Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
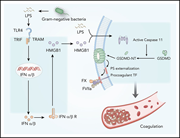
The role of type 1 interferons in coagulation induced by gram-negative bacteria
Sepsis stimulates both innate immunity and the coagulation cascade, and overactivation of coagulation can lead to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). In a study reported in this Plenary Paper, Yang et al demonstrated the role of type 1 interferons in increasing the procoagulant activity of tissue factor, elucidating the pathophysiology of sepsis-related DIC and a pathway for novel preventive therapies.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
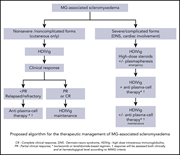
Plasma cell–directed therapies in monoclonal gammopathy–associated scleromyxedema
Clinical Trials & Observations
Scleromyxedema is a rare skin and systemic disorder associated with monoclonal gammopathy. In a retrospective study of 33 patients, the authors documented the efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of mild and moderate cases of scleromyxedema and of antimyeloma therapy in severe cases.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
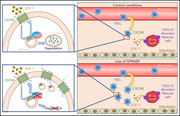
GPRASP proteins are critical negative regulators of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) depends on engraftment and proliferation of donor HSCs. Morales-Hernández and colleagues report that GPRASP proteins are negative regulators of HSCs and that silencing of Gprasp1 or Gprasp2 increases HSC survival, engraftment, and proliferation through downregulation of CXCR4. These findings suggest that disruption of this pathway could enhance HSCT.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
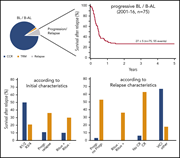
Progressive or relapsed Burkitt lymphoma or leukemia in children and adolescents after BFM-type first-line therapy
Clinical Trials & Observations
While survival for pediatric, adolescent, and young-adult Burkitt lymphoma/leukemia (BL) is over 90%, the prognosis for those with relapsed or primary refractory disease is extremely poor. Woessmann et al reviewed the 3-year survival of 157 out of 1979 children (8%) and adolescents with relapsed or refractory BL and identified risk factors for the failure of intensive salvage therapy and stem cell transplantation.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
Platelet glycoprotein VI promotes metastasis through interaction with cancer cell–derived galectin-3
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
Mutational spectrum and dynamics of clonal hematopoiesis in anemia of older individuals
Anemia increases with age and one-third of cases are unexplained. The authors examined the relationship of clonal hematopoiesis (CH) to the anemia of aging. While common age-related mutations were not increased in the anemia population, deleterious mutations, including TP53 and SF3B1, were increased. However, the higher prevalence of CH was insufficient to account for unexplained anemia, the etiology of which remains elusive.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
Rapid and accurate Bayesian diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
Rapid diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) improves patient management and avoids unnecessary exposure to direct thrombin inhibitors. Marchetti et al present a diagnostic algorithm for HIT using a Bayesian combination of pretest probability and rapid immunoassay results. This algorithm allows identification of HIT within 60 minutes.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Baseline TP53 mutations in adults with SCD developing myeloid malignancy following hematopoietic cell transplantation
Clinical Trials & Observations
The authors report on 3 patients who developed leukemia following allogeneic HSCT for sickle cell disease (SCD). All 3 patients had experienced graft failure; the 2 for whom DNA was available for next-generation sequencing were found to have preexisting TP53 mutations with a variant allele fraction that increased following HSCT graft failure.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Representative spinning disk confocal intravital microscopy images of thrombin (green) and platelet adhesion (blue) within the liver microvasculature in mice pretreated with Iκβ kinase β inhibitor ML120B, then challenged with lipopolysaccharide. See the article by Yang et al on page 1087.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






TRIF turns the switch for DIC in sepsis