Id3 limits PD-1 expression and exuberant effector differentiation of Th1 cells, protecting them from PD-1–mediated suppression during GVHD.
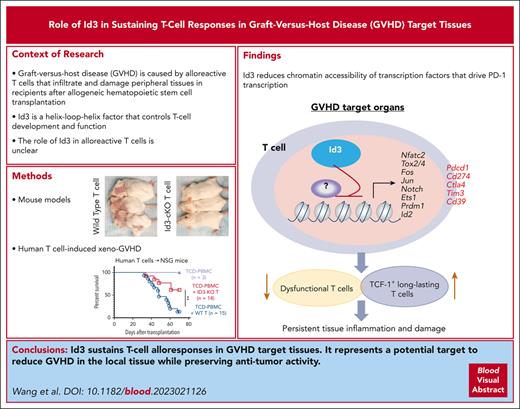
Id3 reduces chromatin accessibility of transcription factors that drive T-cell PD-1 transcription, differentiation, and dysfunction.
Visual Abstract
Persisting alloreactive donor T cells in target tissues are a determinant of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), but the transcriptional regulators that control the persistence and function of tissue-infiltrating T cells remain elusive. We demonstrate here that Id3, a DNA-binding inhibitor, is critical for sustaining T-cell responses in GVHD target tissues in mice, including the liver and intestine. Id3 loss results in aberrantly expressed PD-1 in polyfunctional T helper 1 (Th1) cells, decreased tissue-infiltrating PD-1+ polyfunctional Th1 cell numbers, impaired maintenance of liver TCF-1+ progenitor-like T cells, and inhibition of GVHD. PD-1 blockade restores the capacity of Id3-ablated donor T cells to mediate GVHD. Single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis revealed that Id3 loss leads to significantly decreased CD28- and PI3K/AKT-signaling activity in tissue-infiltrating polyfunctional Th1 cells, an indicator of active PD-1/PD-L1 effects. Id3 is also required for protecting CD8+ T cells from the PD-1 pathway–mediated suppression during GVHD. Genome-wide RNA-sequencing analysis reveals that Id3 represses transcription factors (e.g., Nfatc2, Fos, Jun, Ets1, and Prdm1) that are critical for PD-1 transcription, exuberant effector differentiation, and interferon responses and dysfunction of activated T cells. Id3 achieves these effects by restraining the chromatin accessibility for these transcription factors. Id3 ablation in donor T cells preserved their graft vs tumor effects in mice undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Furthermore, CRISPR/Cas9 knockout of ID3 in human CD19–directed chimeric antigen receptor T cells retained their antitumor activity in NOD/SCID/IL2Rg−/− mice early after administration. These findings identify that ID3 is an important target to reduce GVHD, and the gene-editing program of ID3 may have broad implications in T-cell–based immunotherapy.
Introduction
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is caused by alloreactive T cells that infiltrate and damage peripheral tissues in recipients after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT).1-3 These tissue-infiltrating donor T cells produce a plethora of inflammatory cytokines and cytotoxic molecules to mediate tissue injury.4-9 Although tissue-infiltrating donor T cells are initially activated in the secondary lymphoid organs, they are expanded and maintained locally within the resident tissues during the effector phase.1-3,10 They express a tissue-resident memory-like phenotype1 and may be locally maintained by T cell factor 1 (TCF-1)+ progenitor-like T cells.2 These data suggest that tissue-infiltrating T cells have acquired a transcriptional program that sustains their expansion and function; however, the transcriptional regulators that control these processes remain unknown.
Id3 is a helix-loop-helix factor that controls T-cell development and function through antagonizing the function of the E box–binding family of transcription factors, which are master regulators of thymic development and antigen-driven T-cell responses. Id3 promotes CD8+ T-cell, γδ T-cell, and invariant natural killer T cells (iNKT) cell development but antagonizes CD4+ T-cell fate determination.11-14 Id3 also regulates antigen-specific CD8+ T-cell memory formation, memory recall response and effector survival,15-17 and is associated with CD4+ memory Th1 cells.18 Additionally, Id3 expression may identify precursor exhausted CD8+ T cells during chronic infections.19 However, the precise role of Id3 in alloreactive T cells, specifically tissue-infiltrating pathogenic T cells, has not been previously defined.
Here, we identify that Id3 is critical for the persistence and function of tissue-infiltrating GVHD T cells in mice. Id3 loss increases programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) expression and impairs tissue-infiltrating Th1 cells. Id3 reduces chromatin accessibility (ChrAcc) of transcription factors (TFs) that drive T-cell PD-1 transcription, differentiation, and dysfunction. Id3 may represent a unique target to reduce GVHD in the local tissue while preserving antitumor activity.
Materials and methods
Mice and human T cells
C57BL/6 (B6), B6/SJL (B6/SJL), Balb/c, and NOD/SCID/IL2Rg−/− (NSG) mice were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory. Balb/b mice were maintained in house. CD4-Cre+Id3fl/fl B6 mice (Id3-cKO) were bred by crossing Id3fl/fl B6 mice with CD4-Cre–expressing B6 mice. Experimental protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees of Temple University and Hackensack Meridian Health. Human T cells were isolated from the buffy coat of deidentified healthy donors (New York Blood Center, New York, NY).
Methods
Cell preparation and culture, GVHD mouse models, lentivirus and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell production, xeno-GVHD, human leukemia NSG mice, CRISPR/Cas9 knockout (KO) of ID3, retrovirus preparation and transduction, flow cytometry analysis, real-time polymerase chain reaction, bulk RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) and analysis, transposase-accessible chromatin sequencing (ATAC-seq) and analysis, single-cell RNA-seq (scRNA-seq) analysis, and statistical analysis are detailed in supplemental Methods.
Results
T cells require Id3 to induce GVHD
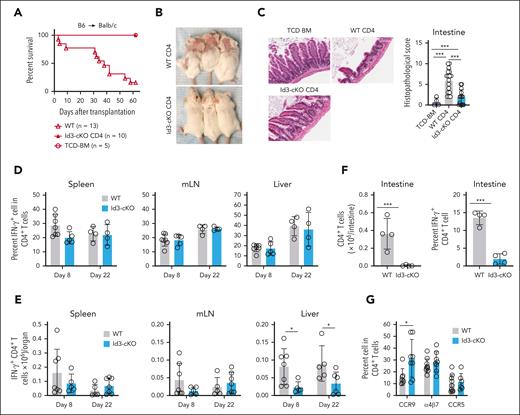
To investigate a role of Id3 in T-cell–mediated GVHD, we isolated naïve CD4+ T cells from wild-type (WT) and Id3-cKO B6 mice, mixed with T-cell–depleted (TCD) bone marrow cells from B6xB6/SJL F1 mice (CD45.1+CD45.2+), and transplanted them into lethally irradiated Balb/c mice (supplemental Figure 1A, available on the Blood website). WT T cells caused GVHD, with 90% of them succumbing to the disease (Figure 1A; supplemental Figure 1B). Id3-cKO T cells failed to induce GVHD, with all recipients surviving during the observation period (Figure 1A; supplemental Figure 1B). This was accompanied by the absence of cutaneous GVHD (Figure 1B; supplemental Figure 1C-D) and reduced inflammation in the intestine (Figure 1C), skin, and liver (supplemental Figure 1C-D).
Id3 maintains the GVHD-inducing capacity of alloreactive T cells. Balb/c mice were subjected to total body irradiation (4.5 Gy on day −1 and 4 Gy on day 0) followed by infusion of 5 × 106 B6 × B6/SJL F1 mouse (CD45.1+CD45.2+) TCD bone marrow (TCD-BM) alone or together with 5 × 105 B6 (CD45.1-CD45.2+) naïve WT or Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells. (A) Survival of Balb/c recipients. (B) Cutaneous GVHD in Balb/c mice receiving WT and Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells, day 22 after transplantation in at least 8 mice per group. (C) Intestine from Balb/c recipients were harvested from day 14 to 22, sectioned, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Slides were scanned with Leica Aperio VERSA slide scanner and visualized with Aperio ImageScope (20×). N = 8. (D-G) Balb/c recipients were euthanized at the indicated time points after HSCT. Tissues were harvested for the analysis of donor T-cell immune response using flow cytometry. Id3-cKO donor CD4+ T cells exhibited normal cytokine-producing capacity represented by the similar percentage (D) and number (E) of IFN-γ+ cells in the spleen, mesenteric lymph node (mLN), and liver. (F) Graphs show the number of intestine-infiltrated donor CD4+ T cells and those with IFN-γ–producing capacity recovered in Balb/c mice that underwent transplantation with Id3-cKO T cells. (G) Graphs show the frequency of donor T cells expressing α4β7, CCR5, and CCR9. ∗P < .05; ∗∗∗P < .001; Student t test was used for 2-group comparison. At least 4 mice per group were analyzed.
Id3 maintains the GVHD-inducing capacity of alloreactive T cells. Balb/c mice were subjected to total body irradiation (4.5 Gy on day −1 and 4 Gy on day 0) followed by infusion of 5 × 106 B6 × B6/SJL F1 mouse (CD45.1+CD45.2+) TCD bone marrow (TCD-BM) alone or together with 5 × 105 B6 (CD45.1-CD45.2+) naïve WT or Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells. (A) Survival of Balb/c recipients. (B) Cutaneous GVHD in Balb/c mice receiving WT and Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells, day 22 after transplantation in at least 8 mice per group. (C) Intestine from Balb/c recipients were harvested from day 14 to 22, sectioned, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Slides were scanned with Leica Aperio VERSA slide scanner and visualized with Aperio ImageScope (20×). N = 8. (D-G) Balb/c recipients were euthanized at the indicated time points after HSCT. Tissues were harvested for the analysis of donor T-cell immune response using flow cytometry. Id3-cKO donor CD4+ T cells exhibited normal cytokine-producing capacity represented by the similar percentage (D) and number (E) of IFN-γ+ cells in the spleen, mesenteric lymph node (mLN), and liver. (F) Graphs show the number of intestine-infiltrated donor CD4+ T cells and those with IFN-γ–producing capacity recovered in Balb/c mice that underwent transplantation with Id3-cKO T cells. (G) Graphs show the frequency of donor T cells expressing α4β7, CCR5, and CCR9. ∗P < .05; ∗∗∗P < .001; Student t test was used for 2-group comparison. At least 4 mice per group were analyzed.
To understand the underlying mechanism, we determined whether Id3 ablation impaired engraftment, proliferation, and expansion of donor T cells. By days 8 and 22 after transplantation, Id3 loss did not significantly reduce the frequency and number of interferon gamma (IFN-γ)–producing CD4+ Th1 cells in the spleen and mesenteric lymph node (Figure 1D-E) but profoundly diminished Th1 cells in the liver (threefold and 2.5-fold, respectively; Figure 1E). Id3 loss also decreased the numbers of IFN-γ–producing Th1 effectors in the intestine 17 days after transplantation (Figure 1F). 5-Bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation assay showed that Id3 loss did not decrease donor T-cell proliferation (supplemental Figure 1E). Chemokine receptors CCR9 and CCR5 and adhesion molecule α4β7 are required for T-cell migration into GVHD tissues.20,21 Id3 ablation did not reduce the expression of CCR5, α4β7, or CXCR3 on the surface of alloreactive T cells in the mesenteric lymph node. Instead, alloreactive Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells produced a higher frequency of CCR9+ effectors (Figure 1G; supplemental Figure 1F-G). Thus, Id3 maintains alloreactive Th1 cells in GVHD target tissues via a mechanism independent of proliferation and tissue migration–associated molecules.
Id3 represses genes driving effector differentiation and inhibitory receptor expression
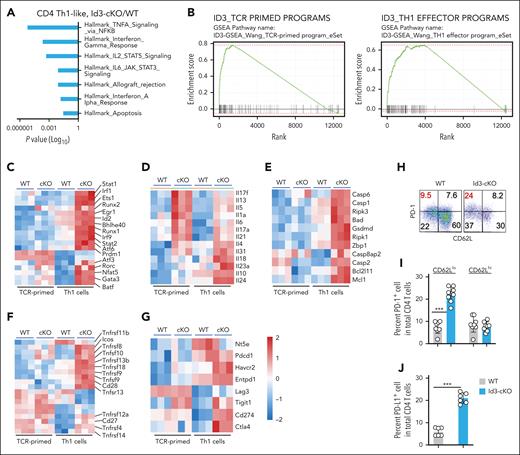
To identify the Id3-targeted genes associated with alloreactive T-cell function, we performed RNA-seq analysis. Effector differentiation is associated with downregulation of Id3 expression.15,18 After 96 hours of culturing under Th1 cell conditions, both WT and Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells upregulated CD44, but the latter showed more profound downregulation of CD62L (supplemental Figure 2A). To avoid the potential contribution of different Th1 cell subsets to Id3 deficiency–mediated gene expression, we performed RNA-seq analysis using messenger RNA from highly purified CD44hiCD62Llo and CD44hiCD62Lhi Th1 cells (supplemental Figure 2A). Additionally, to capture the earliest molecular changes of Id3 deficiency upon Th1 induction, we analyzed the gene profiles of CD4+ T cells 24 hours after T-cell receptor (TCR) activation (TCR-primed CD4+ T cells; Figure 2B). TCR priming induced significant transcriptional diversification between WT and Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells. This diversification was dramatically amplified between WT and Id3-cKO CD44hiCD62Llo Th1 cells (supplemental Figure 2B).
Id3 represses genes associated with T-cell effector differentiation and inhibitory signaling. WT and Id3-cKO naïve CD4+ T cells were activated and cultured under Th1 polarization condition. Cells were harvested 24 hours (TCR primed) and 96 hours after activation. 96 hour-cultured cells were sorted into CD62Lhi and CD62Llo (Th1 cells) populations before library preparation. (A) Gene set enrichment analysis using Hallmark gene set showed significant enrichment of tumor necrosis factor α signaling via NF-κb, IFN-γ response, IL-2–STAT5 signaling, IL-6–STAT3 signaling, allograft rejection, IFN-α response, and apoptosis comparing transcriptome from 4-day cultured Id3-cKO Th1-like cells with WT. (B) Id3-regulated gene signature in TCR-primed CD4+ T cells and effector Th1 CD4+ T cells. (C-G) Heat maps demonstrate 5 categories of differential expressed genes: TFs critical for effector proliferation and differentiation (C); cytokines that distinguish Th1 from Th2 and Th17 cells (D); cell survival and death molecules (E); costimulatory molecules important for GVHD T-cell proliferation and survival (F); and inhibitory receptors (G). Data were collected from 3 independent experiments. (H) Flow cytometry analysis shows that loss of Id3 leads to increased expression of PD-1 (H, I) and PD-L1 (J) in Th1 cells. ∗∗∗P < .001. Experiments were performed >5 times.
Id3 represses genes associated with T-cell effector differentiation and inhibitory signaling. WT and Id3-cKO naïve CD4+ T cells were activated and cultured under Th1 polarization condition. Cells were harvested 24 hours (TCR primed) and 96 hours after activation. 96 hour-cultured cells were sorted into CD62Lhi and CD62Llo (Th1 cells) populations before library preparation. (A) Gene set enrichment analysis using Hallmark gene set showed significant enrichment of tumor necrosis factor α signaling via NF-κb, IFN-γ response, IL-2–STAT5 signaling, IL-6–STAT3 signaling, allograft rejection, IFN-α response, and apoptosis comparing transcriptome from 4-day cultured Id3-cKO Th1-like cells with WT. (B) Id3-regulated gene signature in TCR-primed CD4+ T cells and effector Th1 CD4+ T cells. (C-G) Heat maps demonstrate 5 categories of differential expressed genes: TFs critical for effector proliferation and differentiation (C); cytokines that distinguish Th1 from Th2 and Th17 cells (D); cell survival and death molecules (E); costimulatory molecules important for GVHD T-cell proliferation and survival (F); and inhibitory receptors (G). Data were collected from 3 independent experiments. (H) Flow cytometry analysis shows that loss of Id3 leads to increased expression of PD-1 (H, I) and PD-L1 (J) in Th1 cells. ∗∗∗P < .001. Experiments were performed >5 times.
Without Id3, TCR-primed CD4+ T cells primarily induced gene expression (supplemental Figure 2C). These differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were associated with activation of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFA) signaling via NFκB, apoptosis, and interleukin-6 (IL-6)/JAK/STAT3 signaling (supplemental Figure 2D). Upon Th1 cell differentiation, Id3 deficiency induced 4265 genes and 4150 genes, but repressed 476 genes and 260 genes, in CD44hiCD62Llo Th1 cells and CD44hiCD62Lhi Th1 cells, respectively (supplemental Figure 2C). However, only few DEGs were identified between CD44hiCD62Llo and CD44hiCD62Lhi Th1 cells (supplemental Figure 2E). Thus, CD62L expression did not distinguish Id3-controlled transcription in Th1 cells. We, therefore, focused on analyzing DEGs in CD44hiCD62Llo Th1 cells. Functional annotation of these DEGs indicated strong enrichment of IL-2-STAT5 signaling, IFN-γ response, and allograft rejection besides those identified in TCR-primed CD4+ T cells (Figure 2A-B). Thus, Id3 is important for repressing genes critical for effector differentiation and IFN responses while promoting cell survival.
We characterized those Id3-repressed gene pathways with higher gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) scores (supplemental Figure 2C; Figure 2A), which represented the transcriptional signature repressed by Id3 in TCR-primed T cells and Th1 cells (Figure 2B; supplemental Table 1). We classified them into 5 clusters, including (1) TFs critical for effector proliferation and differentiation; (2) cytokines that distinguish Th1 from other lineages (Il4, Il5, Il13, Il17a, Il17f, and Il21); (3) cell survival and death molecules (e.g., Mcl1, Bcl2l11, Bad, and Zbp1); (4) costimulatory molecules (e.g., Cd28, Icos, Tnfsf8, and Tnfrsf9); and (5) inhibitory receptors (Figure 2C-G). Id3 loss upregulated the expression of TF genes that promote Th1 (Atf3), Th17 (Batf), and Th2 cell (Gata3) differentiation (Figure 2C). Bhlhe40, which promotes the generation of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)–secreting effectors,9 was highly increased in Id3-cKO Th1 cells (Figure 2C). Enhanced gene transcripts encoding Th2 and Th17 cytokines agree with previous observations that Id3 represses Th2- and Th17-cell differentiation.11,22,23 Surprisingly, Id3 inhibition led to marked upregulation of inhibitory receptors (e.g., Pdcd1, Cd274, Ctla4, and Havcr2; Figure 2G). Western blotting assay showed that Id3 loss resulted in a threefold increase in PD-1 protein (supplemental Figure 2F). We verified that Id3 loss caused significant increases in PD-1+ and programmed death-ligand 1(PD-L1)(CD274)+ Th1 cells (Figure 2H-J). Increased expression of cell death genes and inhibitory receptors in Id3-cKO Th1 cells was associated with their impaired expansion at day 5 of culture (supplemental Figure 2G). These results uncover a previously unrecognized role of Id3 in limiting the expression of gene programs that promote effector differentiation and the expression of PD-1 and PD-L1.
Id3 limits PD-1 expression by tissue-infiltrating alloreactive Th1 cells
Activation of PD-1 signaling by PD-L1 causes T-cell death and dysfunction, thereby limiting T-cell–mediated tissue injury24-26 and GVHD.27-30 To test the impact of Id3 deficiency on PD-1 expression in alloreactive T cells, we recovered donor T cells from Balb/c mice 6 and 8 days after allo-HSCT. Alloantigen-reactive effector T cells that simultaneously produce IFN-γ and GM-CSF are responsible for mediating severe GVHD and are enriched for alloantigen-specific T cells.7,31,32 Compared with WT CD4+ T cells, Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells produced similar frequencies of IFN-γ+GM-CSF+ Th1 cells (resembling polyfunctional Th1 cells) in the spleen and liver 8 days after transplantation (Figure 3A-B), but approximately fivefold fewer polyfunctional Th1 cell numbers in the liver (Figure 3C). Id3 loss also led to ∼10-fold fewer polyfunctional Th1 cells in the intestine 17 days after HSCT (Figure 3D-E). Thus, Id3 is critical for sustaining alloreactive Th1 cells that infiltrate GVHD target tissues. Notably, Id3 ablation significantly increased the frequency of PD-1+ polyfunctional Th1 cells and their PD-1 protein levels (mean fluorescence intensity) initially in the spleen 6 days after transplantation and subsequently in the liver by 8 days (Figure 3F-H). Id3 deficiency resulted in a significantly increased percentage of PD-L1–expressing Th1 cells (Figure 3I-J). These data verify the importance of Id3 in repressing the expression of PD-1 and PD-L1 by alloreactive effector T cells.
Id3 deficiency leads to PD-1 upregulation on polyfunctional Th1 cells. (A-C) Approximately 6 to 8 days after allo-HSCT, cells were isolated from the spleen and liver of Balb/c recipients of donor B6 naïve T cells as described in Figure 1, and donor T cells were analyzed for effector function. Plots and graphs show the percentage of IFN-γ+ GM-CSF+ polyfunctional cells (A-B) and the number of Id3-cKO IFN-γ+GM-CSF+ T cells in the spleen and liver (C). (D-E) Plots and graphs show the frequency of lamina-propria lymphocyte (LPL) IFN-γ+GM-CSF+ cells in the intestine of Balb/c recipients 17 days after HSCT. (F-H) The IFN-γ+GM-CSF+ polyfunctional population was gated for the analysis of inhibitory molecule expression (F). The percentage of PD-1+ cells (G) and PD-1 level (mean fluorescence intensity [MFI]) on the surface of individual CD4+ polyfunctional T cells (H) isolated from the spleen and the liver of Balb/c recipients 6 and 8 days after HSCT. (I-J) Plots and graphs show the percentage of PD-L1–expressing donor CD4+ T cells isolated from the spleen and liver of Balb/c recipients. ∗P < .05; ∗∗∗P < .001, Student t test. At least 3 mice per group were analyzed.
Id3 deficiency leads to PD-1 upregulation on polyfunctional Th1 cells. (A-C) Approximately 6 to 8 days after allo-HSCT, cells were isolated from the spleen and liver of Balb/c recipients of donor B6 naïve T cells as described in Figure 1, and donor T cells were analyzed for effector function. Plots and graphs show the percentage of IFN-γ+ GM-CSF+ polyfunctional cells (A-B) and the number of Id3-cKO IFN-γ+GM-CSF+ T cells in the spleen and liver (C). (D-E) Plots and graphs show the frequency of lamina-propria lymphocyte (LPL) IFN-γ+GM-CSF+ cells in the intestine of Balb/c recipients 17 days after HSCT. (F-H) The IFN-γ+GM-CSF+ polyfunctional population was gated for the analysis of inhibitory molecule expression (F). The percentage of PD-1+ cells (G) and PD-1 level (mean fluorescence intensity [MFI]) on the surface of individual CD4+ polyfunctional T cells (H) isolated from the spleen and the liver of Balb/c recipients 6 and 8 days after HSCT. (I-J) Plots and graphs show the percentage of PD-L1–expressing donor CD4+ T cells isolated from the spleen and liver of Balb/c recipients. ∗P < .05; ∗∗∗P < .001, Student t test. At least 3 mice per group were analyzed.
PD-1 blockade rectifies Id3-cKO T cells’ capacity to mediate GVHD
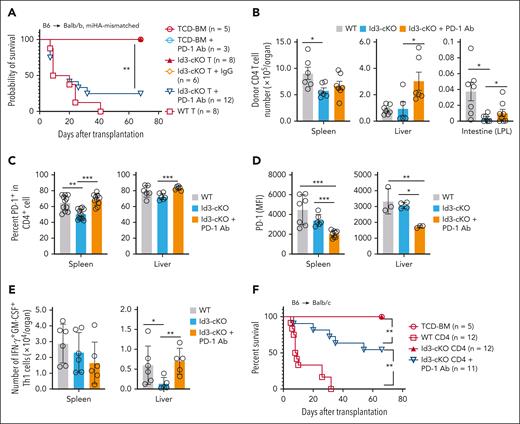
We then examined the impact of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway on Id3 deficiency–mediated GVHD inhibition using 2 different mouse models. First, we used the B6 anti-Balb/b mouse model of GVHD directed against minor histocompatibility antigen, in which both donor CD4+ and CD8+ T cells induce lethal GVHD.33 Id3-cKO T cells failed to induce severe GVHD in Balb/b recipients (Figure 4A). However, anti–PD-1 Ab treatment induced severe GVHD in Id3-cKO T-cell Balb/b recipients, with 80% mortality (Figure 4A). Compared with saline control, PD-1 blockade significantly increased the numbers of donor Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells in the liver and intestine (Figure 4B) and the frequency of PD-1+CD4+ T cells in the spleen and liver (Figure 4C). Alloreactive Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells derived from these PD-1 Ab–treated mice expressed lower levels of PD-1 than their WT counterparts (Figure 4D). This coincides with previous observations that PD-1 blockade reinvigorates tumor-reactive T cells expressing low levels of PD-1.25,34 Notably, although PD-1 blockade did not affect the frequency of polyfunctional Th1 cells in the liver (supplemental Figure 3A-B), it caused a 1.5-fold increase in polyfunctional Th1 cell numbers compared with saline control (Figure 4E). Id3 ablation resulted in markedly increased cell death and decreased numbers of PD-1+ CD4 T cells in the liver, which was significantly alleviated by PD-1 blockade (supplemental Figure 3C-D). Thus, the PD-1 pathway–mediated cell death contributes to decreases in tissue-infiltrating Id3-cKO Th1 cells.
PD-1 blockade restored the GVHD-inducing capacity of Id3-cKO T cells. (A-E) Balb/b mice were subjected to total body irradiation (5 Gy on day −1 and 5 Gy on day 0) followed by infusion of 5 × 106 B6 × B6/SJL F1(CD45.1+CD45.2+) TCD-BM alone or together with 1 × 106 B6 (CD45.1−CD45.2+) naïve CD4+ and 5 × 105 B6 (CD45.1−CD45.2+) naïve CD8+ WT or Id3-cKO T cells. Anti–PD-1 antibody (200 μg per mouse per injection) was administered intraperitoneally on days 0, 3, 5, and 7 after HSCT. In some experiment, isotype immunoglobulin G (IgG) was injected as control. (A) Survival rates of Balb/b mice. (B) Seventeen days after HSCT, cells were isolated from the spleen, liver, and intestine of recipients, enumerated and stained for flow cytometry analysis. (C) Graphs show the percentage of PD-1+ donor CD4+ T cells in the spleen and liver. (D) PD-1 protein levels on the surface of donor CD4+ T cells isolated from the spleen and liver of Balb/b recipients. (E) The number of IFN-γ+GM-CSF+ population in the spleen and liver. (F) Balb/c transplantation was performed as described in Figure 1. Anti-PD1 antibody was administered with the same regimen as in Balb/b recipients. Graph shows the survival rate. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001, Student t test.
PD-1 blockade restored the GVHD-inducing capacity of Id3-cKO T cells. (A-E) Balb/b mice were subjected to total body irradiation (5 Gy on day −1 and 5 Gy on day 0) followed by infusion of 5 × 106 B6 × B6/SJL F1(CD45.1+CD45.2+) TCD-BM alone or together with 1 × 106 B6 (CD45.1−CD45.2+) naïve CD4+ and 5 × 105 B6 (CD45.1−CD45.2+) naïve CD8+ WT or Id3-cKO T cells. Anti–PD-1 antibody (200 μg per mouse per injection) was administered intraperitoneally on days 0, 3, 5, and 7 after HSCT. In some experiment, isotype immunoglobulin G (IgG) was injected as control. (A) Survival rates of Balb/b mice. (B) Seventeen days after HSCT, cells were isolated from the spleen, liver, and intestine of recipients, enumerated and stained for flow cytometry analysis. (C) Graphs show the percentage of PD-1+ donor CD4+ T cells in the spleen and liver. (D) PD-1 protein levels on the surface of donor CD4+ T cells isolated from the spleen and liver of Balb/b recipients. (E) The number of IFN-γ+GM-CSF+ population in the spleen and liver. (F) Balb/c transplantation was performed as described in Figure 1. Anti-PD1 antibody was administered with the same regimen as in Balb/b recipients. Graph shows the survival rate. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001, Student t test.
In this B6 anti-Balb/b model, minor histocompatibility antigen H60-specific (H60+) CD8+ T cells are responsible for inducing GVHD.33,35 Id3 loss resulted in approximately sevenfold fewer H60+CD8+ T cells in the liver on day 10 after transplantation (supplemental Figure 3E-F) and their increased expression of PD-1 protein (supplemental Figure 3G). PD-1 blockade resulted in significantly increased numbers of Id3-cKO H60+CD8+ T cells that expressed lower levels of PD-1 protein (supplemental Figure 3F-G). PD-1+Tim-3+ marks terminally exhausted T cells in tumor settings.36,37 Id3 ablation led to increased frequency of PD-1+Tim-3+ H60+CD8+ T cells and their Tim-3 expression (supplemental Figure 3H-I). These data suggest that Id3 restrains the generation of exhaustion-phenotype alloreactive T cells and protects tissue-infiltrating alloreactive T cells from PD-1–mediated suppression.
We validated this conclusion using the B6 anti-Balb/c model. Compared with saline treatment, PD-1 blockade induced more severe GVHD in Id3-cKO T-cell recipients, with ∼40% mortality by day 65 (Figure 4F; supplemental Figure 4A), increased by twofold polyfunctional Th1 cells that expressed lower levels of PD-1 in the liver (supplemental Figure 4B-C).
Id3 maintains tissue-infiltrating PD-1+TCF-1+ TPROs and polyfunctional PD-1+Th1 cells
We examined the mechanism by which Id3 maintained tissue-infiltrating Th1 cells. Id3 is required for the TCF-1–mediated recall response of memory CD8+ T cells.17 During GVHD, tissue-resident TCF-1+CD4+ progenitor-like T cells (TPROs) are associated with alloreactive T-cell persistence.2,10 To test whether Id3 deficiency may reduce tissue-infiltrating PD-1+TCF-1+ TPROs, we purified PD-1+KLRG-1− donor T cells from primary GVHD Balb/c mice administered with WT and Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells of B6 origin 8 days after transplantation and transferred them into lethally irradiated secondary Balb/c recipients (supplemental Figure 5A). Compared with their WT counterparts, Id3-cKO PD-1+KLRG-1− effectors generated a 2.5-fold lower frequency of liver-infiltrating PD-1+KLRG1− Th1 cells (supplemental Figure 5B-C). Meanwhile, they failed to produce PD-1+TCF-1+ TPROs in the liver (supplemental Figure 5D). In contrast, ectopic expression of Id3 in Id3-cKO T cells produced 4.6-fold more PD-1+ polyfunctional Th1 cells in the liver compared with GFP-expressing Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells (supplemental Figure 5E). Thus, Id3 is important for maintaining tissue-infiltrating PD-1+TCF-1+ TPROs and PD-1+ Th1 cells.
Id3 ablation leads to PD-1–mediated inhibition of tissue-infiltrating Th1 cells
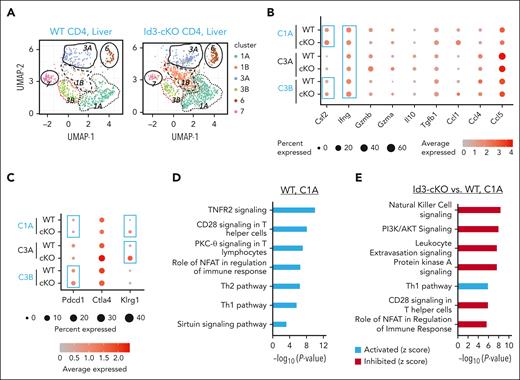
To define the mechanism through which Id3 maintains liver-infiltrating polyfunctional Th1 cells and progenitor-like cells, we performed scRNA-seq analysis using alloreactive CD4+ T cells isolated from the liver of GVHD Balb/c mice. We identified 6 clusters of donor T cells in the liver, including Ifng+ Th1 clusters (C1A, C3A, and C3B), Il17+ cluster (C6), Tcf7+ cluster (C7), and nonactivated T-cell cluster (C1B) (Figure 5A-B; supplemental Figure 6A). Among the 3 Th1 clusters, C1A cells (Ifng+Csf2+) had higher frequency of Csf2 (encoding GM-CSF)–expressing cells, C3B cells (Pdcd1+) had a greater abundance of Pdcd1 transcripts, and C3A cells (Klrg1+) had a higher frequency of cells expressing a greater abundance of Klrg1 transcripts (Figure 5B-C). Id3 loss led to increased expression of Pdcd1 and Klrg1 within C3B and C3A cells, respectively (Figure 5C; supplemental Figure 6A), and decreased frequency of C3B and C3A cells (supplemental Figure 6B). C1B expressed lower levels of genes that characterized all other clusters (supplemental Figure 6A), indicating that they were non-alloantigen–activated T cells. The increased frequency of Id3-cKO C1B cells likely reflects an alleviation of GVHD (supplemental Figure 6B). Interestingly, although WT C7 cells were characterized by Tcf7 (encoding TCF-1) expression, Id3-cKO C7 cells were depleted of Tcf7 (supplemental Figure 6A) and had fourfold fewer cells in frequency than their WT counterparts (supplemental Figure 6B). Thus, Id3 is required for maintaining TCF-1+ TPROs while limiting the maintenance of PD-1+ and KLRG-1+ Th1 cells.
Characterization of liver infiltrated donor CD4 T cells using scRNA-seq. Allo-HSCT was performed as described in Figure 1. Three weeks after HSCT, livers were harvested from recipients for T-cell enrichment. (A) Uniform manifold approximation and projection for dimension reduction (UMAP) analysis of single-cell transcriptome from liver infiltrated WT and Id3-cKO donor CD4+ T cells identified 6 clusters: 1A, 1B, 3A, 3B, 6, and 7. (B) Expression of effector molecules in WT and Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells in clusters 1A, 3A, and 3B. The sizes of balls represent percentage of cells expressing the molecule in that cluster, whereas the shades of red represent the average level of the molecule in the cluster. (C) Expression of inhibitory molecules in WT and Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells in clusters 1A, 3A, and 3B. (D) Characterization of WT cluster 1A using ingenuity pathway analysis of DEGs in 1A compared with the average transcriptome of other clusters. (E) Ingenuity pathway analysis characterization of Id3-cKO cluster 1A relative to WT cluster 1A.
Characterization of liver infiltrated donor CD4 T cells using scRNA-seq. Allo-HSCT was performed as described in Figure 1. Three weeks after HSCT, livers were harvested from recipients for T-cell enrichment. (A) Uniform manifold approximation and projection for dimension reduction (UMAP) analysis of single-cell transcriptome from liver infiltrated WT and Id3-cKO donor CD4+ T cells identified 6 clusters: 1A, 1B, 3A, 3B, 6, and 7. (B) Expression of effector molecules in WT and Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells in clusters 1A, 3A, and 3B. The sizes of balls represent percentage of cells expressing the molecule in that cluster, whereas the shades of red represent the average level of the molecule in the cluster. (C) Expression of inhibitory molecules in WT and Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells in clusters 1A, 3A, and 3B. (D) Characterization of WT cluster 1A using ingenuity pathway analysis of DEGs in 1A compared with the average transcriptome of other clusters. (E) Ingenuity pathway analysis characterization of Id3-cKO cluster 1A relative to WT cluster 1A.
Activation of PD-1 inhibits T-cell responses primarily by inactivating CD28 signaling and/or TCR signaling24,25,38 and the PI3K/Akt pathway.31,34 We found that C1A cells, enriched in polyfunctional Th1 cells, were a dominant cell subset in both WT and Id3-cKO compared with C3B and C7 cells (supplemental Figure 6B). WT C1A cells were characterized with gene programs associated with active tumor necrosis factor receptor-2 (TNFR2) signaling, CD28 costimulatory signaling, and protein kinase C (PKC)-θ signaling activity (Figure 5D). These WT C1A cells expressed molecular features associated with tissue invasiveness and residence (Ccl1, Ccr2, Cxcr6, Ccrl2, and Itgb1; supplemental Table 2), resembling those tissue-resident GVHD T cells,1,2 suggesting their crucial roles in tissue injury. Id3 loss did not affect the molecular features of tissue invasiveness and residence of C1A cells; however, it caused significantly decreased activity of gene programs associated with CD28 costimulatory signaling and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling (Figure 5E) without reducing CD28 expression (supplemental Figure 6C). This agrees with other studies showing that in the GVHD target tissues, activation of T-cell PD-1 by tissue PD-L1 causes inhibition of AKT- mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway and depletion of GM-CSF–producing Th1 cells.31
Id3 reduces ChrAcc to TFs critical for PD-1 expression in Th1 cells
To understand the epigenetic effects by which Id3 loss results in activation of gene programs promoting PD-1 expression and effector differentiation, we performed ATAC-seq analysis. Analysis of ChrAcc diversification showed, defined as ±3.0 kilobase sequence flanking transcription start site, at least threefold or higher enrichment between call peaks and averaged genomic background. Id3-cKO Th1 cells had 5153 ChrAcc sites more accessible but only 1131 ChrAcc sites less accessible (supplemental Figure 7A). These opened ChrAcc sites are located at the promoters, exons, and introns of genes (supplemental Figure 8A), suggesting that Id3 reduces ChrAcc at diverse regulatory loci in Th1 cells.
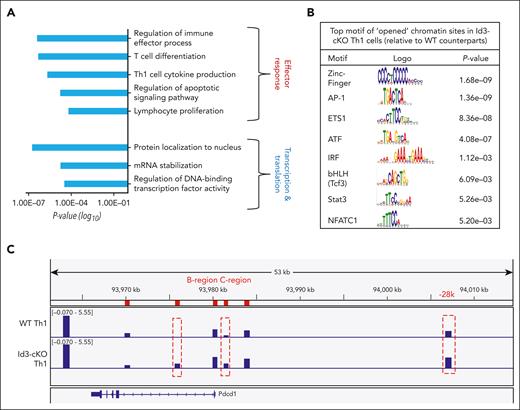
When combining these opened ChrAcc sites with those DEGs detected by RNA-seq analysis, we found a total of 1444 ChrAcc sites distributed at the promoter, exon, and intron regions of 253 DEGs (supplemental Figure 7B). These DEGs overlapped with opening ChrAcc in Th1 cells were enriched for gene programs that promote effector differentiation and function, such as regulation of immune effector processes and Th1 cell cytokine production (Figure 6A). They were also enriched for genes critical for transcription regulation, including protein localization to the nucleus and regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity (Figure 6A).
Id3 restricts chromatin accessibility at specific gene loci. Naïve CD4+ T cells were cultured under Th1 polarization condition for 4 days. CD62lo effector cell population were sorted for ATAC-seq and RNA-seq libraries preparation. (A) differential ChrAcc sites were assigned to genes less than 50 kb upstream and downstream. DEGs associated with opened chromatins in Id3-cKO Th1 cells were subject to gene ontology (GO) term analysis. (B) Motif analysis of opened chromatin sites in Id3-cKO Th1 cells. (C) Differential accessible windows along the gene Pdcd1 regulatory loci. Data were collected from 3 independent experiments. ATF, activating transciption factors; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; mRNA, messenger RNA.
Id3 restricts chromatin accessibility at specific gene loci. Naïve CD4+ T cells were cultured under Th1 polarization condition for 4 days. CD62lo effector cell population were sorted for ATAC-seq and RNA-seq libraries preparation. (A) differential ChrAcc sites were assigned to genes less than 50 kb upstream and downstream. DEGs associated with opened chromatins in Id3-cKO Th1 cells were subject to gene ontology (GO) term analysis. (B) Motif analysis of opened chromatin sites in Id3-cKO Th1 cells. (C) Differential accessible windows along the gene Pdcd1 regulatory loci. Data were collected from 3 independent experiments. ATF, activating transciption factors; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; mRNA, messenger RNA.
The ChrAcc sites opened in Id3-cKO Th1 cells were enriched for motifs of TFs downstream from the TCR and cytokine signals, such as zinc finger TFs, AP-1, bHLH, Stat3, and NFATc1 (Figure 6B). RNA-seq analysis revealed that Id3 deficiency resulted in increased transcription of AP-1 (Fos and Jun), NFAT (Nfatc2), Tox (Tox2/4), and Stat3 (supplemental Figure 8B). Among them, NFATc1, AP-1, and Stat3 contribute to the induction of Pdcd1 transcription.39-41 ATAC-seq identified enhanced accessibility in the intron 1, C-region, and −28kb upstream of the transcription start site of the Pdcd1 gene in Id3-cKO Th1 cells (Figure 6C). C-region is a critical regulatory locus where NFATc1 binds for initiating Pdcd1 transcription.39 The upstream −28 kb region is where Stat3, NFATc1, Stat4, and CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) bind to maintain Pdcd1 expression through the formation of a constitutively interacting chromatin loop.42 These data suggest that Id3 remodels ChrAcc across the Pdcd1 regulatory loci to restrict its expression.
ID3 ablation preserves antitumor activity of both human and murine T cells
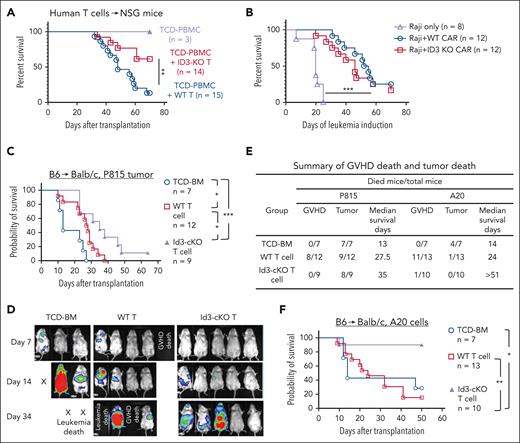
Finally, we examined whether ID3 ablation in human T cells may impair their induction of xeno-GVHD. CRISPR-Cas9/ID3–specific gRNA complex was delivered into human T cells as described.43 The genomic targeting efficacy was >90% (supplemental Figure 9A-B). ID3-CRISPR-KO human T cells were collected after 7 to 9 days of culture and injected (IV) into NSG mice. Mice receiving TCD peripheral blood mononuclear cells did not develop GVHD (Figure 7A; supplemental Figure 9C). Transfer of scrambled guide RNA–transduced T cells (WT) induced xeno-GVHD, with 86.7% of mortality by 70 days after transplantation (Figure 7A; supplemental Figure 9C). In contrast, 64.3% (9 of 14) NSG mice receiving ID3-CRISPR-KO T cells were protected from severe xeno-GVHD and survived by 70 days after transplantation (Figure 7A; supplemental Figure 9C). ID3 ablation led to an increased fraction of liver-infiltrating PD-1+ T cells (supplemental Figure 9D-E), resembling the phenotype of murine Id3-cKO T cells.
ID3 ablation in human T cells reduces xeno-GVHD progression while preserving antitumor activity. ID3 was knocked out from human T cells (including both CD4+ T and CD8+ T cells) using CRISPR-Cas9 technology and maintained in culture for 7 to 9 days. NSG mice were IV infused with T-cell depleted peripheral blood mononuclear cells (TCD-PBMCs; 10 × 106 cells per mouse) alone or together with WT or ID3-CRISPR-KO human CD4+ T cells (10 × 106 cells per mouse) and CD8+ T cells (10 × 106 cells per mouse). (A) Survival rates of NSG mice receiving WT and ID3-CRISPR-KO human T cells. (B) The overall survival of leukemia-bearing mice treated with or without WT or ID3-CRISPR-KO CD19-CAR T cells (n = 8-12). (C-F) Balb/c mice were subjected to total body irradiation (4.5 Gy on day −1 and 4 Gy on day 0) followed by infusion of 5 × 106 B6 TCD-BM alone or together with 3 × 105 B6 (CD45.1-CD45.2+) naïve WT or Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells and 4 × 105 WT or Id3-cKO CD8+ T cells. Recipient mice were challenged with luciferase-expressing P815 mastocytoma cells or A20 lymphoma cells before T-cell infusion. (C) Survival probability. (D) Representative images of tumor luciferase activity detected with live animal in vivo imaging system (IVIS) on days 7, 14, and 34 after transplantation. (E) Summary of GVHD death and tumor death in allo-HSCT mice challenged by P815 cells and A20 cells. (C-E) All Balb/c mice receiving TCD-BM died from tumor; WT donor T cells induced antitumor activity with prolonged median survival time (27.5 days), but all succumbed to tumor and/or GVHD by day 38; in contrast, donor T cells lacking Id3 preserved beneficial GVT effects, leading to significantly improved survival of tumor mice undergoing allo-HSCT. (F) Survival of animals challenged with A20 lymphoma cells. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001. GVT, graft-versus-tumor.
ID3 ablation in human T cells reduces xeno-GVHD progression while preserving antitumor activity. ID3 was knocked out from human T cells (including both CD4+ T and CD8+ T cells) using CRISPR-Cas9 technology and maintained in culture for 7 to 9 days. NSG mice were IV infused with T-cell depleted peripheral blood mononuclear cells (TCD-PBMCs; 10 × 106 cells per mouse) alone or together with WT or ID3-CRISPR-KO human CD4+ T cells (10 × 106 cells per mouse) and CD8+ T cells (10 × 106 cells per mouse). (A) Survival rates of NSG mice receiving WT and ID3-CRISPR-KO human T cells. (B) The overall survival of leukemia-bearing mice treated with or without WT or ID3-CRISPR-KO CD19-CAR T cells (n = 8-12). (C-F) Balb/c mice were subjected to total body irradiation (4.5 Gy on day −1 and 4 Gy on day 0) followed by infusion of 5 × 106 B6 TCD-BM alone or together with 3 × 105 B6 (CD45.1-CD45.2+) naïve WT or Id3-cKO CD4+ T cells and 4 × 105 WT or Id3-cKO CD8+ T cells. Recipient mice were challenged with luciferase-expressing P815 mastocytoma cells or A20 lymphoma cells before T-cell infusion. (C) Survival probability. (D) Representative images of tumor luciferase activity detected with live animal in vivo imaging system (IVIS) on days 7, 14, and 34 after transplantation. (E) Summary of GVHD death and tumor death in allo-HSCT mice challenged by P815 cells and A20 cells. (C-E) All Balb/c mice receiving TCD-BM died from tumor; WT donor T cells induced antitumor activity with prolonged median survival time (27.5 days), but all succumbed to tumor and/or GVHD by day 38; in contrast, donor T cells lacking Id3 preserved beneficial GVT effects, leading to significantly improved survival of tumor mice undergoing allo-HSCT. (F) Survival of animals challenged with A20 lymphoma cells. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001. GVT, graft-versus-tumor.
To examine how ID3-KO might affect human T-cell–mediated antitumor effects, we used CD19 CAR T cells whose anti–B-cell leukemia activity can be convincingly tracked.44,45 We infused WT and ID3-KO CD19-directed CAR T cells into NSG mice bearing human Raji cell leukemia. We observed that WT and ID3-KO CAR T cells showed potent effects on eliminating Raji leukemia and prolonged survival time, with 3 of 12 WT CAR T-cell recipients and 2 of 12 ID3-KO CAR T-cell recipients surviving by day 70 (Figure 7B; supplemental Figure 9F-G). Neither WT nor ID3-KO CAR T cells alone caused xeno-GVHD (supplemental Figure 9H).
We further determined whether Id3 ablation may influence the graft-versus-tumor effects of murine T cells using B6 anti-Balb/c model challenged by P815 mastocytoma cells or A20 lymphoma cells. Donor T cells lacking Id3 preserved beneficial graft-versus-tumor effects, leading to significantly improved survival of tumor mice undergoing allo-HSCT (Figure 7C-F). Thus, inhibiting T-cell Id3 is effective for reducing GVHD without compromising antitumor activity.
Discussion
Our study has demonstrated that Id3 protects tissue-infiltrating alloreactive T cells against PD-1/PD-L1 pathway–mediated suppression. Id3 limits Th1 cell expression of PD-1 and maintains tissue-infiltrating PD-1+ polyfunctional Th1 cells and PD-1+TCF-1+ TPROs. Id3 reduces the chromatin accessibility of TFs that drive effector differentiation and induce PD-1 transcription. CRISPR/Cas9 KO of ID3 in human T cells inhibits their induction of xeno-GVHD, but reassuringly, ID3 ablated CD19-directed CAR T cells retained their antitumor activity. Thus, T-cell ID3 may be an effective target to reduce GVHD in nonhematopoietic tissues.
The expansion and function of organ-infiltrating donor T cells are critical to GVHD development.1-3 When infiltrating the GVHD target tissue, alloreactive T cells acquire transcriptomic and protein profiles associated with local tissues.1-3 How these processes are regulated remains largely unknown.3 Sacirbegovic et al discovered that tissue-resident CD39loTCF-1+ progenitor-like cells possessed greater ability than CD39hiTCF-1− CD4+ effector cells to produce secondary effector cells upon antigen rechallenge.2 We found that loss of Id3 led to depletion of PD-1+TCF-1+ TPROs in the liver. Future studies will characterize the transcriptome profile of this population, establish the developmental hierarchy for tissue-infiltrating alloreactive T cells, and delineate the regulatory mechanism of Id3 herein.
Our findings are important for understanding T-cell–mediated pathogenic inflammation. The protective effect of Id3 on alloreactive T cells against PD-1 suppression is likely associated with the GVHD tissue microenvironment. During GVHD, PD-L1 in the target tissue acts as a molecular shield to limit T-cell attacks. Parenchymal cells produced high levels of PD-L1 in response to IFN-γ produced by alloreactive T cells, and the interaction between PD-L1 and PD-1 becomes dominant in GVHD target tissues relative to that in lymphoid tissues.25,29,31,46 Previous studies suggest that PD-1–mediated suppression is insufficient to inhibit GVHD.28,29 We identify that Id3 controls gene programs that enable alloreactive T-cell resistance against the PD-1 effect. Id3 ablation led to increased PD-1 expression in alloreactive T cells and impaired persistence of tissue-infiltrating alloreactive T cells.
PD-L1 activation of PD-1 leads to impaired T-cell responses via a mechanism of inactivating CD28 signaling and PI3K-AKT signaling activity.24,25,38 We observed that Id3 loss resulted in significantly decreased activity of gene programs associated with CD28 signaling and PI3K/AKT signaling and an enhanced frequency of Pdcd1-expressing polyfunctional Th1 cells. Activated T cells become sensitive to the PD-1 pathway–mediated suppression under suboptimal levels of CD28 costimulation.24 Because nonhematopoietic tissues are known to produce low levels of CD28 ligand CD86, Id3 suppression of PD-1 expression in polyfunctional Th1 cells may reduce their sensitivity to PD-L1–induced suppression.
To our knowledge, we identify for the first time that Id3 modulates the ChrAcc for TFs that drive Pdcd1 transcription. Many TFs have been found to activate PD-1, including NFAT, c-Fos/AP-1, and Stat3.34,39,47 NFAT2 and other TFs (e.g.,Tox and Nr4a) can activate PD-1 transcription in T cells.39-41,48 We found that Id3 may play important roles in orchestrating the expression of these TFs and their ChrAcc sites at the Pdcd1 locus. Id3 loss resulted in upregulation of transcripts encoding TFs (NFAT, Tox2, and AP-1) and the opening of chromatin sites enriched in motifs for TFs (NFAT, AP-1, and STAT3). These Id3-mediated mechanisms add together to orchestrate the expression and function of TFs that promote T-cell dysfunction.
The finding that Id3 sustains tissue-infiltrating Th1 cells and TCF-1+ TPRO cells provides novel insights into GVHD pathogenicity. Stimulation by alloantigens, especially those derived from nonhematopoietic tissues, causes alloreactive T-cell dysfunction.49-51 Interactions between donor T cells and nonhematopoietic cells may block the programming of memory precursors required for producing secondary effectors.51 Recent studies demonstrate that those tissue-infiltrating alloreactive T cells can be reprogrammed by the local tissue, acquiring the ability to persist during GVHD maintenance.1-3 Thus, Id3 is important for alloreactive T cells to deflect persistent alloantigen-induced dysfunction.
As CAR T-cell therapy is increasingly used to treat recurrent hematologic malignancies, GVHD could potentially be a major challenge hindering allogeneic or third-party CAR T-cell therapy. In a preclinical study, 4-1BB(CD137)–costimulated CAR T cells increased the occurrence of GVHD.52 A universal “off-the-shelf” CAR T-cell product remains a goal: such products can be readily available, provide a more consistent product, and improve access to the therapy.53 Targeting ID3 in CAR T cells may be a potential approach to reducing alloreactivity but retaining antitumor activity. A recent study reports that ID3 expression is associated with the transition of exhausted CAR T cells into dysfunctional NK-like cells in an in vitro culture system.43 However, the definitive role of ID3 in human CAR T cells was not tested in vivo using any preclinical models.43 Although our data showed preserved tumor elimination capacity by ID3-KO-CD19–directed CAR T cells, we cannot exclude the possibility that long-term tumor control might be impaired, because the NSG mouse system could depend on the early action of CAR T cells shortly after infusion. Future investigations will test how ID3 might affect longer-term CAR T-cell performance.
In summary, we have identified a key role for Id3 in fostering the maintenance of tissue-infiltrating alloreactive T cells in peripheral tissues. In addition, ablating Id3 in allogeneic T cells reduces GVHD but preserves their antitumor immunity in mice undergoing allo-HSCT. Leukemia mostly occurs in lymphoid-hematopoietic organs, in which alloreactive T-cell responses are not significantly affected by Id3 ablation. This could explain why Id3 loss does not significantly impair antileukemia activity early after T-cell infusion. Furthermore, given the central role of Id3 in tissue-infiltrating T cells, programming Id3 in tumor-reactive T cells might enhance their antitumor activity.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the flow cytometer cores in Temple University and Hackensack Meridian Health, Center for Discovery and Innovation.
This study is supported by grants of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (HL154757) (Y. Zhang) and NIH, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (AI143256) (Y. Zhang), NIH, National Cancer Institute (P50 CA254897 [J.-P.I. and Y. Zhang], and P50 CA100632 [J.-P.I.]).
Authorship
Contribution: Y.W., S.H., and Y. Zhang conceived and designed the project; Y.W., S.H., G.C., T.B., Y.T., C.Y.L., Y. Zhou, X.Z., C.A., W.M., M.C., R.S.B., J.M., and Y. Zhang performed experiments and analyzed the data; Y.W., S.H., H.-H.X., and Y. Zhang designed experiments and analyzed data; G.C., Y. Zhou, J.M., Y.W., J.-P.I., R.R., D.L.W., and Yi Zhang analyzed RNA-seq, scRNA-seq, and ATAC-seq data; Y.W., S.H., E.O.H., J-.P.I., D.L.W., R.R., H.-H.X., and Y. Zhang edited the manuscript; Y.W. and Y. Zhang wrote and edited the manuscript; Y.W. and S.H. started this project; and Y.W. and Y.T. completed this project.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Yi Zhang, Center for Discovery and Innovation, Hackensack University Medical Center, 111 Ideation Way, Nutley, NJ 07110; email: yi.zhang@hmh-cdi.org.
References
Author notes
The data reported in this article have been deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus database (accession numbers, super series: GSE230286; RNA-seq: GSE230274; scRNA-seq: GSE230285; and ATAC-seq: GSE230082).
Information on resources and reagents is available on request from the corresponding author, Yi Zhang (yi.zhang@hmh-cdi.org).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

![Id3 deficiency leads to PD-1 upregulation on polyfunctional Th1 cells. (A-C) Approximately 6 to 8 days after allo-HSCT, cells were isolated from the spleen and liver of Balb/c recipients of donor B6 naïve T cells as described in Figure 1, and donor T cells were analyzed for effector function. Plots and graphs show the percentage of IFN-γ+ GM-CSF+ polyfunctional cells (A-B) and the number of Id3-cKO IFN-γ+GM-CSF+ T cells in the spleen and liver (C). (D-E) Plots and graphs show the frequency of lamina-propria lymphocyte (LPL) IFN-γ+GM-CSF+ cells in the intestine of Balb/c recipients 17 days after HSCT. (F-H) The IFN-γ+GM-CSF+ polyfunctional population was gated for the analysis of inhibitory molecule expression (F). The percentage of PD-1+ cells (G) and PD-1 level (mean fluorescence intensity [MFI]) on the surface of individual CD4+ polyfunctional T cells (H) isolated from the spleen and the liver of Balb/c recipients 6 and 8 days after HSCT. (I-J) Plots and graphs show the percentage of PD-L1–expressing donor CD4+ T cells isolated from the spleen and liver of Balb/c recipients. ∗P < .05; ∗∗∗P < .001, Student t test. At least 3 mice per group were analyzed.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/143/2/10.1182_blood.2023021126/2/m_blood_bld-2023-021126-gr3.jpeg?Expires=1765919514&Signature=gRaqOtgwlvIdB1Jw-Ws4oBhgPny0kQucRUN5yUq9m1mTixp6w6SUgRCKR2SvLkPzJnq4~xCgH~QSru973M0hJX5O0eLsMUSl9nJ2aPCdjXbjKgq8Daq~fNMFSu~sHc9SxvB1x8JG3-GqmDAbwXHqE2za-PPVB7nf6iUIPKz-VhGBvp481osYN6Q2Oj83itB-M536~GHGIwdxKoHnfAywC8U2IfxQ6OWmAt-4owg7DTicoAQl0wBP~~~hxW1krHd6ny4hgyuog-vjj6yMif3Evc2vza~EprSNO6ff8Grf3DJW9l13sOsyqNlS8xm4x46gBDkM7r59bwZ2Yuqjgs7Kug__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal