Key Points
EKLF-null erythroid cells completely fail to enucleate due to a block at the orthochromatic stage of differentiation.
EKLF regulation of cell cycle inhibitor proteins is critical for nuclear expulsion; reintroduction of these targets is sufficient for rescue.
Abstract
The mechanisms regulating the sequential steps of terminal erythroid differentiation remain largely undefined, yet are relevant to human anemias that are characterized by ineffective red cell production. Erythroid Krüppel-like Factor (EKLF/KLF1) is a master transcriptional regulator of erythropoiesis that is mutated in a subset of these anemias. Although EKLF’s function during early erythropoiesis is well studied, its role during terminal differentiation has been difficult to functionally investigate due to the impaired expression of relevant cell surface markers in Eklf−/− erythroid cells. We have circumvented this problem by an innovative use of imaging flow cytometry to investigate the role of EKLF in vivo and have performed functional studies using an ex vivo culture system that enriches for terminally differentiating cells. We precisely define a previously undescribed block during late terminal differentiation at the orthochromatic erythroblast stage for Eklf−/− cells that proceed beyond the initial stall at the progenitor stage. These cells efficiently decrease cell size, condense their nucleus, and undergo nuclear polarization; however, they display a near absence of enucleation. These late-stage Eklf−/− cells continue to cycle due to low-level expression of p18 and p27, a new direct target of EKLF. Surprisingly, both cell cycle and enucleation deficits are rescued by epistatic reintroduction of either of these 2 EKLF target cell cycle inhibitors. We conclude that the cell cycle as regulated by EKLF during late stages of differentiation is inherently critical for enucleation of erythroid precursors, thereby demonstrating a direct functional relationship between cell cycle exit and nuclear expulsion.
Introduction
Enucleated red blood cells in peripheral blood account for >80% of the cells in the human body.1 These cells are produced at a staggering rate of ∼2 million erythrocytes per second as a result of a process that begins with the commitment of multilineage progenitors to lineage-restricted erythroid progenitors that yield fully committed proerythroblasts. These then enter terminal differentiation and undergo 4 to 5 cell divisions to differentiate into basophilic, polychromatic, and finally, orthochromatic erythroblasts that extrude their nuclei and give rise to enucleated reticulocytes. Nucleated erythroblasts mature in physical association with macrophages in the erythroblastic island niche, leading to release of enucleated reticulocytes into circulation and further maturation into discoid erythrocytes.2,3 Although this process has been known for >150 years, the mechanisms that drive successful maturation and enucleation remain largely undefined. Illuminating these mechanisms is directly relevant to human anemias that arise due to defective terminal differentiation (such as congenital dyserythropoietic anemias [CDA]), and to the design of improved ex vivo culture systems that require efficient enucleation for therapeutic RBC synthesis.
During terminal differentiation, erythroblasts undergo a decrease in cell size, chromatin and nuclear condensation, nuclear polarization, hemoglobin accumulation, cell cycle exit, and finally, expulsion of the nucleus.4 Not all of these processes are essential for enucleation. For example, nuclear condensation aided by histone deacetylation5,6 and polarization of the condensed nucleus mediated by microtubules7,8 are essential for enucleation. On the other hand, enucleation remains unperturbed despite aberrations in cell size and deficiencies in hemoglobinization.9,10 Although cell cycle exit has been shown to be important for terminal differentiation,11,12 the evidence on its relationship with the enucleation process has thus far been correlative13 and remains an open question. In addition, how erythroid-specific transcriptional regulators temporally regulate these general mitotic factors to ensure successful enucleation has not yet been well explored.
Here, we show that an erythroid-specific transcription factor, Erythroid Krüppel-like Factor (EKLF/KLF1), upregulates cell cycle inhibitors specifically during terminal differentiation and that this regulation is functionally critical for enucleation. Mutations in human EKLF can lead to anemias, some of which are characterized by inefficient terminal differentiation such as CDA type IV.14,15 Genetic ablation of mouse EKLF leads to embryonic lethality by E15 due to severe anemia.16,17 Eklf−/− fetal livers accumulate morphologically immature erythroid progenitors.16 This accumulation has been attributed to a cell cycle defect, with cells prematurely exiting the cell cycle and failing to enter S phase efficiently due to reduced levels of E2F2, an EKLF target that is important for cell cycle progression.18,19 However, rescue of this cell cycle defect in Eklf−/− erythroid cells by crossing to an Rb-null mouse did not alleviate the defects in erythropoiesis or embryonic lethality.18 Enigmatically, EKLF also transcriptionally upregulates genes that typically aid cell cycle exit, such as p2120 and p18,21 suggesting an additional role for EKLF in coordinating cell cycle exit during terminal erythropoiesis. However, a functional delineation of the roles of EKLF during terminal differentiation has been difficult because of the impaired expression of relevant cell surface markers in Eklf−/− erythroid cells. We have circumvented this problem by utilizing an innovative application of imaging flow cytometry and have performed functional studies using an ex vivo culture system that enriches for terminally differentiating cells. We have distinguished the functions of EKLF during terminal erythropoiesis from those during the earlier stages of erythropoiesis and define a novel block during late terminal differentiation in Eklf−/− erythroblasts in vivo. This block is characterized by a defective cell cycle exit and a failure to enucleate due to low levels of p18 and a new EKLF target, p27. Both the cell cycle and enucleation deficits are completely rescued by reintroduction of either of these 2 EKLF target cell cycle inhibitors, demonstrating that EKLF-mediated cell cycle exit is functionally critical for enucleation, therefore revealing a direct and novel functional relationship between cell cycle and enucleation.
Methods
Mice
Timed matings of Eklf+/− mice on C57Bl6 genetic background were performed to obtain Eklf+/+, Eklf+/−, and Eklf−/− E12.5 and E13.5 embryos. Fetal livers were harvested for image stream analyses and ex vivo cultures. Genotyping on the embryo tails was performed by polymerase chain reaction using primers for EKLF and neomycin. All protocols were approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Mount Sinai School of Medicine.
Cell culture
Extensively self-renewing erythroblasts (ESREs) were derived from E12.5 fetal livers and subjected to terminal differentiation as previously described.22 Eklf−/− fetal liver cultures entered extensive expansion more efficiently (9 of 9) compared with Eklf+/+ cultures (5 of 9). Briefly, ESRE expansion media were composed of Stemspan serum-free expansion medium (Stem Cell Technologies) supplemented with 2 U/mL human recombinant Epo (Procrit), 100 ng/mL stem cell factor (Pepro-Tech), 10−6 M dexamethasone (D2915; Sigma), 40 ng/mL insulinlike growth factor-1 (R&D Systems), and Cholesterol Mix (Sigma) at a final concentration of 0.4%, and penicillin/streptomycin (Invitrogen). ESRE terminal differentiation media were composed of 1× Iscove modified Dulbecco medium, 2 U/mL Epo, 100 ng/mL stem cell factor , 10% serum replacement (Invitrogen), 5% plasma-derived serum (Animal Technologies), 1× glutamine, 10% Protein-Free Hybridoma Media II (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and 12.7 µL/100 mL 1:10 monothioglycerol (Sigma). Cells were grown on gelatin-coated plates.
Imaging flow cytometry
E13.5 fetal liver cells and cultured cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes, washed with phosphate-buffered saline, and stained with 1:200 dilution of antibodies Ter119-APC, Kit-PE, CD71-FITC (all from eBioscience), and 10 µM DRAQ5 (Biostatus) in PB2 buffer (Dulbecco phosphate-buffered saline; Thermo Fisher Scientific, 0.1% glucose; Thermo Fisher Scientific, and 0.3% bovine serum albumin; Gemini Bioproducts)23 plus 5% normal rat serum (Invitrogen). For 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdU; BD Pharmingen) studies, cells were processed as per BrdU flow kit (BD Pharmingen) manufacturer’s protocol and stained with BrdU-FITC (provided in the kit), CD71-PE, Kit-PEcy594 (all from eBioscience), and 5 µg/mL 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; Invitrogen). Cells were run on the ImageStreamX (Amnis EMD Millipore) and analyzed with IDEAS software (Amnis EMD Millipore) as previously published.24 Briefly, single, focused, CD71+ cells were analyzed for cell size (area CD71 morphology mask) and nuclear size (area DRAQ5 morphology mask) to gate for various stages of terminal differentiation (see supplemental Figure 1, available on the Blood Web site, for examples of gating and controls). Enucleating orthochromatic erythroblasts were gated using increased asymmetry of nucleus (δ centroid X/Y of CD71 morphology mask and DRAQ5 morphology mask) within an elongated cell.
Cell cycle analysis
For ex vivo studies, 10 µM BrdU was added to cultures for 30 minutes, following which cells were harvested. Cells were fixed and stained with BrdU–antigen-presenting cell antibody and 7-aminoactinomycin D using BrdU flow kit (BD Pharmingen) as per the manufacturer’s protocol. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using an LSRII flow cytometer and analyzed using FlowJo software. For in vivo studies, 100 µL of 10 mg/mL BrdU solution (BD Pharmingen) was injected intraperitoneally into pregnant mice, and E13.5 embryos were harvested after 1 hour. BrdU staining was performed as per manufacturer’s protocol, and imaging flow was performed as detailed above. For propidium iodide (PI) staining, cells were fixed with ethanol and stained with PI prior to flow cytometric analysis for cell cycle.
Statistics
Error bars indicate standard error of the mean, unless mentioned. For measuring statistical significance, unpaired 2-sample Student t test was used. A P value of <0.05 was considered to be significant (*P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001).
Results
EKLF is essential for the enucleation of orthochromatic erythroblasts in vivo
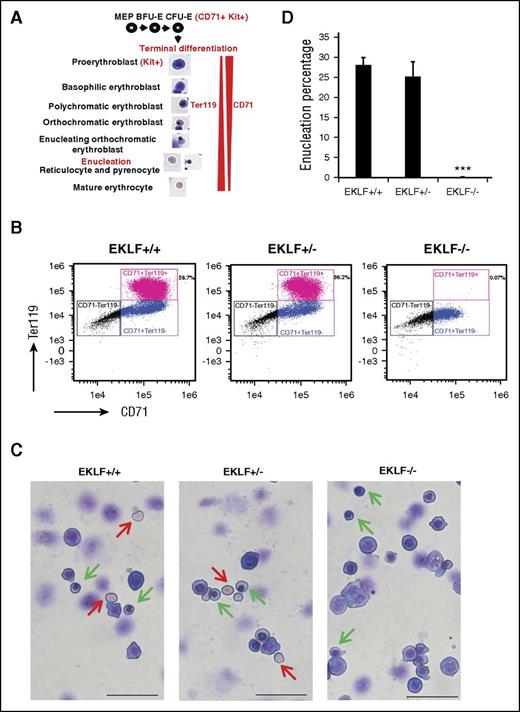
A standard way to assess erythroid differentiation status is by cell surface marker expression; for example, CD71 is expressed during both early erythropoiesis in colony-forming unit–erythroid (CFU-E) progenitors and during terminal differentiation, whereas Ter119 is expressed only at late stages (Figure 1A). More recently, expression of CD44 has provided an improved means to monitor distinct stages.25 However, Eklf−/− cells lack expression of CD44 and Ter119.26 For example, flow cytometric analyses of E13.5 Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− fetal liver cells show that Ter119 is absent in Eklf−/− erythroblasts, whereas CD71 is present at reduced levels (Figure 1B). This lack of expression of many erythroid cell surface markers significantly complicates the study of terminal differentiation of Eklf−/− cells and necessitates the morphological assessment of erythroid maturation. In contrast to the cell surface marker profile, May-Grünwald-Giemsa (MGG) staining reveals that Eklf−/− fetal livers contain cells in various stages of terminal differentiation, including orthochromatic erythroblasts, which is the stage just prior to enucleation (Figure 1C). In addition, we do not detect any evidence for enucleated cells (Figure 1D). Taken together, these results suggest that the Eklf−/− erythroblasts are stalled at orthochromatic stage during terminal differentiation and are defective in attaining enucleation.
E13.5 Eklf−/− erythroblasts can undergo terminal differentiation reaching the orthochromatic erythroblast stage but do not enucleate. (A) Schematic of the stages of terminal differentiation of E13.5 fetal liver erythroid cells showing the expression profile of Kit, CD71, and Ter119 cell surface markers. During terminal differentiation, erythroid precursors express both CD71 and Ter119. (B) Profile of total intensity of CD71 and Ter119 staining analyzed by imaging flow cytometry of E13.5 Eklf+/+, Eklf+/−, and Eklf−/− fetal liver cells. In Eklf+/+ and Eklf+/− livers, populations of erythroid cells (CD71+) progress from Ter119lo to Ter119+ as they mature. In Eklf−/− livers, the CD71+ cells, although present, lack Ter119 expression. (C) MGG staining of cytospins from E13.5 fetal liver cells show that although Eklf+/+ and +/− fetal livers contain enucleated definitive erythroid cells (red arrows), Eklf−/− fetal livers do not. In addition, Eklf−/− fetal livers contain orthochromatic erythroblast cells (green arrows) similar to Eklf+/+ and Eklf+/− fetal livers. Scale bars correspond to 50 µm length. Original magnification ×40. Slides were processed at the same time. (D) Quantification of percentage of enucleated cells from cytospins of E13.5 Eklf+/+ (n = 34 fields; a total of 1237 cells), Eklf+/− (n = 12 fields; a total of 530 cells), and Eklf−/− (n = 85 fields; a total of 2805 cells) fetal livers. ***P < .001.
E13.5 Eklf−/− erythroblasts can undergo terminal differentiation reaching the orthochromatic erythroblast stage but do not enucleate. (A) Schematic of the stages of terminal differentiation of E13.5 fetal liver erythroid cells showing the expression profile of Kit, CD71, and Ter119 cell surface markers. During terminal differentiation, erythroid precursors express both CD71 and Ter119. (B) Profile of total intensity of CD71 and Ter119 staining analyzed by imaging flow cytometry of E13.5 Eklf+/+, Eklf+/−, and Eklf−/− fetal liver cells. In Eklf+/+ and Eklf+/− livers, populations of erythroid cells (CD71+) progress from Ter119lo to Ter119+ as they mature. In Eklf−/− livers, the CD71+ cells, although present, lack Ter119 expression. (C) MGG staining of cytospins from E13.5 fetal liver cells show that although Eklf+/+ and +/− fetal livers contain enucleated definitive erythroid cells (red arrows), Eklf−/− fetal livers do not. In addition, Eklf−/− fetal livers contain orthochromatic erythroblast cells (green arrows) similar to Eklf+/+ and Eklf+/− fetal livers. Scale bars correspond to 50 µm length. Original magnification ×40. Slides were processed at the same time. (D) Quantification of percentage of enucleated cells from cytospins of E13.5 Eklf+/+ (n = 34 fields; a total of 1237 cells), Eklf+/− (n = 12 fields; a total of 530 cells), and Eklf−/− (n = 85 fields; a total of 2805 cells) fetal livers. ***P < .001.
Quantitation and delineation of the precise defects in erythropoiesis in Eklf−/− fetal livers using imaging flow cytometry
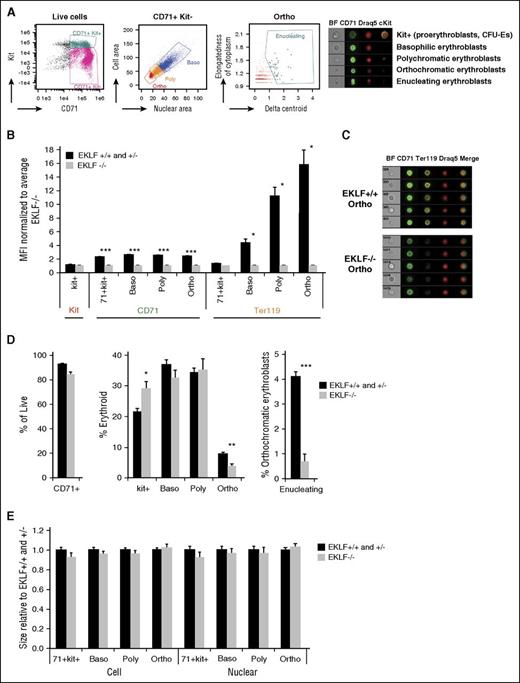
As an alternative approach to standard flow cytometry, we used imaging flow cytometric analysis of erythroblasts,23,24,27,28 which combines the power of flow cytometry and microscopy, to systematically measure the defects in terminal differentiation of Eklf−/− fetal liver cells (Figure 2A; supplemental Figure 1). Here, the classic morphological criteria of decreasing cell area (quantified using CD71 staining) and nuclear condensation (quantified using DRAQ5/DAPI staining) were used to gate for progressive stages of terminal erythroblast differentiation, without reliance on Ter119 and CD44 markers. Superimposed on this, expression of the surface markers Kit and CD71 were used to gate for erythroid progenitors (CFU-Es) and early erythroid precursors (proerythroblasts). Enucleating cells were identified by their asymmetric nuclei (δ centroid) within an elongated cell shape.29 Quantification by median fluorescence intensity analysis of staged image flow data shows that, compared with Eklf+/+, Eklf−/− cells have no significant differences in surface Kit expression in progenitors, a 50% reduced expression of CD71 at all erythroblast differentiation stages, but only 1% expression of Ter119 in orthochromatic erythroblasts (Figure 2B-C), demonstrating again that CD71 and Kit but not Ter119 can be used as a suitable surface marker to sort these cells from either source. Together, these imaging flow analyses enable precise quantification of erythroid differentiation status using morphology without relying on the changes in cell surface marker expression. Our imaging flow results in E13.5 Eklf+/+ fetal livers also agree with a published report of erythroid precursor proportions, which are shifted to more immature forms during the onset of definitive erythropoiesis in the fetal liver.23
Imaging flow cytometry analyses in E13.5 fetal livers reveals 2 main blocks in erythropoiesis: one in Kit+ cells and the other in orthochromatic erythroblasts. (A, left) Gating strategies (of wild-type cells) used for imaging flow cytometry to quantitate Kit+ cells and progressive stages of terminal differentiation (for a more complete gating strategy, see supplemental Figure 1). Cells were stained with CD71, Kit, and DRAQ5/DAPI nuclear stain. BF indicates bright field images. (Right) Representative images of Kit+ (CFU-Es and proerythroblasts), basophilic (baso), polychromatic (poly), orthochromatic (ortho), and enucleating erythroblasts obtained using imaging flow cytometry. (B) Quantitation of median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of Kit, CD71, and Ter119 staining in Eklf−/− fetal livers (n = 4 for kit and CD71; n = 2 for Ter119) normalized to Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− (n = 8 for kit and CD71; n = 3 for Ter119). Ter119 expression is drastically reduced in Eklf−/− erythroblasts during terminal differentiation. (C) Representative Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− orthochromatic erythroblasts identified by imaging flow cytometry show the absence of Ter119 in Eklf−/− cells. CD71 is in green, Ter119 in yellow, and DRAQ5 in red. (D) Alterations in relative proportions of live cells, erythroid cells that are Kit+, and progressive stages of terminal differentiation (basophilic, polychromatic, orthochromatic erythroblasts, and percentage of orthochromatic erythroblasts that were enucleating) were quantified using imaging flow cytometry for Eklf+/+ and Eklf+/− (n = 8), and Eklf−/− (n = 4) E13.5 fetal liver cells. (E) Relative cell size (using CD71 area) and nuclear size (using DRAQ5/DAPI DNA stain area) of Eklf−/− cells normalized to Eklf+/+ and Eklf+/− at progressive stages of differentiation. No significant differences were found between biological replicates of Eklf+/+ and Eklf+/− fetal livers (n = 8) vs Eklf−/− fetal livers (n = 4). *P < .05, **P < .001, ***P < .0001.
Imaging flow cytometry analyses in E13.5 fetal livers reveals 2 main blocks in erythropoiesis: one in Kit+ cells and the other in orthochromatic erythroblasts. (A, left) Gating strategies (of wild-type cells) used for imaging flow cytometry to quantitate Kit+ cells and progressive stages of terminal differentiation (for a more complete gating strategy, see supplemental Figure 1). Cells were stained with CD71, Kit, and DRAQ5/DAPI nuclear stain. BF indicates bright field images. (Right) Representative images of Kit+ (CFU-Es and proerythroblasts), basophilic (baso), polychromatic (poly), orthochromatic (ortho), and enucleating erythroblasts obtained using imaging flow cytometry. (B) Quantitation of median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of Kit, CD71, and Ter119 staining in Eklf−/− fetal livers (n = 4 for kit and CD71; n = 2 for Ter119) normalized to Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− (n = 8 for kit and CD71; n = 3 for Ter119). Ter119 expression is drastically reduced in Eklf−/− erythroblasts during terminal differentiation. (C) Representative Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− orthochromatic erythroblasts identified by imaging flow cytometry show the absence of Ter119 in Eklf−/− cells. CD71 is in green, Ter119 in yellow, and DRAQ5 in red. (D) Alterations in relative proportions of live cells, erythroid cells that are Kit+, and progressive stages of terminal differentiation (basophilic, polychromatic, orthochromatic erythroblasts, and percentage of orthochromatic erythroblasts that were enucleating) were quantified using imaging flow cytometry for Eklf+/+ and Eklf+/− (n = 8), and Eklf−/− (n = 4) E13.5 fetal liver cells. (E) Relative cell size (using CD71 area) and nuclear size (using DRAQ5/DAPI DNA stain area) of Eklf−/− cells normalized to Eklf+/+ and Eklf+/− at progressive stages of differentiation. No significant differences were found between biological replicates of Eklf+/+ and Eklf+/− fetal livers (n = 8) vs Eklf−/− fetal livers (n = 4). *P < .05, **P < .001, ***P < .0001.
Although E13.5 Eklf−/− fetal livers have only about half the numbers of cells compared with Eklf+/+ fetal livers (supplemental Figure 2), the proportions of erythroid cells, quantified by CD71 expression, are similar to Eklf+/+ (Figure 2D left) fetal livers. Within this erythroid population however, there are 2 notable differences (Figure 2D center). First, there is a substantial increase in the proportion of kit-positive cells in Eklf−/− livers compared with Eklf+/+ livers, suggesting an accumulation of CFU-E progenitors and proerythroblasts in fetal livers lacking EKLF, consistent with previous studies.19 Second, a significant proportion of Eklf−/− cells escapes the block in early erythropoiesis and proceeds with little differences in the percentages of basophilic and polychromatophilic erythroblasts until the orthochromatic stage, where they are present at a 2-fold reduced level compared with Eklf+/+ cells. Across all stages, there are no differences in cell or nuclear size (Figure 2E). Nonetheless, within the gated orthochromatic population there is a dramatic 6-fold reduction in the percentage of enucleating erythroblasts (Figure 2D right). These observations demonstrate that Eklf−/− cells stall at the progenitor stage, and although those that escape are able to efficiently condense in cell size and nuclear size during terminal differentiation, they give rise to a decreased number of orthochromatic erythroblasts that are unable to enucleate. Thus, EKLF is absolutely necessary to establish proper levels of late-stage erythroblasts and enucleated reticulocytes.
Eklf−/− orthochromatic erythroblasts are still in S phase in vivo
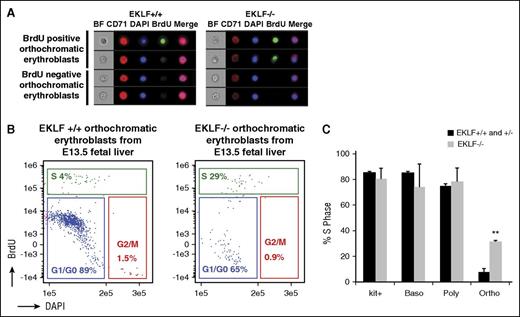
At the orthochromatic erythroblast stage, a majority of cells exit the cell cycle.4,30 As a result, we addressed whether cell cycle defects at this stage may be accompanying the absence of enucleation. Pregnant mice were injected with BrdU, E13.5 Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− fetal livers were harvested after 1 hour, and imaging flow cytometry was performed to quantify the percentage of cells in S phase (BrdU positive cells) at different stages of terminal differentiation (Figure 3A-B; supplemental Figure 3). Although the S-phase percentages are similar between Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− cells in progenitors/proerythroblasts, basophilic, and polychromatic erythroblasts (supplemental Figure 3), there is a surprising 5-fold increase in the percentage of Eklf−/− orthochromatic erythroblasts in S phase compared with Eklf+/+ (Figure 3C). This increase confirms that there is a cell cycle defect in vivo during late stages of terminal differentiation in Eklf−/− erythroblasts, which may lead to an inability of orthochromatic erythroblasts to enucleate.
Orthochromatic erythroblasts in the E13.5 Eklf−/− fetal liver have increased proportion of cells in S phase compared with Eklf+/− and Eklf+/+ fetal livers. (A) E13.5 Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− fetal livers retrieved 1 hour after BrdU injection of pregnant mice were stained for BrdU, CD71, Kit, and DNA (DAPI) and analyzed by imaging flow cytometry. Representative images of Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− BrdU positive and BrdU negative orthochromatic erythroblasts are shown. See supplemental Figure 3 for images of other maturing erythroblasts. (B) Gating of Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− BrdU positive (S phase) orthochromatic erythroblasts by imaging flow cytometry is shown. See supplemental Figure 3 for cell cycle analysis of other maturing erythroblasts. (C) Quantitation of percentage of Eklf+/+, Eklf+/−, and Eklf−/− BrdU positive (S phase) cells during progressive stages of erythropoiesis, as analyzed by imaging flow cytometry. Eklf+/+ and Eklf+/− fetal livers (n = 5); Eklf−/− fetal livers (n = 2). **P < .001.
Orthochromatic erythroblasts in the E13.5 Eklf−/− fetal liver have increased proportion of cells in S phase compared with Eklf+/− and Eklf+/+ fetal livers. (A) E13.5 Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− fetal livers retrieved 1 hour after BrdU injection of pregnant mice were stained for BrdU, CD71, Kit, and DNA (DAPI) and analyzed by imaging flow cytometry. Representative images of Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− BrdU positive and BrdU negative orthochromatic erythroblasts are shown. See supplemental Figure 3 for images of other maturing erythroblasts. (B) Gating of Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− BrdU positive (S phase) orthochromatic erythroblasts by imaging flow cytometry is shown. See supplemental Figure 3 for cell cycle analysis of other maturing erythroblasts. (C) Quantitation of percentage of Eklf+/+, Eklf+/−, and Eklf−/− BrdU positive (S phase) cells during progressive stages of erythropoiesis, as analyzed by imaging flow cytometry. Eklf+/+ and Eklf+/− fetal livers (n = 5); Eklf−/− fetal livers (n = 2). **P < .001.
An ex vivo culture system that enriches for terminally differentiating erythroblasts faithfully recapitulates the defects observed in vivo for Eklf−/− erythroblasts
To test the hypothesis that EKLF-dependent cell cycle alteration at late stages of terminal maturation accounts for the inability of these cells to enucleate, we used an ex vivo culture system. ESREs are highly enriched for proerythroblasts and basophilic erythroblasts, but when subjected to appropriate media conditions can undergo terminal differentiation and high rates of enucleation.22 We established ESRE cultures from Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− E12.5 fetal liver cells (Figure 4A). The similar rates of expansion indicate that EKLF function is not necessary for erythroid precursor self-renewal ex vivo. We next verified that Eklf−/− ESREs undergoing terminal differentiation recapitulate the defects observed in vivo. Similar to their in vivo counterparts, Eklf−/− ESREs do not express Ter119, even at day 3 of differentiation, unlike Eklf+/+ ESREs (supplemental Figure 4). In addition, the differentiated Eklf−/− cells remain pale, unlike the Eklf+/+ cells that accumulate hemoglobin and become red (supplemental Figure 4).
Ex vivo cultures of Eklf−/− erythroblasts recapitulate enucleation and cell cycle defects observed in vivo during terminal differentiation. (A) E12.5 fetal liver definitive erythroid cells were grown in expansion media to derive ESREs. Representative growth curves of Eklf+/+, Eklf−/−, and Eklf+/− fetal liver cultures are shown (from a total of 15). (B) MGG staining of Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− ESREs at day 0 and at day 3 of terminal differentiation. The red arrow shows enucleated cells present at day 3 of differentiation in Eklf+/+ cultures but absent in Eklf−/− cultures. The green arrow shows representative orthochromatic erythroblasts, which are present in both cultures at day 3 of differentiation. Scale bars correspond to 50 µm length. Original magnification ×40. (C) (Left) Cells were stained with CD71, Kit, and DAPI and analyzed using imaging flow cytometry to identify progressive stages of erythroid differentiation. Representative images of Eklf+/+ kit+ (CFU-Es and proerythroblasts), basophilic, polychromatic, orthochromatic, enucleating orthochromatic erythroblasts and pyrenocytes at day 2 of differentiation obtained by imaging flow cytometry are shown. (Right) Quantification of the progressive stages of erythroid differentiation in ESRE cultures using imaging flow cytometry at day 0 and day 2 of differentiation. Eklf+/+ and +/− (n = 8), Eklf−/− (n = 4). (D) Enucleated cells were measured by flow cytometry using DRAQ5 nuclear stain in Eklf+/+, Eklf−/−, and EKLF wild-type rescue in Eklf−/− cells at day 3 of terminal differentiation. (Left) Flow cytometry gating for the DRAQ5-negative population. (Right) Quantification of biological replicates (n = 3) for all 3 cultures show almost complete absence of enucleation in Eklf−/− erythroid cultures. (Bottom) MGG staining was also performed on Eklf−/− cells with wild-type EKLF rescue at day 3 of terminal differentiation. Red arrows show enucleated cells present at day 3 of differentiation of Eklf+/+ cultures and in Eklf−/− cultures with wild-type EKLF rescue, whereas absent in Eklf−/− cultures. Scale bars correspond to 50 µm length. Original magnification ×40. (E) Cell cycle flow cytometric analysis was performed using ethanol-fixed cells stained with PI before (day 0; top) and after (day 2; bottom) erythroid differentiation in ESRE cultures (n = 3). Eklf−/− cultures show a decrease in percentage of cells at G0/G1 and an increase of cells in S phase in Eklf−/− cultures compared with Eklf+/+ cultures. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001.
Ex vivo cultures of Eklf−/− erythroblasts recapitulate enucleation and cell cycle defects observed in vivo during terminal differentiation. (A) E12.5 fetal liver definitive erythroid cells were grown in expansion media to derive ESREs. Representative growth curves of Eklf+/+, Eklf−/−, and Eklf+/− fetal liver cultures are shown (from a total of 15). (B) MGG staining of Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− ESREs at day 0 and at day 3 of terminal differentiation. The red arrow shows enucleated cells present at day 3 of differentiation in Eklf+/+ cultures but absent in Eklf−/− cultures. The green arrow shows representative orthochromatic erythroblasts, which are present in both cultures at day 3 of differentiation. Scale bars correspond to 50 µm length. Original magnification ×40. (C) (Left) Cells were stained with CD71, Kit, and DAPI and analyzed using imaging flow cytometry to identify progressive stages of erythroid differentiation. Representative images of Eklf+/+ kit+ (CFU-Es and proerythroblasts), basophilic, polychromatic, orthochromatic, enucleating orthochromatic erythroblasts and pyrenocytes at day 2 of differentiation obtained by imaging flow cytometry are shown. (Right) Quantification of the progressive stages of erythroid differentiation in ESRE cultures using imaging flow cytometry at day 0 and day 2 of differentiation. Eklf+/+ and +/− (n = 8), Eklf−/− (n = 4). (D) Enucleated cells were measured by flow cytometry using DRAQ5 nuclear stain in Eklf+/+, Eklf−/−, and EKLF wild-type rescue in Eklf−/− cells at day 3 of terminal differentiation. (Left) Flow cytometry gating for the DRAQ5-negative population. (Right) Quantification of biological replicates (n = 3) for all 3 cultures show almost complete absence of enucleation in Eklf−/− erythroid cultures. (Bottom) MGG staining was also performed on Eklf−/− cells with wild-type EKLF rescue at day 3 of terminal differentiation. Red arrows show enucleated cells present at day 3 of differentiation of Eklf+/+ cultures and in Eklf−/− cultures with wild-type EKLF rescue, whereas absent in Eklf−/− cultures. Scale bars correspond to 50 µm length. Original magnification ×40. (E) Cell cycle flow cytometric analysis was performed using ethanol-fixed cells stained with PI before (day 0; top) and after (day 2; bottom) erythroid differentiation in ESRE cultures (n = 3). Eklf−/− cultures show a decrease in percentage of cells at G0/G1 and an increase of cells in S phase in Eklf−/− cultures compared with Eklf+/+ cultures. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001.
Morphological analyses (MGG staining) show that although actively expanding Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− ESREs appears similar, after differentiation, Eklf−/− cells fail to enucleate, accumulate binucleate forms, and contain many orthochromatic erythroblasts at a time when many Eklf+/+ cells have enucleated (Figure 4B). Imaging flow cytometry (supplemental Figure 4) indicates that expanding cultures are exclusively Kit+ and rapidly downregulate Kit expression upon maturation (Figure 4C middle). However, there are dramatic quantitative differences in maturation profiles at day 2 of differentiation: although Eklf+/+ cultures are mostly orthochromatic with some polychromatic cells, Eklf−/− cultures are notably less mature, containing substantial numbers of basophilic and polychromatic cells in addition to orthochromatic erythroblasts (Figure 4C). Even within the orthochromatic population, there is a 4-fold reduction in the percentage of Eklf−/− enucleating erythroblasts compared with Eklf+/+ cells (Figure 4C). Strikingly, the level of pyrenocytes (extruded nuclei) in Eklf−/− cultures is only 3% compared with 31% in Eklf+/+ cultures (Figure 4C). Consistent with these data, direct assessment by flow cytometry of cells that lack DRAQ5 DNA staining (ie, reticulocytes) reveals only 2% of Eklf−/− cells enucleated, compared with ∼45% of Eklf+/+ cells (Figure 4D). Importantly, retroviral rescue of EKLF expression in Eklf−/− ESREs restores enucleation and hemoglobinization as observed by morphology and quantified by flow cytometry (Figure 4D). These data demonstrate that the Eklf−/− cells cultured ex vivo display defects similar to those observed in vivo, but in addition, the ability to quantify pyrenocyte and reticulocyte production shows the extent of the terminal deficit, and the ability to rescue the pure population shows that the deficits are cell-intrinsic.
ESREs were analyzed for cell cycle profile. During the expansion phase (day 0 of differentiation), no significant difference is documented between Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− ESREs. However, at day 2 of differentiation, there are fewer cells exiting the cell cycle and increased numbers of cells in the S phase in Eklf−/− compared with Eklf+/+ erythroid cells (Figure 4E). We confirmed these results by BrdU pulsing of ESREs (supplemental Figure 5). Thus, although expanding Eklf−/− cells behave as Eklf+/+ cells, they display cell cycle defects similar to those observed in vivo and do not exit cell cycle efficiently during late stages of terminal differentiation.
Cdkn1b (p27) is a novel cell cycle target of EKLF during terminal differentiation
A quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) array of 85 cell cycle genes was used to identify the changes in cell cycle gene expression in Eklf−/− vs Eklf+/+ ESREs. There are no significant differences in expression of the genes during the expansion phase; however, at day 2 of differentiation, 15 genes show differential expression greater than 2-fold (not shown). Among these is a known direct cell cycle target of EKLF, p18 (Cdkn2c), with its transcripts showing a 4-fold higher expression in Eklf+/+ erythroid cells (Figure 5A). In addition, p27 (Cdkn1b) is among the most differentially expressed genes, showing a 16-fold higher expression in Eklf+/+ erythroid cells compared with Eklf−/− cells during terminal differentiation (Figure 5A). Consistent with the transcript quantification, protein expression of both is dramatically low in the absence of EKLF during terminal differentiation (supplemental Figure 6). This novel effect on p27 gene expression is direct as it is bound by EKLF in differentiating cells (Figure 5B). Thus, regulation by EKLF of these 2 CDK inhibitors likely plays a significant role in the ability of Eklf+/+ cells to exit the cell cycle and enter the terminal phase of erythroid maturation and explains the increased percentage of orthochromatic cells in S phase that we find in the absence of EKLF (Figures 3C and 4E).
Reexpression of p18/p27 rescues cell cycle defect and enucleation in Eklf−/− ex vivo cultures. (A) qRT-PCR of cell cycle genes before (day 0) and after (day 2) erythroid differentiation of Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− ESRE cultures (n = 3). p18, a previously characterized EKLF target, and p27, a novel EKLF target, were significantly downregulated at day 2 in Eklf−/− cells compared with Eklf+/+ cells. (B) EKLF chromatin immunoprecipitation performed before (day 0) and after (day 2) erythroid differentiation of Eklf+/+ ESRE culture (technical replicate; n = 3) shows that EKLF binds to Cdkn1b (p27) gene specifically during terminal differentiation, indicating that Cdkn1b is a novel direct target of EKLF. (C) Eklf−/− ESREs were retrovirally transduced with Empty vector, EKLF wild-type, or CDKN2C (p18) constructs as indicated. Cells were stained with DRAQ5, and cell cycle flow cytometric analysis was performed at day 3 of erythroid differentiation. Cell cycle defects are rescued in CDKN2C (p18) transduced cells (n = 3). (D) Eklf−/− ESREs were retrovirally transduced with Empty vector, EKLF wild-type, or CDKN1B (p27) construct as indicated. Cells were stained with DRAQ5, and cell cycle flow cytometric analysis was performed at day 3 of erythroid differentiation. Cell cycle defects are rescued in CDKN1B (p27) transduced cells (n = 3). (E) Quantification of enucleation percentage from biological replicates (n = 3) reveals robust rescue of enucleation in CDKN2C (p18) transduced cells. (F) Quantification of enucleation, gated among FSC low cells, at day 3 of differentiation from biological replicates (n = 3) demonstrates a partial rescue of enucleation in CDKN1B (p27) transduced cells. (G) MGG staining of enucleated cells that were sorted for Eklf+/+, p18, or p27 transduced Eklf−/− ESRE cultures at day 3 of differentiation. Scale bars correspond to 50 µm length. Original magnification ×40. Data for p18 are a composite image. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001.
Reexpression of p18/p27 rescues cell cycle defect and enucleation in Eklf−/− ex vivo cultures. (A) qRT-PCR of cell cycle genes before (day 0) and after (day 2) erythroid differentiation of Eklf+/+ and Eklf−/− ESRE cultures (n = 3). p18, a previously characterized EKLF target, and p27, a novel EKLF target, were significantly downregulated at day 2 in Eklf−/− cells compared with Eklf+/+ cells. (B) EKLF chromatin immunoprecipitation performed before (day 0) and after (day 2) erythroid differentiation of Eklf+/+ ESRE culture (technical replicate; n = 3) shows that EKLF binds to Cdkn1b (p27) gene specifically during terminal differentiation, indicating that Cdkn1b is a novel direct target of EKLF. (C) Eklf−/− ESREs were retrovirally transduced with Empty vector, EKLF wild-type, or CDKN2C (p18) constructs as indicated. Cells were stained with DRAQ5, and cell cycle flow cytometric analysis was performed at day 3 of erythroid differentiation. Cell cycle defects are rescued in CDKN2C (p18) transduced cells (n = 3). (D) Eklf−/− ESREs were retrovirally transduced with Empty vector, EKLF wild-type, or CDKN1B (p27) construct as indicated. Cells were stained with DRAQ5, and cell cycle flow cytometric analysis was performed at day 3 of erythroid differentiation. Cell cycle defects are rescued in CDKN1B (p27) transduced cells (n = 3). (E) Quantification of enucleation percentage from biological replicates (n = 3) reveals robust rescue of enucleation in CDKN2C (p18) transduced cells. (F) Quantification of enucleation, gated among FSC low cells, at day 3 of differentiation from biological replicates (n = 3) demonstrates a partial rescue of enucleation in CDKN1B (p27) transduced cells. (G) MGG staining of enucleated cells that were sorted for Eklf+/+, p18, or p27 transduced Eklf−/− ESRE cultures at day 3 of differentiation. Scale bars correspond to 50 µm length. Original magnification ×40. Data for p18 are a composite image. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001.
Reexpression of Cdkn2c (p18) or Cdkn1b (p27) during terminal differentiation rescues cell cycle defects and enucleation in Eklf−/− erythroblasts
This scheme predicts that reestablishing p18 or p27 expression in Eklf−/− erythroid cells should rescue at least some features of terminal differentiation (eg, the cell cycle defect). We tested this idea by transducing Eklf−/− cells with p18- or with p27-expressing virus, identified by expression derived from the IRES-GFP cassette in the retrovirus, and monitoring the phenotypic effects at day 2 of differentiation. In parallel, cells were transduced with EKLF-expressing or empty virus for comparison. The levels of expression of the transduced constructs in Eklf−/− cells were monitored using western blot or qRT-PCR (supplemental Figure 7). We find that reexpression of p18 (Figure 5C) or p27 (Figure 5D) in Eklf−/− cells enables them to exit the cell cycle more efficiently and attain a G0/G1 level similar to that seen with EKLF rescue, and concomitantly to a lower percentage of cells in S phase compared with rescue with empty vector. These data show that expression of either CDK inhibitor EKLF target is sufficient to establish the terminal differentiation phenotype in EKLF-null cells, as gauged by cell cycle status.
A surprise came when we monitored the effects of p18 or p27 rescue on enucleation. Enucleation percentages were quantified by flow cytometry at day 3 of terminal ESRE differentiation. Reexpression of p18 in Eklf−/− cells rescues enucleation to similar levels as obtained by reexpression of EKLF (Figure 5E; supplemental Figure 8). However, p27 did not show similar effects (supplemental Figure 9). To eliminate the confounding effects of p27 overexpression on renewal divisions during earlier stages of terminal differentiation,31 we gated specifically for forward scatter–low cells to enrich for cells at late stages of terminal differentiation (supplemental Figure 9). Using this criterion, we find there is also a partial rescue of enucleation in Eklf−/− cells expressing p27 that approaches that seen with EKLF (Figure 5F). Not surprisingly, Eklf−/− erythroid cells that enucleate after introduction of p18 or p27 expression show little evidence of hemoglobinization (Figure 5G). Collectively, these results show that inability to exit the cell cycle and continued cycling at the late stages of terminal differentiation contribute to the enucleation defect in Eklf−/− fetal liver definitive erythroid cells, and that expression of cell cycle gene targets of EKLF in Eklf−/− erythroblasts rescues both cell cycle and enucleation defects, demonstrating the critical complementary relationship between cell cycle status and physical enucleation of the red cell. On the other hand, hemoglobinization is not necessary for enucleation in definitive erythropoiesis, in agreement with previous observations in hemoglobin-null mice.10
Discussion
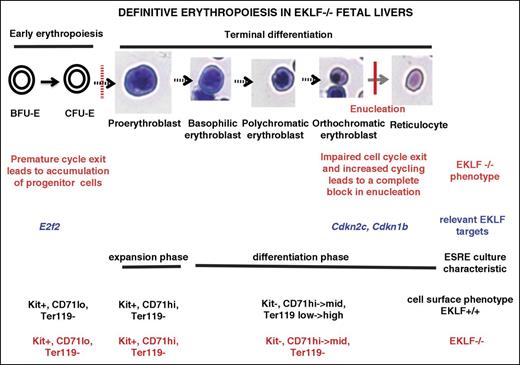
Our studies have uncovered 2 previously unrecognized and important roles for EKLF during late stages of erythroid terminal differentiation. One follows from our use of imaging flow cytometry–based analysis of cells from E13.5 fetal livers to identify populations at different stages of erythropoiesis using cell size, nuclear size, and nuclear position without relying on late-expressing cell surface markers. Although we readily identified orthochromatic erythroblasts in Eklf−/− fetal livers, we did not find enucleated cells. Nonetheless, Eklf−/− cells are able to efficiently decrease cell size, condense their nucleus, and undergo nuclear polarization, enabling us to precisely pinpoint the enucleation block. In vivo analyses show that although Eklf+/+ orthochromatic erythroblasts exit the cell cycle efficiently, significant proportions of orthochromatic Eklf−/− cells are still in S phase. These defects are recapitulated in Eklf−/− ex vivo cultures designed to enrich for terminally differentiating cells. When interpreted together with previous studies,18,19 these results suggest there is a 2-stage block in cell cycle during erythropoiesis in Eklf−/− fetal livers: one at the progenitor stage, which results in a premature cell cycle exit leading to impaired entry into terminal differentiation, and another at the orthochromatic erythroblast stage, where cells exhibit impaired cell cycle exit, with significant proportions still in S phase, yielding late-stage erythroblasts that are not able to enucleate and even become binucleated (Figure 6).
Model of the 2-stage block in erythropoiesis in Eklf−/− definitive erythroid cells. The first block, as described previously,16,18,19 occurs during early erythropoiesis and causes an increased proportion of erythroid progenitor cells and inefficient entry into terminal differentiation. This is attributed to premature cell cycle exit due to reduced levels of E2F2. The cells that escape the first block proceed into terminal differentiation, reaching the orthochromatic erythroblast stage where they undergo a second block leading to an absence of enucleation. This latter block is due to impaired cell cycle exit and an increased proportion of orthochromatic erythroblasts in S phase as a result of reduced levels of p18 (Cdkn2c) and p27 (Cdkn1b). Restoring the levels of p18 or p27 in Eklf−/− cells rescues the cell cycle defects and restores enucleation. A novel aspect that is critical for understanding terminal erythroid differentiation is that the 2-stage block in cell cycle follows from almost diametrically opposed control deficits: the first results in a premature cell cycle exit leading to impaired entry into terminal differentiation, but the second at the orthochromatic erythroblast stage results in impaired cell cycle exit, yielding late-stage erythroblasts still in S phase that are not able to enucleate.
Model of the 2-stage block in erythropoiesis in Eklf−/− definitive erythroid cells. The first block, as described previously,16,18,19 occurs during early erythropoiesis and causes an increased proportion of erythroid progenitor cells and inefficient entry into terminal differentiation. This is attributed to premature cell cycle exit due to reduced levels of E2F2. The cells that escape the first block proceed into terminal differentiation, reaching the orthochromatic erythroblast stage where they undergo a second block leading to an absence of enucleation. This latter block is due to impaired cell cycle exit and an increased proportion of orthochromatic erythroblasts in S phase as a result of reduced levels of p18 (Cdkn2c) and p27 (Cdkn1b). Restoring the levels of p18 or p27 in Eklf−/− cells rescues the cell cycle defects and restores enucleation. A novel aspect that is critical for understanding terminal erythroid differentiation is that the 2-stage block in cell cycle follows from almost diametrically opposed control deficits: the first results in a premature cell cycle exit leading to impaired entry into terminal differentiation, but the second at the orthochromatic erythroblast stage results in impaired cell cycle exit, yielding late-stage erythroblasts still in S phase that are not able to enucleate.
Second and quite surprisingly, epistasis experiments reveal that expression of either of 2 cell cycle inhibitors that are downstream EKLF targets is sufficient to rescue enucleation in EKLF-null cells. E2F2, p18, and p21 have been previously documented as EKLF target genes,18-21 and we now show that p27 is a new direct target of EKLF and that its levels are directly and dramatically affected by EKLF. Paradoxically, this group of EKLF target genes is necessary both for cell cycle progression and for cell cycle exit. We have found that p18 and p27 are highly differentially regulated by EKLF during terminal stages of erythroid maturation, whereas E2F2 and p21 are minimally affected at this stage. E2F2 has been shown to play a role during erythropoiesis,32,33 and in the context of Eklf−/− erythroid cells, reduced E2F2 expression led to an accumulation of progenitors and impaired entry into terminal differentiation due to premature exit in cell cycle.18,19 However, rescue of this cell cycle defect in Eklf−/− erythroid cells by crossing to an Rb-null mouse did not alleviate the defects in erythropoiesis or embryonic lethality.18 Our E2F2 data at late stages are in contrast to the dramatic dependence of its expression on EKLF during early stages of erythropoiesis (ie, in CD71lo/Ter119neg, BFU-E/CFU-E progenitors).18,19 A reasonable synthesis of these observations is that EKLF differentially regulates genes during erythroid maturation in 2 distinct ways: during preterminal, early erythropoiesis by activation of E2F2 in order to promote transition to S phase and consequent cell divisions, and during late stages of terminal differentiation by activation of p18/p27 to promote cell cycle exit and enucleation (Figure 6).
A key, novel aspect that is critical for understanding terminal erythroid differentiation is that the 2-stage block in cell cycle follows from almost diametrically opposed control deficits that result from the absence of EKLF: the first results in a premature cell cycle exit leading to impaired entry into terminal differentiation due to lower levels of E2F2; the second at the orthochromatic erythroblast stage results in impaired cell cycle exit due to low levels of p18 and p27, yielding late-stage erythroblasts still in S phase that are not able to enucleate (Figure 6).
E2F4 is also known to play a role in erythroid differentiation34,35 and is another direct EKLF target.36 Although E2F4 was included in our qRT-PCR cell cycle array analyses, and we saw a slight but significant drop in expression (<2-fold) in the absence of EKLF during terminal differentiation, the effect was not as dramatic as for p27; hence, we focused on this new target and included p18, another CDK inhibitor that is also EKLF-regulated for functional rescue experiments.
The epistasis experiments also reveal a functional link between the regulation of cell cycle exit by EKLF and effective enucleation. Although cell cycle exit is known to be important for terminal differentiation onset, evidence for its relationship with the final enucleation steps that lead to reticulocyte formation has thus far been correlative.13 Our study, using functional rescue experiments, demonstrates that cell cycle exit of orthochromatic erythroblasts is essential for enucleation and further implicates roles for p18 and p27 in this process. There are multiple lines of evidence supporting a role for cell cycle inhibitors, p18 and p27, in late erythropoiesis. p18 levels increase during terminal stages of erythroid differentiation,37,38 as does p27 specifically at the orthochromatic stage in both primitive and definitive erythropoiesis.37-39 p27 plays critical roles in growth arrest during terminal erythropoiesis in definitive cells by inhibiting CDK211,12,40 and in Epo-regulated cell cycle exit in primitive erythropoiesis.39 p18 and p27 have been previously implicated in GATA1- and Myc-mediated cell cycle arrest during erythroid terminal differentiation.38 Enforced expression of p27 in human and mouse erythroleukemia cell lines has been shown to cause differentiation along the erythroid pathway and expression of erythroid markers.12,40,41 Interestingly, loss of p27 did not affect erythroid terminal differentiation in mice.42 One reason for the difference could be compensation by other CDK inhibitors in p27-deficient mice. In the context of Eklf−/− erythroid cells, this may not be possible because the expression of other CDK inhibitors such as p21 and p18 is also aberrant.
Our observations are most directly relevant to patients with mutations in human EKLF/KLF1, such as CDA type IV,14,15 chronic nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia,43 and hydrops fetalis.44 All of these patients’ peripheral blood present with an abnormally high level of nucleated erythroblasts and even some binucleate cells, suggesting a deficiency in enucleation as a result of the EKLF mutation. It will be of interest to test whether cell cycle inhibition is sufficient to enable effective enucleation in those cases. Our studies are also pertinent to approaches that attempt to generate effective levels of human mature red blood cells but are impeded by poor enucleation efficiencies in ex vivo cultures.4 As a result, monitoring and enhancing EKLF levels and/or cell cycle exit of late-stage erythroblasts may improve enucleation efficiencies in order to achieve this therapeutic goal.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Merav Socolovsky, Velia Fowler, Kevin Gillinder, Andrew Perkins, and Saghi Ghaffari for discussion, and Antanas Planutis for technical help.
These studies were supported by the Public Health Service of the National Institutes of Health grants DK102260 from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (J.J.B.) and HL116364 from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (J.P.).
Authorship
Contribution: M.N.G. and J.J.B. designed research; M.N.G., K.E.M., and S.C. performed experiments; M.N.G., K.E.M., J.P., and J.J.B. analyzed the data; L.X. provided murine husbandry; M.N.G. and J.J.B. wrote the paper with input from the others.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: James J. Bieker, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, Department of Developmental and Regenerative Biology, Box 1020, One Gustave L. Levy Pl, New York, NY 10029; e-mail: james.bieker@mssm.edu.