Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PERSPECTIVE
Epigenetic therapies in acute myeloid leukemia: where to from here?
Clinical Trials & Observations
In a Perspective, Fennell et al review the current state of epigenetic therapies for acute myeloid leukemia, highlighting their proposed mechanisms of action, the role of the immune system in mediating their response, and the outlook for new agents and combined therapies to maximize their potential efficacy.
REVIEW ARTICLE
From Budd-Chiari syndrome to acquired von Willebrand syndrome: thrombosis and bleeding complications in the myeloproliferative neoplasms
Stein and Martin provide a review of the thrombotic and bleeding complications of myeloproliferative neoplasms and provide a roadmap for appropriate therapy.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
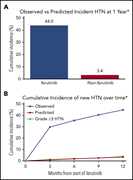
Hypertension and incident cardiovascular events following ibrutinib initiation
Clinical Trials & Observations
In a retrospective analysis, Dickerson et al report that the incidence of hypertension in patients treated with ibruitinib is nearly 80% and is associated with an increased rate of adverse cardiovascular events, primarily atrial fibrillation. Cardiac events can be reduced by treating the hypertension.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
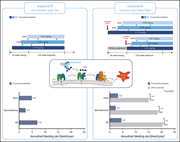
The architecture of the IgG anti-carbohydrate repertoire in primary antibody deficiencies
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
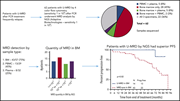
Minimal residual disease undetectable by next-generation sequencing predicts improved outcome in CLL after chemoimmunotherapy
Clinical Trials & Observations
Thompson and colleagues report that detection of minimal residual disease using next-generation sequencing, which is 2 orders of magnitude more sensitive than flow cytometry, is a much better predictor of progression-free survival.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
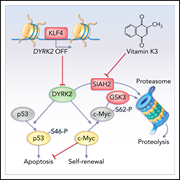
A KLF4-DYRK2–mediated pathway regulating self-renewal in CML stem cells
Park et al describe a novel KLF4-mediated pathway that promotes chromic myeloid leukemia (CML) stem cell (LSC) survival. Deletion of KLF4 in a mouse model of CML decreases LSC survival through repression of Dyrk2, resulting in c-Myc depletion and increased p53 activity.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
Subcutaneous concizumab prophylaxis in hemophilia A and hemophilia A/B with inhibitors: phase 2 trial results
Clinical Trials & Observations
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) inhibits coagulation initiation, and TFPI inhibition enhances the activation of factor X by tissue factor. Shapiro et al report the results of a phase 2 study of prophylactic administration of the TFPI inhibitor concizumab for bleeding prevention in hemophilia, reporting efficacy in Factor VIII and IX deficiency even in patients with inhibitors to Factor VIII or IX.
TRANSFUSION MEDICINE
TRANSPLANTATION
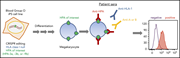
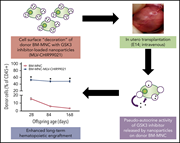
Donor cell engineering with GSK3 inhibitor–loaded nanoparticles enhances engraftment after in utero transplantation
Intrauterine transplantation induces tolerance in the setting of the immature immue system but is hampered by low levels of engraftment. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) inhibition enhances stem cell proliferation, and Loukogeorgakis and colleagues report excellent engraftment in utero in mice following surface attachment of nanoparticles loaded with GSK3 inhibitor to donor stem cells.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Long-term engraftment of donor cells (green fluorescent protein positive; brown) in the bone marrow of an allogeneic recipient mouse 6 months after in utero hematopoietic cell transplantation. See the article by Loukogeorgakis et al on page 1983.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon AdvertisingAdvertising
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals