Key Points
CAR-37 T cells expanded to >98% of T cells and led to complete responses but caused severe cytopenia associated with high levels of IL-18.
Depleting CAR-37 T cells using cetuximab to target the safety switch was unsuccessful in the setting of neutropenia.
Visual Abstract
We report a first-in-human clinical trial using chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells targeting CD37, an antigen highly expressed in B- and T-cell malignancies. Five patients with relapsed or refractory CD37+ lymphoid malignancies were enrolled and infused with autologous CAR-37 T cells. CAR-37 T cells expanded in the peripheral blood of all patients and, at peak, comprised >94% of the total lymphocytes in 4 of 5 patients. Tumor responses were observed in 4 of 5 patients with 3 complete responses, 1 mixed response, and 1 patient whose disease progressed rapidly and with relative loss of CD37 expression. Three patients experienced prolonged and severe pancytopenia, and in 2 of these patients, efforts to ablate CAR-37 T cells, which were engineered to coexpress truncated epidermal growth factor receptor, with cetuximab were unsuccessful. Hematopoiesis was restored in these 2 patients after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. No other severe, nonhematopoietic toxicities occurred. We investigated the mechanisms of profound pancytopenia and did not observe activation of CAR-37 T cells in response to hematopoietic stem cells in vitro or hematotoxicity in humanized models. Patients with pancytopenia had sustained high levels of interleukin-18 (IL-18) with low levels of IL-18 binding protein in their peripheral blood. IL-18 levels were significantly higher in CAR-37–treated patients than in both cytopenic and noncytopenic cohorts of CAR-19–treated patients. In conclusion, CAR-37 T cells exhibited antitumor activity, with significant CAR expansion and cytokine production. CAR-37 T cells may be an effective therapy in hematologic malignancies as a bridge to hematopoietic stem cell transplant. This trial was registered at www.ClinicalTrials.gov as #NCT04136275.
Introduction
Autologous T cells transduced with chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) are now licensed treatments for patients with several types of B-cell malignancies and multiple myeloma.1-12 Despite impressive outcomes, up to 50% of patients relapse following CD19 CAR T-cell therapy,5,13,14 with approximately one-third losing CD19 expression from selective pressure.15-18 Therefore, additional CAR T-cell targets for B-cell malignancies and other lymphoid malignancies are needed. CD37 is a promising target because its expression is restricted to lymphoid tissues, in particular mature B cells, with low levels of expression on plasma cells and dendritic cells. CD37 expression has also been reported in cutaneous and peripheral T-cell lymphoma.19-21 These rarer T-cell malignancies have a significantly inferior prognosis when compared with their B-cell counterparts, making the development of CAR T-cell approaches for these malignancies a high priority.22-24 Clinical trials targeting CD37 with antibody-based therapies have demonstrated evidence of single-agent activity (with only transient toxicities attributed to the payload)25-28 and in combination with chemotherapy29 or ibrutinib.30 However, there are currently no US Food and Drug Administration–approved therapeutics targeting CD37.
We designed and evaluated a novel CAR targeting CD37.31 We demonstrated that CAR-37 had similar effectiveness against B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL) when compared with CD19-directed CARs. CAR-37 also had antitumor effects in vitro and led to prolonged remissions in cell line–based and patient-derived xenograft models of T-cell lymphoma.31 Despite reports of low-level expression of CD37 at the RNA level on normal immune cell subsets, we did not observe CAR-37 T-cell activation in response to coculture with subsets of white blood cells derived from the peripheral blood of healthy donors.31 Following clearance of an investigational new drug application and approval from all local regulatory committees, we started a phase 1 clinical trial of CAR-37 T cells in patients with relapsed or refractory CD37+ hematologic malignancies (NCT04136275) at our institution.
Methods
CAR-37 T cells
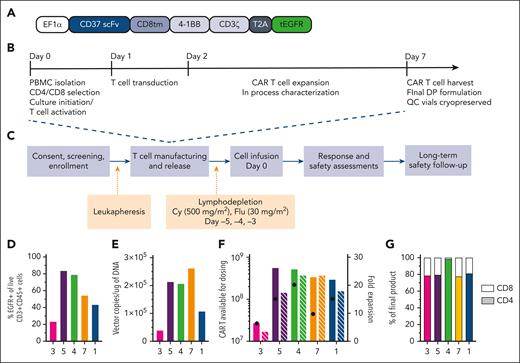
CAR-37 is an autologous T-cell product produced by lentiviral transduction using a bicistronic vector encoding a CAR that comprises a CD37-binding single-chain variable fragment (scFv), a 4-1BB costimulatory domain, and a truncated epidermal growth factor receptor (tEGFR) molecule to facilitate enumeration of transduced T cells (Figure 1A; supplemental Methods, available on the Blood website). The CAR-37 T-cell manufacturing process was conducted according to the current Good Manufacturing Practices (Figure 1B; supplemental Methods).
Study design and CAR-37 T-cell manufacturing. (A) Design of the lentiviral vector construct used to produce CAR-37 T cells. (B) Study design and (C) CAR-37 manufacturing process. (D) End-product percentage transduction of patient T cells as measured by the percentage EGFR+CD3+CD45+ cells in the live cell population (by 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole staining) via flow cytometry. (E) Copies of CAR-37 vector per microgram of DNA in the final product as measured by PCR. (F) The total number of CAR-37 T cells produced per patient and available for dosing (left y-axis, solid bars) and the fold expansion of the patient’s T cells during manufacturing (x-axis, striped bars), along with the dose of CAR-37 T cells they received (black dots), are shown. (G) Percent of the final product that is CD4+ (colored bar, bottom) vs CD8+ (white bar, top). Cy, cyclophosphamide; DP, drug product; flu, fludarabine; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; scFv, single-chain variable fragment.
Study design and CAR-37 T-cell manufacturing. (A) Design of the lentiviral vector construct used to produce CAR-37 T cells. (B) Study design and (C) CAR-37 manufacturing process. (D) End-product percentage transduction of patient T cells as measured by the percentage EGFR+CD3+CD45+ cells in the live cell population (by 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole staining) via flow cytometry. (E) Copies of CAR-37 vector per microgram of DNA in the final product as measured by PCR. (F) The total number of CAR-37 T cells produced per patient and available for dosing (left y-axis, solid bars) and the fold expansion of the patient’s T cells during manufacturing (x-axis, striped bars), along with the dose of CAR-37 T cells they received (black dots), are shown. (G) Percent of the final product that is CD4+ (colored bar, bottom) vs CD8+ (white bar, top). Cy, cyclophosphamide; DP, drug product; flu, fludarabine; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; scFv, single-chain variable fragment.
Clinical study design
This was an open-label, single-site, phase 1 trial of CAR-37 T cells in patients with relapsed or refractory CD37+ hematologic malignancies. The protocol was approved by our institutional review board, and the trial was performed in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. An external data safety monitoring board provided additional oversight. Study patients provided written informed consent, were screened and enrolled, and underwent subsequent leukapheresis for CAR T-cell manufacturing. Five days before cell infusion, patients started lymphodepleting chemotherapy (Figure 1C).
Dose escalation followed a 3 + 3 design, with a target dose of 100 million CAR-37 T cells at dose level 1 (DL1), 300 million CAR-37 T cells at DL2, or 30 million CAR-37 T cells (DL−1) if toxicities were encountered at DL1. Eligible patients required diagnosis of measurable CD37+ hematologic malignancy (confirmed by flow cytometry and/or immunohistochemistry; supplemental Methods) with at least 2 previous regimens of systemic therapy. Eligibility criteria also included adequate organ function (creatinine clearance ≥50 mL per minute and left ventricular ejection fraction ≥45%) and an Eastern Cooperative Group Performance Status of 0 to 2. Patients who previously received CD37-targeted therapies, treatment with any investigational cellular therapy within 8 weeks before apheresis, any systemic anticancer therapy within 1 week of leukapheresis, or ongoing treatment with immunosuppressants were excluded.
Blood samples were collected postinfusion to monitor CAR T-cell expansion and persistence and to evaluate correlative biologic immune effects, such as serum cytokines (supplemental Methods). Patients were monitored for the first 28 days for dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) and were monitored for safety and disease progression up to 24 months. At the time of disease progression or at 24 months if progression did not occur, patients were transferred to a long-term follow-up protocol in which patients are monitored for up to 15 years after CAR-37 treatment. The primary and secondary endpoints of the study and the statistical analyses are described in the supplemental Methods, and the most recent version of the protocol is included.
Statistical analysis
Sample size was based on a 3 + 3 dose escalation design. A total of 4 patients were enrolled at target DL1 (∼100 million CAR T cells) and 1 at target DL −1 (∼30 million CAR T cells). The data are presented as the median or mean and range for continuous variables and frequency for categorical variables. The fold change from baseline in cytokine levels was compared between groups using Mann-Whitney U tests or t tests. The distributions of time-to-event endpoints were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and 95% confidence intervals were calculated using the complementary log-log transformation. Analyses were performed with GraphPad Prism software, version 9. All patients who were infused were included in this analysis.
This study was approved by the institutional review board at Massachusetts General Hospital. Animal experiments were done at Washington University and were approved by their institutional animal care and use committee.
Results
Patients
Between October 2020 and August 2021, 5 patients were enrolled in the study with a diverse set of B, T, and natural killer (NK)/T lymphoid malignancies and high baseline tumor burden (Table 1). Two additional patients were screened but not enrolled. All patients were heavily pretreated and refractory to second-line or subsequent therapy, and 2 patients relapsed after CD19–directed CAR T-cell therapy. Four patients were enrolled at DL1 in the order of their patient number (Table 2); 2 patients (patients 2 and 6) who provided consent did not meet the eligibility criteria and were not enrolled; and 2 patients (patients 1 and 3) were not evaluable for DLT because of disease progression before day 28 and because of manufacturing failure, respectively. Two patients evaluable for DLT at DL1 (patients 4 and 5) experienced DLT, prompting dose de-escalation to DL −1 for the fifth enrolled patient (patient 7).
Summary of the baseline patient characteristics
| Age, median (range), y | 61 (35-70) |
| Sex | 4 female, 1 male |
| Disease type | |
| Double-hit HGBCL | 2 |
| CTCL | 1 |
| Hodgkin lymphoma | 1 |
| NK/T-cell lymphoma | 1 |
| Previous lines of therapy, median (range) | 6 (3-8) |
| No. of patients with primary refractory disease | 3 |
| No. of patients refractory to second-line or subsequent therapy | 5 |
| No. of patients with previous CAR-19 | 2 |
| No. of patients with previous allogeneic HSCT | 1 |
| Tumor burden | |
| Baseline LDH, median (range) | 796 U/L (200-1 416) |
| Baseline SPD, median (range) | 2 516 mm2 (142-12 354) |
| Bone marrow involvement at baseline | 1 |
| Age, median (range), y | 61 (35-70) |
| Sex | 4 female, 1 male |
| Disease type | |
| Double-hit HGBCL | 2 |
| CTCL | 1 |
| Hodgkin lymphoma | 1 |
| NK/T-cell lymphoma | 1 |
| Previous lines of therapy, median (range) | 6 (3-8) |
| No. of patients with primary refractory disease | 3 |
| No. of patients refractory to second-line or subsequent therapy | 5 |
| No. of patients with previous CAR-19 | 2 |
| No. of patients with previous allogeneic HSCT | 1 |
| Tumor burden | |
| Baseline LDH, median (range) | 796 U/L (200-1 416) |
| Baseline SPD, median (range) | 2 516 mm2 (142-12 354) |
| Bone marrow involvement at baseline | 1 |
The data for n = 5 patients are shown. Data are numbers of patients unless otherwise indicated.
CTCL, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; HGBCL, high-grade B-cell lymphoma; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; SPD, sum of the products of diameters.
CAR-37 and previous treatments by patient
| Patient no. . | Age/sex . | Disease . | Previous therapies . | Baseline BM involvement . | CAR37 dose level (actual no. received) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 61/F | Double-hit HGBCL | R-EPOCH, IT MTX/cytarabine, HD-MTX, R/Gem/Ox, cy/flu/tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah), XRT, and pembrolizumab | No | DL1 (120 e6) frozen |
| 3 | 70/M | CTCL | Photopheresis, alemtuzumab (Campath), total skin electron beam radiation, flu/cy/TBI/MMF-RIC, haplo PBSCT, brentuximab, DLI, and XRT | No | DL1 (19 e6) fresh |
| 4 | 63/F | Double-hit HGBCL | DA-EPOCH-R, R-DHAP, and cy/flu/axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) | No | DL1 (229 e6) fresh |
| 5 | 35/F | Classical Hodgkin | ABVD, brentuximab, GDP, ICE, nivolumab, and everolimus | No | DL1 (120 e6) frozen |
| 7 | 46/F | NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type | Dex/etoposide/ifosfamide/carboplatin; XRT to soft palate and LN; pembrolizumab; ulixertinib | Yes | DL −1 (30 e6) frozen |
| Patient no. . | Age/sex . | Disease . | Previous therapies . | Baseline BM involvement . | CAR37 dose level (actual no. received) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 61/F | Double-hit HGBCL | R-EPOCH, IT MTX/cytarabine, HD-MTX, R/Gem/Ox, cy/flu/tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah), XRT, and pembrolizumab | No | DL1 (120 e6) frozen |
| 3 | 70/M | CTCL | Photopheresis, alemtuzumab (Campath), total skin electron beam radiation, flu/cy/TBI/MMF-RIC, haplo PBSCT, brentuximab, DLI, and XRT | No | DL1 (19 e6) fresh |
| 4 | 63/F | Double-hit HGBCL | DA-EPOCH-R, R-DHAP, and cy/flu/axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) | No | DL1 (229 e6) fresh |
| 5 | 35/F | Classical Hodgkin | ABVD, brentuximab, GDP, ICE, nivolumab, and everolimus | No | DL1 (120 e6) frozen |
| 7 | 46/F | NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type | Dex/etoposide/ifosfamide/carboplatin; XRT to soft palate and LN; pembrolizumab; ulixertinib | Yes | DL −1 (30 e6) frozen |
ABVD, doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, dacarbazine; BM, bone marrow; CTCL, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; cy, cyclophosphamide; DA, dose-adjusted; Dex, dexamethasone; DHAP, dexamethasone, cytarabine, cisplatin; DLI, donor leukocyte infusion; EPOCH, etoposide phosphate, prednisone, vincristine sulfate (Oncovin), cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin hydrochloride (hydroxydaunorubicin); F, female; flu, fludarabine; GDP, gemcitabine, dexamethasone, cisplatin; Gem, gemcitabine; haplo, haploidentical; HD, high-dose; HGBCL, high-grade B-cell lymphoma; ICE, ifosfamide, carboplatin, etoposide phosphate; IT, intrathecal methotrexate; LN, lymph node; M, male; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; MTX, methotrexate; Ox, oxaliplatin; PBSCT, peripheral blood stem cell transplant; R, rituximab; RIC, reduced intensity conditioning; TBI, total body irradiation; XRT, radiotherapy.
CAR-37 T-cell manufacturing characteristics
CAR-37 T cells were manufactured with a median vein-to-vein time of 10 days (range, 8-14). Patient 1 was treated with a frozen product to ensure successful manufacturing, because fresh products require lymphodepleting chemotherapy to be initiated before the completion of cell manufacturing. Patients 3 and 4 were infused with fresh CAR-37 T cells (Table 2). We initially intended to use fresh products for all subsequent patients in the study. However, because of the onset of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) during the study period, we elected to proceed with frozen products for patients 5 and 7 to minimize the risk to the patients because of the increased challenge of coordinating manufacturing with bed availability, staffing, and infectious considerations. Transduction frequency ranged from 23.4% to 83.7% of T cells based on staining for truncated EGFR (Figure 1D). Infusion product vector copy number (VCN) ranged from 39 385 to 262 325 copies per μg genomic DNA (Figure 1E). Per our manufacturing protocol, doses prepared in the infusion bags included a 20% overage to account for cells lost in the tubing. We manufactured more than the required dose for a patient’s respective dose level, except for patient 3 (Figure 1F) who was infused with a lower number of cells (Table 2), as allowed per protocol. Patient 4 received a larger dose of cells, because of an aberrancy in flow cytometry staining that led to a miscalculation, which was noted and reported immediately. The infusion products were consistently 80% CD4+ cells and 20% CD8+ cells, except for patient 4, whose product was predominantly (98.4%) CD4+ cells (Figure 1G). No specific CD4:CD8 ratios were mandated per protocol. Patient data in Figure 1 and throughout the manuscript are presented in the order of longest to shortest overall survival (Figure 2A).
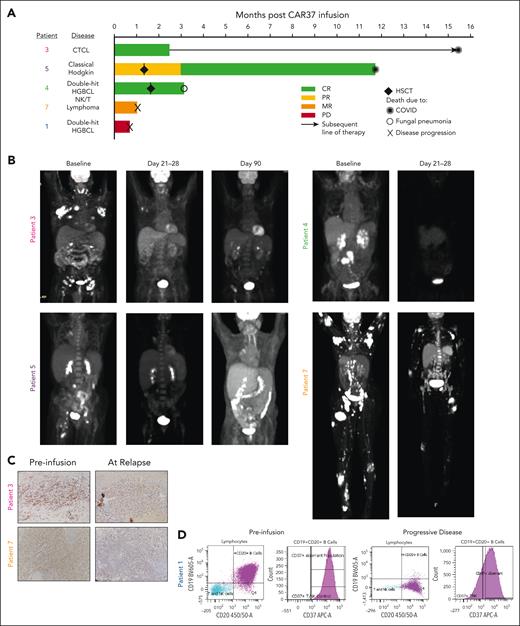
Patient response to CAR-37 T cells. (A) Swimmer plot of patient’s responses to CAR-37 T cells. Two patients received HSCT as a consequence of cytopenia at the time points indicated by the diamonds. Other symbols indicate the cause of death for each patient, as noted. (B) Positron emission tomography (PET) scans of patients with CR, PR, or MR at the indicated time points. (C) Immunohistochemistry for CD37 in lesion biopsies before CAR T-cells infusion (preinfusion) and at the time of relapse by PET scan. Images were taken at 20×. (D) CD19, CD20, and CD37 expression in tumor from patient 1 as measured by flow cytometry performed by the clinical pathology laboratory. The purple dots and histogram represent the aberrant population. CTCL, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; HGBCL, high-grade B-cell lymphoma; PD, progressive disease; PR, partial response.
Patient response to CAR-37 T cells. (A) Swimmer plot of patient’s responses to CAR-37 T cells. Two patients received HSCT as a consequence of cytopenia at the time points indicated by the diamonds. Other symbols indicate the cause of death for each patient, as noted. (B) Positron emission tomography (PET) scans of patients with CR, PR, or MR at the indicated time points. (C) Immunohistochemistry for CD37 in lesion biopsies before CAR T-cells infusion (preinfusion) and at the time of relapse by PET scan. Images were taken at 20×. (D) CD19, CD20, and CD37 expression in tumor from patient 1 as measured by flow cytometry performed by the clinical pathology laboratory. The purple dots and histogram represent the aberrant population. CTCL, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; HGBCL, high-grade B-cell lymphoma; PD, progressive disease; PR, partial response.
Efficacy, resistance, and long-term outcomes
As the best overall response, 3 patients (patients 3, 5, and 4) achieved a complete response (CR) and 1 patient (patient 7) had a mixed response (MR; Figure 2A). At day 21 after CAR-37 T-cell infusion, patient 3 had a small area of positron emission tomography avidity in the right axilla. This was biopsied, found to contain a significant amount of CAR-37 with no evidence of lymphoma, and was therefore deemed to be CR (Figure 2B). At month 3, this patient developed a skin lesion. Biopsy demonstrated recurrent cutaneous T-cell lymphoma with decreased CD37 expression when compared with the preinfusion biopsy (Figure 2C). Following this recurrence, the patient was treated with brentuximabvedotin, and lenalidomide and did well for more than a year but ultimately succumbed to COVID-19 at month 15.5 after CAR-37 T-cell infusion. Patient 4 achieved CR at day 28. Patient 5 initially achieved a partial response at day 21, which became a CR at month 4, the first assessment after allogeneic stem cell transplant. Unfortunately, this patient refused standard vaccinations and died from COVID-19 at 11.7 months after CAR-37 treatment.
Two patients (1 and 7) showed evidence of rapid CD37 loss after CAR-37 treatment. Patient 1 had rapid progression with a new malignant pleural effusion detected on day 13 after CAR-37 infusion and died on day 22. Clinical pathology and flow cytometry data revealed large B-cell lymphoma that was CD19 dim/negative and had decreased CD37 expression at progression, which was notably different from the fresh tumor biopsy obtained during screening (Figure 2D). Patient 7 had MR with dramatic regression of nodal and cutaneous disease but residual disease in the marrow (Figure 2B). This patient underwent a biopsy of a residual positron emission tomography-avid skin lesion, which demonstrated CD37 loss when compared with their screening biopsy (Figure 2C). Unfortunately, patient 7 died from what was attributed to progression of disease on day 32 despite this MR.
Safety: moderate but prolonged CRS and severe prolonged cytopenia
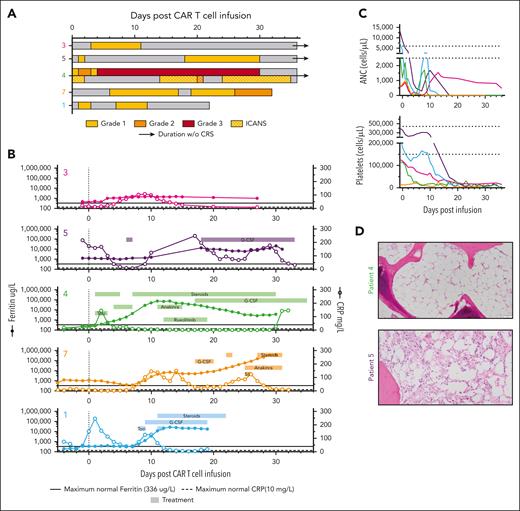
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and immune effector cell–associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) toxicity grading was performed according to the American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy 2019 consensus criteria.32 All patients experienced CRS after CAR-37 T-cell infusion (Figure 3A). The median time to onset of CRS was 1 day (range, 0-6) with a median continuous duration of 9.5 days (range, 1-30). Patient 4, who received the largest CAR-37 dose, was the only patient to experience any grade of ICANS with a maximum of grade 2 that lasted 1 day but had a prolonged course of grade 1 ICANS. There were no deaths related to CRS or ICANS. Of the 5 patients, 4 received intervention with tocilizumab and/or dexamethasone for CRS. Only patient 4 required additional intervention with ruxolitinib/siltuximab for prolonged ICANS. All patients received growth factory support for cytopenia according to institutional guidelines (Figure 3B).
Toxicity in CAR-37 patients correlates with increased serum cytokines. (A) The timing, grade, and duration of CRS (open bars) and ICANS (dotted bars) after CAR-37 T-cell infusion (day 0) are shown. The bar color indicates grade, as noted. Open/white bars indicate duration with no CRS or ICANS symptoms. (B) As part of the diagnostic workup for CRS and ICANS, ferritin (left y-axis, closed symbols) and c-reactive protein (CRP; right y-axis, open symbols) were measured in patient serum over time. The solid black line indicates the maximum normal ferritin level. The dashed black line indicates the maximum normal CRP level. The underlaying horizontal bars indicate the timing and duration of treatment for CRS or ICANS, as noted by the treatment name in the bar. Bars in the same row represent the same treatment. (C) Cell counts per microliter of blood pre- and post-CAR-37 infusion (day 0). Dashed lines indicate the normal range for each cell type. (D) Hematoxylin and eosin staining (20× original magnification) of bone marrow biopsies taken from patients 4 and 5 on day 27 after CAR-37 T-cell infusion. ANC, absolute neutrophil count; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; Sil, siltuximab; Toci, tocilizumab; WBC, white blood cell.
Toxicity in CAR-37 patients correlates with increased serum cytokines. (A) The timing, grade, and duration of CRS (open bars) and ICANS (dotted bars) after CAR-37 T-cell infusion (day 0) are shown. The bar color indicates grade, as noted. Open/white bars indicate duration with no CRS or ICANS symptoms. (B) As part of the diagnostic workup for CRS and ICANS, ferritin (left y-axis, closed symbols) and c-reactive protein (CRP; right y-axis, open symbols) were measured in patient serum over time. The solid black line indicates the maximum normal ferritin level. The dashed black line indicates the maximum normal CRP level. The underlaying horizontal bars indicate the timing and duration of treatment for CRS or ICANS, as noted by the treatment name in the bar. Bars in the same row represent the same treatment. (C) Cell counts per microliter of blood pre- and post-CAR-37 infusion (day 0). Dashed lines indicate the normal range for each cell type. (D) Hematoxylin and eosin staining (20× original magnification) of bone marrow biopsies taken from patients 4 and 5 on day 27 after CAR-37 T-cell infusion. ANC, absolute neutrophil count; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; Sil, siltuximab; Toci, tocilizumab; WBC, white blood cell.
Although the severity of the CRS was not markedly different from our clinical experience with CD19 CAR T cells, the duration was prolonged with sustained elevation in inflammatory markers (Figure 3B). Peak ferritin of >20 000 μg/L occurred in 4 of 5 patients treated with CAR-37 with a maximum of 401 446 μg/L (patient 7); however, ferritin elevation >10 000 μg/L was sustained for more than a week in these 4 patients, which suggested an ongoing hyperinflammatory state. Patient 4 had some features consistent with the recent definition of immune effector cell–associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocystosis-like syndrome (IEC-HS),33 including cytopenia, hyperferritinemia, and coagulopathy, but a transient transaminitis did not reach >5 times the upper limit of normal. Although patients 1 and 7 also exhibited symptoms of prolonged hyperinflammation, lymphoma progression precludes the diagnosis of IEC-HS (supplemental Table 1).
Consistent with receiving lymphodepleting chemotherapy before CAR-37 infusion, all patients developed cytopenia. Only patient 3, whose CAR T cells expanded minimally during manufacturing and only transiently expanded after infusion, demonstrated count recovery by day 28. In 3 of 4 evaluable patients (patients 4, 5, and 7), the grade 4 reduction in neutrophil and platelet count lasted >28 days with a neutrophil count of 0 cells per μL blood (Figure 3C) and required blood and platelet transfusion support. A bone marrow aspirate evaluation in patient 4 demonstrated aplasia with a near total absence of hematopoietic elements; the bone marrow aspirate in patient 5 demonstrated a hypocellular marrow with 20% cellularity (Figure 3D). The bone marrow biopsy from patient 7 who had received a lower dose of CAR-37 T cells was also hypocellular (30%) but contained ∼60% involvement by known NK/T-cell lymphoma (CD56+, CD5−, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)/Epstein-Barr encoding region (EBER)+, CD4−CD8−) that stained dimly and rarely for CD37. The remaining cells appeared to be small CD3+CD5+ T cells (consistent with CAR-37).
Patients 4 and 5 underwent rescue allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT) after transplant conditioning and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis (supplemental Methods). Patient 4 received cryopreserved matched peripheral blood stem cells from an unrelated donor on day 50 after CAR-37 infusion and was engrafted on day 25 after transplant with 100% donor chimerism. Because of their prolonged neutropenia and antifungal prophylaxis, the patient ultimately developed azole-resistant aspergillus pneumonia and died from infection on day 46 after transplant (day 96 after CAR-37 infusion). This and all other infections that patients experienced during the DLT window are noted in supplemental Table 2. The absolute neutrophil count at the time of death was 4.6 × 103 cells per μL, and there was no evidence of disease. Patient 5 underwent haploidentical peripheral blood stem cells transplant on day 41 after CAR-37 T-cell infusion, was engrafted on day +35 after transplant with 100% donor chimerism, and was discharged home on day +37.
All other adverse events (grade ≥3) are reported in supplemental Table 3.
CAR-37 T cells underwent expansion in patients and persisted beyond 21 days
In the patients who experienced grade 4 neutropenia and thrombocytopenia, lymphocytes made up the majority of their white blood cell count (>94%) with a clear transition between days 10 and 15 after CAR T-cell infusion (Figure 4A). To determine what percentage of these were CAR T cells, we measured CAR-37 by flow cytometry for truncated EGFR (tEGFR) and by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) for VCN, defined as the vector copies per microgram of DNA from whole blood (supplemental Methods). All patients had expansion of CAR-37 T cells by day 10. By day 14, the frequency of transduced T cells as a portion of the total circulating CD3+ T cells was remarkably high (>96%) in 4 of 5 patients (Figure 4B), which increased to >98% through day 28 (Figure 4C). Despite the high proportion of CAR-37 cells through day 28, the absolute number of CAR-37 T cells in circulation peaked at a median of day 14 (range, 14-21) and then decreased in 4 of 5 patients. The exception was patient 7, who had sustained levels of >300 CAR-37 T cells per μL of blood at day 28 (Figure 4D). The median number of CAR T cells on the day of peak expansion was 621.8 (range, 2.44-15306.6) cells per μL blood. Similarly, CAR-37 T cells were detectable by qPCR in patient whole blood and peaked at day 14 with a median of 200 417 (range, 73-262 325) copies of vector transgene per microgram of genomic DNA (Figure 4D). Of note, the high VCN values are in part because of the concurrent relative leukopenia with measurements from whole blood. The VCN per cell, which is normalized for the amount of genomic DNA, was a median of 1.08 (range, 0.00-1.45) at peak. These data suggest that at peak, on average, every cell with genomic DNA in the peripheral blood was a CAR-37 T cell with a single copy of the transgene. The ratio of CD4:CD8 CAR-37+ T cells in the peripheral blood varied; it increased over time in the peripheral blood of patient 3, was maintained and similar to the infusion product in patients 4 and 5, and decreased over time in patients 1 and 7 (supplemental Figure 1).
CAR-37 T-cell expansion after infusion. (A) The absolute numbers of neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes per microliter of blood after CAR-37 infusion (day 0) are shown. (B) Flow cytometry dot plots of CD3+EGFR+ CAR-37 T cells in peripheral blood are shown on day −5 (before CAR-37 T-cell infusion) and day 14 after CAR-37 T-cell infusion. (C) The percentage of CD3+ cells that were EGFR+ as detected in patient peripheral blood by flow cytometry over time after CAR-37 T-cell infusion on day 0 is shown. (D) The number of CAR-37 T cells per microliter of peripheral blood is shown as calculated from the percentage of CD3+EGFR+ cells detected by flow cytometry and the absolute lymphocyte count (left y-axis, closed symbols), as well as the VCN, reported as copies per microgram of DNA (right y-axis, open symbols), over time after CAR-37 T-cell infusion. PE, phycoerythrin.
CAR-37 T-cell expansion after infusion. (A) The absolute numbers of neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes per microliter of blood after CAR-37 infusion (day 0) are shown. (B) Flow cytometry dot plots of CD3+EGFR+ CAR-37 T cells in peripheral blood are shown on day −5 (before CAR-37 T-cell infusion) and day 14 after CAR-37 T-cell infusion. (C) The percentage of CD3+ cells that were EGFR+ as detected in patient peripheral blood by flow cytometry over time after CAR-37 T-cell infusion on day 0 is shown. (D) The number of CAR-37 T cells per microliter of peripheral blood is shown as calculated from the percentage of CD3+EGFR+ cells detected by flow cytometry and the absolute lymphocyte count (left y-axis, closed symbols), as well as the VCN, reported as copies per microgram of DNA (right y-axis, open symbols), over time after CAR-37 T-cell infusion. PE, phycoerythrin.
Given the unexpected level of CAR-37 T-cell expansion in most patients, we examined their clonality. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients 4, 5, and 7 were analyzed for T-cell receptor (TCR) Vβ phenotyping via flow cytometry (supplemental Methods), which demonstrated polyclonal expansion of CAR+ T cells (supplemental Figure 2). In patient 7, 2 TCR Vβ clones expanded more than the others between day 10 and day 28 (supplemental Figure 2). Because their underlying disease was an NK/T-cell lymphoma, we evaluated whether NK/T-cell lymphoma cells were unintentionally transduced with the CAR vector. We performed next-generation sequencing to detect tumor-specific mutations in their preinfusion tumor sample, progressive disease biopsy, and CAR-37 infusion product. The initial tumor had mutations in BRAF and NOTCH1 that were also present in the recurrence, along with another mutation in BCR. However, none of these mutations were detected in the CAR-37 T-cell infusion product (supplemental Figure 3). In addition, we performed Vβ sequencing on the NK/T-cell lymphoma cells and found no TCR rearrangements of TCRβ or TCRγδ, whereas the CAR-37 T cells that expanded in the patient had surface Vβ chains. Together, this evidence suggests that the high expansion of CAR-37 T cells was not because of the transduction of a tumor cell or the expansion of a single clonal population.
Cetuximab triggered the tEGFR safety switch but did not effectively deplete CAR-37 cells
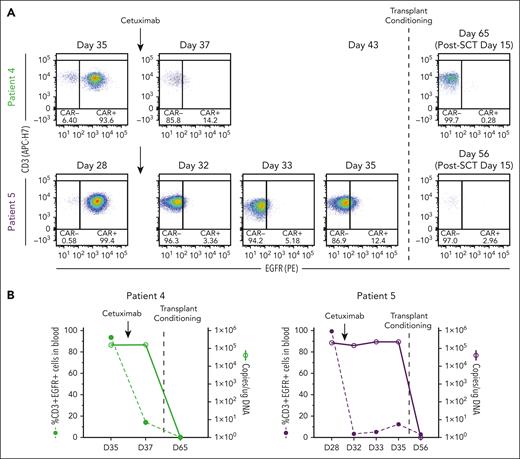
In preclinical models, cetuximab (an αEGFR monoclonal antibody that is used to treat colon and head and neck cancers)34 depletes transduced T cells that express tEGFR,35,36 making it a potential safety switch. Indeed, tEGFR is included in lisocabtagene maraleucel, an US Food and Drug Administration–approved CD19-targeting CAR T-cell therapy,37 but its use as a safety switch clinically has not been reported. We incorporated tEGFR in the CAR-37 vector primarily to measure transduction efficiency by flow cytometry but also recognized its potential use as a safety switch. Because of the unexpected level of CAR-37 expansion and prolonged cytopenia in patients 4 and 5, we administered cetuximab in an effort to eliminate CAR-37 T cells. Following a single infusion of 250 mg/m2 cetuximab, CAR-37 T cells were no longer detected by flow cytometry, which detects membrane-bound EGFR (Figure 5B); however, the VCN did not change (Figure 5B). Therefore, CAR-37 T cells were not actually eliminated and cetuximab only masked the binding of the anti-EGFR detection antibody.
Cetuximab treatment to deplete CAR-37 T cells via tEGFR. (A) Flow cytometry dot plots of CD3+EGFR+ cells in peripheral blood at the indicated time points. Patients 4 and 5 who experienced bone marrow aplasia at day 27 after CAR-37 therapy were treated with cetuximab on day 28 (patient 5) or day 35 (patient 4) to deplete their CAR-37 T cells (indicated by the arrows). On day 35 (patient 5) or day 43 (patient 4), the patients were treated with transplant conditioning chemotherapy and underwent a HSCT (indicated by the dashed line). The post-HSCT flow plots are also shown. (B) The percentage of CD3+EGFR+ cells in peripheral blood (left axis, bar graphs) in comparison with the VCN, reported as copies per microgram of DNA, detected by PCR in peripheral blood (right y-axis, line graphs) at the indicated time points is shown. Arrows indicate the timing of cetuximab treatment. The dashed line indicates the timing of the transplant conditioning treatment as shown in panel A.
Cetuximab treatment to deplete CAR-37 T cells via tEGFR. (A) Flow cytometry dot plots of CD3+EGFR+ cells in peripheral blood at the indicated time points. Patients 4 and 5 who experienced bone marrow aplasia at day 27 after CAR-37 therapy were treated with cetuximab on day 28 (patient 5) or day 35 (patient 4) to deplete their CAR-37 T cells (indicated by the arrows). On day 35 (patient 5) or day 43 (patient 4), the patients were treated with transplant conditioning chemotherapy and underwent a HSCT (indicated by the dashed line). The post-HSCT flow plots are also shown. (B) The percentage of CD3+EGFR+ cells in peripheral blood (left axis, bar graphs) in comparison with the VCN, reported as copies per microgram of DNA, detected by PCR in peripheral blood (right y-axis, line graphs) at the indicated time points is shown. Arrows indicate the timing of cetuximab treatment. The dashed line indicates the timing of the transplant conditioning treatment as shown in panel A.
In contrast, following transplant conditioning and GVHD prophylaxis, CAR-37 became undetectable by qPCR and flow cytometry 15 days after hematopoietic SCT (HSCT; when early engraftment occurred because there were no white blood cells to measure VCN before then), consistent with the eradication of transduced cells (Figure 5B-C). The failure of cetuximab to eliminate CAR-37 T cells in these 2 patients may have been caused by the severe neutropenia, because cetuximab requires antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity,38 which is affected by Fc receptor–positive leukocytes.
Assessment of the mechanisms underlying CAR-37–induced cytopenia
The severe pancytopenia with bone marrow hypocellularity in 2 of 5 patients without detectable disease was unexpected. We had confirmed, before initiating the study, that CD37 was expressed in high levels on malignant cells but was low to negative on other immune cells.31 We further confirmed this in an analysis of publicly available single-cell RNA sequencing data sets (supplemental Figure 4). To examine whether CAR-37 T cells are activated in response to normal immune cells, T cells, B cells, and hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) collected from normal donors were mixed 1:1 with CAR-37, CAR-19, or untransduced T cells in culture. CAR T-cell activation was quantified by flow cytometry for CD107a and interferon gamma (IFN-γ; supplemental Methods). As expected, normal B cells activated CAR-37 and CAR-19 T cells. In response to normal T cells and HSPCs, CAR-37 T cells had slightly higher CD107a (but not IFN-γ) than CAR-19 (supplemental Figure 5), but these increases were minimal relative to the response to normal B cells. We also examined this possibility in vivo using an NSG-SGM3 (NSGS) humanized mouse model. CAR T cells were generated from human T cells autologous to the CD34+ cells used to humanize the mice. In this model, CAR-37 and CAR-19 T cells depleted normal B cells in the peripheral blood from day 7 after T-cell infusion until the last measurement on day 22. CAR-37–treated mice maintained their bone marrow composition, consistent with the lack of CD37 expression on bone marrow cells (supplemental Figure 6). However, CAR-19 treated mice lacked B cells and HSPCs in their bone marrow, unexpectedly recapitulating CAR-19–induced cytopenia.
We hypothesized that the rapid expansion of CAR37 T cells and the sustained inflammatory effects may have been associated with significant cytokine production. We examined cytokine profiles in CAR-37–treated patients using serially collected serum samples (supplemental Methods). The highest fold changes from baseline were seen in interleukin-8 (IL-8), IL-10, chemokine ligand 2 (CCL-2), IL-18, and C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL-10) (Figure 6A). Peak levels of cytokines correlated with the timing and severity of peak CRS. Because of the cytopenia observed with CAR-19 treatment in our humanized mouse model, we also examined cytokines in their peripheral blood over time (supplemental Figure 7). Cytokines with the highest fold change in the CAR-19–treated humanized mice were similar to those observed in CAR-37 patients with cytopenia, including IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-18, suggesting a general role of these cytokines in cytopenia.
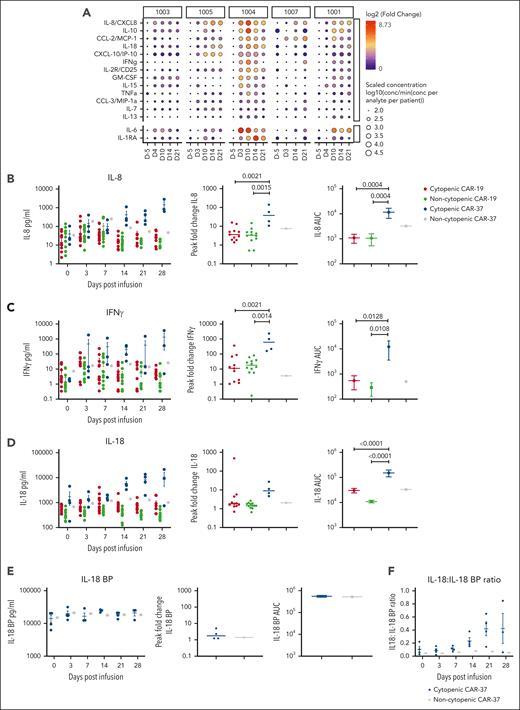
Peripheral cytokine levels in patients with and without cytopenia treated with CAR-37 in comparison with CAR-19. (A) Serum protein levels were measured using the Luminex at the indicated time points. Circle size corresponds to the log10 scaled concentration of the analyte in comparison with the minimum concentration (conc) of the analyte across patients. Circle color corresponds to the log2 fold change of the analyte in comparison with the day 5 time point for each patient. (B-D) Banked serum samples from patients treated at our institution with a licensed CD19 CAR for lymphoma were analyzed using a custom kit measuring (B) IL-8, (C) IFN-γ, and (D) IL-18 on the Ella, bio-techne and were compared with serum samples from our CAR-37 patients measured with the same kit. Patients were classified as having prolonged cytopenia if they had an ANC <0.5 x103 cells per μL blood at ≥28 days after CAR T-cell infusion. Patients were excluded if they had another cause of cytopenia, such as myelodysplasia or constitutional bone marrow failure. We compared CD19 CAR patients without cytopenia (n = 12) and cytopenia (n = 12) with CAR-37 patients without cytopenia (n = 1) and with cytopenia (n = 4). (E) IL-18 BP levels were measured on the Ella (Bio-Techne) for CAR-37 patients. Absolute values, AUC, and peak fold change from baseline are shown. (F) The ratio of IL-18 to IL-18 BP is shown over time after infusion. P values were calculated using a 1-way analysis of variance test with Tukey multiple comparisons test.
Peripheral cytokine levels in patients with and without cytopenia treated with CAR-37 in comparison with CAR-19. (A) Serum protein levels were measured using the Luminex at the indicated time points. Circle size corresponds to the log10 scaled concentration of the analyte in comparison with the minimum concentration (conc) of the analyte across patients. Circle color corresponds to the log2 fold change of the analyte in comparison with the day 5 time point for each patient. (B-D) Banked serum samples from patients treated at our institution with a licensed CD19 CAR for lymphoma were analyzed using a custom kit measuring (B) IL-8, (C) IFN-γ, and (D) IL-18 on the Ella, bio-techne and were compared with serum samples from our CAR-37 patients measured with the same kit. Patients were classified as having prolonged cytopenia if they had an ANC <0.5 x103 cells per μL blood at ≥28 days after CAR T-cell infusion. Patients were excluded if they had another cause of cytopenia, such as myelodysplasia or constitutional bone marrow failure. We compared CD19 CAR patients without cytopenia (n = 12) and cytopenia (n = 12) with CAR-37 patients without cytopenia (n = 1) and with cytopenia (n = 4). (E) IL-18 BP levels were measured on the Ella (Bio-Techne) for CAR-37 patients. Absolute values, AUC, and peak fold change from baseline are shown. (F) The ratio of IL-18 to IL-18 BP is shown over time after infusion. P values were calculated using a 1-way analysis of variance test with Tukey multiple comparisons test.
In patients 4 and 5, who developed hypocellular bone marrow without disease involvement, we noted that IL-8 and IL-18 levels were particularly high in the peripheral blood. To put these values into further context, we compared levels of IL-8, IL-18, and IFN-γ (because of its association with aplasia39-42) in CAR-37–treated patients with those in a cohort of CAR-19–treated patients with lymphoma who did or did not have prolonged severe cytopenia (excluding patients with bone marrow involvement at day 28 after infusion). We found that the IL-18 area under the curve (AUC) from day 0 to 28 was much higher in CAR-37 patients with cytopenia than in CAR-19 patients (P < .001). In addition, peak fold change and the AUC for IFN-γ and IL-8 were significantly higher for CAR-37 patients with cytopenia than for CAR-19 patients (Figure 6B-D).
To explore whether these cytokines could also be playing a role in prolonged cytopenia in CAR-19–treated patients, we performed a subanalysis of this group. IL-18, but not IL-8 or IFN-γ, was significantly higher postinfusion in CAR-19 patients with prolonged cytopenia (n = 12) compared with non-cytopenic patients (n = 12) across multiple time points and the AUC from day 0 to 28 (supplemental Figure 8). However, the peak fold change was not significantly different, likely because of the higher baseline inflammation in CAR-19 patients who went on to develop prolonged cytopenia, a known risk factor.43 Because IL-18 activity is naturally opposed by IL-18 binding protein (IL-18 BP) and free IL-18 has been associated with CAR T cell–associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocystosis-like toxicities,44 we measured IL-18 BP levels in CAR-37 patients. We found only a minimal increase in IL-18 BP (1.76 median peak fold change) when compared with the large increase in IL-18 (9.05 median peak fold change) in the patients who developed cytopenia (Figure 6E-F), suggesting an inadequate negative feedback loop in this hyperinflammatory state.
To explore whether CAR-37 T cells produced higher levels of cytokines than CAR-19 T cells, we performed coculture experiments with a K562 cell line transduced with a bicistronic vector to express equal amounts of CD37 and CD19 (supplemental Methods). CAR-19 T cells tended to produce more inflammatory cytokines after activation (supplemental Figure 9), whereas CAR-37 T cells tended to constitutively produce low levels of IFN-γ and CXCL10 at baseline. Neither CAR-19 nor CAR-37 produced IL-18 in coculture. Evaluation of a single-cell data set of peripheral blood mononuclear cell from CAR-19–treated patients45 and lung tissue from COVID-19 patients at autopsy46 found that IL-18 is not produced by T cells but is produced by myeloid cells (in particular myeloid dendritic cells and monocytes) and epithelial cells (supplemental Figure 10). We therefore hypothesize that IL-18 is produced by endogenous myeloid and epithelial cells in response to inflammation and induces further IFN-γ production by T cells (a known T-cell response to IL-18),47 leading to sustained inflammation and insult to the hematopoietic stem cell compartment. In the absence of IL-18 BP, the sustained high levels of IL-18 are likely related to the clinical prolonged cytopenia observed in the CAR-37–treated patients.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this clinical study was the first in-human trial of CAR T cells that targeted CD37. We demonstrated that rapid production of CAR-37 T cells was feasible with both fresh and cryopreserved products, thereby meeting the established release specifications and demonstrating potency. The short vein-to-vein time allowed patients with rapidly progressive, high-grade diseases to be treated. In all but 1 patient, the prespecified dose of CAR-37 T cells was manufactured. In total, antitumor activity was seen in 4 of 5 patients treated with 3 CRs and 1 MR. Although we treated a small number of patients, we observed antitumor responses across heterogeneous lymphoid malignancies, and resistance seems to have been driven by antigen loss rather than CAR T-cell dysfunction.48,49
The toxicity profile of CAR-37 was broadly similar in scope to other CAR T products and independent of dose.4,5,11,12,50,51 CRS was generally low grade and observed in all patients but was unexpectedly prolonged, requiring multiple interventions in 2 patients. Prolonged and profound cytopenia also developed more frequently than expected.43,52 This is an increasingly recognized CAR T-cell toxicity that, in severe cases, is managed with allogeneic or autologous HSCT or stem cell boost.43,53-58 Two CAR-37 patients with prolonged cytopenia necessitated allogeneic HSCT and engrafted slowly but had full count recovery. Because of these toxicities, future clinical development of CAR-37 may focus on patients with relapsed and refractory T-cell and NK/T-cell lymphoma who lack effective treatment options.59,60 This disease group can achieve long-term remission with allogeneic HSCT, but the benefit is predominantly seen in patients who enter transplant with complete remission.61 Thus, CAR-37 may be used as induction therapy to obtain disease remission before allograft, which may also be a useful strategy to mitigate the risk of toxicity from prolonged cytopenia. A similar approach may also be used in patients with acute myeloid leukemia in which CD37 expression has been reported62 and allogeneic HSCT is the standard of care in patients with high-risk features.63
The patients who developed cytopenia had particularly high levels of IL-8, IL-18, and IFN-γ that were associated with high levels of CAR-37 T-cell expansion after infusion. It is likely that this cytokine-driven inflammatory process damaged hematopoietic stem cell reserves, which has been implicated in the pathophysiology of prolonged cytopenia after other CAR T-cell therapies and may be a class effect.39,52,56,64-68 It is interesting that a similar cytokine profile has also been described in patients who developed IEC-HS after treatment with an anti-CD22 CAR.69 Although none of the CAR-37 patients were diagnosed with IEC-HS, there was overlap with some hyperinflammatory features, such as dramatically and sustained elevated ferritin levels in the serum.33,69-71 In CAR-22 patients, there was a corresponding rise in IL-18 BP44; however, only minimal production of IL-18 BP was observed in CAR-37–treated patients. Using available single-cell sequencing data, we observed that IL-18 is made by epithelial and myeloid cells, whereas IL-18 BP is primarily produced by myeloid cells. Therefore, we hypothesize that CAR-37 patients failed to produce IL-18 BP because of a lack of myeloid cells, leading to unopposed IL-18 activity in its absence.
Our data demonstrate that IL-18 was the cytokine most highly associated with severe pancytopenia in patients who had been treated with CAR-19 T cells. The mechanism for such cytopenia is unclear; however, given the observation of such a phenomenon across CAR T products, including B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) and CD19, a broader inflammatory process may be at play. This may be particularly important because IL-18–secreting CAR T cells have now entered clinical trials managed by multiple groups and seem to be efficacious at very low doses.72 Our data suggest that increased vigilance may be necessary, particularly for cytopenia and immune dysregulation. Future studies are warranted to further investigate the mechanisms and correlations of these cytokines in driving CAR T-cell–associated cytopenia.
We also demonstrated that using cetuximab to trigger a suicide gene in CAR T cells is not effective in the background of severe pancytopenia. This has significance for other CAR T-cell products, such as lisocabtagene maraleucel or experimental CAR T-cell products that contain tEGFR with the intention of using it as a safety switch. To our knowledge, this use of cetuximab has not been reported in patients. In this study, we demonstrated that cetuximab effectively blocked EGFR detection via flow cytometry but did not lead to CAR-37 T-cell ablation, likely because of the lack of other leukocytes to perform antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Therefore, this approach should be used with caution, especially if the side effects of the CAR T-cell products are relatively unknown. Other safety switches, such as rimiducid to kill inducible caspase 9–transduced cells, have been deployed recently73 and may be a more effective strategy for eliminating CAR T cells. In addition, standard chemotherapies, such as cyclophosphamide, are readily available and can reduce CAR T-cell numbers and reverse certain toxicities even in the absence of a specific suicide gene.74 Likewise, in this study, we demonstrated that the conditioning and GVHD prophylaxis regimen used as part of an allogeneic stem cell transplant completely ablated the CAR T cells. This may be particularly useful in the setting of pancytopenia, a toxicity that is not immediately lethal and in which case hematopoiesis is routinely restored by the graft.
Our clinical study was limited by the small sample size of 5 patients, and long-term outcomes were significantly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. Two deaths occurred as a consequence of COVID-19 in patients who had achieved complete remission following CAR-37 T-cell therapy; unfortunately, patient 3 had ongoing T-cell lymphoma at the time, likely leading to immunodeficiency, and patient 5 refused vaccination. Prevalence in the community was particularly high with the more contagious delta variant at the time of infection.75 It is known that COVID-19 poses a significant threat to hemato-oncology patients who are already immunocompromised and that CAR T-cell therapy and/or HSCT increase this risk further.76-78
In conclusion, we demonstrated that CAR-37 T cells are feasible to manufacture and significantly expand in the peripheral blood with associated elevations in serum cytokine levels, which likely contributed to the hematotoxicity observed in a subset of our patients. CAR-37 T cells are also potent across a heterogenous population of CD37+ hematologic malignancies. Future strategies will harness the potency of CAR-37 to obtain deep remissions before allogeneic HSCT in high-risk patient groups.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Shannon Himber, Jennifer Yam, Gabrielle Brini, Elba Gonzalez, Jami Brown, Keagan Casey, Kit Shaw, Patricia Brunker, Tom Spitzer, Betsy Valles, Lindsey Perry, and Cheryl Tierno for their assistance in carrying out the clinical trial. They thank Nirali Shah for helpful comments on the manuscript.
This work was supported by funding from the National Cancer institute (NCI)/National Institutes of Health (NIH) (R01CA252940 [M.V.M]). M.J.F. was supported by the NCI/NIH (K12CA087723). M.W. was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation Postdoc Mobility fellowship (P400p.m. 186739). C.E.G. was supported by the 2022 AACR-Genmab Non-Hodgkin B-cell Lymphoma Research Fellowship (grant number 22-40-72-GRAH). M.B.L. was supported by the NCI/NIH (grants 2T32CA071345-21A1 and K12CA087723), ASCO Young Investigator Award (2021YIA-0768568550), and the Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation (PST-37-22). I.S. was supported by the Leukemia Research Foundation. A.S. was supported by Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienstand and a DKMS John Hansen Research Grant (DKMS-SLS-JHRG-2020-04). J.F.D. was supported grant from NCI/NIH (grant R35 CA210084). This study was also supported by the National Gene Vector Biorepository at Indiana University, which was funded through the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/NIH and NCI/NIH (contracts 75N92019D00018 and HSN261201500003I Task Order number HHSN26100077, respectively).
Authorship
Contributions: M.J.F. and M.V.M. conceived the clinical study; C.E.G., T.R.B., M.J.F., and M.V.M. wrote the manuscript; M.J.F., A.E.-J., and Y.-B.C. performed the clinical trial; C.E.G., K.M.E.G., E.L.E., K.K., A.S., W.-H.L., H.R.W., M.W., A.B., and J.R. performed the experiments; C.E.G., K.M.E.G., T.R.B., J.R., N.J.H., A.D., M.V.M., and M.J.F. analyzed the data; and all authors contributed intellectually to the experiments and edited and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflicts-of-interest disclosure: M.V.M. and I.S. report being inventors on patents describing chimeric antigen receptor-37 (CAR-37) therapy titled “CD37-Targeted Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells for Lymphomas/Leukemias” (PCT/US2018/022974); “Anti-CD37 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma” (PCT/US2019/038518). In addition, M.V.M. reports being an inventor on patents related to adoptive cell therapies, held by Massachusetts General Hospital and the University of Pennsylvania (some licensed to Novartis). M.V.M. reports holding equity in AffyImmune, Century Therapeutics, Oncternal Therapeutics, Neximmune, and TCR2; serving on the board of directors of 2seventy bio; and has served as a consultant for multiple companies involved in cell therapies. M.V.M.’s interests were reviewed and are managed by the Massachusetts General Hospital and Mass General Brigham in accordance with their conflict-of-interest policies. J.F.D. reports holding equity in Magenta Therapeutics and Wugen Inc; receiving research support from MacroGenics, Bioline, and Incyte; and serving as a consultant for Vertex, bluebird bio, SPARC, and RiverVest. J.R. reports receiving research funding from Equillium, Kite/Gilead, Novartis, and Oncternal Therapeutics; and serving on the scientific advisory boards of Akron Biotech, Clade Therapeutics, Garuda, LifeVault Bio, Novartis, Smart Immune, and TScan Therapeutics. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Marcela V. Maus, Cancer Center, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, 149 13th St, Charlestown, MA 02129; email: mvmaus@mgh.harvard.edu.
References
Author notes
M.J.F., C.E.G., and T.R.B. contributed equally to this study.
Data are available on request from the corresponding author, Marcela V. Maus (mvmaus@mgh.harvard.edu).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal