Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
BLOOD SPOTLIGHT
Imetelstat: a new addition to the therapeutic landscape of lower-risk MDS
Clinical Trials & Observations
Imetelstat is an oligonucleotide telomerase inhibitor recently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for adults with lower-risk myelodysplasia who are red cell transfusion–dependent and are ineligible for or failed prior erythropoiesis-stimulating agent therapy. In this Blood Spotlight, Abaza and DeZern succinctly review the biologic basis for this agent and the clinical data leading to approval. The authors provide a useful outline of how imetelstat may be incorporated in treatment options for lower-risk myelodysplasia.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Genetic and clinical spectrum of SAMD9 and SAMD9L syndromes: from variant interpretation to patient management
Sterile alpha motif domain–containing protein 9 (SAMD9) and SAMD9-like (SAMD9L) syndromes are relatively new leukemia predisposition syndromes caused by germ line mutations in SAMD9 and SAMD9L genes that result in multisystem abnormalities, including bone marrow failure, immunodeficiency, and a risk for myelodysplasia and monosomy 7. Sahoo and colleagues review these disorders using registry data to better understand their clinical spectrum, challenges in genetic testing, molecular biology, clonal evolution, and treatment strategies. The authors emphasize the need for natural history studies, particularly for patients acquiring monosomy 7, to inform evidence-based surveillance and optimize transplant timing.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
A phase 1 study of the amino acid modulator pegcrisantaspase and venetoclax for relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia
Clinical Trials & Observations
Pegcrisantaspase (PegC), a pegylated form of Erwinia asparaginase used for patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who have hypersensitivity to Escherichia coli–derived asparaginase products, depletes cells of glutamine and affects protein translation. In a phase 1 clinical trial of PegC in combination with venetoclax in adults with relapsed and refractory acute myeloid leukemia, Liu and colleagues report a 33% rate of either a complete remission (CR) or a CR with incomplete blood count recovery. Given that this cohort has limited treatment options, these promising findings merit further evaluation.
Zanubrutinib, obinutuzumab, and venetoclax for first-line treatment of mantle cell lymphoma with a TP53 mutation
Clinical Trials & Observations
The TP53 mutation is the most significant negative prognostic feature in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), and more effective treatment for these high-risk patients is needed. Kumar and colleagues report on a multicenter phase 2 study of zanubrutinib, obinutuzumab, and venetoclax in untreated patients with TP53-mutated MCL and show a high response rate in 25 patients, with 22 attaining a complete response and a 2-year progression-free survival of 72%. These promising results support future evaluation of this regimen and possible use of consolidation regimens to further extend the observed benefits.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
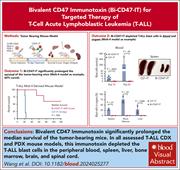
Bivalent CD47 immunotoxin for targeted therapy of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
CD47 is overexpressed on the surface of many cancer cells, providing a “don’t eat me” signal that allows the tumor cells to evade phagocytosis; however, immunotherapy approaches targeting CD47 have largely proved disappointing in the clinic. Ma et al report on a novel, bivalent CD47 immunotoxin that demonstrates strong antitumor responses in vitro and in vivo in a mouse model of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, without affecting CD47 on red blood cells. The authors’ data suggest an approach that improves therapeutic efficacy while minimizing side effects like anemia, supporting the rationale for future clinical trials.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Development of hyperdiploidy starts at an early age and takes a decade to complete
Brief Report
Hyperdiploidy is considered an initiating event in multiple myeloma, but it is not clear how long the time is from the first genetic event to a diagnosis of myeloma. Samur et al used whole-genome sequencing and advanced analyses to suggest that the presence of clonal plasma cells likely precedes the clinical detection of a monoclonal protein by decades. While this discovery is biologically intriguing, further research is required to assess its clinical relevance and whether early screening could help intercept cases that might progress to myeloma.
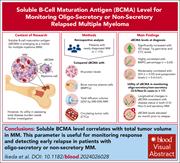
Soluble B-cell maturation antigen levels for disease monitoring in oligosecretory and nonsecretory relapsed multiple myeloma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
LETTER TO BLOOD
Beyond static measurements: dynamic frailty improves survival prediction in multiple myeloma
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
RETRACTION
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Bone marrow histopathology of a child with pathogenic SAMD9 variant presenting with refractory cytopenia of childhood and monosomy 7. Bone marrow biopsy is hypocellular and shows clusters of proerythroblasts (hematoxylin and eosin stain, 400× magnification). See the article by Sahoo et al on page 475.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals