Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
IL-7 receptor signaling drives human B-cell progenitor differentiation and expansion
In mice, absent interleukin-7 (IL-7) signaling abrogates both T and B lymphopoiesis. However, in patients with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) resulting from IL-7 receptor mutations, B lymphopoiesis is preserved, suggesting that IL-7 signaling is not required to make B cells. In a Plenary Paper, Kaiser et al report that IL-7 is in fact critical for B-cell proliferation and cell fate decisions, although its absence does not eliminate all B cells. Further study will be needed to determine whether this subset of SCID patients who have undergone transplantation achieve true B-cell immunocompetence.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Fixed-duration venetoclax plus obinutuzumab improves quality of life and geriatric impairments in FCR-unfit patients with CLL
Clinical Trials & Observations
van der Straten and colleagues examined the impact of venetoclax plus obinutuzumab (Ven-O) on 67 previously untreated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who were deemed unfit for fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR). They evaluated impact on patient-related outcomes, including geriatric assessments and health-related quality of life (HRQoL). Geriatric impairments were present in 90% of patients at baseline and predicted for nonhematological toxicity. However, Ven-O treatment is associated with decreased impairment and improved HRQoL.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
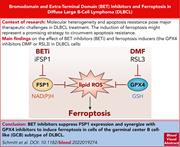
BRD4 inhibition sensitizes diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells to ferroptosis
First-line immunochemotherapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) fails to produce a durable remission in about one-third of patients. Previous studies have suggested that the germinal center B-cell-like subset of DLBCL is sensitive to triggering of ferroptosis (iron-mediated cell death). Schmitt and colleagues screened a library of epigenetic modulators and demonstrate that bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) inhibitors enhance ferroptosis, suggesting the combination of BET inhibitors and ferroptosis-inducing agents as a novel therapy for DLBCL.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
Low-density lipoprotein promotes microvascular thrombosis by enhancing von Willebrand factor self-association
Chung et al examined the role of low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) in modifying von Willebrand factor (VWF) self-association. They previously demonstrated that at high shear stress, VWF self-association increases and is attenuated by high density lipoproteins. Here, they show that LDL binds to VWF at high shear stress and enhances self-association and microvascular thrombosis. They propose that targeting the LDL-VWF interaction may improve thrombotic microangiopathy, atherosclerosis, and other disorders of defective microvascular circulation.
LETTER TO BLOOD
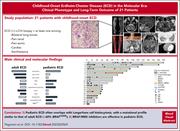
Childhood-onset Erdheim-Chester disease in the molecular era: clinical phenotypes and long-term outcomes of 21 patients
Clinical Trials & Observations
Erdheim-Chester disease (ECD) is a rare histiocytic disorder that can present as a localized infiltration of foamy histiocytes or a multisystem disease that may be life-threatening. It is extremely rare in children. Pegoraro and colleagues present the clinical and molecular features of 21 patients with pediatric ECD through a large international collaboration, documenting that it resembles its adult counterpart, with similar molecular features and responses to agents targeting BRAF and MEK.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Low-density lipoprotein enhances platelet von Willebrand factor thrombus formation in mesenteric microvessels of wild-type mice after 5 and 11 minutes of stimulation with calcium ionophore. See the article by Chung et al on page 1156.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






The “B” side of IL-7Rα–deficient SCID