Key Points
The HIF inhibitor ACF suppresses TKI-insensitive CML stem cells.
The FDA-approved drug ACF may represent a novel treatment to prevent CML relapse and, in combination with TKIs, improve remission.
Abstract
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a hematopoietic stem cell (HSC)-driven neoplasia characterized by expression of the constitutively active tyrosine kinase BCR/Abl. CML therapy based on tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) is highly effective in inducing remission but not in targeting leukemia stem cells (LSCs), which sustain minimal residual disease and are responsible for CML relapse following discontinuation of treatment. The identification of molecules capable of targeting LSCs appears therefore of primary importance to aim at CML eradication. LSCs home in bone marrow areas at low oxygen tension, where HSCs are physiologically hosted. This study addresses the effects of pharmacological inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1), a critical regulator of LSC survival, on the maintenance of CML stem cell potential. We found that the HIF-1 inhibitor acriflavine (ACF) decreased survival and growth of CML cells. These effects were paralleled by decreased expression of c-Myc and stemness-related genes. Using different in vitro stem cell assays, we showed that ACF, but not TKIs, targets the stem cell potential of CML cells, including primary cells explanted from 12 CML patients. Moreover, in a murine CML model, ACF decreased leukemia development and reduced LSC maintenance. Importantly, ACF exhibited significantly less-severe effects on non-CML hematopoietic cells in vitro and in vivo. Thus, we propose ACF, a US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drug for nononcological use in humans, as a novel therapeutic approach to prevent CML relapse and, in combination with TKIs, enhance induction of remission.
Introduction
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), a clonal disease affecting hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), is driven by the 9;22(q34.1;q11.2) chromosomal translocation, which results in expression of the BCR/Abl oncoprotein, a constitutively active tyrosine kinase. Chronic-phase CML patients are treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) targeting BCR/Abl, such as imatinib-mesylate (IM).1 In most cases, successful TKI therapy leads, rather than to CML cure, to a state of minimal residual disease, apparently sustained by the persistence of TKI-resistant leukemia stem cells (LSCs).2-6 Thus, the search for drugs capable of targeting these cells is of primary importance in order to eradicate CML.
In bone marrow (BM), LSCs most likely reside in stem cell niches located within tissue areas at very-low-oxygen tension, where HSCs are physiologically hosted.7,8 Studies from our group9,10 and others11,12 demonstrated that low oxygen maintains HSC survival and stem cell potential, favoring HSC self-renewal. The same applies to LSCs,13 those of CML in particular.4,5,14 Interestingly, the BCR/Abl oncoprotein is suppressed in low oxygen.4,5,15 This mechanism, among others,16,17 well explains the refractoriness of LSCs to BCR/Abl-targeting TKIs, provided they manage to survive in the absence of BCR/Abl kinase signaling.
Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are key regulators of cell adaptation to low oxygen.18 HIF-1 is a transcription factor composed of an α and a β subunit and regulated mainly by oxygen tension. Oxygen levels lower than 7% stabilize HIF-1α, which binds the HIF-1β subunit and drives the transcription of genes regulating energetic metabolism, cell survival/proliferation, and angiogenesis.18 HIF-1 also drives cancer progression.19 In CML cell populations, HIF-1α and HIF-responsive genes are upregulated by BCR/Abl.20,21 In murine models of CML, the genetic knockout of HIF-1α prevents CML development by impairing cell cycle progression and inducing apoptosis in LSCs.21 Thus, HIF-1α represents a critical factor in CML and its targeting appears as a potential therapeutic strategy to eradicate LSCs.
In this study, we addressed the effects of pharmacological inhibition of HIF-1α in CML. Using CML cell lines and primary cells as well as a murine model of CML, we found that LSCs that survive TKI treatment are instead sensitive to acriflavine (ACF), a HIF-1 inhibitor22 approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for nononcological human use. On this basis, we propose ACF as a novel therapeutic approach to prevent CML relapse.
Materials and methods
Cells and culture conditions
Cell lines were cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 medium (K562,23 KCL22,24 and LAMA-8425 CML cells) or Dulbecco's modification of Eagle's minimum essential medium (DMEM) (HEK293T26 and NIH/3T327 cells) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 50 U/mL penicillin, 50 mg/mL streptomycin, 2 mM glutamine (Euro-Clone, Paington, United Kingdom).
K562 cells transfected with short hairpin RNA (shRNA) against HIF-1α (shHIF-1α) or control shRNA against red fluorescent protein were sorted on the basis of green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression.28 The shRNA sequence targeting HIF-1α was gatgttagctccctatatcccTTCAAGAGAgggatatagggagctaacatc; the control shRNA sequence was gctccaaggtgtacgtgaaTTCAAGAGAttcacgtacaccttggagc (uppercase, loop; lower case, shRNA sequence).
Mononuclear cells (MCs) from BM (BMMCs) of CML patients (supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood Web site) or peripheral blood (PB, buffy coat; PBMCs) of healthy donors were cultured in Iscove's modification of DMEM (IMDM) supplemented with 20% FBS, 50 U/mL penicillin, 50 mg/mL streptomycin, 2 mM glutamine, and cytokines (supplemental Methods).
Exponentially growing cells were plated at 3 × 105/mL and incubated at 37°C in low oxygen (water-saturated atmosphere containing 0.1% O2, 94.9% N2, and 5% CO2) in a DG250 Anaerobic Workstation (Don Whitley Scientific, Bridgend, United Kingdom) or normoxia (21% O2 and 5% CO2). The O2 concentration used for low oxygen incubation mimics that of endosteal areas,29,30 in which most primitive stem cells reside.7
Cell viability was measured by trypan blue (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) exclusion test.
Reagents
3-(5′-Hydroxymethyl-2′-furyl)-1-benzyl-indazole (YC1; Sigma-Aldrich) and dasatinib (Dasa; Biovision, Milpitas, CA) were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). IM (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX) and ACF (Sigma-Aldrich) were dissolved in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). ACF decreases HIF transcriptional activity by inhibiting α/β dimerization22 ; YC1 inhibits HIF-1α activity by promoting its degradation, inhibiting its translation,31-33 stimulating “factor-inhibiting HIF,” and reducing binding of p300, a coactivator indispensable for transcription initiation of HIF-1α downstream genes.34
Cell lysis and western blotting
Whole-cell lysates were obtained using Laemmli buffer. Hypotonic buffer was used for cytosol/nucleus separation. Protein concentration was determined by the bicinchoninic acid method (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) and 30 μg to 50 μg of protein per sample were subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (Merck-Millipore, Billerica, MA) by electroblotting.35 Membranes were incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibody (supplemental Methods). Antibodies were diluted 1/1000 or 1/500 (anti-c-Abl, anti-vascular endothelial growth factor [VEGF], anti-HIF-1α, anti-Sox2) in Odyssey Blocking Buffer (LI-COR Biosciences, Lincoln, NE) 1/1 with PBS–0.1% Tween 20. Washed membranes were incubated for 1 hour at room temperature in Odyssey Blocking Buffer 1/1 with PBS containing IRDye800CW (1/20 000)–conjugated or IRDye680 (1/30 000)–conjugated secondary antibody (LI-COR Biosciences). Antibody-coated protein bands were visualized by Odyssey Infrared Imaging System Densitometry (LI-COR Biosciences).
RNA extraction and q-PCR
Cells (9 × 106) incubated in low oxygen or normoxia were washed with PBS and total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent (ThermoFisher Scientific) following the manufacturer’s protocol. Residual DNA was removed by DNase-I (Roche Diagnostics, Lewes, United Kingdom). RNA quality was evaluated in a 2% agarose gel. Complementary DNA was synthesized using the ImProm-II Reverse Transcription System kit (Promega, Madison, WI) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (q-PCR) was carried out using Green GoTaq qPCR Master Mix (Promega). Primers were from Qiagen (CAIX, HIF-1α; Hilden, Germany) or designed as in supplemental Table 2.
Culture repopulation ability (CRA) assay
The CRA assay is an in vitro cognate of marrow repopulation ability assay in vivo where cells to be assayed are, rather than transplanted into syngeneic animals, transferred into growth-permissive liquid cultures (LC2) to monitor the entity and kinetics of their repopulation.16,36,37 Peak value and time-to-peak of LC2 repopulation are indicators of the stem cell potential of input cells. In this study, cells were subjected to drug treatment in liquid cultures (3 × 105 cells per mL) incubated in low oxygen (LC1) for 7 or 9 days, washed free of drug, and transferred in fresh medium to normoxic LC2 (3 × 104 cells per mL), where viable cell number was determined at different times. Medium was never renewed during incubation in LC1 and LC2.
Isolation of human MCs and CD34+ cell enrichment
BM aspirates from CML patients or PB samples from healthy donors were obtained following informed consent and under the approval of the Ethics Committee of AOUC (authorization no. 520/10, 18 October 2010, renewed with no. 2015/0032965, 4 November 2015). MCs were Ficoll-isolated (Cedarlane Laboratories, Burlington, ON, Canada) following the manufacturer’s instructions, centrifuged, and plated in cytokine-supplemented IMDM (supplemental Methods).
CD34+ cells were enriched from Ficoll-isolated PBMCs or BMMCs using the CD34 Microbead kit (MACS; Miltenyi Biotec, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany) following the manufacturer’s protocol. The percentage of CD34+ cells was determined by flow cytometry.
Colony formation ability (CFA) assay
BMMCs from CML patients (2.5 × 104 to 5.0 × 104), or CD34+ PBMCs from healthy donors (0.5 × 103 to 1.0 × 103) were suspended in IMDM containing 2% FBS, 100 U/mL penicillin/streptomycin. Cells were plated in methylcellulose-containing medium (StemCell Technologies, Vancouver, BC, Canada) in 35-mm dishes, treatments were applied at time 0, and colonies were counted after 7, 14, or 21 days of incubation. Colony formation efficiency was calculated by dividing the number of colonies scored by the number of cells plated. In some experiments, cells were serially replated after 7 or 14 days of culture.
Long-term culture-initiating cell (LTC-IC) assay
BMMCs from CML patients were drug-treated in low oxygen for 2 days, resuspended in human long-term medium (Myelocult; StemCell Technologies) supplemented with hydrocortisone (10−6 M) and plated onto irradiated (8000 cGy) M2-10B4 cells in collagen-coated 35-mm dishes. Half of medium was replaced weekly. After 5 weeks, cells were replated (5 × 104/35-mm dish) in methyl-cellulose–containing medium (StemCell Technologies) and colonies scored after 14 days.
Mice
C57BL/6J-CD45.1 mice (The Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, ME) were handled in accordance with protocols and regulations approved by the institutional animal care and use committee of University of Massachusetts Medical School. CML mice were treated daily with ACF (8 mg/kg) or PBS via intraperitoneal injection for 10 days starting from day 7 after BM transplantation.
Murine CML model
Retroviruses were prepared and CML induced in mice as previously described.38,39 The retroviral construct MSCV-BCR/abl-IRES-GFP was used to generate high-titer, helper-free, replication-defective ecotropic viruses by transient transfection of 293T cells. Viral titer was evaluated by flow cytometry following infection of NIH/3T3 cells. Donor mice were injected with fluorouracil (200 mg/kg; Sigma-Aldrich) via tail vein and euthanized after 4 days. BM cells were flushed out of femurs and tibiae, infected with the above viruses, counted, and transplanted (5 × 105 cells in 300 μL per mouse) into recipient mice pretreated with 2 doses of 550 cGy γ 2 hours apart from each other.
Flow cytometry
Apoptosis was quantified in K562 or KCL22 cells by annexin V–allophycocyanin (APC) (Immunotools, Friesoythe, Germany), following the manufacturer’s instructions. Murine BM or PB cells were incubated with red blood cell lysis buffer, washed, resuspended in PBS, and antibody labeled (supplemental Methods). 7-Aminoactinomycin D (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA) was added before flow cytometry with a FACSAria (BD, Franklin Lakes, NJ). Results were analyzed using FlowJo software (Ashland, OR).
Statistical analyses
Statistical analysis for pairwise comparisons was performed using the Student t test for paired samples (data following a normal distribution), whereas that for multiple comparisons was performed by analysis of variance, when values followed normal distribution, or nonparametric tests, using GraphPad software (La Jolla, CA). A P value <.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
ACF reduces cell number, c-Myc expression, and stem cell potential in CML cells
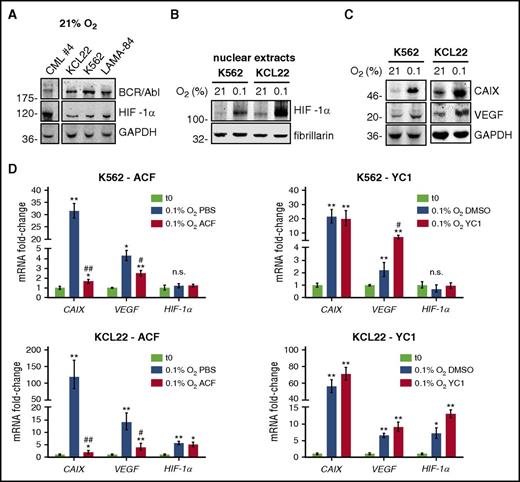
We evaluated the effects of CML cell incubation in low oxygen on HIF-1α expression and activity. We found that HIF-1α protein is expressed in primary and stabilized CML cells in normoxia (Figure 1A), as observed in other blood cancers.40 Nevertheless, in K562 or KCL22 cells, the expression of nuclear HIF-1α protein increased in low oxygen (Figure 1B). Hypoxia also increased HIF-1α activity, as indicated by the enhanced expression of carbonic anhydrase 9 (CAIX) and VEGF, both encoded for by HIF-1α–targeted genes (Figure 1C). To identify drugs suitable for HIF-1α targeting in CML cells, we tested 2 HIF inhibitors with different mechanisms of action. ACF, but not YC1 (Figure 1D), at concentrations around 50% inhibitory concentration (supplemental Figure 1A), inhibited the increase of CAIX and VEGF messenger RNA (mRNA) induced by a 2-day incubation in low oxygen. ACF or YC1 did not reduce HIF-1α mRNA, in agreement with their mechanisms of action. These results suggested that the reduction of viable cell numbers determined by YC1 in low oxygen (supplemental Figure 1A-B) was due to effects different from the inhibition of transcriptional activity of HIF-1α. Thus, we decided to use ACF for further investigations.
HIF-1α was expressed in CML cells and ACF inhibited the increase of HIF-1α target genes in low oxygen. (A) Primary (CML case 4) or CML cell lines were lysed and total cell lysates subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) expression was used as a loading control. Migration of molecular weight markers is indicated on the left (in kilodaltons). One representative experiment of 3 is shown. (B-C) Cells were incubated at the indicated oxygen concentrations for 3 days. (B) Nuclear lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Fibrillarin was used to verify the equalization of protein loading. Migration of molecular weight markers is indicated on the left (in kilodaltons). One representative experiment of 3 is shown. (C) Total cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. GAPDH was used to verify equalization of protein loading. Migration of molecular weight markers is indicated on the left (in kilodaltons). One representative experiment of 3 is shown. (D) Cells were incubated for 2 days at 0.1% O2, in the presence of 5 µM ACF or 50 µM YC1, or their solvents (PBS or DMSO, respectively). CAIX, VEGF, or HIF-1α mRNA were measured by q-PCR. Data were normalized with respect to β-actin and expressed as fold-change with respect to the values obtained for time 0 (t0) cells. Values represent mean ± standard deviation (S.D.) of 3 independent experiments, each carried out in triplicate; vs t0: *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01; vs control (PBS or DMSO) 0.1% O2: #P ≤ .05, ##P ≤ .01; either comparison: n.s., not significant.
HIF-1α was expressed in CML cells and ACF inhibited the increase of HIF-1α target genes in low oxygen. (A) Primary (CML case 4) or CML cell lines were lysed and total cell lysates subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) expression was used as a loading control. Migration of molecular weight markers is indicated on the left (in kilodaltons). One representative experiment of 3 is shown. (B-C) Cells were incubated at the indicated oxygen concentrations for 3 days. (B) Nuclear lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Fibrillarin was used to verify the equalization of protein loading. Migration of molecular weight markers is indicated on the left (in kilodaltons). One representative experiment of 3 is shown. (C) Total cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. GAPDH was used to verify equalization of protein loading. Migration of molecular weight markers is indicated on the left (in kilodaltons). One representative experiment of 3 is shown. (D) Cells were incubated for 2 days at 0.1% O2, in the presence of 5 µM ACF or 50 µM YC1, or their solvents (PBS or DMSO, respectively). CAIX, VEGF, or HIF-1α mRNA were measured by q-PCR. Data were normalized with respect to β-actin and expressed as fold-change with respect to the values obtained for time 0 (t0) cells. Values represent mean ± standard deviation (S.D.) of 3 independent experiments, each carried out in triplicate; vs t0: *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01; vs control (PBS or DMSO) 0.1% O2: #P ≤ .05, ##P ≤ .01; either comparison: n.s., not significant.
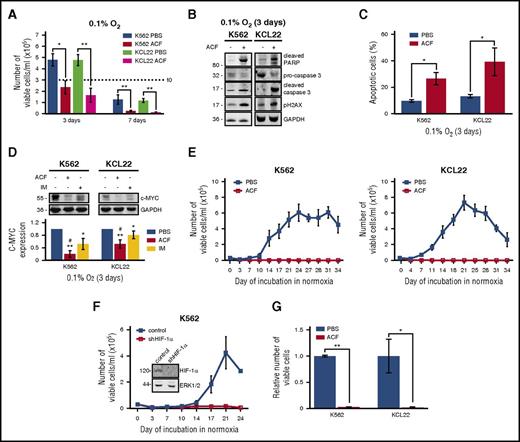
ACF treatment reduced the number of viable KCL22 or K562 cells in low oxygen (Figure 2A), an effect paralleled by the induction of apoptosis (Figure 2B-C). The antiproliferative effect of ACF was supported by the fact that ACF suppressed the expression of c-Myc (Figure 2D), a proto-oncogene important for cell cycle regulation and BCR/Abl-driven transformation.41,42 ACF inhibited c-Myc expression at the transcriptional (data not shown) and protein expression levels, exhibiting in the latter case higher efficiency than IM. We previously demonstrated that leukemia cell lines, including CML lines, are functionally heterogeneous and comprise cell subsets endowed with different stem/progenitor cell potential. Such a heterogeneity emerged following incubation in low oxygen.4,5,13,14 On this basis, using K562 and KCL22 cells, we tested the effects of ACF on the maintenance of CML stem cell potential in low oxygen (Figure 2E). Cells were drug-treated or not (PBS addition) from time 0 in primary cultures (LC1) in low oxygen and transferred on day 7 to drug-free secondary cultures (LC2) incubated in normoxia, to exploit their repopulation potential. LC2 repopulation was indeed used as a readout of maintenance of stem cell potential in LC1. This assay is an in vitro cognate of the marrow repopulation assay (see “Materials and methods”).16,36,37 It is worth noting here that around 1% of cells rescued from a 7-day incubation in low-oxygen LC1 is responsible for LC2 repopulation (data not shown). Untreated LC1 cells repopulated LC2 after a 7- to 10-day lag phase as previously reported.4,5 LC2 repopulation was abolished by ACF (Figure 2E). To exclude that the lack of LC2 repopulation was due to residual ACF from LC1, we measured the amount of ACF in LC2 culture medium by LC-MS/MS (supplemental Methods). ACF concentration resulted 81.3 nM ± 4.6 nM (vs 5 μM at time 0 of LC1). Such a concentration was found unable to affect growth kinetics of K562 or KCL22 cells (supplemental Figure 2).
ACF induced apoptosis and suppressed c-Myc expression and stem cell potential in CML cells. Cells were treated with PBS or 5 µM ACF or 1 µM IM and incubated at 0.1% O2 for the indicated times (primary culture; LC1). (A) Viable cells were counted at the indicated times of LC1. Dashed line indicates the number of plated cells. Values represent mean ± S.D. of data obtained from 3 independent experiments, each carried out in triplicate; *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01. (B) Total cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. GAPDH was used to verify equalization of protein loading. Migration of molecular weight markers is indicated on the left (in kilodaltons). One representative experiment of 3 is shown. (C) Cells were stained with annexin V–APC and analyzed by flow cytometry. Values represent mean ± S.D. of data obtained from 3 independent experiments, each carried out in triplicate; *P ≤ .05. (D) Total cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. GAPDH was used to verify equalization of protein loading. Migration of molecular weight markers is indicated on the left (in kilodaltons). One representative experiment and densitometric analysis of data from 4 independent experiments are shown; values represent mean ± S.D.; vs PBS: *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01; vs IM: #P ≤ .05. (E) Cells were transferred from day 7 LC1 to drug-free normoxic secondary cultures (LC2) to determine the maintenance of stem cell potential in LC1 via the counting of viable cells at the indicated times of incubation in LC2. Values represent mean ± S.D. of 3 independent experiments. (F) K562 cells stably transfected with shRNA against HIF-1α (shHIF-1α) or control shRNA were incubated in low-oxygen LC1 for 7 days and then transferred to normoxic LC2, to count viable cells at the indicated times of incubation in LC2. Values represent mean ± S.D. of 3 independent experiments. (F, inset) Cells from time 0 LC1 were lysed and subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. ERK1/2 was used to verify equalization of protein loading. Migration of molecular weight markers is indicated on the left (in kilodaltons). (G) Cells were treated with PBS or 5 µM ACF from day 6 to day 9 of incubation in low-oxygen LC1 and then transferred to drug-free normoxic LC2 to count viable cells. Data, relative to the peak of LC2 repopulation (day 21), are expressed as fraction of the value obtained for PBS. Values represent mean ± S.D. of data obtained from 4 independent experiments; *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01.
ACF induced apoptosis and suppressed c-Myc expression and stem cell potential in CML cells. Cells were treated with PBS or 5 µM ACF or 1 µM IM and incubated at 0.1% O2 for the indicated times (primary culture; LC1). (A) Viable cells were counted at the indicated times of LC1. Dashed line indicates the number of plated cells. Values represent mean ± S.D. of data obtained from 3 independent experiments, each carried out in triplicate; *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01. (B) Total cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. GAPDH was used to verify equalization of protein loading. Migration of molecular weight markers is indicated on the left (in kilodaltons). One representative experiment of 3 is shown. (C) Cells were stained with annexin V–APC and analyzed by flow cytometry. Values represent mean ± S.D. of data obtained from 3 independent experiments, each carried out in triplicate; *P ≤ .05. (D) Total cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. GAPDH was used to verify equalization of protein loading. Migration of molecular weight markers is indicated on the left (in kilodaltons). One representative experiment and densitometric analysis of data from 4 independent experiments are shown; values represent mean ± S.D.; vs PBS: *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01; vs IM: #P ≤ .05. (E) Cells were transferred from day 7 LC1 to drug-free normoxic secondary cultures (LC2) to determine the maintenance of stem cell potential in LC1 via the counting of viable cells at the indicated times of incubation in LC2. Values represent mean ± S.D. of 3 independent experiments. (F) K562 cells stably transfected with shRNA against HIF-1α (shHIF-1α) or control shRNA were incubated in low-oxygen LC1 for 7 days and then transferred to normoxic LC2, to count viable cells at the indicated times of incubation in LC2. Values represent mean ± S.D. of 3 independent experiments. (F, inset) Cells from time 0 LC1 were lysed and subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. ERK1/2 was used to verify equalization of protein loading. Migration of molecular weight markers is indicated on the left (in kilodaltons). (G) Cells were treated with PBS or 5 µM ACF from day 6 to day 9 of incubation in low-oxygen LC1 and then transferred to drug-free normoxic LC2 to count viable cells. Data, relative to the peak of LC2 repopulation (day 21), are expressed as fraction of the value obtained for PBS. Values represent mean ± S.D. of data obtained from 4 independent experiments; *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01.
In contrast to ACF, YC1 was ineffective in preventing LC2 repopulation (supplemental Figure 1C), likely because of its inefficacy in inhibiting HIF-1α activity (Figure 1D). The effect of HIF-1α inhibition in abolishing LC2 repopulation was confirmed in K562 cells by shRNA (Figure 2F). Finally, the effects of ACF on the maintenance of stem cell potential in low-oxygen culture were tested under conditions likely to better mimic the in vivo scenario, where LSCs are adapted to the low-oxygen stem cell niche before the beginning of drug treatment. Thus, ACF was administered to K562 or KCL22 cultures at day 6 of incubation in low oxygen, and cells were transferred to LC2 at day 9. ACF suppressed LC2 repopulation, indicating that a previous LSC adaptation to low oxygen did not reduce the drug’s effectiveness on stem cell potential (Figure 2G). We also determined, in K562 cells, the effects of low oxygen and ACF treatment on stemness-related genes, such as NANOG, OCT4, and SOX2 (supplemental Figure 3). The expression of these genes was markedly increased in low oxygen43 and ACF treatment reduced this increase. Thus, low oxygen boosts stem cell potential, which is targeted by ACF.
As TKIs represent a consolidated standard for CML therapy, it was important to determine whether the combination with ACF could affect the action of IM negatively and vice versa (Figure 3). K562 or KCL22 cells were incubated in low oxygen for 3 days in the absence or presence of ACF or IM or their combination. As expected, IM reduced the number of viable cells in culture. Interestingly, drug combination enhanced the effects of single-drug treatments (Figure 3A). Furthermore, cells incubated in low oxygen and treated as in Figure 3A were transferred to normoxic LC2 on day 7. Despite its effect on cell bulk, IM did not affect LC2 repopulation (Figure 3B), as we previously reported,4,5 in keeping with the refractoriness of LSCs to TKIs.2,3,6 ACF completely suppressed LC2 repopulation, irrespective of the presence or absence of IM (Figure 3B). Thus, ACF targets TKI-insensitive LSCs while contributing to the debulking of disease.
IM did not interfere with the ACF-driven suppression of stem cell potential. Cells were treated with PBS or 5 µM ACF or 1 µM IM, alone or in combination (ACF+IM), and incubated at 0.1% O2 (LC1). (A) Viable cells were counted at day 3 of LC1. Data are expressed as fraction of the value obtained for PBS. Values represent mean ± S.D. of data obtained from 3 independent experiments; vs PBS: *P ≤ .01; vs ACF: #P ≤ .05; vs IM: §P ≤ .05. (B) Cells were transferred from day 7 LC1 to drug-free normoxic secondary cultures (LC2), to determine the maintenance of stem cell potential in LC1 via the counting of viable cells at the indicated times of incubation in LC2. Values represent mean ± S.D. of data obtained from 3 independent experiments.
IM did not interfere with the ACF-driven suppression of stem cell potential. Cells were treated with PBS or 5 µM ACF or 1 µM IM, alone or in combination (ACF+IM), and incubated at 0.1% O2 (LC1). (A) Viable cells were counted at day 3 of LC1. Data are expressed as fraction of the value obtained for PBS. Values represent mean ± S.D. of data obtained from 3 independent experiments; vs PBS: *P ≤ .01; vs ACF: #P ≤ .05; vs IM: §P ≤ .05. (B) Cells were transferred from day 7 LC1 to drug-free normoxic secondary cultures (LC2), to determine the maintenance of stem cell potential in LC1 via the counting of viable cells at the indicated times of incubation in LC2. Values represent mean ± S.D. of data obtained from 3 independent experiments.
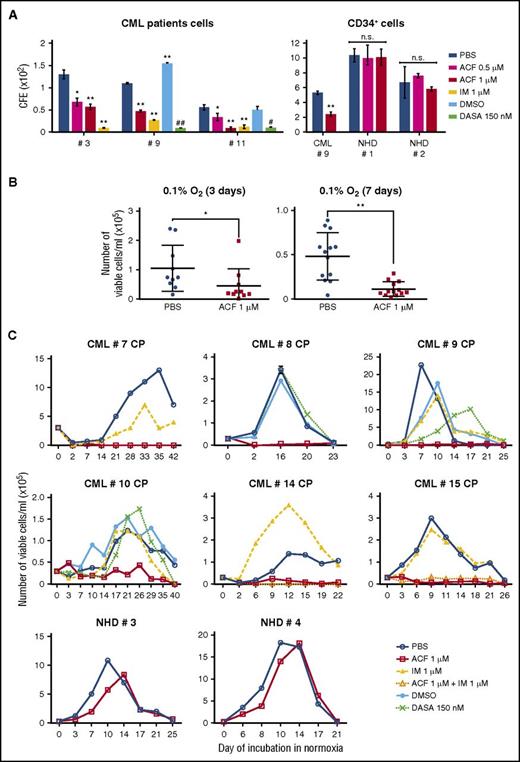
ACF reduces CFA and stem cell potential of primary CML cells
The effectiveness of ACF on primary CML cells was then tested and compared with that of TKIs. ACF concentration-dependently inhibited CFA of primary human (Figure 4A; supplemental Figure 4A) or murine (data not shown) CML cells. As expected, IM or Dasa also inhibited CFA. ACF was similarly active on CD34+ CML cells (CML #9). On CD34+ cells from normal healthy donors (NHDs), the effects of ACF were, for NHD#2, not significant throughout the incubation, or for NHD#1, significant at day 14, but not days 7 and 21 (Figure 4A; supplemental Figure 4A). Furthermore, the effects of 0.5 μM ACF were never significant for NHDs, differently from what was obtained for CML patients. ACF was at least as effective as IM or Dasa in reducing the number of viable cells in low-oxygen LC1 (Figure 4B; supplemental Figure 4B). Finally, ACF suppressed LC2 repopulation by CML cells selected in low-oxygen LC1 (Figure 4C; supplemental Figure 4C), in keeping with what was observed for CML cell lines. IM or Dasa, on the contrary, did not affect LC2 repopulation significantly (Figure 4C). Thus, the stem cell potential of patient-derived CML cells selected in low oxygen was sensitive to ACF and resistant to TKIs. Moreover, ACF did not affect LC2 repopulation by CD34+ NHD cells. Overall, these results point to a good therapeutic index of ACF.
ACF impaired stem cell potential and reduced colony formation ability of primary CML cells, but not normal cells. (A) Total (left) or CD34+ (right) light-density BMMCs from CML patients or CD34+ light-density PBMCs from NHDs (right) were plated in methylcellulose-containing medium and treated as indicated from time 0 of incubation (PBS, vehicle for ACF or IM; DMSO, vehicle for DASA). Colony number was scored after 7 days. Values represent mean ± S.D. of data obtained from experiments performed in duplicate; vs PBS: *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01; vs DMSO: #P ≤ .05, ##P ≤ .01. (B-C) Light-density BMMCs from CML patients or light-density PBMCs from NHDs were treated as indicated (PBS, vehicle for ACF or IM; DMSO, vehicle for DASA) and incubated at 0.1% O2 (LC1). (B) Viable cells from CML patients were counted at day 3 (n = 10) or day 7 (n = 12) of incubation at 0.1%O2 (LC1). Values represent mean ± S.D.; *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01. (C) Cells were transferred from day 7 LC1 to drug-free normoxic LC2 to determine the maintenance of stem cell potential in LC1 via the counting of viable cells at the indicated times of incubation in LC2. Values represent results from single experiments or mean ± S.D. of data obtained in triplicate (CML #8).
ACF impaired stem cell potential and reduced colony formation ability of primary CML cells, but not normal cells. (A) Total (left) or CD34+ (right) light-density BMMCs from CML patients or CD34+ light-density PBMCs from NHDs (right) were plated in methylcellulose-containing medium and treated as indicated from time 0 of incubation (PBS, vehicle for ACF or IM; DMSO, vehicle for DASA). Colony number was scored after 7 days. Values represent mean ± S.D. of data obtained from experiments performed in duplicate; vs PBS: *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01; vs DMSO: #P ≤ .05, ##P ≤ .01. (B-C) Light-density BMMCs from CML patients or light-density PBMCs from NHDs were treated as indicated (PBS, vehicle for ACF or IM; DMSO, vehicle for DASA) and incubated at 0.1% O2 (LC1). (B) Viable cells from CML patients were counted at day 3 (n = 10) or day 7 (n = 12) of incubation at 0.1%O2 (LC1). Values represent mean ± S.D.; *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01. (C) Cells were transferred from day 7 LC1 to drug-free normoxic LC2 to determine the maintenance of stem cell potential in LC1 via the counting of viable cells at the indicated times of incubation in LC2. Values represent results from single experiments or mean ± S.D. of data obtained in triplicate (CML #8).
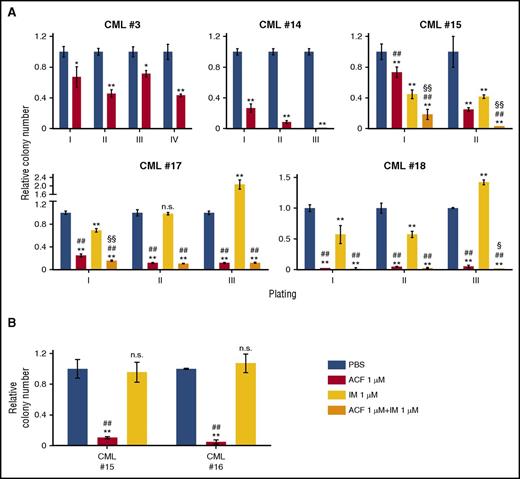
The effects of ACF in the inhibition of stem cell potential of primary CML cells were confirmed using serial CFA and LTC-IC assays (Figure 5). ACF, alone or in combination with IM, reduced replating efficiency in all patients. In contrast, IM, in 2 of 3 patients, not only did not reduce, but actually enhanced CFA starting from tertiary cultures (Figure 5A). In the highly stringent LTC-IC assay, ACF, differently from IM, was strongly effective (Figure 5B).
ACF impaired serial colony formation and long-term culture-initiation abilities of primary CML cells. (A) Light-density BMMCs from CML patients were plated in methylcellulose-containing medium (I) and treated as indicated from time 0 of incubation (PBS, vehicle for ACF or IM). After 7 to 14 days, colony number was scored and cells replated in secondary, tertiary, or quaternary cultures (II, III, IV). Data are expressed as a fraction of the value obtained for PBS-treated cultures. Values represent mean ± S.D. of data obtained from experiments performed in duplicate; vs PBS: *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01; vs IM: #P ≤ .05, ##P ≤ .01; vs ACF: §P ≤ .05, §§P ≤ .01. (B) Light-density BMMCs from CML patients were treated as indicated, incubated at 0.1% O2 for 2 days and transferred to drug-free liquid cultures incubated at 21% O2. After 5 weeks, cells were replated in methylcellulose-containing medium and colony number was scored after 14 days. Data are expressed as fraction of the value obtained for PBS-treated cultures. Values represent mean ± S.D. of data obtained from experiments performed in duplicate; vs PBS: **P ≤ .01; ACF vs IM: ##P ≤ .01.
ACF impaired serial colony formation and long-term culture-initiation abilities of primary CML cells. (A) Light-density BMMCs from CML patients were plated in methylcellulose-containing medium (I) and treated as indicated from time 0 of incubation (PBS, vehicle for ACF or IM). After 7 to 14 days, colony number was scored and cells replated in secondary, tertiary, or quaternary cultures (II, III, IV). Data are expressed as a fraction of the value obtained for PBS-treated cultures. Values represent mean ± S.D. of data obtained from experiments performed in duplicate; vs PBS: *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01; vs IM: #P ≤ .05, ##P ≤ .01; vs ACF: §P ≤ .05, §§P ≤ .01. (B) Light-density BMMCs from CML patients were treated as indicated, incubated at 0.1% O2 for 2 days and transferred to drug-free liquid cultures incubated at 21% O2. After 5 weeks, cells were replated in methylcellulose-containing medium and colony number was scored after 14 days. Data are expressed as fraction of the value obtained for PBS-treated cultures. Values represent mean ± S.D. of data obtained from experiments performed in duplicate; vs PBS: **P ≤ .01; ACF vs IM: ##P ≤ .01.
ACF reduces CML development and LSC maintenance in vivo
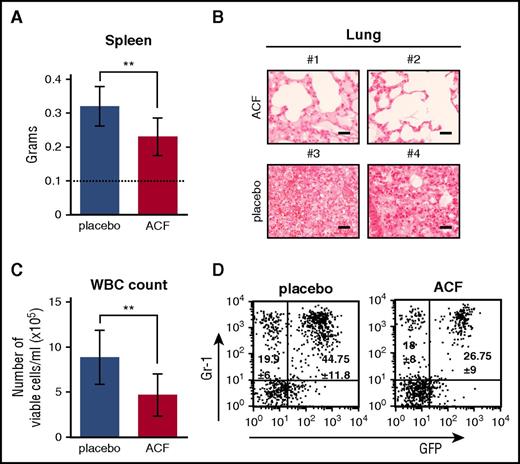
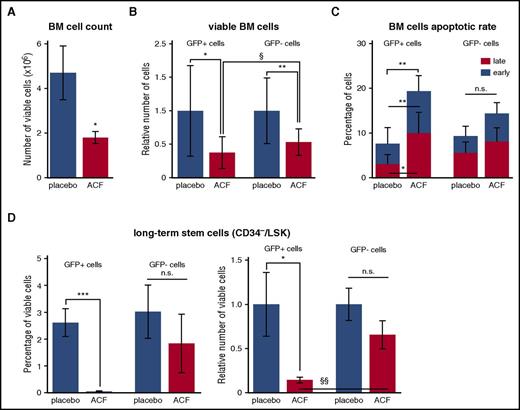
The effects of ACF were tested in vivo using mice transplanted with BCR/abl-transduced BM cells.21,38,39,44 CML mice were treated daily with ACF (8 mg/kg) or placebo for 10 days starting 1 week after transplantation. ACF treatment was well tolerated in unmanipulated healthy mice, even at concentrations higher than 8 mg/kg, as far as overall physical appearance, behavior, and weight changes are concerned (data not shown). Splenomegaly, lung infiltrate with myeloid cells, and white blood cell (WBC) count in PB of CML mice were reduced in the ACF-treated when compared with the placebo-treated group (Figure 6A-C). Fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis of PB cells showed that ACF reduced the percentage of GFP+ (BCR/abl-expressing), but not GFP− (BCR/abl−) myeloid (Gr-1+) cells (Figure 6D). In BM of ACF-treated mice, viable cell numbers decreased significantly when compared with the placebo-treated group (Figure 7A). The reduction of GFP+ cell numbers under ACF treatment was significantly higher than that of GFP− cells (Figure 7B). Accordingly, the percentage of apoptotic cells increased among GFP+, but not GFP−, cells (Figure 7C). In the same experiments, we tested whether ACF affected the LSC compartment. The CD34−/Lineage−/Sca-1+/c-Kit+ (CD34−/LSK) cell subset was analyzed in particular, which in mice includes the long-term LSC subset capable of inducing CML when transplanted.3 ACF markedly reduced percentage and number of GFP+/CD34−/LSK cells (Figure 7D). By contrast, the effect of ACF on GFP−/CD34−/LSK cells was not significant. Overall, the in vivo data indicated that ACF is active on CML cells, CD34−/LSCs, in particular, with negligible effects on non-CML cells.
ACF reduced CML development in vivo. CML mice were treated daily for 10 days with ACF or placebo and euthanized after 1 additional day. (A) Spleen weight; dotted line: non-CML mice. Data are mean ± S.D. of 8 mice per experimental variant; **P ≤ .01. (B) Hematoxylin-stained lung sections (original magnification ×40) from 2 representative mice per experimental variant (scale bar, 25 µm). (C) Total PB WBCs. Data are mean ± S.D. from 8 mice per experimental variant; **P ≤ .01. (D) Percentage of GFP+ (leukemic) or GFP− (nonleukemic) myeloid cells (Gr-1+) in PB. Plots show data from 1 representative mouse per experimental variant. Means ± S.D. from 8 mice per experimental variant are reported inside the plots.
ACF reduced CML development in vivo. CML mice were treated daily for 10 days with ACF or placebo and euthanized after 1 additional day. (A) Spleen weight; dotted line: non-CML mice. Data are mean ± S.D. of 8 mice per experimental variant; **P ≤ .01. (B) Hematoxylin-stained lung sections (original magnification ×40) from 2 representative mice per experimental variant (scale bar, 25 µm). (C) Total PB WBCs. Data are mean ± S.D. from 8 mice per experimental variant; **P ≤ .01. (D) Percentage of GFP+ (leukemic) or GFP− (nonleukemic) myeloid cells (Gr-1+) in PB. Plots show data from 1 representative mouse per experimental variant. Means ± S.D. from 8 mice per experimental variant are reported inside the plots.
ACF reduced CML development and decreased the number of long-term LSCs in vivo. CML mice were treated daily for 10 days with ACF or placebo and euthanized after 1 additional day. (A) Number of BM viable cells. (B) Relative number of GFP+ (leukemic) or GFP− (nonleukemic) cells in BM; data are expressed as fraction of the value obtained for placebo. (C) Apoptotic rate of GFP+ or GFP− BM cells. (D) Percentage (left) and relative number (right) of GFP+ or GFP−/LT-LSK cells in BM; data are expressed as fraction of the value obtained for placebo. (A-D) Values represent mean ± S.D. of data from 8 mice per experimental variant. ACF- vs PBS-treated mice: *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01, ***P ≤ .001; ACF-treated mice, GFP− vs GFP+ cells: §P ≤ .05, §§P ≤ .01.
ACF reduced CML development and decreased the number of long-term LSCs in vivo. CML mice were treated daily for 10 days with ACF or placebo and euthanized after 1 additional day. (A) Number of BM viable cells. (B) Relative number of GFP+ (leukemic) or GFP− (nonleukemic) cells in BM; data are expressed as fraction of the value obtained for placebo. (C) Apoptotic rate of GFP+ or GFP− BM cells. (D) Percentage (left) and relative number (right) of GFP+ or GFP−/LT-LSK cells in BM; data are expressed as fraction of the value obtained for placebo. (A-D) Values represent mean ± S.D. of data from 8 mice per experimental variant. ACF- vs PBS-treated mice: *P ≤ .05, **P ≤ .01, ***P ≤ .001; ACF-treated mice, GFP− vs GFP+ cells: §P ≤ .05, §§P ≤ .01.
Discussion
The development of new therapeutic strategies able to target TKI-insensitive LSCs appears of extreme importance in view of CML eradication. Low oxygen is a condition frequently occurring in neoplastic cell masses, including leukemias,45 and in tissue sites where normal and neoplastic stem cells are preferentially hosted.16,46 Previous work of ours showed that LSCs selected under low oxygen tension are TKI-insensitive4,5 and that HIF-1α–dependent signaling is relevant to LSC maintenance in CML.21 This established a rationale for HIF targeting as a possible strategy for CML treatment. A number of HIF inhibitors have been developed,31,32,47-50 including those targeting a specific step of HIF-1 signaling, such as dimerization, coactivator recruitment,51,52 or DNA binding.53 Here, we showed that ACF, an inhibitor of HIF dimerization,22 is capable of suppressing the maintenance of LSCs in vitro and in vivo as well as inhibiting CML cell growth.
That ACF targets LSCs of CML was first demonstrated in vitro. ACF suppressed stem cell potential in low oxygen in 2 cell lines and primary cells from 15 patients, including 1 in blast crisis, as determined by CRA, serial CFA, and LTC-IC assays. Importantly, in the same experiments, IM or Dasa were unable to affect stem cell potential significantly (see the following paragraphs). ACF suppressed stem cell potential even when administered to cells long after the beginning of incubation in low oxygen. This is very important in view of the facts that, when patients receive treatments, LSCs are already hosted within low-oxygen stem cell niches and that adaptation to low oxygen can protect cancer stem cells from drug treatments.14,54,55 Furthermore, in low oxygen, ACF significantly reduced the expression of the stemness-related genes NANOG, OCT4, and SOX2, in keeping with the inhibition of stem cell potential. As these genes seem to be under HIF-2α, rather than HIF-1α, transcriptional control,56,57 this effect of ACF is likely due to the fact that the drug is also capable of inhibiting HIF-2α.22
LSC targeting by ACF was confirmed in vivo. Using a murine model of BCR/abl-induced CML,21,38,39,44 we demonstrated that ACF markedly reduces the maintenance of the LSK cell subset containing long-term LSCs (CD34−/LSK)3 in BM. Thus, ACF emerged as a possible therapeutic strategy to suppress LSCs and thereby prevent CML relapse. ACF was also capable of reducing the overall CML burden in mice, as indicated by the less severe splenomegaly and the fewer leukemia cells in BM, PB, and lungs. Thus, ACF targeted significantly not only LSCs, but also less immature CML cell subsets. This is consistent with the marked reduction of cell bulk in ACF-treated primary or stabilized CML cell cultures.
ACF-induced growth inhibition may be mediated, at least in part, by the reduction of c-Myc expression observed. ACF could interfere with the complex crosstalk between HIF proteins and c-Myc,58 which collaborate to reprogram tumor cell metabolism toward glycolysis and sustain survival of oxygen-deprived cells.59 In CML, besides interacting with HIF proteins, c-Myc upregulates BCR/Abl expression,41,42 is necessary for BCR/abl-induced transformation, increases genomic instability, and participates in disease progression from chronic phase to blast crisis.60 Accordingly, in patients, an increase of c-Myc expression is related to a worse prognosis. The pharmacological inhibition of c-Myc has been reported to have an antileukemic effect which is synergistic with that of IM.61 Interestingly, in our experiments, ACF was more effective than IM in the reduction of c-Myc expression. It is worth pointing out that the inhibition of c-Myc by ACF may be also HIF-independent. Such a property, while detracting from the specificity of ACF effects on HIF, may prove useful to increase the therapeutic activity of the drug.
We previously showed that IM reduces CML cell bulk but does not affect the maintenance of stem cell potential in low oxygen.4,5 Here, we extended these findings, on one hand, to primary CML cells, on the other, to a second-generation TKI such as Dasa. These results are in agreement with the notion of the refractoriness to TKIs, irrespective of TKI generation, exhibited by LSCs2,3,6,17 capable of standing low oxygen.4,5,16,46 Moreover, we confirmed that this refractoriness was not due to mutations of the BCR/abl kinase domain, as the tested patients were negative for BCR/abl mutations. Finally, we observed that the combination of IM with ACF was more effective than either drug alone in reducing CML cell bulk in low oxygen and that IM did not interfere with the detrimental effect of ACF on stem cell potential or CFA. Both findings are of interest in view of a clinical use of the ACF/TKI combination.
The translational projection of our work prompted us to test ACF on nonleukemic cells and mice. ACF did not inhibit significantly CFA and stem cell potential of CD34+ PBMCs from healthy donors. In the murine CML model, when we compared, within individual mice (averaged), the effects of ACF on GFP+ (leukemic) cells with those on GFP− (nonleukemic) cells, we found that the latter were significantly less sensitive to ACF, as far as total PB or BM cells or CD34−/LSK are concerned. This is well in keeping with the less severe addiction to HIF-1α of HSCs when compared with LSCs.21 Finally, ACF was well tolerated by unmanipulated (non-BCR/abl-transduced) mice even when administered at doses higher than that used for the experiments reported in this study (data not shown). This points to a good therapeutic index of ACF in discriminating leukemic from normal hematopoietic cells.
On the basis of the results shown here, ACF emerges as a good candidate to target, at one time, CML cell bulk and LSCs, thus inducing remission and preventing late relapse of disease. It is worth noting that ACF is an already FDA-approved drug for nononcological uses in humans,22 and that ACF was administered to patients for at least 5 months without major adverse effects.62 Thus, we propose ACF as a novel therapeutic approach to prevent CML relapse and, in combination with TKIs, enhance induction of remission.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Matteo Lulli and Davide Tavella for helpful data discussion and suggestions.
This work was supported by research funding from: Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC; grants IG5220 and IG13466), Istituto Toscano Tumori (ITT; grants 1-12-2008 and 15-12-2014), Ministero della Salute (grant RF-TOS-2008-1163728); Regione Toscana–Programma per la Ricerca in Materia di Salute 2009 and Ente Cassa di Risparmio di Firenze.
Authorship
Contribution: G.C., M.T., I.T., N.H.D., and Y.S. carried out the experiments; G.C., E.R., P.D.S., and S.L. designed the experiments; F.M. developed HIF k/o K562 cells; A.G. handled the patients; G.C., E.R., and P.D.S. analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript; and F.M. and S.L. revised the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Persio Dello Sbarba, Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche Sperimentali e Cliniche “Mario Serio,” viale G.B. Morgagni 50, 50134 Firenze, Italy; e-mail: persio@unifi.it; and Elisabetta Rovida, Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche Sperimentali e Cliniche “Mario Serio”, viale G.B. Morgagni 50, 50134 Firenze, Italy; e-mail: elisabetta.rovida@unifi.it.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal