Skip Nav Destination
Close Modal
Update search
- Title
- Author
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- Title
- Author
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- Title
- Author
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- Title
- Author
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- Title
- Author
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- Title
- Author
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
NARROW
Publications
Format
Subjects
Article Type
Topics
Date
Availability
1-20 of 334689
Follow your search
Access your saved searches in your account
Would you like to receive an alert when new items match your search?
1
Sort by
Journal Articles
Next-Generation JAK Inhibitors in the Treatment of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
Available to Purchase
Journal:
Blood
Blood blood.2025028645.
Published: 2026
Journal Articles
Gastrin for the treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease of the stomach
Available to PurchaseJana Gawron, Marie Czech, Tamina Rückert, Verena Holzmüller, Grigor Andreev, Ann-Cathrin Burk, Alina Hartmann, Sangya Chatterjee, Geoffroy Andrieux, Franziska Elisabeth Marquard, Anna-Sophia Baur, Anna-Verena Stell, Máté Krausz, Lukas M Braun, Natascha Osswald, Wolfgang Melchinger, Tobias Wertheimer, Andrea Isabel Proano-Vasco, Kristina Maas-Bauer, Annette Schmitt-Graeff, Melanie Boerries, Natalie Köhler, Francis Ayuketang Ayuk, Christoph Schell, Michael Quante, Robert Zeiser
Journal:
Blood
Blood blood.2025031080.
Published: 2026
Includes: Supplemental data
Journal Articles
Journal Articles
Journal Articles
Acute promyelocytic leukemia diagnosed on soft tissue biopsy: a rare extramedullary presentation
Free
Journal:
Blood
Blood (2026) 147 (2): 215.
Published: 2026
Journal Articles
Journal Articles
Journal Articles
Journal Articles
The treatment of marginal zone lymphoma
Available to Purchase
Journal:
Blood
Blood (2026) 147 (2): 115–126.
Published: 2026
Journal Articles
Hongwei Ren, Natalina Elliott, Bryan Lye, Mohammad Umer Sharif Shohan, Joe W. Cross, Lucy Field, Kanagaraju Ponnusamy, Siobhan Rice, Thomas Jackson, Ilia Leontari, Nouhad El Ouazzani, Rebecca Thomas, Sarah Inglott, Jack Bartram, Owen Smith, Jonathan Bond, Irene A. G. Roberts, Christina Halsey, Rachael Bashford-Rogers, Thomas A. Milne, Anindita Roy, Anastasios Karadimitris
Journal:
Blood
Blood (2026) 147 (2): 180–196.
Published: 2026
Includes: Supplemental data
Journal Articles
Drug development in MZL: caring for the forgotten child
Available to Purchase
Clinical Trials & Observations
Journal:
Blood
Blood (2026) 147 (2): 127–137.
Published: 2026
Journal Articles
Telomere content and genomics of myeloid neoplasia by whole-genome sequencing
Available to PurchaseLuca Guarnera, Adam Wahida, Carmelo Gurnari, Stephan Hutter, Sabine A. Stainczyk, Nakisha D. Williams, Arda Durmaz, Yasuo Kubota, Carlos Bravo-Perez, Naomi Kawashima, Mark Orland, Simona Pagliuca, Yimin Huang, Thomas LaFramboise, Valeria Visconte, Wencke Walter, Manja Meggendorfer, Wolfgang Kern, Frank Westermann, Lars Feuerbach, Torsten Haferlach, Jaroslaw P. Maciejewski
Journal:
Blood
Blood (2026) 147 (2): 197–208.
Published: 2026
Includes: Supplemental data
Journal Articles
Clinical Trials & Observations
Uli S. Herrmann, Matthias Felber, Austen Worth, Sule Haskologlu, Figen Dogu, Victor A. Lewis, Brigitte Strahm, Andreas Groll, Andrew R. Gennery, Fabian Hauck, Robert Wynn, Mary Coussons, Isabelle Meyts, Caroline Lindemans, Victoria Bordon, Robbert G. M. Bredius, Jörn-Sven Kühl, Mirjam Völler, Felix Zirngibl, Irina Zaidman, Alexandra Laberko, Ulrike Zeilhofer, Mathias Hauri-Hohl, Arjan Lankester, Aydan Ikinciogullari, Gregory M. T. Guilcher, Annette Hackenberg, Akif Yeşilipek, Graham Davies, Kanchan Rao, Michael Steven Hershfield, Suhag H. Parikh, Patrick Gilbert, Claudia Bettoni da Cunha Riehm, Michael H. Albert, Ansgar S. Schulz, Manfred Hönig, Bénédicte Neven, Tayfun Güngör
Journal:
Blood
Blood (2026) 147 (2): 138–163.
Published: 2026
Includes: Supplemental data
Journal Articles
The biology of marginal zone lymphoma subtypes: challenge and relevance of classification
Available to Purchase
Journal:
Blood
Blood (2026) 147 (2): 105–114.
Published: 2026
Includes: Supplemental data
Journal Articles
A Notch trans- activation to cis -inhibition switch underlies hematopoietic stem cell aging
Available to PurchaseFrancesca Matteini, Roshana Thambyrajah, Sara Montserrat-Vazquez, Sascha Jung, Alba Ferrer-Perez, Patricia Herrero Molinero, Dina El Jaramany, Javier Lozano-Bartolomé, Eva Mejia-Ramirez, Jessica Gonzalez, Antonio Del Sol, Anna Bigas, Maria Carolina Florian
Journal:
Blood
Blood (2026) 147 (2): 164–179.
Published: 2026
Includes: Multimedia, Supplemental data
Journal Articles
High-grade/large B-cell lymphoma-11q has a very good prognosis in children and young people without a predisposition
Available to Purchase
Clinical Trials & Observations
Leila Ronceray, Minke H. W. Huibers, Katrin Reutter, Oussama Abla, Mara Andrés, Olga Balagué, Monika Csóka, Gil Gilad, Melanie M. Hagleitner, Daiki Hori, Lisa L. Hjalgrim, Janez Jazbec, Wolfram Klapper, Atsuko Nakazawa, Jaime Verdú-Amorós, Hannah von Mersi, Wilhelm Wössmann, Ana C. Xavier, Birgit Burkhardt, Itziar Salaverria, Andishe Attarbaschi
Journal:
Blood
Blood (2026) 147 (2): 209–214.
Published: 2026
Includes: Supplemental data
Images
Published: 2026
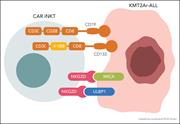
CAR-mediated and NKG2D-dependent targeting of KMT2Ar leukemia by bispecific CAR-iNKT cells. More about this image found in CAR-mediated and NKG2D-dependent targeting of KMT2Ar leukemia by bispecific...
Images
Published: 2026
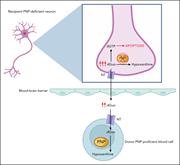
“Cross-correction” of PNP deficiency in neuronal cells after allogeneic HCT. In the recipient’s PNP-deficient neurons, the absence of functional PNP enzyme prevents the phosphorolysis of substrates such as deoxyguanosine (dGuo) into hypoxanthine, leading to accumulation of dGTP. This disrupts the ce... More about this image found in “Cross-correction” of PNP deficiency in neuronal cells after allogeneic HCT...
Images
Published: 2026
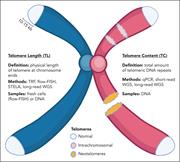
Overview of contributors to TC. TL reflects the physical length of telomeric DNA repeats at the natural ends of chromosomes, which can be measured using methods such as TRF, flow-FISH, STELA, and long-read WGS. TC measures the total amount of telomeric DNA repeats and may include sources such as int... More about this image found in Overview of contributors to TC. TL reflects the physical length of telomeri...
Images
Outcome measures of the 72 patients with HGBCL-11q that were studied. (A) ...
Available to Purchase
in High-grade/large B-cell lymphoma-11q has a very good prognosis in children and young people without a predisposition
> Blood
Published: 2026
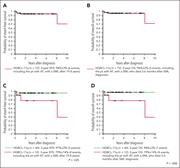
Figure 1. Outcome measures of the 72 patients with HGBCL-11q that were studied. (A) EFS and (B) OS of the 72 patients with HGBCL-11q. (C) EFS and (D) OS of the 60 patients with HGBCL-11q without a preexisting disorder compared with those of the 12 patients with HGBCL-11q with a preexisting disor... More about this image found in Outcome measures of the 72 patients with HGBCL-11q that were studied. (A) ...
1
Advertisement intended for health care professionals