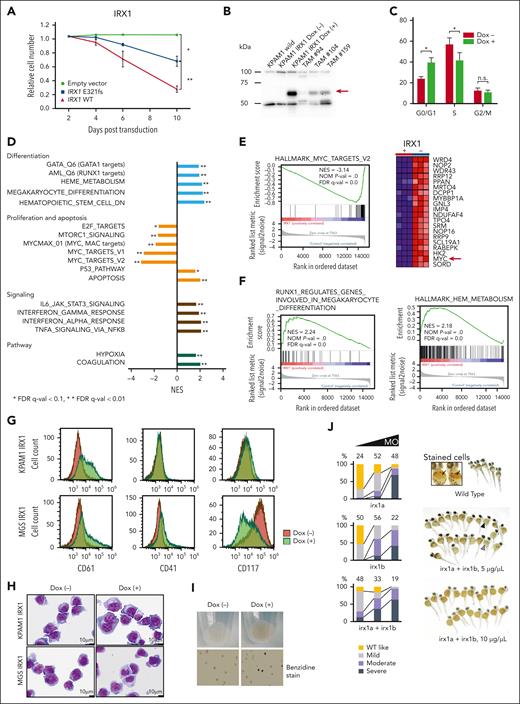
Initially, we examined the effect of forced expression of wild-type (WT) IRX1 on the proliferation of the IRX1-mutated (p.E321fs) ML-DS cell line KPAM1 (supplemental Table 15). Constitutive expression of WT IRX1 significantly suppressed KPAM1 cell growth (Figure 3A). Then, WT IRX1 was expressed under the control of a doxycycline (Dox)–inducible promoter in KPAM1 cells (Figure 3B). WT IRX1 induction led to a distinct G1 arrest with reduced S-phase populations (Figure 3C). Gene Set Enrichment Analysis of RNA-seq data revealed an enhanced expression of genes implicated in apoptosis and p53 pathways related to cell growth suppression after WT IRX1 induction (Figure 3D). Furthermore, in KPAM1 cells with forced WT IRX1 expression, the expression of genes associated with MYC targets and the mTOR/E2F signaling pathway was downregulated compared with that in the control cells (Figure 3D), although the detailed mechanism remains unknown. Notably, MYC, a critical target gene controlled by GATA1 and an effector of GATA1s-mediated transformation of TAM,25 was significantly downregulated upon WT IRX1 expression (Figure 3E). In addition, genes involved in megakaryocytic and erythroid differentiation, including GATA1 and RUNX1 target genes, heme metabolism, and RUNX1-regulated genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function were increased in KPAM1 cells after WT IRX1 induction (Figure 3D-F). In addition to KPAM1, we established IRX1-mutated (p.S259Gfs∗82) ML-DS cell line MGS expressing WT IRX1 under the control of a Dox-inducible promoter. The RNA-seq analysis results were similar for both cell lines (supplemental Figure 8). Flow cytometric analysis revealed that induction of WT IRX1 increased CD61 expression in KPAM1 cells and increased CD41 and CD61 expression, but decreased CD117 expression in MGS cells, which was accompanied by morphological changes toward megakaryocytic differentiation (Figure 3G-H; supplemental Figure 9).
IRX1 expression induces megakaryocytic and erythroid differentiation in ML-DS cells. (A) Growth of KPAM1 cells stably expressing either WT or mutant IRX1 (E321fs). KPAM1 cells were transduced with the IRX1-ZsGreen bicistronic retrovirus. Cell fate was monitored using flow cytometry. Ratios of ZsGreen-positive cells were determined on the days after infection with the viral transgenes. The combined results from 3 independent experiments are shown. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01 by Welch t test. (B) Western blot analysis of IRX1 expression. The analyzed cells included WT KPAM1 (lane 1), KPAM1-expressing WT IRX1 under the control of a Dox-inducible promoter before (lane 2), and after (lane 3) Dox treatment, and TAM (lanes 4, 5, and 6). The red arrow indicates IRX1 expression. (C) Cell cycle analysis of IRX1-inducible KPAM1 cells. The combined results from 3 independent experiments are shown. WT IRX1 induction led to an increase in the G0/G1-phase population and a decrease in the S-phase population. Data are presented as mean ± SD; ∗P < .05, Welch t test. (D) RNA-seq analysis of KPAM1 cells. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of transcriptomes in WT IRX1-inducible KPAM1 cells after vs before IRX1 induction. (E) GSEA using a gene set of MYC targets, showing that MYC was significantly downregulated upon WT IRX1 expression. The red arrow indicates MYC expression. (F) GSEA using a gene set for megakaryocytic (left) and erythroid (right) differentiation. (G) Flow cytometric analysis of IRX1-inducible KPAM1 and MGS cells. KPAM1 and MGS cells were treated with Dox for 6 days. Representative data are shown for 1 of 4 independent experiments. (H) Morphology of IRX1-inducible KPAM1 and MGS cells before and after WT IRX1 induction for 7 days. Cytospin specimens were stained with May-Grünwald Giemsa (original magnification ×10 000). (I) Cell pellets from KPAM1 cells before and after WT IRX1 induction. KPAM1 cells were treated with Dox for 7 days. (J) Zebrafish orthologs of human IRX1, irx1a, and irx1b (GenBank accession numbers: NM_207184 and NM_ 131823) were knocked down using morpholino antisense oligos (MOs) that targeted the translational initiation sites of each gene. One-cell–stage embryos were injected with these MOs, and the density of blood cells around the cardiac vein at 48 hours after fertilization was detected by hemoglobin staining using o-dianisidine. Embryos injected with irx1a MO and/or irx1b MO displayed anemia (severe, moderate, or mild anemia) depending on the concentration of the injected MOs (1, 5, and 10 μg/μL). Black arrows indicate hemoglobin-stained blood cells (orange dots) in wild-type embryos. Black and gray arrowheads indicate embryos with severe and moderate anemia, respectively. The number of embryos analyzed for hemoglobin staining is shown at the top of the bars. FDR, false discovery rate; NES, normalized enrichment score; n.s., not significant.
IRX1 expression induces megakaryocytic and erythroid differentiation in ML-DS cells. (A) Growth of KPAM1 cells stably expressing either WT or mutant IRX1 (E321fs). KPAM1 cells were transduced with the IRX1-ZsGreen bicistronic retrovirus. Cell fate was monitored using flow cytometry. Ratios of ZsGreen-positive cells were determined on the days after infection with the viral transgenes. The combined results from 3 independent experiments are shown. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01 by Welch t test. (B) Western blot analysis of IRX1 expression. The analyzed cells included WT KPAM1 (lane 1), KPAM1-expressing WT IRX1 under the control of a Dox-inducible promoter before (lane 2), and after (lane 3) Dox treatment, and TAM (lanes 4, 5, and 6). The red arrow indicates IRX1 expression. (C) Cell cycle analysis of IRX1-inducible KPAM1 cells. The combined results from 3 independent experiments are shown. WT IRX1 induction led to an increase in the G0/G1-phase population and a decrease in the S-phase population. Data are presented as mean ± SD; ∗P < .05, Welch t test. (D) RNA-seq analysis of KPAM1 cells. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of transcriptomes in WT IRX1-inducible KPAM1 cells after vs before IRX1 induction. (E) GSEA using a gene set of MYC targets, showing that MYC was significantly downregulated upon WT IRX1 expression. The red arrow indicates MYC expression. (F) GSEA using a gene set for megakaryocytic (left) and erythroid (right) differentiation. (G) Flow cytometric analysis of IRX1-inducible KPAM1 and MGS cells. KPAM1 and MGS cells were treated with Dox for 6 days. Representative data are shown for 1 of 4 independent experiments. (H) Morphology of IRX1-inducible KPAM1 and MGS cells before and after WT IRX1 induction for 7 days. Cytospin specimens were stained with May-Grünwald Giemsa (original magnification ×10 000). (I) Cell pellets from KPAM1 cells before and after WT IRX1 induction. KPAM1 cells were treated with Dox for 7 days. (J) Zebrafish orthologs of human IRX1, irx1a, and irx1b (GenBank accession numbers: NM_207184 and NM_ 131823) were knocked down using morpholino antisense oligos (MOs) that targeted the translational initiation sites of each gene. One-cell–stage embryos were injected with these MOs, and the density of blood cells around the cardiac vein at 48 hours after fertilization was detected by hemoglobin staining using o-dianisidine. Embryos injected with irx1a MO and/or irx1b MO displayed anemia (severe, moderate, or mild anemia) depending on the concentration of the injected MOs (1, 5, and 10 μg/μL). Black arrows indicate hemoglobin-stained blood cells (orange dots) in wild-type embryos. Black and gray arrowheads indicate embryos with severe and moderate anemia, respectively. The number of embryos analyzed for hemoglobin staining is shown at the top of the bars. FDR, false discovery rate; NES, normalized enrichment score; n.s., not significant.
Gene ontology analysis revealed a significant enrichment of hemoglobin complex in IRX1-inducible genes (supplemental Figure 10; supplemental Table 16). Indeed, a cell pellet of KPAM1 turned red with benzidine positivity after WT IRX1 induction, suggesting hemoglobin production (Figure 3I). Furthermore, when zebrafish orthologs of human IRX1 (irx1a and irx1b) were knocked down using morpholino antisense oligos, impaired erythrocyte production was observed in zebrafish embryos (Figure 3J). These findings suggest that the restoration of WT IRX1 expression leads to differentiation toward megakaryocytic and erythroid lineages and growth arrest of ML-DS cells.
Multiple mutational targets are involved in the MYC pathway in ML-DS
Initially, the effect of WT ZBTB7A on the proliferation of the ZBTB7A-mutated (p.Q392X) ML-DS cell line, CMK11-5 (supplemental Table 15), was examined. Constitutive expression of WT ZBTB7A induced rapid growth suppression in CMK11-5 cells (Figure 4A). To analyze the mechanism of growth suppression by WT ZBTB7A, we attempted to establish CMK11-5 cells expressing WT ZBTB7A under the control of a Dox-inducible promoter. However, the Tet-on inducible system did not function in CMK11-5 cells, the only ML-DS cell line with a ZBTB7A mutation. Therefore, WT ZBTB7A was expressed under the control of a Dox-inducible promoter in KPAM1 cells, in which the expression level of ZBTB7A was reduced (Figure 4B). Induction of WT ZBTB7A led to G1 arrest with reduced S-phase populations (Figure 4C). RNA-seq data analysis showed that the induction of WT ZBTB7A increased the expression of genes involved in apoptosis, p53 pathways, and GATA1 target genes and downregulated a group of genes related to MYC and E2F targets (Figure 4D-E). ZBTB7A acts as a transcriptional repressor.22 ChIP–quantative PCR analysis confirmed that ZBTB7A binds to the P1 promoter of MYC in ML-DS cells (Figure 4F), indicating that MYC is a direct target of ZBTB7A, which is consistent with a previous report.26 In this regard, genetic alterations involving MYC mutations were found in 5 ML-DS samples (Figure 1B; supplemental Table 7). Taken together, these results suggest that similar to IRX1, ZBTB7A acts as tumor suppressor through the MYC/E2F pathway, and MYC is a potential therapeutic target in ML-DS. ML-DS cell lines were highly sensitive to the bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) inhibitors JQ1 and ARV-825,27,28 which suppressed MYC expression (Figure 4G), with the half maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50s) of <200 nM and <20 nM, respectively (Figure 4H-I; supplemental Table 17). Because MYC can activate E2Fs and their target genes by upregulating cyclin D-CDK4 and CDK6 complex activity,29 whether ML-DS cell lines were sensitive to the clinically relevant CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib (PD-0332991) was explored. Three of the 4 cell lines tested were highly sensitive to palbociclib, with IC50 value of <100 nM (Figure 4J). These results further supported the hypothesis that the MYC pathway is a good molecular target for ML-DS treatment.
Downregulation of MYC targets in ML-DS cells expressing WT ZBTB7A. (A) Growth of CMK11-5 cells constitutively expressing WT ZBTB7A or its mutants. CMK11-5 cells were infected with various ZBTB7A-ZsGreen bicistronic retroviruses, and cell fate was monitored by flow cytometry. The combined results from 3 independent experiments are shown. Data are presented as mean ± SD. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01 by Welch t test. (B) Western blot analysis of ZBTB7A expression. The analyzed cells include WT KPAM1 (lane 1), KPAM1-expressing WT ZBTB7A under the control of a Dox-inducible promoter before (lane 2) and after (lane 3) Dox treatment, and TAM (lanes 4, 5, and 6). The red arrow indicates ZBTB7A expression. (C) Cell cycle analysis of ZBTB7A-inducible KPAM1 cells. Combined results from 3 independent experiments are shown. WT ZBTB7A induction led to an increase in the G0/G1-phase population and a decrease in the S-phase population; ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, Welch t test. Error bars indicate SD. (D) RNA-seq analysis of KPAM1 cells. GSEA of transcriptomes in WT ZBTB7A-inducible KPAM1 cells after vs before ZBTB7A induction. (E) GSEA using a gene set of MYC targets shows that MYC was significantly downregulated upon WT ZBTB7A expression. The red arrow indicates MYC expression. (F) Quantification of ZBTB7A binding to the P1 promoter of MYC by ChIP-qPCR in WT ZBTB7A-inducible KPAM1 cells before and after ZBTB7A induction. ZBTB7A, anti-ZBTB7A antibody (13E9); IgG, IgG isotype control. (G) Western blot analysis of MYC before and after treatment of the ML-DS cell lines (CMK11-5, MGS, KPAM1, and CHYNA) with 500 nM JQ1 for 24 hours (top) or 50 nM ARV-825 for 12 hours (bottom). β-actin served as the loading control. (H) ML-DS cells were treated with various concentrations of JQ1 or (I) ARV-825 for 72 h. Viable cell numbers were determined using the Cell Counting Kit-8. Combined results from at least 3 independent experiments are shown. Data are presented as mean ± SD. (J) ML-DS cell lines were treated for 72 hours with palbociclib at a wide range of concentrations, and viable cell numbers were determined using Cell Counting Kit-8. Representative cell viability curves are shown from 1 of 3 independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SD. FDR, false discovery rate; NES, normalized enrichment score; qPCR, quantitative PCR.
Downregulation of MYC targets in ML-DS cells expressing WT ZBTB7A. (A) Growth of CMK11-5 cells constitutively expressing WT ZBTB7A or its mutants. CMK11-5 cells were infected with various ZBTB7A-ZsGreen bicistronic retroviruses, and cell fate was monitored by flow cytometry. The combined results from 3 independent experiments are shown. Data are presented as mean ± SD. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01 by Welch t test. (B) Western blot analysis of ZBTB7A expression. The analyzed cells include WT KPAM1 (lane 1), KPAM1-expressing WT ZBTB7A under the control of a Dox-inducible promoter before (lane 2) and after (lane 3) Dox treatment, and TAM (lanes 4, 5, and 6). The red arrow indicates ZBTB7A expression. (C) Cell cycle analysis of ZBTB7A-inducible KPAM1 cells. Combined results from 3 independent experiments are shown. WT ZBTB7A induction led to an increase in the G0/G1-phase population and a decrease in the S-phase population; ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, Welch t test. Error bars indicate SD. (D) RNA-seq analysis of KPAM1 cells. GSEA of transcriptomes in WT ZBTB7A-inducible KPAM1 cells after vs before ZBTB7A induction. (E) GSEA using a gene set of MYC targets shows that MYC was significantly downregulated upon WT ZBTB7A expression. The red arrow indicates MYC expression. (F) Quantification of ZBTB7A binding to the P1 promoter of MYC by ChIP-qPCR in WT ZBTB7A-inducible KPAM1 cells before and after ZBTB7A induction. ZBTB7A, anti-ZBTB7A antibody (13E9); IgG, IgG isotype control. (G) Western blot analysis of MYC before and after treatment of the ML-DS cell lines (CMK11-5, MGS, KPAM1, and CHYNA) with 500 nM JQ1 for 24 hours (top) or 50 nM ARV-825 for 12 hours (bottom). β-actin served as the loading control. (H) ML-DS cells were treated with various concentrations of JQ1 or (I) ARV-825 for 72 h. Viable cell numbers were determined using the Cell Counting Kit-8. Combined results from at least 3 independent experiments are shown. Data are presented as mean ± SD. (J) ML-DS cell lines were treated for 72 hours with palbociclib at a wide range of concentrations, and viable cell numbers were determined using Cell Counting Kit-8. Representative cell viability curves are shown from 1 of 3 independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SD. FDR, false discovery rate; NES, normalized enrichment score; qPCR, quantitative PCR.
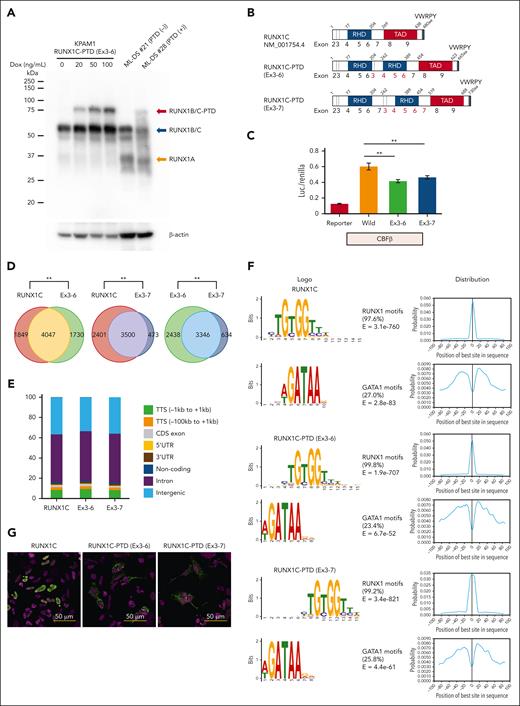
Functional analysis of RUNX1-PTD in vitro
Western blot analysis using an anti-RUNX1 antibody recognizing amino acids 186 to 250 indicated the expression of a protein with the molecular size expected of RUNX1C-PTD protein in samples from patients with ML-DS with RUNX1-PTD (Figure 5A). Subsequently, the transcriptional activities of RUNX1C-PTDs were assessed by a luciferase assay using the promoter of GP1BA, as previously described.30 Two types of RUNX1-PTDs were observed: 1 with duplication of exons 3 to 6 (RUNX1C-PTD [Ex 3-6]), which was found in most cases; and another with duplication of Ex 3-7 [RUNX1C-PTD (Ex 3-7)], which was observed in 2 ML-DS cases (Figures 2C and 5B). Transcriptional activation of both RUNX1C-PTD types was slightly, but significantly, reduced compared with that of WT RUNX1 (Figure 5C). ChIP-seq analysis revealed that 70.1% of RUNX1C-PTD (Ex 3-6) and 88.1% of RUNX1C-PTD (Ex 3-7) peaks overlapped with WT RUNX1 (RUNX1C) peaks (Figure 5D). PeakPermTest showed that the observed overlaps were more significant than expected by chance. The portion of peak regions of the RUNX1C-PTDs distributed in the genome was almost the same as that of RUNX1C (Figure 5E). Canonical RUNX1 motifs were observed in >97% of both RUNX1C and RUNX1C-PTD peaks, accompanied by enrichment of binding motifs for the GATA1 factor (Figure 5F). These findings indicated that there was no significant difference in the binding specificity between RUNX1C-PTD and WT RUNX1C. Subsequently, the subcellular localization of RUNX1C-PTD protein in HEK293 cells transfected with Xpress-tagged RUNX1-PTD was examined. Consistent with a previous report,31 RUNX1C was localized to the nucleus. However, the relative abundance of nuclear vs cytosolic RUNX1C-PTDs was significantly lower in HEK293 cells (Figure 5G). These results suggest the partial loss-of-function nature of RUNX1C-PTD.
Functional analysis of RUNX1-PTD in vitro. (A) Western blot analysis of RUNX1-PTD expression. The analyzed cells included KPAM1 expressing RUNX1C-PTD under the control of a Dox-inducible promoter (lanes 1, 2, 3, and 4), ML-DS (number 21) without RUNX1-PTD (lane 5), and ML-DS (number 28) with RUNX1-PTD (lane 6). Dox treatment concentrations are indicated. (B) Protein domains of RUNX1C, RUNX1C-PTD (Ex3-6), and RUNX1C-PTD (Ex3-7). The structures of RUNX1C and RUNX1C-PTDs comprise runt-homology domains (RHD), a transactivation domain (TAD), and a VWRPY motif. (C) Luciferase reporters from the GP1BA promoter were cotransfected with the indicated constructs in QT6 cells. Reporter, mock vector; Wild, WT RUNX1C; Ex3–6, RUNX1C-PTD with duplication of Ex3-6; Ex3-7, RUNX1C-PTD with duplication of exons 3 to 7; ∗∗P < .01 by Student t test. Data are presented as mean ± SD. (D) Overlap of ChIP-seq peaks of WT RUNX1C and RUNX1-PTDs. KPAM1 cells were transfected with Xpress-tagged RUNX1C, RUNX1C-PTD (Ex3-6), and RUNX1C-PTD (Ex3-7). ChIP-seq was performed using anti-Xpress antibody. The significance of the overlap was assessed using the peakPermTest function of the ChIPpeakAnno package; ∗∗P = .001 by peakPermTest. (E) Relative distribution of the RUNX1C and RUNX1-PTD ChIP-seq peak regions in the genome. (F) Results of de novo motif analysis of ChIP-seq data. The 2 most significant motifs were found by the MEME algorithms in RUNX1C (top), RUNX1C-PTD (Ex3-6) (middle), and RUNX1C-PTD (Ex3-7) (bottom) ChIP-seq data. RUNX1 binding motifs were the most significantly enriched (>97%). The second most frequently occurring motif, which was found in ∼25% of the peaks, was GATA1. (G) Subcellular localization of RUNX1C and RUNX1C-PTD proteins in HEK293 cells transfected with Xpress-tagged RUNX1C-PTD or WT RUNX1C.
Functional analysis of RUNX1-PTD in vitro. (A) Western blot analysis of RUNX1-PTD expression. The analyzed cells included KPAM1 expressing RUNX1C-PTD under the control of a Dox-inducible promoter (lanes 1, 2, 3, and 4), ML-DS (number 21) without RUNX1-PTD (lane 5), and ML-DS (number 28) with RUNX1-PTD (lane 6). Dox treatment concentrations are indicated. (B) Protein domains of RUNX1C, RUNX1C-PTD (Ex3-6), and RUNX1C-PTD (Ex3-7). The structures of RUNX1C and RUNX1C-PTDs comprise runt-homology domains (RHD), a transactivation domain (TAD), and a VWRPY motif. (C) Luciferase reporters from the GP1BA promoter were cotransfected with the indicated constructs in QT6 cells. Reporter, mock vector; Wild, WT RUNX1C; Ex3–6, RUNX1C-PTD with duplication of Ex3-6; Ex3-7, RUNX1C-PTD with duplication of exons 3 to 7; ∗∗P < .01 by Student t test. Data are presented as mean ± SD. (D) Overlap of ChIP-seq peaks of WT RUNX1C and RUNX1-PTDs. KPAM1 cells were transfected with Xpress-tagged RUNX1C, RUNX1C-PTD (Ex3-6), and RUNX1C-PTD (Ex3-7). ChIP-seq was performed using anti-Xpress antibody. The significance of the overlap was assessed using the peakPermTest function of the ChIPpeakAnno package; ∗∗P = .001 by peakPermTest. (E) Relative distribution of the RUNX1C and RUNX1-PTD ChIP-seq peak regions in the genome. (F) Results of de novo motif analysis of ChIP-seq data. The 2 most significant motifs were found by the MEME algorithms in RUNX1C (top), RUNX1C-PTD (Ex3-6) (middle), and RUNX1C-PTD (Ex3-7) (bottom) ChIP-seq data. RUNX1 binding motifs were the most significantly enriched (>97%). The second most frequently occurring motif, which was found in ∼25% of the peaks, was GATA1. (G) Subcellular localization of RUNX1C and RUNX1C-PTD proteins in HEK293 cells transfected with Xpress-tagged RUNX1C-PTD or WT RUNX1C.
Other novel mutations in ML-DS
NFIA, which encodes a member of the NFI family of TFs,32 is believed to be involved in erythropoiesis.33 Fusion of the NFIA has been reported with multiple partners in leukemia and solid tumors.34,35NFIA alterations were identified in 11 (5.4%) ML-DS and 1 TAM samples (Figures 1A-B; supplemental Figure 4). Most mutations were nonsense or frameshift mutations (supplemental Figure 11).
GSE1 is a proline-rich protein whose function is largely unknown.36 GSE1 alterations were found in 9 (4.4%) ML-DS and 5 non-DS-AMKL cases (Figure 1A-B; supplemental Figure 5A). All GSE1 mutations, except for 1 missense mutation (p.Q53R), were frameshift mutations (supplemental Figure 11).
MBNL1 encodes a splicing factor involved in erythropoiesis.37,38 Focal MBNL1 deletions have been reported in a subset of pediatric AML.39MBNL1 alterations were found in 15 (7.4%) ML-DS and 2 non-DS-AMKL cases (Figure 1A-B; supplemental Figures 3B, 5A, and 11).
IRF2 is a novel site of recurrent mutations in human cancers. IRF2 is a TF involved in interferon signaling40 and contributes to adult stage-specific enhancer activities during human erythroid development.41IRF2 alterations were found in 8 (3.9%) ML-DS cases (Figure 1A-B; supplemental Figure 11).
NFE2 is a TF critical for megakaryocyte development and platelet production. NFE2 mutations have been reported in 2% and 3.2% of cases of myeloproliferative neoplasms and de novo AML, respectively.42,43 In this study, NFE2 mutations were found in 5 (2.5%) ML-DS cases (Figure 1A-B; supplemental Figure 11).
Erythropoietin receptor (EPOR) signaling is required for erythroid development. EPOR rearrangements have been reported in up to 8.9% of the cases of Ph-like B-precursor (BCP) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and acute erythroleukemia.44,45 These mutations led to truncations of the C-terminal negative growth-regulatory domain, such as primary familial congenital polycythemia.46 In this study, truncating EPOR mutations were found in 7 (3.4%) ML-DS and 3 non-DS-AMKL cases (Figure 1A-B; supplemental Figure 5A). These truncations were located at the same residues that are mutated in primary familial congenital polycythemia, suggesting activating mutations (supplemental Figure 11).
CDKN2A encodes p14ARF and p16INK4a by alternative exon use, both of which inhibit cell cycle progression.47CDKN2A deletion is one of the most common alterations in ALL,48 however, its prevalence is low in AML.49,50CDKN2A alterations were found in 7 (3.4%) ML-DS cases and 4 (11.8%) non-DS-AMKL cases. All CDKN2A alterations were deletions, except for 1 ML-DS case also with a missense mutation (P81R) (supplemental Tables 7 and 10).
Somatic mutations at diagnosis predict outcomes
As shown in the patient selection flowchart (supplemental Figure 12), 51, 74, and 52 patients were included in the pooled analysis of the AML-D05 cohort,14 AML-D11 cohort,13 and a retrospective cohort of patients who did not participate in the clinical trials but received the same treatment, respectively. The background characteristics of patients in the 3 cohorts were comparable (supplemental Tables 18-19).
Prognostic somatic mutations in the 36 candidate genetic regions were identified separately by univariable Cox regression of EFS and the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator of binary outcomes. CDKN2A, TP53, JAK2, and ZBTB7A remained as prognostic factors after screening using both procedures (supplemental Tables 20-21). In the univariable Cox regression analysis, CDKN2A and TP53 were significantly associated with EFS, even after adjustment for multiplicity using the Hochberg method (supplemental Table 20). Although the number of patients was small, EFS and OS rates were substantially low in patients with CDKN2A mutations (n = 7) or TP53 mutations (n = 4; supplemental Table 22). The estimated 3-year EFS rates were 28.6% and 25.0% in patients with CDKN2A deletion/mutations and TP53 mutations, respectively. Of the 7 patients with CDKN2A deletion/mutation, 3 relapsed, and 2 failed to induce the first remission (supplemental Table 23).
CDKN2A, TP53, and JAK2 mutations were highly correlated (supplemental Table 24). However, multivariable analysis using Cox regression with these 4 mutations showed that ZBTB7A (hazard ratio [HR], 3.308; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.285-8.515; P = .013), JAK2 (HR, 3.100; 95% CI, 1.069-8.989; P = .037), CDKN2A (HR, 10.842; 95% CI, 3.431-34.256; P < .001), and TP53 mutations (HR, 21.634; 95% CI, 5.088-91.981; P < .001) were significant prognostic factors for EFS (Table 1; Figure 6). Furthermore, this result remained unchanged even after adjusting other relevant prognostic factors (Table 1).
Multivariable Cox regression for associations between EFS and somatic mutations identified by univariable Cox regression and LASSO
| . | Frequency . | Events∗ . | Mutations not combined (unadjusted for other prognostic factors) . | Mutations not combined (adjusted for other prognostic factors†) . | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR . | 95% CI . | P value . | HR . | 95% CI . | P value . | |||||
| ZBTB7A | 24 | 7 | 3.308 | 1.285 | 8.515 | .013 | 3.119 | 1.150 | 8.459 | .025 |
| JAK2 | 12 | 5 | 3.100 | 1.069 | 8.989 | .037 | 3.119 | 0.953 | 10.208 | .060 |
| CDKN2A | 7 | 5 | 10.842 | 3.431 | 34.256 | <.001 | 9.815 | 1.702 | 56.591 | .011 |
| TP53 | 4 | 3 | 21.634 | 5.088 | 91.981 | <.001 | 12.229 | 2.516 | 59.435 | .002 |
| Age at diagnosis, y | 1.401 | 0.793 | 2.476 | .246 | ||||||
| Complex | 0.962 | 0.269 | 3.441 | .953 | ||||||
| Trisomy 8 | 0.182 | 0.024 | 1.392 | .101 | ||||||
| Monosomy 7 | 1.116 | 0.235 | 5.306 | .890 | ||||||
| Frequency | Events∗ | Mutations combined (unadjusted for other prognostic factors) | Mutations combined (adjusted for other prognostic factors†) | |||||||
| HR | 95% CI | Pvalue | HR | 95% CI | Pvalue | |||||
| Any of 4 mutations | 39 | 14 | 7.295 | 3.055 | 17.420 | <.001 | 5.762 | 2.341 | 14.186 | <.001 |
| Age at diagnosis, y | 1.366 | 0.841 | 2.219 | .207 | ||||||
| Complex | 1.648 | 0.624 | 4.356 | .313 | ||||||
| Trisomy 8 | 0.206 | 0.027 | 1.560 | .126 | ||||||
| Monosomy 7 | 0.753 | 0.167 | 3.401 | .712 | ||||||
| . | Frequency . | Events∗ . | Mutations not combined (unadjusted for other prognostic factors) . | Mutations not combined (adjusted for other prognostic factors†) . | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR . | 95% CI . | P value . | HR . | 95% CI . | P value . | |||||
| ZBTB7A | 24 | 7 | 3.308 | 1.285 | 8.515 | .013 | 3.119 | 1.150 | 8.459 | .025 |
| JAK2 | 12 | 5 | 3.100 | 1.069 | 8.989 | .037 | 3.119 | 0.953 | 10.208 | .060 |
| CDKN2A | 7 | 5 | 10.842 | 3.431 | 34.256 | <.001 | 9.815 | 1.702 | 56.591 | .011 |
| TP53 | 4 | 3 | 21.634 | 5.088 | 91.981 | <.001 | 12.229 | 2.516 | 59.435 | .002 |
| Age at diagnosis, y | 1.401 | 0.793 | 2.476 | .246 | ||||||
| Complex | 0.962 | 0.269 | 3.441 | .953 | ||||||
| Trisomy 8 | 0.182 | 0.024 | 1.392 | .101 | ||||||
| Monosomy 7 | 1.116 | 0.235 | 5.306 | .890 | ||||||
| Frequency | Events∗ | Mutations combined (unadjusted for other prognostic factors) | Mutations combined (adjusted for other prognostic factors†) | |||||||
| HR | 95% CI | Pvalue | HR | 95% CI | Pvalue | |||||
| Any of 4 mutations | 39 | 14 | 7.295 | 3.055 | 17.420 | <.001 | 5.762 | 2.341 | 14.186 | <.001 |
| Age at diagnosis, y | 1.366 | 0.841 | 2.219 | .207 | ||||||
| Complex | 1.648 | 0.624 | 4.356 | .313 | ||||||
| Trisomy 8 | 0.206 | 0.027 | 1.560 | .126 | ||||||
| Monosomy 7 | 0.753 | 0.167 | 3.401 | .712 | ||||||
LASSO, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator.
Events included induction failure, relapse, or nonrelapse mortality.
DS karyotype was also examined, but none of events developed in patients with DS karyotype, and DS karyotype was not included in the adjustment.
Kaplan–Meier curves of EFS and OS according to identified somatic mutations. (A-E) EFS according to ZBTB7A mutations (A), JAK2 mutations (B), CDKN2A mutations (C), TP53 mutations (D), and the combination of 4 mutations (E); and OS according to the combination of 4 mutations (F). P values for unadjusted Cox regression and for Cox regression adjusted for relevant prognostic factors (age at diagnosis, complex, trisomy 8, and monosomy 7) are reported.
Kaplan–Meier curves of EFS and OS according to identified somatic mutations. (A-E) EFS according to ZBTB7A mutations (A), JAK2 mutations (B), CDKN2A mutations (C), TP53 mutations (D), and the combination of 4 mutations (E); and OS according to the combination of 4 mutations (F). P values for unadjusted Cox regression and for Cox regression adjusted for relevant prognostic factors (age at diagnosis, complex, trisomy 8, and monosomy 7) are reported.
In the entire cohort, a total of 22 events (2 induction failures, 16 relapses, and 4 nonrelapse deaths) occurred, and 14 events (2 induction failures, 10 relapses, and 2 nonrelapse deaths) occurred in 39 patients who had some mutations in the 4 genetic regions (supplemental Table 22). Figure 6 shows that the EFS and OS rates were significantly less favorable in 39 patients who had any of the 4 mutations than in the remaining 138 patients (3-year EFS: 66.6% vs 94.2%; P for unadjusted Cox regression <.001; 3-year OS: 69.0% vs 95.6%; P for unadjusted Cox regression <.001).
Discussion
Molecular profiling of tumors is a fundamental component of precision oncology and identifies genomic alterations in genes and pathways that are potential therapeutic targets. We identified 16 novel driver genes and SVs in ML-DS, including frequent mutational targets such as IRX1, ZBTB7A, and RUNX1 using mutational analysis of a large cohort of patients. These results considerably changed the mutational landscape of ML-DS.
By taking advantage of ML-DS cell lines with mutations in new recurrent mutational targets, we demonstrated that IRX1 and ZBTB7A act as tumor suppressors in ML-DS through their action on a common MYC/E2F pathway. These results suggest that mutations within the MYC/E2F cascade play an important role in promoting the progression of TAM to ML-DS. These findings implied the existence of common molecular functions that could be targeted in the treatment of ML-DS. Indeed, all ML-DS cell lines tested were highly sensitive to the BRD4 inhibitors, which suppressed MYC expression. Notably, all 4 ML-DS cell lines examined were established in relapsed cases. Although these results suggest that BRD4 inhibitors may have therapeutic effects for ML-DS, including relapsed cases, substantial preclinical evidence using primary patient samples or in vivo models is warranted.
Alterations in CDKN2A, JAK2, and EPOR identified in patients with ML-DS are frequently observed in high-risk BCP-ALL.44,51,52CDKN2A alterations are deletions in most cases of both diseases, although deletions are less common in ML-DS than in BCP-ALL.53JAK2 alterations are fusions or missense mutations in high-risk BCP-ALL52 but only missense mutations in ML-DS. In ML-DS, these mutations were more commonly detected in myeloid V617F-proximal sites than in lymphoid R683G-proximal sites (supplemental Table 7). EPOR alterations are nonsense mutations and fusions in ML-DS and high-risk ALL, respectively, and both lead to C-terminal truncations.44,52
ML-DS and DS-associated ALL (DS-ALL) share common mutational targets such as JAK2, CDKN2A, STAG2, RUNX1, EPOR, SH2B3, KRAS, NRAS, PTPN11, GNB1, and IKZF1.54 Despite differences in the observed frequencies, these findings suggest common molecular mechanisms shared by ML-DS and DS-ALL.
The rate of progression from TAM to ML-DS does not differ between Asian and non-Asian patients.16,55,56 Furthermore, somatic mutations in ML-DS are similar in Asians and non-Asians.8,9 These findings suggest that differences in germ line variants between these populations do not affect progression from TAM to ML-DS.
RUNX1 is a master TF of hematopoiesis, and its alteration by gene fusion or point mutation leads to leukemogenesis.57RUNX1 is located in a critical region of chromosome 21 and may contribute to the increased risk of both TAM and ML-DS.58-60 At present, the role of RUNX1 in multistep leukemogenesis in ML-DS is not fully understood. In this study, we demonstrated frequent and highly specific RUNX1-PTD in ML-DS, suggesting that RUNX1 plays an essential role in multistep leukemogenesis in DS. Excess RUNX1A isoform plays a crucial role in leukemogenesis in DS.60RUNX1-PTD involves duplicated P2 promoters, producing RUNX1A-PTD and RUNX1B-PTD in addition to RUNX1A and RUNX1B. In contrast, RUNX1-PTD only produces a partial loss-of-function mutant protein, RUNX1C-PTD, from the P1 promoter. Indeed, 1 patients with ML-DS with RUNX1-PTD (ML-DS 28) appeared to have a lower level of RUNX1B/C protein than a patient without RUNX1-PTD (ML-DS 21). However, the protein and messenger RNA expression levels of RUNX1-PTD were very low in this patient with RUNX1-PTD. In contrast, this patient showed a band with the expected molecular weight for RUNX1A at the same level as that of the patient without RUNX1-PTD (Figure 5A; supplemental Figure 7). These results suggest that the primary consequence of RUNX1-PTD may not be the generation of a significant RUNX1-PTD transcript but rather the introduction of further RUNX1 isoform disequilibrium, which may contribute to the progression from TAM to ML-DS. Our results also revealed a significant concomitant occurrence of RUNX1-PTD and acquired +21 (Figure 2E). Whether acquired +21 results in further isoform disequilibrium should be investigated in future studies.
This study showed that CDKN2A alterations at diagnosis have prognostic value in patients with ML-DS who received modern reduced-intensity chemotherapy. Most patients with CDKN2A alterations died of disease progression within 6 months. Thus, a novel or more intensive chemotherapy regimen other than CET is necessary in these patients. P14ARF activates p53 by binding to the p53 repressor MDM2 and rescuing it from proteasomal proteolysis, whereas p16INK4a antagonizes CDK4/6 to inhibit phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma (RB) gene product, both of which inhibit cell cycle progression.47 In the absence of mutation in RB1, the regulatory function of p16INK4a could be modulated by direct pharmacological inhibition of CDK4/6, even in cases with CDKN2A deficiency. The ML-DS cell line CMK11-5, with a CDKN2A homozygous deletion (supplemental Table 15), was sensitive to the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib, suggesting that CDK4/6 inhibitors are promising candidates for drug development for ML-DS with CDKN2A alterations.
In summary, this study identified an overall picture of genetic mutations in ML-DS. These results may help elucidate the mechanisms of progression from TAM to ML-DS and identify new therapeutic targets for ML-DS. To our knowledge, CDKN2A, TP53, ZBTB7A, and JAK2 are the first genes to be associated with poor prognosis in ML-DS. Although their effects on survival must be confirmed in further studies, they can be used for risk stratification in future clinical trials to test the efficacy of more intensive or alternative therapies. CDKN2A and TP53 mutations/deletions are promising targets for precision oncology in patients with ML-DS.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all of the patients and their families for making this work possible. The authors thank T. Kitamura for providing PLAT-E and H. Kudo, Y. Kudo, M. Kushibiki, and K. Kojima for their technical assistance.
This work was supported by grants-in-aid for scientific research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (26253061, 18H04039, and 21H02877 [E.I.]; 18K07782 and 21K07766 [T.S.]; 17K10094 and 20K08249 [R.K.]; and 20K08201 [T. Toki]) and the Project for Cancer Research and Therapeutic Evolution (JP20cm0106407) from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (E.I.).
Authorship
Contribution: K. Yoshida, S.T., S.O., and E.I. designed the study; K.T., A.K., T.K., S. Sasaki, H. Muramatsu, A.H., Daisuke Hasegawa, A.S., K. Koh, S.K., M.K., J.H., Y.T., C.I., Daiichiro Hasegawa, N.F., M. Yoshitomi, S.I., G.Y., S. Saida, N. Kiyokawa, T.D., M.I., S.A., Y.H., T. Taga, A.M.S., K.H., K.W., and D.T. collected patient materials and clinical data; K.Y., T. Toki, R.S., and H. Matsuo performed sequencing experiments; Y.K., R.S., H. Matsuo, Y.S., K.C., H.T., and S. Miyano performed sequencing data analyses; T.S., T. Toki, R.K., O.Y., M.O., Y.O., S. Mizuno, M. Yoshihara, T.U., N. Kenmochi, K. Kudo, K. Yuzawa, Y.T., T. Tanaka, Y.Y., and T.D. performed functional assays; S. Tanaka, J.M., K. Kisai, and E.I. performed statistical analysis; Y.K., T. Toki, T.U., T.S., and J.M. generated figures and tables; T.S., Y.K., T. Toki, R.K., T.U., S. Tanaka, J.M., S.O., and E.I. wrote the manuscript; S. Takahashi, S.O., and E.I. supervised the study; and all authors participated in discussions and interpretation of the data and results.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: S.O. reports leadership position/advisory role for KAN Research Institute, Inc and Chordia Therapeutics, Inc; is a stockholder in Asahi Genomics Co, Ltd; reports grant/research funding from KAN Research Institute, Inc, Chordia Therapeutics, Inc, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co, Ltd, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd, and Eisai Co, Ltd; and accepted a researcher from Chordia Therapeutics, Inc into the laboratory. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Etsuro Ito, Department of Pediatrics, Hirosaki University Graduate School of Medicine, 5 Zaifu-cho, Hirosaki, Aomori 036-8562, Japan; email: eturou@hirosaki-u.ac.jp; and Seishi Ogawa, Department of Pathology and Tumor Biology, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University, Yoshida-honmachi, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 160-8582, Japan; email: sogawa-tky@umin.ac.jp.
References
Author notes
T.S., K.Y., T. Toki, R.K., and K.T. contributed equally to this study.
Sequencing data were deposited in the European Genome-Phenome Archive (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ega/; accession ID: EGAS00001004691).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

![Distribution of driver mutations. (A-B) Distribution of IRX1 (A) and ZBTB7A alterations (B). Frameshift and nonsense mutations are shown in red and orange, respectively, and missense mutations are shown in blue. (C) The 33 regions of the partial tandem duplication of RUNX1 (RUNX1-PTD) found in 28 ML-DS samples (top) and a schematic representation of the RUNX1-PTD structure (bottom). The most common SVs result from the duplication of a genomic region encompassing RUNX1 exons 3 to 6 (RUNX1C-PTD [Ex3-6]). The variant was annotated as RUNX1C (NM_001754.4). Filled squares indicate coding exons and orange squares indicate runt-homology domains (RHD). P1: distal promoter; P2: proximal promoter; A: RUNX1A isoform-specific last exon. (D) Schematic presentation of RUNX1 isoforms produced from RUNX1-PTD. Only RUNX1C-PTD is expressed from the P1 promoter, whereas RUNX1A and RUNX1B and their PTD isoforms are expressed from the duplicated P2 promoters. (E) Paired associations among somatic mutations and cytogenetic abnormalities observed in at least 3% of patients with ML-DS. Significantly co-occurring and mutually exclusive mutations are indicated by red and blue circles, respectively. Odds ratios and associated q-values are indicated by the color gradient and size of the circles, respectively. Proteindel, protein in-frame deletion; Proteinins, protein in-frame insertion. Lollipop plots were generated using ProteinPaint (https://pecan.stjude.cloud/proteinpaint).](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/143/25/10.1182_blood.2023022247/2/m_blood_bld-2023-022247-gr2b.jpeg?Expires=1769081781&Signature=lHMFEB9Qy9i8rFg-Hl6sp1q5MqDxSLXglihn5eXFnvAx2ODzZe6OTD7WZDPqVG1MOVdUIuaAEA8qwWie6IQlLsGWa8QE-d1rsuNbMdJKC9BmUxI2ZKQRRlQ-Lj6Q2SMr0Y1d~hSURYMIUDJuJkh9aJj6YTQhLiTFG~Bfz3Unuyo4cAk3p5mttMVOHS8m0BuDAbFh1uzHExFu6dvD8Dg05Z~SphWHIAfMJPA4pVXUE~Y9NLuct7A-W8klprpt67MAH4~348RgCjoePW00FwIAYR~UPA9BrhDM3lFeNYYgHQigJrE7Mg0srT3GL1sdYvvFLOaBoLsDCRiB6uSnn~Mr3Q__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal