Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
SPECIAL REPORT
Management of adult patients with CMML undergoing allo-HCT: recommendations from the EBMT PH&G Committee
Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) is a rare disease with poor prognosis, for which the only potentially curative treatment is allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (allo-HCT). The evidence base for deciding who, when, and how to perform allo-HCT is growing but remains underdeveloped. In this Special Report, an international panel of experts reviews current knowledge and provides recommendations for patient selection and transplant-regimen choices.
REVIEW ARTICLE
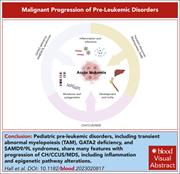
Malignant progression of preleukemic disorders
As we recognize and diagnose an increasing number of preleukemic hematological states, we need to reconsider previously accepted notions about progression to acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Hall and colleagues provide a review that focuses on 4 disparate preleukemic states and what is known about the mechanisms of progression to AML, highlighting stem cell intrinsic changes in transcription and splicing factors as well as extrinsic changes. The authors identified some common features, such as monosomy 7 and inflammation, suggesting a paradigm to help us understand this complex process.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Fitusiran prophylaxis in people with hemophilia A or B who switched from prior BPA/CFC prophylaxis: the ATLAS-PPX trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Fitusiran is a novel, small interfering RNA oligonucleotide directed against antithrombin that is subcutaneously injected monthly. Kenet and colleagues report on an open label, before-after design, phase 3 trial for patients with hemophilia A or B, with or without inhibitors, comparing fitusiran with a bypassing agent or clotting factor prophylaxis, respectively. Fitusiran reduces bleeding events significantly but may increase thrombotic events. These data suggest fitusiran could provide a new treatment option for some patients.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
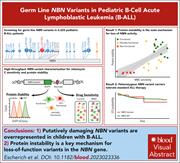
Germ line genetic NBN variation and predisposition to B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children
Biallelic loss-of-function germ line variants in the DNA damage repair gene nibrin (NBN) cause Nijmegen breakage syndrome, which carries an increased risk of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). By studying a cohort of >4000 patients with ALL, Escherich et al reveal that deleterious heterozygous germ line variants in NBN result in a loss of protein stability and are associated with an increased risk of pediatric B-cell ALL. The authors’ findings further our knowledge of germ line predisposition for sporadic cases of childhood ALL and will prompt the search for more predisposition genes.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
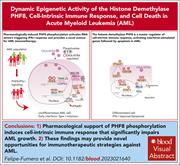
Epigenetic control over the cell-intrinsic immune response antagonizes self-renewal in acute myeloid leukemia
Avoiding immune destruction is a key evasion strategy acquired by leukemic cells. Fumero et al show that activating the histone demethylase PHF8 can trigger cell-intrinsic immune responses and specifically target acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells. Pharmacologically induced PHF8 phosphorylation activated RNA sensors, triggering an interferon response. This study opens the possibility of targeting PHF8 as a new immunotherapy modality for AML.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
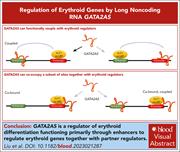
Long noncoding RNA GATA2AS influences human erythropoiesis by transcription factor and chromatin landscape modulation
Our knowledge of how erythropoiesis is so exquisitely coordinated remains incomplete. Using various strategies, Liu et al report on the acceleration of erythroid differentiation and reduction of fetal hemoglobin expression after depletion of a GATA2 gene–associated antisense long noncoding RNA (GATA2AS) in both erythroid cell lines and primary human erythroblasts. This occurs through modulation of several transcription factors and chromosome accessibility.
VASCULAR BIOLOGY
Mutations causing premature termination codons discriminate and generate cellular and clinical variability in HHT
Clinical Trials & Observations
LETTER TO BLOOD
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization of long noncoding RNA GATA2AS labeled with Alexa Fluor 594 (red) in K562 cells. Distribution of GATA2AS in DAPI-stained nuclei is revealed, showing some clustering. See the article by Liu et al on page 2300.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals