Background : Point mutations in isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) genes are seen in 20% of adult patients (pts) with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Prognostic significance of each IDH1/2 mutation (mut) analyzed with co-occurring mutations treated with intensive chemotherapy (IC) remains inconsistent, particularly with the advent of IDH inhibitors. Furthermore, the role of allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT) in IDH-mutated without favorable-risk features is not known.
Patients & Methods: Between 2009 and 2016, 262 pts with IDH1/2 mutated AML (101 IDH1mut, 115 IDH2R140Qmutand 46 IDH2R172mut) were treated with IC in younger ALFA-0702 (NCT00932412, n = 133) and older ALFA-1200 (NCT01966497, n = 129) prospective trials. Median age was 50 [42-54] and 67 y [64-71], respectively (resp). Targeted 37-gene next-generation sequencing (NGS) information was available for all pts. According to ELN 2010 classification, non-favorable CR/CRp pts were eligible for SCT if they had a sibling or matched unrelated donor. Correlation between IDHmutand covariates was realized by Pearson correlation coefficient and point biserial correlation for continuous and dichotomic variables, resp. Impact on response and survival was assessed for all covariates present in at least 10% of patients. SCT was considered as a time-dependent variable. Informative variables selected by LASSO were included in multivariate logistic regression for response and multivariate Cox model for survival. All analyses were stratified on the clinical trial.
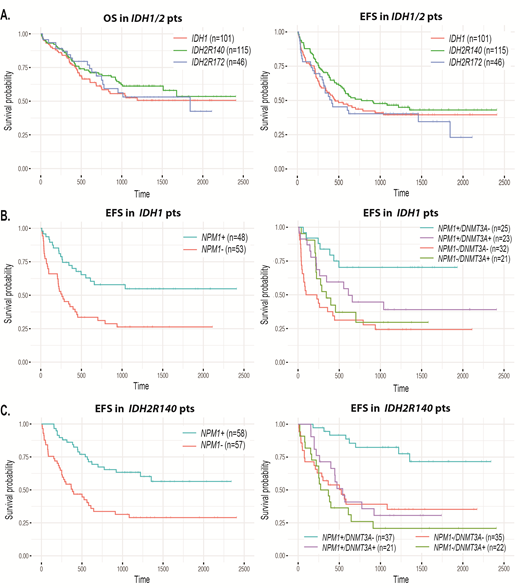
Results:IDH1mutwas significantly associated with NPM1mut(p=0.025), DNMT3Amut(p=0.009) and mutually exclusive with TET2mut(p=0.009). 80% (81/101) of IDH1 mutated pts achieved CR/CRp [96 % (46/48) if concomitant NPM1mut vs 66% (35/53) if not (p=0.0009)]. With a median FU of 39 months, overall median OS was not reached and median EFS was 15 months (Fig 1A). Presence of NPM1mutwas the only variable associated with longer OS (HR=0.33, p=0.001) and EFS (HR = 0.4, p = 0.001) in multivariate analysis. At 5 years, OS was estimated at 68% and 35% and EFS at 55% and 26%, resp (Fig 1B). Effect of concomitant NPM1mutwas reinforced in the absence of DNMT3Amut(HR=0.14, p=0.0006 and HR=0.16, p<0.0001, for OS and EFS resp). At 5 years, EFS was estimated at 70% in IDH1+/NPM1+/DNMT3A- AML pts vs 30% for other IDH1+ AML pts (Fig 1B).
IDH2R140Qmutwas significantly associated with NPM1mut(p=0.0004) and SRSF2mut(p<0.0001) and normal karyotype (p=0.002), but negatively correlated with complex karyotype (p=0.01). 91% (105/125) pts with IDH2R140Q mutated AML achieved CR/CRp [100 % (58/58) if concomitant NPM1mutvs 82% (47/57) if not (NS)]. With a median FU of 40 months, overall median OS was not reached and median EFS was 25 months (Fig 1A). Again, the presence of NPM1mutwas associated with a longer OS and EFS (HR=0.47, p=0.02 and HR= 0.24, p<0.0001, resp). Presence of DNMT3Amutwas associated with shorter OS (HR = 2.1, p=0.02) and EFS (HR = 2, p=0.008) along with high WBC (HR = 1.9, p=0.005) for decreased EFS. At 5 years, OS was estimated at 67% in IDH2R140Q+/NPM1+ AML pts vs 40% in those with IDH2R140Q+/NPM1- AML. At 5 years, EFS was estimated at 56% vs 29% in these two subgroups, resp (Fig 1B). Again, the effect of concomitant NPM1mutwas reinforced in the absence of DNMT3Amut(HR = 0.26, p=0.0009 and HR = 0.15, p<0.0001, for OS and EFS resp). At 5 years, EFS was estimated at 72% in IDH2R140Q+/NPM1+/DNMT3A- AML pts vs 29% in other IDH2R140Q+ AML pts (Fig 1C).
IDH2R172Kmutwas significantly associated with DNMT3Amut(p=0.0004) and BCORmut(p<0.001), as well as +11 (p=0.002), but negatively correlated with NPM1mut(p=0.001). 78% (36/46) pts with IDH2R172Kmutachieved CR/CRp. No genetic alteration was associated with outcome, perhaps due to limited number of pts. With a median FU of 43 months, overall median OS and EFS were 60 and 14 months, resp (Fig 1A).
Finally, in non-favorable ELN 2010 pts (74, 74 and 46 with IDH1mut, IDH2R140Qmutand IDH2R172Kmut, resp), SCT in first CR only benefited to pts with IDH1mut(p=0.004 for OS) or with IDH2R172Kmut(p=0.03 for EFS).
Conclusion: In a large prospective series, NPM1mutis the main better risk factor in the IDH1mutand IDH2R140Qmutsubgroups and may be used as stratification factor in clinical trials testing frontline specific IDH inhibitors with IC. Allogeneic SCT in first CR appears to improve the outcome of pts with non-favorable IDH1 or IDH2R172K mutated AML.
Micol:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy. Thomas:ABBVIE: Honoraria; DAICHI: Honoraria; INCYTE: Honoraria; PFIZER: Honoraria. Braun:Institut de Recherches Internationales Servier (IRIS): Research Funding. Ades:Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Research Funding; Agios: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Helsinn Healthcare: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Silence Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Berthon:PFIZER: Other: DISCLOSURE BOARD; JAZZPHARMACEUTICAL: Other: DISCLOSURE BOARD; CELGEN: Other: DISCLOSURE BOARD. Boissel:NOVARTIS: Consultancy. Vey:Janssen: Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Pigneux:Astellas: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Jazz: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Daichi: Honoraria; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Honoraria. Recher:Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Incyte: Honoraria; Jazz: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Astellas: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sunesis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Astellas: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Macrogenics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Dombret:CELGENE: Consultancy, Honoraria; AGIOS: Honoraria; Institut de Recherches Internationales Servier (IRIS): Research Funding. De Botton:Daiichi: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy, Research Funding; Astellas: Consultancy; Pierre Fabre: Consultancy; Servier: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Forma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Syros: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy; Celgene Corporation: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Bayer: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal