Abstract
Current therapeutic options for myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis (MMM) are limited. A pilot study was conducted of autologous peripheral blood stem cell (PBSC) collection in 27, followed by transplantation in 21 patients with MMM. The median age was 59 (range 45-75) years. PBSCs were mobilized at steady state (n = 2), after granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) alone (n = 17), or after anthracycline-cytarabine induction plus G-CSF (n = 8). A median of 11.6 × 106 (range 0 to 410 × 106) CD34+ cells per kilogram were collected. Twenty-one patients then underwent myeloablation with oral busulfan (16 mg/kg) and PBSC transplantation. The median times to neutrophil and platelet recovery after transplantation were 21 (range 10-96) and 21 (range, 13 to ≥ 246) days, respectively. Five patients received back-up PBSC infusion because of delayed neutrophil or platelet recovery. The median follow-up is 390 (range 70-1623) days after transplantation, and the 2-year actuarial survival is 61%. After transplantion, 6 patients died: 3 of nonrelapse causes (1 within 100 days of PBSC infusion) and 3 of disease progression. Erythroid response (hemoglobin ≥ 100 g/L [10 gm/dL] without transfusion for ≥ 8 weeks) occurred in 10 of 17 anemic patients. Four of 8 patients with a platelet count less than 100 × 109/L (100 000/μL) responded with a durable platelet count more than 100 × 109/L (100 000/μL). Symptomatic splenomegaly improved in 7 of 10 patients. It is concluded that (1) PBSC collection was feasible and stable engraftment occurred after transplantation in most patients with MMM, (2) myeloablation with busulfan was associated with acceptable toxicity, (3) a significant proportion of patients derived clinical benefit after treatment, and (4) further investigation of this novel approach is warranted.
Introduction
Agnogenic myeloid metaplasia (AMM), one of the chronic myeloid disorders, is characterized by marrow fibrosis, splenomegaly, extramedullary hematopoiesis (ie, myeloid metaplasia), and a leukoerythroblastic peripheral blood smear.1 The other members of the group, which include chronic myeloid leukemia, essential thrombocytosis, and polycythemia vera, occasionally progress into a clinical picture that is similar to AMM. The termmyelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia (MMM) encompasses AMM and the progressive, fibrotic phase of essential thrombocytosis and polycythemia vera. In MMM, the hematopoietic stem cell—and resulting hematopoiesis—is clonally derived.2,3 It is assumed that clonal megakaryocyes and monocytes secrete inflammatory cytokines that stimulate nonclonal fibroblasts to proliferate and deposit extracellular matrix proteins.1,4-6 Because bone marrow fibrosis is a dynamic process, reduction of fibrosis has been shown to occur in some patients treated with myelosuppressive chemotherapy and many patients with myeloablative therapy followed by allogeneic transplantation.7-10 An additional important observation regarding the disease pathophysiology is the increased number of committed progenitor cells in the peripheral blood of patients with MMM.11-13 Furthermore, preliminary data suggest that these patients also have a high number of circulating CD34+cells.14
The median survival after diagnosis of MMM is less than 5 years.1 Progressive peripheral cytopenias occur frequently in MMM and may in part be related to hypoproliferative marrow, fibrotic marrow, and splenomegaly. Standard treatments, which consist primarily of transfusions, androgens, corticosteroids, hydroxyurea, and splenectomy, are of limited value due to toxicities and/or minimal efficacy.1 For example, anemia improves in only 25% to 30% of patients treated with hormonal therapy or splenectomy, and it often worsens with use of hydroxyurea.
In this communication we report on a novel approach to the treatment of advanced MMM with autologous peripheral blood stem cell (PBSC) collection followed by myeloablative chemotherapy and PBSC infusion. We hypothesized that there would be a high level of hematopoietic stem cells in the peripheral blood of patients with MMM, allowing for collection of PBSCs. We further hypothesized that myeloablation with a single-drug regimen of busulfan would be safely tolerated and would result in reduction of marrow fibrosis and splenomegaly and improvement in anemia despite reinfusion of clonal hematopoietic stem cells to rescue the ablated marrow.
Patients, materials, and methods
Patient enrollment and eligibility
Between January 1996 and March 2000, 27 patients with MMM were enrolled on a single treatment protocol at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle, WA (n = 11); the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (n = 6); the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN (n = 5); the Seattle Veterans Hospital, Seattle, WA (n = 4); or the Hospital St Louis, Paris, France (n = 1). One patient (02-001) enrolled at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center received treatment at the University of California at San Francisco. All patients signed informed consent using forms approved by the institutional review boards of these institutions. Patients were required to have evidence of advanced disease,1,15,16which included features such as hemoglobin less than 100 g/L (10 g/dL), platelet count less than 100 × 109/L (100 000/μL), white blood cell count (WBC) less than 4 × 109/L (4000/μL), or symptomatic splenomegaly or disease-related symptoms inadequately controlled with conventional therapy. Patients with postpolycythemic or postthrombocythemic myelofibrosis were eligible because of their expected short survival.17 One patient (02-011) without features of advanced disease underwent PBSC mobilization with the plan for transplantation upon disease progression. Additional eligibility criteria included decision against allogeneic transplantation because of advanced patient age, poor medical condition, lack of an allogeneic donor, or patient preference; serum creatinine level less than twice the upper limits of normal; liver function tests less than twice the upper limits of normal (unless due to extramedullary hematopoiesis); WBC less than 30 × 109/L (30 000/μL); and adequate pulmonary function (generally defined as total lung capacity and diffusion capacity more than 50% predicted). One patient (02-010) with a WBC above 30 × 109/L (30 000/μL) was enrolled because she received cytoreduction with induction chemotherapy (see below) prior to PBSC collection. Initially, patients older than 65 years were excluded. However, this upper age limit was raised to 75 years after acceptable toxicity was demonstrated in the initial patients.
PBSC mobilization
In most cases, patients underwent PBSC mobilization with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) at doses of 16 μg/kg/d for a minimum of 3 days. The initial protocol design prohibited use of G-CSF if the baseline WBC was more than 20 × 109/L (20 000/μL) and allowed for apheresis to be performed with fewer days of G-CSF administration if the peripheral blood CD34+level was at least 0.02 ×109/L (20/μL). Consequently, 2 patients underwent PBSC collection without mobilization with G-CSF. However, the first patient (02-002) who underwent transplantation using PBSCs collected at steady state had delayed platelet recovery after transplantation. Because of the possibility that G-CSF administration results in a qualitative difference in collected PBSCs that may affect engraftment, the protocol was subsequently modified to require G-CSF mobilization for all patients. Eight patients received induction chemotherapy followed by G-CSF; 7 received idarubicin (12 mg/m2/d for 3 days) and cytarabine (100 mg/m2/d for 7 days) and, because of poor performance status, 1 (02-015) received daunorubicin (45 mg/m2/d for 2 days) and cytarabine (100 mg/m2/d for 5 days). The reason for use of induction chemotherapy was leukemic progression in 4 cases (02-008, 02-012, 02-015, 03-001), cytoreduction in 1 case (02-010), a desire to maximize the chance of collecting cytogenetically normal stem cells in 1 case (02-006), and physician choice in 2 cases (02-013, 02-014).
PBSC collection
Patients underwent apheresis on the fourth day after starting G-CSF or, in the case of patients receiving induction chemotherapy, when the circulating CD34+ level was at least 0.01 × 109/L (10/μL) or WBC was more than 3000 × 109/L (3 × 106/μL). Apheresis was performed according to standard techniques for each institution. Although the goal was to collect at least 10 × 106CD34+ cells per kilogram, apheresis was stopped prior to reaching that number in 10 cases at the physician's choice. No PBSCs were collected in 3 patients (02-008, 02-014, 02-015) after induction chemotherapy, 2 of whom (02-008, 02-014) then underwent mobilization with G-CSF (32 μg/kg/d) alone. PBSCs were cryopreserved according to standard techniques for each institution.
Myeloablation
All patients who underwent transplantation received busulfan 1 mg/kg orally every 6 hours for a total of 16 doses. No busulfan pharmacokinetic studies were performed. Phenytoin was given for seizure prophylaxis during busulfan administration.
PBSC infusion
PBSCs were infused 36 to 48 hours after the last dose of busulfan according to the standard practice at each institution. The general guidelines were to reinfuse 5 × 106 to 10 × 106 CD34+ cells per kilogram. However, because of the recognized arbitrary nature of this range, alternative cell infusion numbers were chosen in 6 cases.
Posttransplantation supportive care
Myeloid growth factors were not routinely used because of concern for stimulating growth of clonal hematopoietic stem cells. However, in 6 cases, myeloid growth factors were used because of neutropenic fever or graft failure. Other supportive care, including prophylactic antimicrobial agents and transfusions, was provided according to the standard practice at each institution.
Disease measurement and end points
Neutrophil recovery was defined as the first of 2 days with an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) at least 0.5 × 109/L (500 cells/μL). Platelet transfusion independence was defined as the first of 7 days with platelet counts above 20 × 109/L (20 000/μL) and without transfusion. Red blood cell transfusion independence was defined as the first of 8 weeks without transfusion. Survival was calculated from the day of PBSC infusion to the day of last contact or death. Survival curves were calculated according to the method of Kaplan and Meier.18 The study was designed to close early if any of these 3 end points were met, using 80% one-sided confidence intervals: (1) the occurrence of graft failure (defined as ANC below 0.1× 109/L [100/μL] on day 28 after transplantation) exceeded 10%; (2) the occurrence of death by day 100 after transplantation exceeded 10%; or (3) the occurrence of death during hypoplasia or ANC below 0.5 × 109/L (500/μL) on day 28 after induction chemotherapy exceeded 20%.
Bone marrow biopsies (and aspirates when possible) were performed before transplantation and at approximately 1, 3, and 12 months after transplantation. Biopsies were reviewed in a blinded fashion (except cases from San Antonio, which were not blinded) by a single hematopathologist (F.C.). Cellularity, reticulin fibrosis, collagen fibrosis, and osteosclerosis were graded according to modifications of published systems19-21 (Table1).
Pathology scoring system
| Fibrosis (modified from reference 19) | |
| 0 | No reticulin fibers demonstrable or only occasional fine individual fibers |
| 1 | Occasional fine individual fibers plus foci of fine fiber network |
| 2 | Fine fiber network throughout most of the section; no coarse fibers demonstrated |
| 3 | Diffuse, fiber network with scattered thick, coarse fibers, but no fine collagen (negative trichrome stain) |
| 4a | Diffuse, often coarse, fiber network with focal (< 10% marrow area) areas of collagenization (positive trichrome stain). |
| 4b | Diffuse coarse fiber network with < 50% marrow area collagenized (positive trichrome stain) |
| 4c | Diffuse coarse fiber network with > 50% marrow area collagenized (positive trichrome stain) |
| Osteosclerosis (modified from reference 21) | |
| 0 | Normal bone |
| 1 | New bone formation |
| 1a | 1 or 2 foci of appositional new bone formation |
| 1b | 3 or more foci of appositional new bone formation |
| 1c | Severely abnormal trabeculae composed of woven bone |
| 2 | Thickened lamella bone with disordered matrix |
| Cellularity | Percentage of bone marrow space occupied by hematopoietic cells |
| Fibrosis (modified from reference 19) | |
| 0 | No reticulin fibers demonstrable or only occasional fine individual fibers |
| 1 | Occasional fine individual fibers plus foci of fine fiber network |
| 2 | Fine fiber network throughout most of the section; no coarse fibers demonstrated |
| 3 | Diffuse, fiber network with scattered thick, coarse fibers, but no fine collagen (negative trichrome stain) |
| 4a | Diffuse, often coarse, fiber network with focal (< 10% marrow area) areas of collagenization (positive trichrome stain). |
| 4b | Diffuse coarse fiber network with < 50% marrow area collagenized (positive trichrome stain) |
| 4c | Diffuse coarse fiber network with > 50% marrow area collagenized (positive trichrome stain) |
| Osteosclerosis (modified from reference 21) | |
| 0 | Normal bone |
| 1 | New bone formation |
| 1a | 1 or 2 foci of appositional new bone formation |
| 1b | 3 or more foci of appositional new bone formation |
| 1c | Severely abnormal trabeculae composed of woven bone |
| 2 | Thickened lamella bone with disordered matrix |
| Cellularity | Percentage of bone marrow space occupied by hematopoietic cells |
Results
The baseline clinical characteristics of all 27 patients enrolled are shown in Table 2. The median age was 59 (range 45-75) years. In 15 patients, the baseline number of CD34+ cells per microliter in the peripheral blood was measured before the PBSC mobilization procedure of G-CSF or chemotherapy, and the median was 0.08 × 109/L (range, 0.0032 × 109 to 3.575 × 109/L) (80/μL; range 3.2 to 3575/μL) (Table 2). The lowest value was seen in the one patient (02-003) with polycythemia vera with early development of myelofibrosis. PBSC mobilization and collection was generally well tolerated. Three patients were noted to have a mild increase in spleen size during G-CSF administration. One patient (01-002) with baseline ascites had progressive ascites and dyspnea during this period. The details of PBSC mobilization are shown in Table3. In all patients but one (02-015), a minimum of 4.8 × 106 CD34+ cells per kilogram was collected. Patient 02-015, who had 20% blasts at time of induction chemotherapy, failed collection and subsequently died of disease progression. Cytogenetics of the PBSC product were normal in 3 of 4 with baseline cytogenetic abnormalities. Two patients mobilized with GCSF alone had the same cytogenetic abnormalities in the PBSC product as the marrow prior to mobilization. Five patients in whom PBSCs were collected have not proceeded to transplantation: 2 (02-004, 04-001) because of poor performance status and 3 (02-003, 02-009, 02-011) because of planned delay for transplantation until time of disease progression.
Baseline characteristics of patients enrolled in study
| Patient study number . | Age at mobilization, y . | MPD diagnosis (years' duration) . | Prior treatment . | Blood counts at study entry . | Spleen size* . | Baseline cytogenetics . | Indication for transplantation . | Peripheral blood CD34+ (cells/μL) . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (× 109/L) . | HCT (%) . | PLT (× 109/L) . | ||||||||
| 01-001 | 67 | AMM (1.5) | RBC TX | 28.2 | 29.2 | 272 | 18 | Normal | Anemia, splenomegaly, leukemic progression (12% blasts) | 3,575 |
| 01-002 | 69 | AMM (4) | IFN, EPO, RBC TX | 7 | 26 | 143 | 17 | del(12q)der(15), t(1;15) | Anemia, splenomegaly | 62 |
| 01-003 | 75 | AMM (0.75) | RBC TX | 13.3 | 31‡ | 166 | 20 | Normal | Anemia, splenomegaly | 128 |
| 01-004 | 45 | AMM (0.5) | HU, RBC TX | 3.6 | 22.6 | 193 | Tip palpable | Normal | Anemia | 119 |
| 01-005 | 68 | AMM (0.4) | EPO, HU, RBC TX | 17.5 | 27.1 | 224 | 8 | del(12p) | Anemia, leukocytosis | ND |
| 01-006 | 65 | AMM (6.3) | RBC TX | 10.2 | 27.8 | 338 | 12 | inv(12p) | Anemia, splenomegaly | 131.6 |
| 02-001 | 54 | AMM (2.25) | EPO, RBC TX | 4.1 | 31.22-153 | 167 | 21 | Normal | Anemia, splenomegaly | 80 |
| 02-002 | 61 | AMM (17) | Steroids, Splen, RBC TX | 23.3 | 21.5 | 109 | Absent | (7;?7), del(13q) | Anemia | 299 |
| 02-003 | 54 | PPMF (1.7) PV (14) | Splen, HU | 6.5 | 38 | 390 | Absent | Normal | Too early for transplantation | 3.2 |
| 02-004 | 69 | AMM (3.5) | Steroids, RBC TX | 7.4 | 29.4 | 60 | Into pelvis | Normal | Anemia, splenomegaly | 108.6 |
| 02-005 | 54 | AMM (0.8) | RBC TX | 5.8 | 26.4 | 121 | Not palpable† | Normal | Anemia | 11.7 |
| 02-006 | 64 | AMM (1.7) | EPO, RBC TX | 4.0 | 28.0 | 79 | 2 | −7, del(20q) | Anemia | 9.7 |
| 02-007 | 59 | AMM (0.3) | Steroids, RBC TX | 3.2 | 26 | 192 | Not palpable† | Normal | Anemia | ND |
| 02-008 | 58 | AMM (3) ET (10) | RBC + platelet TX, steroids, HU | 1.6 | 22.8 | 29 | 7 | +16, +8, del(1) | Pancytopenia, bone pain, leukemic progression (17% blasts) | 284 |
| 02-009 | 52 | AMM (1) | None | 4.5 | 28.7 | 276 | 2 | Normal | Anemia | 27.4 |
| 02-010 | 62 | PPMF (0.7) PV (5) | CHL, DXR phlebotomy, HU | 5.6 | 32.5 | 15 | Into pelvis | Normal | Leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia | ND |
| 02-011 | 51 | AMM (0.8) | None | 5.6 | 32.4 | 188 | 8 | Normal | Too early for transplantation | 42.5 |
| 02-012 | 49 | AMM (1) ET (20) | None | 27.6 | 32.1 | 55 | 17 | del(13q) | Organomegaly, portal hypertension, leukemic progression (12% blasts) | ND |
| 02-013 | 57 | AMM (> 10) | Splen | 15.3 | 35.7 | 31 | Absent | ND | Thrombocytopenia, bone pain | ND |
| 02-014 | 52 | AMM (9) | HU, Steroids, RBC TX | 5.4 | 24.2 | 290 | 232-155 | add (9p), add (21q) | Anemia | ND |
| 02-015 | 54 | AMM (24) | Platelet + RBC TX, HU, Splen, IFN, G-CSF, steroids | 28.8 | 30.7 | 15 | Absent | normal | Anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukemic progression (20% blasts) | ND |
| 03-001 | 52 | AMM (0.2) ET (18) | Platelet + RBC TX | 3.6 | 21.6 | 10 | 14 | Complex, including del(5q), del(7q) | Leukemic progression (13% blasts), pancytopenia, splenomegaly | ND |
| 03-002 | 62 | PPMF (3) PV (14) | Phelbotomy, steroids, HU, EPO, CSP, IFN, AZO, Splen, RBC TX, Pamid | 11.3 | 35.9 | 56 | Absent | Normal | Anemia, bone pain | ND |
| 03-003 | 49 | AMM (3.3) | IFN, HU, steroids, Pamid, Thal | 5.0 | 27.5 | 252 | 11 | del(13q) | Bone pain, splenomegaly, leukocytosis, thrombocytosis | ND |
| 03-004 | 65 | AMM (0.3) | HU, EPO | 5.5 | 24.2 | 72 | 26 | −7, del(7q) | Organomegaly, anemia | 73.2 |
| 03-005 | 64 | AMM (0.3) ET (11) | Steroids, RBC TX, HU | 0.8 | 19.6 | 119 | 13.5 | Normal | Leukemic progression (15% blasts), pancytopenia, organomegaly | ND |
| 04-001 | 48 | AMM (2) ET (10) | RBC TX | 2.6 | 22 | 36 | 23 | ND | Anemia, splenomegaly | ND |
| Patient study number . | Age at mobilization, y . | MPD diagnosis (years' duration) . | Prior treatment . | Blood counts at study entry . | Spleen size* . | Baseline cytogenetics . | Indication for transplantation . | Peripheral blood CD34+ (cells/μL) . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (× 109/L) . | HCT (%) . | PLT (× 109/L) . | ||||||||
| 01-001 | 67 | AMM (1.5) | RBC TX | 28.2 | 29.2 | 272 | 18 | Normal | Anemia, splenomegaly, leukemic progression (12% blasts) | 3,575 |
| 01-002 | 69 | AMM (4) | IFN, EPO, RBC TX | 7 | 26 | 143 | 17 | del(12q)der(15), t(1;15) | Anemia, splenomegaly | 62 |
| 01-003 | 75 | AMM (0.75) | RBC TX | 13.3 | 31‡ | 166 | 20 | Normal | Anemia, splenomegaly | 128 |
| 01-004 | 45 | AMM (0.5) | HU, RBC TX | 3.6 | 22.6 | 193 | Tip palpable | Normal | Anemia | 119 |
| 01-005 | 68 | AMM (0.4) | EPO, HU, RBC TX | 17.5 | 27.1 | 224 | 8 | del(12p) | Anemia, leukocytosis | ND |
| 01-006 | 65 | AMM (6.3) | RBC TX | 10.2 | 27.8 | 338 | 12 | inv(12p) | Anemia, splenomegaly | 131.6 |
| 02-001 | 54 | AMM (2.25) | EPO, RBC TX | 4.1 | 31.22-153 | 167 | 21 | Normal | Anemia, splenomegaly | 80 |
| 02-002 | 61 | AMM (17) | Steroids, Splen, RBC TX | 23.3 | 21.5 | 109 | Absent | (7;?7), del(13q) | Anemia | 299 |
| 02-003 | 54 | PPMF (1.7) PV (14) | Splen, HU | 6.5 | 38 | 390 | Absent | Normal | Too early for transplantation | 3.2 |
| 02-004 | 69 | AMM (3.5) | Steroids, RBC TX | 7.4 | 29.4 | 60 | Into pelvis | Normal | Anemia, splenomegaly | 108.6 |
| 02-005 | 54 | AMM (0.8) | RBC TX | 5.8 | 26.4 | 121 | Not palpable† | Normal | Anemia | 11.7 |
| 02-006 | 64 | AMM (1.7) | EPO, RBC TX | 4.0 | 28.0 | 79 | 2 | −7, del(20q) | Anemia | 9.7 |
| 02-007 | 59 | AMM (0.3) | Steroids, RBC TX | 3.2 | 26 | 192 | Not palpable† | Normal | Anemia | ND |
| 02-008 | 58 | AMM (3) ET (10) | RBC + platelet TX, steroids, HU | 1.6 | 22.8 | 29 | 7 | +16, +8, del(1) | Pancytopenia, bone pain, leukemic progression (17% blasts) | 284 |
| 02-009 | 52 | AMM (1) | None | 4.5 | 28.7 | 276 | 2 | Normal | Anemia | 27.4 |
| 02-010 | 62 | PPMF (0.7) PV (5) | CHL, DXR phlebotomy, HU | 5.6 | 32.5 | 15 | Into pelvis | Normal | Leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia | ND |
| 02-011 | 51 | AMM (0.8) | None | 5.6 | 32.4 | 188 | 8 | Normal | Too early for transplantation | 42.5 |
| 02-012 | 49 | AMM (1) ET (20) | None | 27.6 | 32.1 | 55 | 17 | del(13q) | Organomegaly, portal hypertension, leukemic progression (12% blasts) | ND |
| 02-013 | 57 | AMM (> 10) | Splen | 15.3 | 35.7 | 31 | Absent | ND | Thrombocytopenia, bone pain | ND |
| 02-014 | 52 | AMM (9) | HU, Steroids, RBC TX | 5.4 | 24.2 | 290 | 232-155 | add (9p), add (21q) | Anemia | ND |
| 02-015 | 54 | AMM (24) | Platelet + RBC TX, HU, Splen, IFN, G-CSF, steroids | 28.8 | 30.7 | 15 | Absent | normal | Anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukemic progression (20% blasts) | ND |
| 03-001 | 52 | AMM (0.2) ET (18) | Platelet + RBC TX | 3.6 | 21.6 | 10 | 14 | Complex, including del(5q), del(7q) | Leukemic progression (13% blasts), pancytopenia, splenomegaly | ND |
| 03-002 | 62 | PPMF (3) PV (14) | Phelbotomy, steroids, HU, EPO, CSP, IFN, AZO, Splen, RBC TX, Pamid | 11.3 | 35.9 | 56 | Absent | Normal | Anemia, bone pain | ND |
| 03-003 | 49 | AMM (3.3) | IFN, HU, steroids, Pamid, Thal | 5.0 | 27.5 | 252 | 11 | del(13q) | Bone pain, splenomegaly, leukocytosis, thrombocytosis | ND |
| 03-004 | 65 | AMM (0.3) | HU, EPO | 5.5 | 24.2 | 72 | 26 | −7, del(7q) | Organomegaly, anemia | 73.2 |
| 03-005 | 64 | AMM (0.3) ET (11) | Steroids, RBC TX, HU | 0.8 | 19.6 | 119 | 13.5 | Normal | Leukemic progression (15% blasts), pancytopenia, organomegaly | ND |
| 04-001 | 48 | AMM (2) ET (10) | RBC TX | 2.6 | 22 | 36 | 23 | ND | Anemia, splenomegaly | ND |
MPD indicates myeloproliferative disorder; WBC, white blood cell count; HCT, hematocrit; PLT, platelet count; AMM, agnogenic myeloid metaplasia; RBC TX, red cell transfusion; IFN, interferon; EPO, erythropoietin; HU, hydroxyurea; Splen, splenectomy; ND, not done; PPMF, postpolycythemia myelofibrosis; PV, polycythemia vera; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; ET, essential thrombocytosis; CHL, chlorambucil; DXR, doxorubicin; CSP, cyclosporine; AZO, azothioprine; Pamid, pamidronate; Thal, thalidomide.
Number of centimeters below the left costal margin.
Imaging studies showed enlarged spleen.
RBC TX-dependent, pretransfusion HCT was < 27.
Pre-EPO treatment HCT was 25.7.
Spleen size measured as craniocaudal length by ultrasound.
Methods and results of the peripheral blood stem cell mobilization
| Mobilization procedure . | No. of patients . | Median (range) no. of days of G-CSF . | Median (range) no. of days of apheresis . | Median (range) no. of PBSCs collected (CD34+ cells/kg × 106) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steady state3-150 | 2 | 0 | 1.5 (1-2) | 16.8 (14.4-19.1) |
| G-CSF3-151 | 17 | 5 (3-9) | 2 (1-5) | 11.0 (5.4-410) |
| Chemotherapy → G-CSF3-152 | 8 | 19 (17-40)3-153 | 3 (0-8)3-155 | 10.0 (0-18.0)3-155 |
| Mobilization procedure . | No. of patients . | Median (range) no. of days of G-CSF . | Median (range) no. of days of apheresis . | Median (range) no. of PBSCs collected (CD34+ cells/kg × 106) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steady state3-150 | 2 | 0 | 1.5 (1-2) | 16.8 (14.4-19.1) |
| G-CSF3-151 | 17 | 5 (3-9) | 2 (1-5) | 11.0 (5.4-410) |
| Chemotherapy → G-CSF3-152 | 8 | 19 (17-40)3-153 | 3 (0-8)3-155 | 10.0 (0-18.0)3-155 |
PBSC indicates peripheral blood stem cell; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor.
No treatment given prior to apheresis (patients 02-002, 02-004).
Sixteen patients received G-CSF at 16 μg/kg/d. One patient (04-001) received G-CSF at 10 μg/kg/d for 4 days with 3.7 × 106 CD34+ cells per kilogram collected followed by G-CSF at 15 μg/kg/d for 4 days with 4.8 × 106 CD34+ cells per kilogram collected.
See text for details of chemotherapy given to patients 02-006, 02-008, 02-010, 02-012, 02-013, 02-014, 02-015, 03-001. G-CSF was given at 16 μg/kg/d, except patient 03-001, who received 10 μg/kg/d.
Data not available for 1 patient (02-015).
Patient 02-015 had no apheresis or stem cells collected because of residual circulating blasts (11%).
Twenty-one patients have undergone myeloablation and PBSC transplantation, and their outcome is shown in Table4. Regimen-related toxicity (Table 4) consisted predominantly of gastrointestinal tract symptoms (less than grade II in all patients except 01-003, with grade III diarrhea on 1 day, and in 03-003, with grade IV nausea and vomiting) and mucositis that was severe enough to require parenteral nutrition in 11 patients (ie, grade III by National Cancer Institute common toxicity criteria). The sole death attributable to the tranplantation procedure was due to graft failure, described as follows.
Outcome after peripheral blood stem cell transplantation
| Patient study number . | No. of PBSCs given (cells/kg × 106) . | ANC 0.5 × 109/L . | PLT 20 × 109/L . | RBC TX-independent4-150 . | Spleen size . | Current status4-154 . | Toxicities . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01-001 | 100.0 | 10 | 30 | 51 | 7 cm, day 466 | Alive, day 615; progressive disease, day 539 | M, D, F, pretibial pain |
| 01-002 | 6.8 | 15 | 27 | 199 | 6 cm, day 431 not palpable, day 531 | Alive, day 531; WBC 5.2, HCT 26.7, PLT 75 | M, D, V, F |
| 01-003 | 6.7 | 15 | 15 | NR | 15 cm, day 175 | Alive, day 266; RBC TX-dependent on EPO | M, N, V, D, F |
| 01-004 | 7.5 | 21 | 21 | 273 | Not palpable | Died, day 531; fungal infection | M, N, V, D, F |
| 01-005 | 10.7 (1st) 10.6 (2nd, day 28) | 96 | NR | NR | Increase (see text) | Died, day 185; progressive disease | F |
| 01-006 | 9.6 | 14 | 12 | 186 | 3 cm, day 20 | Alive, day 241; WBC 9.8, HCT 30, PLT 133 on EPO | M, N, V, D, F |
| 02-001 | 11.2 | 34 | 23 | 48 | 14 cm, day 1623 | Alive, day 1623; WBC 4.9, HCT 37, PLT 328 | M |
| 02-002 | 10.4 (1st) 5.9 (2nd, day 38) | 17 | 75 | 200 | Absent | Alive, day 1008; progressive disease, day 648 | F, R |
| 02-003 | No tranplantation | ||||||
| 02-004 | No tranplantation | ||||||
| 02-005 | 3.0 | 21 | 15 | 15 | Not palpable | Alive, day 752; progressive disease, day 357 | M |
| 02-006 | 9.2 | 21 | 15 | 9 | Not palpable | Alive, day 407; progressive disease, day 360 | M |
| 02-007 | 4.2 | 19 | 13 | NR | Not palpable | Alive, day 370; RBC TX-dependent | M, F |
| 02-008 | 5.63 (1st) 5.46 (2nd, day 22) | NR | NR | NR | No data | Died, day 31; graft failure | M |
| 02-009 | No tranplantation | ||||||
| 02-010 | 6.3 | 16 | 12 | No RBC given | Resected before transplantation | Alive, day 97; progressive disease, day 245 | M |
| 02-011 | No tranplantation | ||||||
| 02-012 | 7.9 | 22 | 18 | 18 | No significant change | Alive, day 233; WBC 3.4, HCT 27, PLT 141, ascites resolved | M, N, F |
| 02-013 | 4.8 | 17 | 22 | 40 | Absent | Alive, day 218; WBC 6.4, HCT 31, PLT 73 | M, N, F4-151 |
| 02-014 | 8.4 | 25 | 52 | 49 | 17 cm,‡ day 126 | Alive, day 150; WBC 4.8, HCT 39, PLT 82 | M, N, D4-153 |
| 02-015 | No tranplantation | ||||||
| 03-001 | 6.5 (1st) 6.5 (2nd, day 26) | 32 | 59 | NR | 10 cm, day 54 | Died, day 238; progressive disease | F, M, V, D, R |
| 03-002 | 8.9 (1st) 8.1 (2nd, day 106) | 21 | 138 | 133 | Absent | Alive, day 415; WBC 5.8, HCT 31, PLT 160 | M, F, |
| 03-003 | 10.5 | 17 | 13 | 14 | 5 cm, day 104 | Alive, day 390; WBC 4.7, HCT 31, PLT 272 | M, N, V, F |
| 03-004 | 27.6 | 28 | NR | NR | 12 cm, day 31 | Died, day 246; progressive disease | M, N, V, D, R |
| 03-005 | 15.0 | 91 | NR | NR | 7 cm, day 35 | Died, day 223; respiratory failure | M, N, V, D, F,4-155 R |
| 04-001 | No tranplantation |
| Patient study number . | No. of PBSCs given (cells/kg × 106) . | ANC 0.5 × 109/L . | PLT 20 × 109/L . | RBC TX-independent4-150 . | Spleen size . | Current status4-154 . | Toxicities . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01-001 | 100.0 | 10 | 30 | 51 | 7 cm, day 466 | Alive, day 615; progressive disease, day 539 | M, D, F, pretibial pain |
| 01-002 | 6.8 | 15 | 27 | 199 | 6 cm, day 431 not palpable, day 531 | Alive, day 531; WBC 5.2, HCT 26.7, PLT 75 | M, D, V, F |
| 01-003 | 6.7 | 15 | 15 | NR | 15 cm, day 175 | Alive, day 266; RBC TX-dependent on EPO | M, N, V, D, F |
| 01-004 | 7.5 | 21 | 21 | 273 | Not palpable | Died, day 531; fungal infection | M, N, V, D, F |
| 01-005 | 10.7 (1st) 10.6 (2nd, day 28) | 96 | NR | NR | Increase (see text) | Died, day 185; progressive disease | F |
| 01-006 | 9.6 | 14 | 12 | 186 | 3 cm, day 20 | Alive, day 241; WBC 9.8, HCT 30, PLT 133 on EPO | M, N, V, D, F |
| 02-001 | 11.2 | 34 | 23 | 48 | 14 cm, day 1623 | Alive, day 1623; WBC 4.9, HCT 37, PLT 328 | M |
| 02-002 | 10.4 (1st) 5.9 (2nd, day 38) | 17 | 75 | 200 | Absent | Alive, day 1008; progressive disease, day 648 | F, R |
| 02-003 | No tranplantation | ||||||
| 02-004 | No tranplantation | ||||||
| 02-005 | 3.0 | 21 | 15 | 15 | Not palpable | Alive, day 752; progressive disease, day 357 | M |
| 02-006 | 9.2 | 21 | 15 | 9 | Not palpable | Alive, day 407; progressive disease, day 360 | M |
| 02-007 | 4.2 | 19 | 13 | NR | Not palpable | Alive, day 370; RBC TX-dependent | M, F |
| 02-008 | 5.63 (1st) 5.46 (2nd, day 22) | NR | NR | NR | No data | Died, day 31; graft failure | M |
| 02-009 | No tranplantation | ||||||
| 02-010 | 6.3 | 16 | 12 | No RBC given | Resected before transplantation | Alive, day 97; progressive disease, day 245 | M |
| 02-011 | No tranplantation | ||||||
| 02-012 | 7.9 | 22 | 18 | 18 | No significant change | Alive, day 233; WBC 3.4, HCT 27, PLT 141, ascites resolved | M, N, F |
| 02-013 | 4.8 | 17 | 22 | 40 | Absent | Alive, day 218; WBC 6.4, HCT 31, PLT 73 | M, N, F4-151 |
| 02-014 | 8.4 | 25 | 52 | 49 | 17 cm,‡ day 126 | Alive, day 150; WBC 4.8, HCT 39, PLT 82 | M, N, D4-153 |
| 02-015 | No tranplantation | ||||||
| 03-001 | 6.5 (1st) 6.5 (2nd, day 26) | 32 | 59 | NR | 10 cm, day 54 | Died, day 238; progressive disease | F, M, V, D, R |
| 03-002 | 8.9 (1st) 8.1 (2nd, day 106) | 21 | 138 | 133 | Absent | Alive, day 415; WBC 5.8, HCT 31, PLT 160 | M, F, |
| 03-003 | 10.5 | 17 | 13 | 14 | 5 cm, day 104 | Alive, day 390; WBC 4.7, HCT 31, PLT 272 | M, N, V, F |
| 03-004 | 27.6 | 28 | NR | NR | 12 cm, day 31 | Died, day 246; progressive disease | M, N, V, D, R |
| 03-005 | 15.0 | 91 | NR | NR | 7 cm, day 35 | Died, day 223; respiratory failure | M, N, V, D, F,4-155 R |
| 04-001 | No tranplantation |
ANC indicates absolute neutrophil count; M, mucositis; D, diarrhea; F, fever; V, vomiting; NR, not reached; N, nausea; R, rash; for other abbreviations, see Tables 2 and 3.
Number of days after transplantation (see text for definitions).
Infection due to bacteremia.
Spleen size measured as craniocaudal length by ultrasound.
Clostridium dificile colitis.
Infection due to bacteremia and pneumonia.
Units for WBC and PLT, × 109/L; HCT, %.
Three patients met the criteria of graft failure (ANC < 0.1 × 109/L [100/μL] on day 28) (02-008, 01-005, 03-005). One patient (02-008) died because of graft failure on day 31; this patient had been neutropenic both before and after chemotherapy mobilization for PBSCs. The second patient with graft failure (01-005) received a second infusion of stored PBSCs (10.6 × 106CD34+ cells/kg) on day 28. This patient recovered to ANC of at least 0.5 × 109/L (500/μL) 68 days later (day 96) but soon thereafter progressed to acute leukemia and died. The third patient with graft failure (03-005), who was neutropenic before transplantation, recovered neutrophils on day 91 but died on day 223 with respiratory failure. One additional patient (03-001) received a second infusion of stored PBSCs (6.5 × 106CD34+ cells/kg) on day 26 (ANC 0.16 × 109/L [160/μL]) because of a life-threatening infection and engrafted to ANC of at least 0.5 × 109/L (500/μL) on day 32. For the entire group of 21 patients, the median time to achieve neutrophil engraftment was 21 (range 10 to 96) days.
Seventeen patients achieved platelet transfusion independency with a median time to platelet recovery of 21 (range 13 to ≥ 246) days. Two of 8 patients with prolonged thrombocytopenia (ie, beyond day 30) suffered grade IV hemorrhage (03-004, gastrointestinal, and 03-005, intracranial). Two patients (02-002, 03-002) received stored PBSCs (5.9 × 106 CD34+ cells/kg on day 38 and 8.1 × 106 CD34+ cells/kg on day 106) because of persistent platelet transfusion dependence. One patient (03-001) underwent splenectomy after transplantation because of persistent thrombocytopenia and anemia requiring transfusions. Among the 8 patients with thrombocytopenia who received transplants (platelet counts < 100 × 109/L [100 000/μL] at study enrollment), all but 2 received induction chemotherapy for PBSC mobilization. Following induction chemotherapy and transplantation, 4 of these patients responded with platelet counts above 100 × 109/L (100 000/μL). An additional 2 of these 8 patients with thrombocytopenia had at least a 50% increase in platelet count, and 1 of 2 platelet transfusion–dependent patients became transfusion independent.
Red cell transfusion independency developed in 14 patients at a median of 49 days (range 9 to 273) after transplantation. The erythroid response has been maintained in all but 4 patients (01-001, 02-002, 02-005, 02-006) between 97 and 1623 days (median 316) after transplantation. Seventeen patients received transplants at least in part because of anemia (all but one requiring red cell transfusions). Ten of these 17 became transfusion independent, with durable hemoglobin levels at least 100 g/L (10 g/dL).
There was significant reduction in spleen size (defined as at least a one-third reduction in spleen span) and improvement in related symptoms after transplantation in 7 of 10 patients with splenomegaly. In one patient with splenomegaly (02-008) there is a lack of data due to early death. One patient (01-005) had progressive splenomegaly and received 150 cGy splenic irradiation on days 34 to 37. Two of 3 patients in whom symptoms of bone pain were noted reported improvement. One (02-012) of 2 patients with severe ascites had clinical resolution of portal hypertension and ascites.
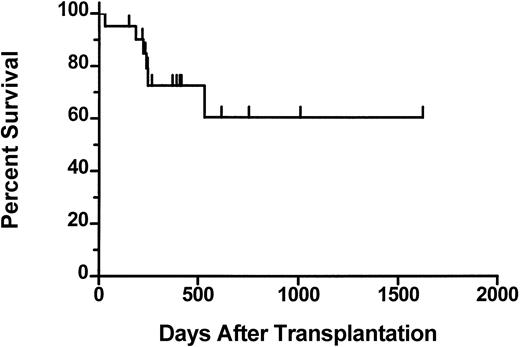
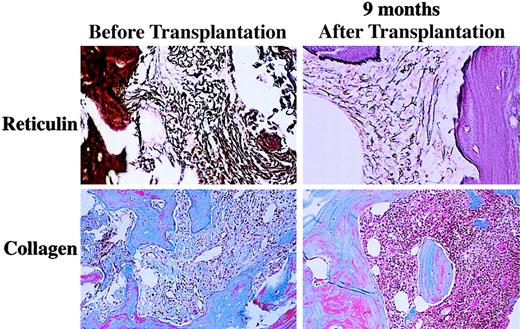
The median follow-up of the patients who received transplants is 390 days (range 70 to 1623). The 2-year actuarial survival from time of transplantation is 61% (Figure 1). Six patients died after transplantation. One patient (01-004) who achieved a complete hematologic response died on day 531 from fungal infection of the sinuses and brain. This patient had underlying diabetes and was on iron chelation therapy because of iron overload secondary to transfusion requirements prior to achieving hematologic remission after transplantation. One patient (02-008) died on day 31 with graft failure, and 1 patient (03-005) died on day 223 from respiratory failure. Three patients (01-005, 03-001, 03-004) died with progressive disease. Results of the morphologic review of bone marrow cellularity and fibrosis before transplantation and after transplantation are shown in Table 5. In several patients there was convincing evidence of regression of fibrosis (eg, 01-004, Figure2). However, in some patients there was either no change (eg, 01-001) or variable findings over time (eg, 03-001). Osteosclerosis was present in all examined samples and did not change significantly after transplantation in any patient. No association was detected between histologic findings and engraftment or clinical response.
Actuarial survival from day 0 for 21 patients who underwent transplantation.
Tick marks represent surviving patients.
Actuarial survival from day 0 for 21 patients who underwent transplantation.
Tick marks represent surviving patients.
Bone marrow histology before and after transplantation
| Patient study no. . | Day relative to transplantation . | Cellularity, % . | Fibrosis score . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01-001 | − 105 | 100 | 4a |
| 36 | 60 | 4a | |
| 92 | 90 | 4a | |
| 01-002 | − 17 | < 10 | 4b |
| 32 | 50 | 4a | |
| 440 | 80 | 4a | |
| 01-003 | − 40 | < 10 | 3 |
| 36 | < 10 | 4a | |
| 106 | < 10 | Inadequate sample | |
| 01-004 | − 90 | 10 | 4c |
| − 21 | 20 | 4c | |
| 91 | 35 | 4a | |
| 175 | 95 | 4a | |
| 280 | 100 | 4a | |
| 365 | 80 | 4a | |
| 01-006 | − 17 | 70 | 4a |
| 28 | 0-50 | 4b | |
| 91 | 0-60 | 4b | |
| 02-001 | − 896 | 80 | 4a |
| 415 | 75 | 4a | |
| 02-002 | − 103 | 50 | 4c |
| − 103 | 70 | 4b | |
| 30 | < 10 | 4b | |
| 58 | < 10 | 4c | |
| 67 | 90 | 4a | |
| 86 | 90 | 4b | |
| 281 | 70 | Inadequate sample | |
| 02-005 | − 220 | < 10 | 4c |
| − 56 | < 10 | 4c | |
| 29 | < 10 | 4c | |
| 53 | 80 | 4a | |
| 02-006 | − 68 | 95 | 4c |
| 30 | 50 | 4b | |
| 02-007 | − 33 | 95 | 4a |
| 30 | 80 | 4a | |
| 140 | 80 | ND | |
| 02-008 | − 87 | < 10 | 4c |
| 20 | < 10 | 4c | |
| 02-010 | − 77 | 80 | 4c |
| 28 | 100 | 4b | |
| 03-001 | − 70 | < 10 | 4b |
| − 48 | < 10 | 4a | |
| − 22 | 50 | 4c | |
| − 9 | < 10 | 4c | |
| 34 | 50 | 4b | |
| 03-002 | − 14 | < 10 | 4c |
| 46 | < 10 | 4a | |
| 101 | < 10 | 4a | |
| 03-003 | − 20 | 100 | 4b |
| 40 | 25 | 4b | |
| 103 | 10 | 4b |
| Patient study no. . | Day relative to transplantation . | Cellularity, % . | Fibrosis score . |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01-001 | − 105 | 100 | 4a |
| 36 | 60 | 4a | |
| 92 | 90 | 4a | |
| 01-002 | − 17 | < 10 | 4b |
| 32 | 50 | 4a | |
| 440 | 80 | 4a | |
| 01-003 | − 40 | < 10 | 3 |
| 36 | < 10 | 4a | |
| 106 | < 10 | Inadequate sample | |
| 01-004 | − 90 | 10 | 4c |
| − 21 | 20 | 4c | |
| 91 | 35 | 4a | |
| 175 | 95 | 4a | |
| 280 | 100 | 4a | |
| 365 | 80 | 4a | |
| 01-006 | − 17 | 70 | 4a |
| 28 | 0-50 | 4b | |
| 91 | 0-60 | 4b | |
| 02-001 | − 896 | 80 | 4a |
| 415 | 75 | 4a | |
| 02-002 | − 103 | 50 | 4c |
| − 103 | 70 | 4b | |
| 30 | < 10 | 4b | |
| 58 | < 10 | 4c | |
| 67 | 90 | 4a | |
| 86 | 90 | 4b | |
| 281 | 70 | Inadequate sample | |
| 02-005 | − 220 | < 10 | 4c |
| − 56 | < 10 | 4c | |
| 29 | < 10 | 4c | |
| 53 | 80 | 4a | |
| 02-006 | − 68 | 95 | 4c |
| 30 | 50 | 4b | |
| 02-007 | − 33 | 95 | 4a |
| 30 | 80 | 4a | |
| 140 | 80 | ND | |
| 02-008 | − 87 | < 10 | 4c |
| 20 | < 10 | 4c | |
| 02-010 | − 77 | 80 | 4c |
| 28 | 100 | 4b | |
| 03-001 | − 70 | < 10 | 4b |
| − 48 | < 10 | 4a | |
| − 22 | 50 | 4c | |
| − 9 | < 10 | 4c | |
| 34 | 50 | 4b | |
| 03-002 | − 14 | < 10 | 4c |
| 46 | < 10 | 4a | |
| 101 | < 10 | 4a | |
| 03-003 | − 20 | 100 | 4b |
| 40 | 25 | 4b | |
| 103 | 10 | 4b |
Table 1 describes details of the scoring system.
ND indicates not done.
Reticulin and trichrome staining for marrow fibrosis in patient 01-004 before and 9 months after transplantation.
Reticulin and trichrome staining for marrow fibrosis in patient 01-004 before and 9 months after transplantation.
Discussion
MMM comprises a group of myeloproliferative disorders that are associated with a short median survival and few effective therapies. Symptomatic peripheral cytopenias and symptomatic splenomegaly are common clinical problems requiring medical attention. In this pilot study we investigated the feasibility of a novel therapy designed to reduce complications associated with the disease without causing undue morbidity or mortality. Twenty-seven patients were enrolled at 5 centers and underwent PBSC collection; 21 patients have received myeloablation with busulfan followed by PBSC infusion. The results presented here are encouraging and suggest that further investigation is warranted.
Following PBSC mobilization, there were no unforeseen difficulties with the mobilization procedures. Following transplantation, 15 of 21 patients showed evidence of clinical improvement. Ten of 17 patients with anemia, 7 of 10 patients with symptomatic splenomegaly, and 6 of 8 patients with thrombocytopenia had clinically significant responses, with the longest response duration continuing more than 4 years. Only 2 of 6 patients with a high peripheral blast count (> 10%) appeared to obtain durable benefit, but these numbers of patients are too small to make significant conclusions. There were insufficient numbers of patients with neutropenia or with other symptoms to judge the likelihood of clinical benefit, although clinical improvement was observed in 2 patients with bone pain and 1 with portal hypertension.
The mechanism for response among the patients with improvement in cytopenias is not clear. Possible explanations include (1) reduction in fibrosis resulting in restored intramedullary hematopoiesis, (2) reduction in spleen size resulting in reduced sequestation, (3) preferential stimulation of nonclonal stem cells, and (4) overall debulking of the disease burden resulting in decreased ineffective hematopoiesis. It is likely that all of these mechanisms occurred to varying degrees in this group of patients.
Evidence for reduction in fibrosis was noted in 6 patients, all of whom had improvement in cytopenias. In several patients there was no consistent pattern of fibrosis over time, suggesting intrapatient variability, which decreases the predictive ability of scoring fibrosis. However, in one patient (01-004) with minimal splenomegaly at baseline, serial posttransplantation marrows demonstrated gradual reduction in fibrosis from grade 4c to 4a and improvement in cellularity concomittently with resolution of biweekly transfusion requirements (Figure 2). The possibility of reduced splenic sequestration as the mechanism for response to cytopenia is supported by the results in patient 02-001. In this patient, there was no demonstrable change in fibrosis (although lack of immediate pretransplantation marrow evaluation prohibits definitive comparison), but there was marked reduction in spleen size. Cytogenetic studies performed before transplantation detected an abnormal clone in 10 of 23 patients studied. Two patients (02-006, 02-012) demonstrated reduction in the percentage of clonal cells in the marrow after transplantation, both of whom had received induction chemotherapy for PBSC mobilization. Finally, there is a possibility that ablation of the patient's clonal stem cells followed by infusion of a comparatively smaller number of clonal stem cells resulted in reduction of clonal megakaryocytes and monocyte function and reduction in release of cytokines inhibiting hematopoiesis, such as tumor necrosis factor-α and transforming growth factor-β. This possibility, however, was not investigated in this study.
This tranplantation procedure was designed to be palliative, not curative, and to be suitable for older patients with MMM. Therefore, we chose a preparative regimen of single-agent busulfan with the goal of minimizing toxicity.22 Despite the median age of 59 years with 6 patients aged 65 to 75, the only regimen-related toxicities were mucositis (n = 16) and gastrointestinal symptoms (n = 8). Although the number of patients receiving transplants in this study is small, the day 100 mortality (1 of 21 patients) did not appear to be greater than the 10% reported for splenectomy for AMM23 and was considerably lower than the approximately 25% for allogeneic transplantation for AMM.10 Furthermore, the occurrence of prolonged cytopenias appears no higher than that reported for patients receiving palliative splenic irradiation for AMM.24
The main risk associated with this procedure was that of the period of pancytopenia. The median time for both neutrophil and platelet recovery was 21 days despite the infusion of a median of 8.4 × 106 CD34+ cells per kilogram. We initiated this study with the hypothesis that the high level of circulating progenitor cells in the peripheral blood of patients with MMM11-13 would allow for adequate PBSC collection and engraftment. Our data confirm recent observations that such patients also have a high level of circulating CD34+cells14,25 in addition to committed progenitor cells.11-13 We collected large numbers of CD34+ cells from patients at steady state, after G-CSF alone, or after induction chemotherapy and G-CSF. However, we observed longer times to engraftment than those observed for autologous PBSC transplantation for other diseases in which similar quantities of CD34+ cells are infused. Three of the 8 patients in this study with delayed neutrophil or platelet recovery after transplantation had evidence of leukemic progression prior to enrollment, suggesting that leukemic evolution might be a risk factor for delayed engraftment. Although the methods we used to mobilize and enumerate PBSCs are standard for other diseases, these methods may not be ideal for this disease in part because myeloblasts, which are increased in the peripheral blood of patients with MMM, often express CD34+ cell surface markers. Clearly, further studies are needed to determine the in vivo and in vitro factors that predict for delayed engraftment and to determine approaches that can effectively prevent this complication. Furthermore, it is possible that collection of PBSCs soon after diagnosis to be used later in the disease course might be an approach that optimizes the stem cell collection.
In summary, the results of our pilot study suggest that in most patients with MMM we obtained adequate PBSC collection to allow for engraftment after transplantation. We also found that the toxicity of this busulfan-only preparative regimen was acceptable, even in patients up to 75 years of age. Finally, these results suggest that a significant proportion of patients derived clinical benefit, mostly in regard to anemia and symptomatic splenomegaly. However, because this was a pilot study, there was great heterogenicity in the patient population studied and in the actual treatment received. Therefore, generalization of these results for future transplantation patients or comparisons to patients who do not receive transplants is not possible. Further evaluation of this promising therapy is ongoing.
Supported in part by National Institutes of Health grants HL-36444, CA-18029, and CA-87948. J.E.A. is an award recipient of the Paul Beeson Physician Faculty Scholars in Aging Research Program.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Jeanne E. Anderson, Katmai Oncology Group, 3260 Providence Dr, Suite 526, Anchorage, AK 99508-4627.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal