Abstract
About 20-25% of patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) have primary drug resistant disease and fail to achieve complete remission after induction therapy. These patients have an extremely poor prognosis and cannot reliably be identified prior to therapy with current methods. The aim of this work was to develop a predictive tool that can identify therapy resistant patients with high accuracy at the time of diagnosis.
We used two independent Affymetrix gene expression (GE) data sets and standard molecular and clinical variables to develop a predictive score for response to cytarabine/anthracycline-based induction chemotherapy. The "training set 1" consisted of 407 adult AML patients enrolled in the AMLCG-1999 trial (GSE37642). Training set 2 included 449 adults treated in various HOVON trials (GSE6891). GE-based classifiers for primary treatment resistance were developed in training set 1 using a penalized logistic regression approach (Lasso). A cut off with a specificity of 90% was predefined in training set 1. Training set 2 was used to select the best classifier. The predictive score and cut off were then validated in a third, fully independent data set, comprising 260 patients enrolled in AMLCG-1999 and 2008 trials studied by RNA sequencing. Additionally, targeted amplicon sequencing data for 68 recurrently mutated genes in AML was available for training set 1 and the validation set.
The final classifier (Predictive score 29 MRC - PS29MRC) consisted of 29 gene expression values and the cytogenetic risk group (defined according to the United Kingdom Medical Research Council (MRC) classification) and was calculated as a weighted sum of Lasso coefficients and predictor values.
PS29MRC was a highly significant predictor of resistant disease in the validation set with an odds ratio of 2.32 (p=1.53x10-8, AUC: 0.75). We tested the signature in a multivariable model including all variables with univariate p-value <0.05. TP53 mutations, age and PS29MRC (OR: 1.70; p=0.0020) were left significant in the validation set. In comparison to published predictive classifiers like the model by Walter et al. (integrating information on age, performance status, white blood cell count, platelet count, bone marrow blasts, gender, type of AML, cytogenetics and NPM1 and FLT3-ITD status; OR: 1.27; p=0.00083; AUC: 0.70) or the modified molecular version of this score (OR: 1.37; p=0.0027; AUC: 0.63) PS29MRC reached superior predictive accuracy. (Walter et al.; Leukemia 2015)
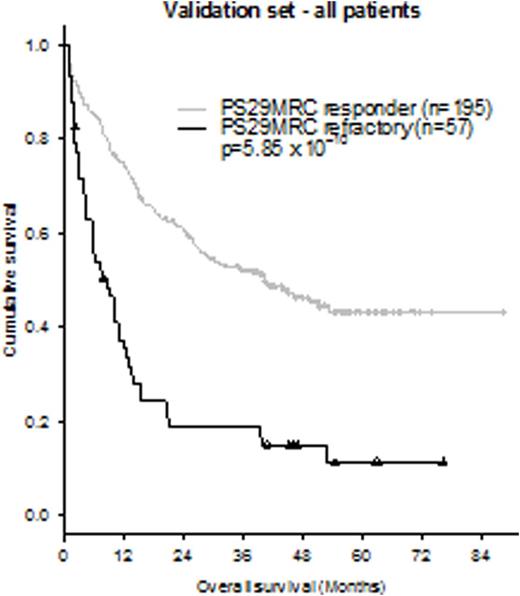
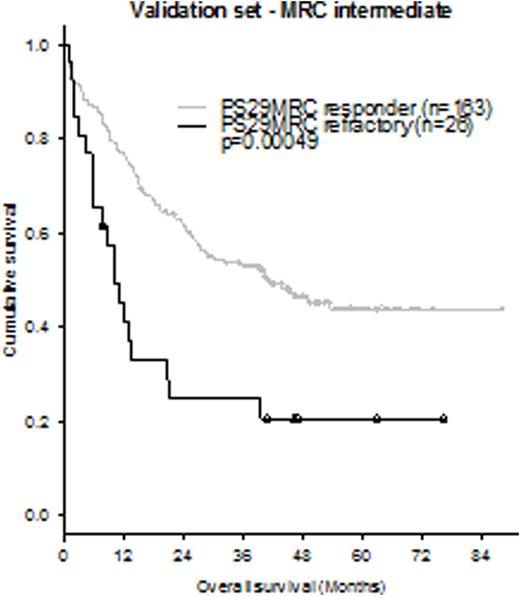
Since we aimed to develop a clinically useful score, we categorized PS29MRC to distinguish between patients who have a high probability of refractory disease and those who are likely to benefit from induction therapy (complete remission or complete remission with incomplete hematologic recovery). By applying the predefined cut off, we were able to reach a specificity of 90% and sensitivity of 46% in the validation set (OR: 7.83; p=6.06x10-9). The accuracy of PS29MRC was 77%. In the multivariable model the categorized classifier was highly significant (OR: 4.45; p=0.00040) and only age and TP53 mutations were left as significant variables again. Within the cytogenetic subgroups favorable (n=14; refractory: n=0; responders: n=13), intermediate (n=189; refractory: n=43; responders: n=136) and adverse (n=49; refractory: n=29; responders: n=15) the classifier showed an accuracy of 100%, 78% and 66%, respectively. Furthermore, the classifier predicted survival and was able to unravel the intermediate MRC subgroup (Figure).
Additionally, genes included in our predictive signature seem to be involved in AML pathogenesis and potentially actively contribute to mechanisms responsible for primary therapeutic resistance. For example MIR-155HG, an already known parameter of inferior outcome in AML, contributed significantly to PS29MRC. There are currently ongoing trials with the novel inhibitor Pevonedistat that aim to modulate this target in AML.
In summary we were able to develop a predictive risk classifier summarizing 29 gene expression values and the MRC classification that outperformed all currently used methods to predict refractory disease in intensively treated adult AML patients. PS29MRC demonstrates that it is possible to identify patients at risk of treatment failure in AML at diagnosis with high specificity.
Kaplan-Meier estimates showing overall survival of AML patients in the validation set according to PS29MRC
Kaplan-Meier estimates showing overall survival of AML patients in the validation set according to PS29MRC
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal