Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Brentuximab vedotin in combination with nivolumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: 3-year study results
Clinical Trials & Observations
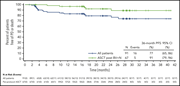
The emergence of brentuximab vedotin and checkpoint inhibitor therapy has expanded the therapeutic landscape of relapsed and/or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), and combinations are being explored to improve cure rates. Advani et al provide a 3-year follow-up analysis of the combination of brentuximab and the checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab as initial salvage therapy with subsequent autologous stem cell transplant in some patients, reporting that >75% remain progression free. These data should prompt a reexamination of current salvage strategies for HL.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
A comprehensive transcriptome signature of murine hematopoietic stem cell aging
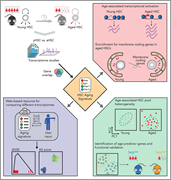
How hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) age and how to measure the age of HSCs remain research challenges. Taking advantage of novel computational biology tools, Svendsen and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 16 transcriptomic datasets of aged HSCs and defined a unique and robust signature of aging murine HSCs from both bulk and single-cell studies. They demonstrate its utility by functionally defining how 1 informative gene, Selp, influences stem cell behavior and by outlining how young and aged HSCs could be identified prospectively.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
A composite single-nucleotide polymorphism prediction signature for extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
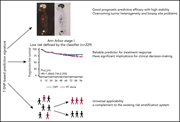
Extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma is a molecularly heterogeneous disease that is most common in Asia and Latin America. Accurate staging and prognostication are central to the delivery of appropriate care. Tian and colleagues et al report that prognostication can be improved by the application of a novel 7–single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) classifier. The authors provide a nomogram that incorporates the 7-SNP classifier and previously established independent clinical variables to facilitate its translation into practice.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
GADD45g acts as a novel tumor suppressor, and its activation suggests new combination regimens for the treatment of AML
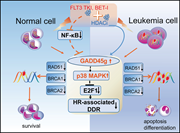
The growth arrest and DNA damage–induced 45 (GADD45) proteins are stress sensors implicated in the regulation of cell survival and genomic stability. Guo et al identified GADD45g as a tumor suppressor in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) whose expression is downregulated by epigenetic silencing and oncogene activity. They used in vitro and in vivo models to investigate the mechanisms by which GADD45 is silenced in some AMLs and conversely demonstrate that it can be activated for therapeutic advantage in primary AML cells by currently available targeted therapies.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
CALR mutant protein rescues the response of MPL p.R464G variant associated with CAMT to eltrombopag
Much is known about the regulation of signaling by thrombopoietin through its receptor, MPL, and congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia is a consequence of loss-of-function mutations in MPL. Basso-Valentina and colleagues add to our knowledge through identification and functional evaluation of a novel mutation (MPL p.R464G) in a patient, revealing its abnormal retention in the endoplasmic reticulum. They also made an additional novel finding, reporting that mutant calreticulin can partially rescue megakaryocyte differentiation by progenitor cells from the patient in response to eltrombopag.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
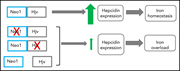
Hepatocyte neogenin is required for hemojuvelin-mediated hepcidin expression and iron homeostasis in mice
Neogenin (NEO1) is a transmembrane receptor responsible for crucial functions in diverse cellular processes ranging from cell motility and adhesion to survival and differentiation. To mediate these functions, neogenin binds different ligands, one of which is hemojuvelin (HJV), the protein mutated in juvenile hemochromatosis. But its role in iron homeostasis has been controversial. Enns et al resolve this by reporting compelling evidence in murine models that hepatocyte NEO1 is essential for systemic iron homeostasis, upregulating hepcidin expression via its association with HJV.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Overexpression of mutant calreticulin (red) combined with eltrombopag treatment of congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia patient cells restores megakaryopoiesis as shown by CD41 (green) and von Willebrand factor (cyan) staining. See the article by Basso-Valentina et al on page 480.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals


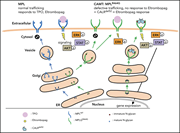

Expanding landscape for relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations