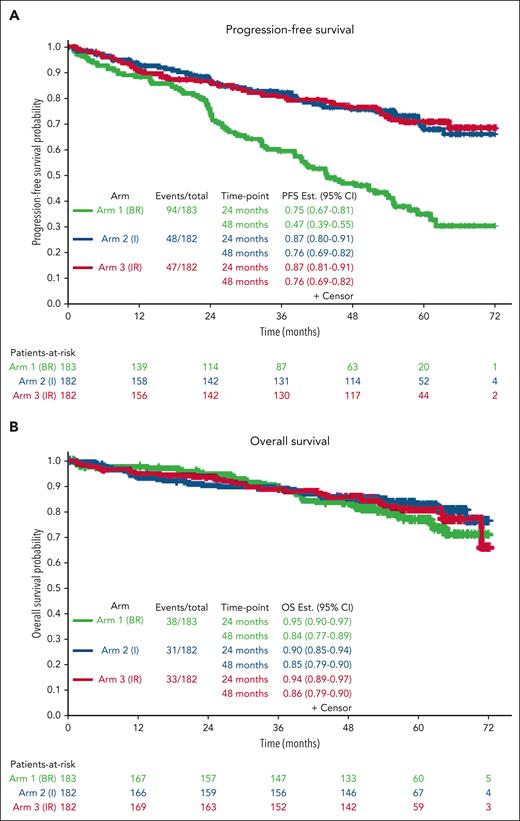
PFS estimates at 48 months were 47%, 76%, and 76% for the BR, I, and IR arms, respectively.
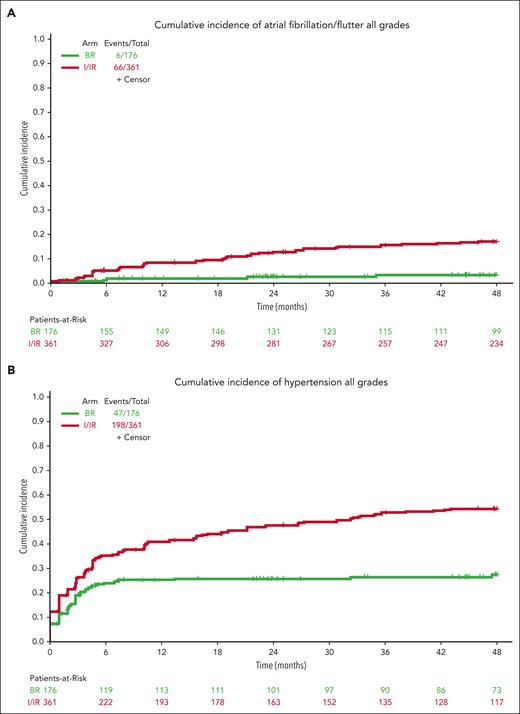
Atrial fibrillation and hypertension incidence increase over time with ibrutinib, with an atrial fibrillation rate of 18% at this time.
Visual Abstract
A041202 (NCT01886872) is a phase 3 study comparing bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) with ibrutinib and the combination of ibrutinib plus rituximab (IR) in previously untreated older patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). The initial results showed that ibrutinib-containing regimens had superior progression-free survival (PFS) and rituximab did not add additional benefits. Here we present an updated analysis. With a median follow-up of 55 months, the median PFS was 44 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 38-54) for BR and not yet reached in either ibrutinib-containing arm. The 48-month PFS estimates were 47%, 76%, and 76% for BR, ibrutinib, and IR, respectively. The benefit of ibrutinib regimens over chemoimmunotherapy was consistent across subgroups of patients defined by TP53 abnormalities, del(11q), complex karyotype, and immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (IGHV). No significant interaction effects were observed between the treatment arm and del(11q), the complex karyotype, or IGHV. However, a greater difference in PFS was observed among the patients with TP53 abnormalities. There was no difference in the overall survival. Notable adverse events with ibrutinib included atrial fibrillation (afib) and hypertension. Afib was observed in 11 patients (pts) on BR (3%) and 67 pts on ibrutinib (18%). All-grade hypertension was observed in 95 pts on BR (27%) and 263 pts on ibrutinib (55%). These data show that ibrutinib regimens prolong PFS compared with BR for older patients with treatment-naïve CLL. These benefits were observed across subgroups, including high-risk groups. Strikingly, within the ibrutinib arms, there was no inferior PFS for patients with abnormalities in TP53, the highest risk feature observed in CLL. These data continue to demonstrate the efficacy of ibrutinib in treatment-naïve CLL.
Medscape Continuing Medical Education online

In support of improving patient care, this activity has been planned and implemented by Medscape, LLC and the American Society of Hematology. Medscape, LLC is jointly accredited with commendation by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME), the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education (ACPE), and the American Nurses Credentialing Center (ANCC), to provide continuing education for the healthcare team.
Medscape, LLC designates this Journal-based CME activity for a maximum of 1.0 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s)™. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
Successful completion of this CME activity, which includes participation in the evaluation component, enables the participant to earn up to 1.0 MOC points in the American Board of Internal Medicine's (ABIM) Maintenance of Certification (MOC) program. Participants will earn MOC points equivalent to the amount of CME credits claimed for the activity. It is the CME activity provider's responsibility to submit participant completion information to ACCME for the purpose of granting ABIM MOC credit.
All other clinicians completing this activity will be issued a certificate of participation. To participate in this journal CME activity: (1) review the learning objectives; (2) study the education content; (3) take the post-test with a 75% minimum passing score and complete the evaluation at https://www.medscape.org/journal/blood; and (4) view/print certificate. For CME questions, see page 1678.
Disclosures
CME questions author Laurie Barclay, freelance writer and reviewer, Medscape, LLC, declares no competing financial interests.
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this activity, participants will:
Describe efficacy and survival outcomes for ibrutinib (I) and ibrutinib plus rituximab (IR) vs bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treatment, based on long-term outcome data from the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology study (A041202)
Determine safety and toxicity outcomes for I and IR vs BR in CLL treatment, based on long-term outcome data from A041202
Identify clinical implications of efficacy and safety outcomes for I and IR vs BR in CLL treatment, based on long-term outcome data from A041202
Release date: April 18, 2024; Expiration date: April 18, 2025
Introduction
Therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has changed dramatically over the last 2 decades with the introduction of targeted therapies for this disease. Ibrutinib, a first-in-class covalent inhibitor of Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK), was the first targeted therapy to show improvements in progression-free survival (PFS)1,2 and overall survival (OS)3,4 compared with chemotherapy and chemoimmunotherapy in the frontline setting.
The Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology A041202 is a National Clinical Trials Network multicenter, randomized phase 3 trial designed to compare ibrutinib-based regimens with standard chemoimmunotherapy for previously untreated older patients with CLL. Because the median age of patients with CLL is 70 years and 75% of patients with CLL are more than age of 65 years at diagnosis, reviewed in,5 this trial was intended to provide data that could be generalized to most patients with CLL. Patients were randomized to standard chemoimmunotherapy with bendamustine plus rituximab (arm 1; BR), ibrutinib alone (arm 2; I), or ibrutinib plus rituximab (arm 3; IR). In May 2018, the Alliance Data and Safety Monitoring Board made the decision to release the study results based on protocol–specified second interim analysis for the comparisons of the 2 ibrutinib-containing regimens with BR and protocol–specified first interim analysis for the comparison of IR with I. The results demonstrated that PFS was significantly longer in arms 2 (I) and 3 (IR) than in arm 1 (BR), and that a futility threshold had been crossed to suggest little likelihood of a significant difference between IR and I.1 Patients in the trial continued to be followed per protocol for long-term safety, progression, and survival.
Long-term data from clinical trials of ibrutinib as well as retrospective analyses have shown that although many ibrutinib-associated toxicities decrease in frequency over time, cardiac side effects, including hypertension and atrial fibrillation, can occur at any time during treatment.6-9 In the initial report of the A041202 trial, atrial fibrillation rates of 17% and 14% were observed for I and IR, respectively. This is higher than that reported in most other clinical trials, likely because of the older age of the patient population and the observation bias. Therefore, a longer follow-up is critical to understand the rate of these and other cardiovascular toxicities, especially for a drug that is dosed indefinitely.
Here, we present long-term outcome data for patients with CLL treated with A041202 based on the protocol-planned third interim analysis of PFS for I and IR vs BR and the second planned interim analysis of I vs IR.
Patients and methods
Patients
These analyses included 547 eligible patients who were randomized into 1 of 3 treatment arms. Patients were stratified on Rai stage, ZAP-70 methylation was performed centrally, and del(17)(p13.1) or del(11)(q22.3) by local interphase cytogenetics, and were randomized 1:1:1 to each arm. Patients on arm 1 (BR) could cross over to arm 2 (I) within 1 year of documented disease progression. Each participant signed an institutional review board–approved, protocol-specific, informed consent document in accordance with federal and institutional guidelines.
Statistical considerations
Pairwise comparisons of PFS were conducted in an intent-to-treat manner for the third planned interim analysis of PFS for arms 2 (I) and 3 (IR) vs arm 1 (BR) and the second planned interim analysis of arm 3 (IR) vs arm 2 (I). PFS is defined as the time from the randomization date until the earliest date of progression (as defined by the International Workshop on CLL 2008 criteria10) or death from any cause. Data from patients who were alive without disease progression were censored on the date of the last assessment. Data from patients who started therapy for CLL that was not specified in the protocol or withdrew consent for further follow-up were censored on the date of the last assessment. OS is defined as the time from the date of randomization to death from any cause. All time-to-event analyses were performed using the Kaplan-Meier method and between the arms using the log-rank test. Hazard ratios and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were estimated using univariable Cox proportional hazards models.
PFS subgroup analyses were conducted for genetic features of interest: karyotype abnormalities, TP53 abnormality, ZAP-70 methylation and immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (IGHV) mutational status using cases with complete information. Although missing data are a concern, approaches to impute missing genetic features are not realistic and are subject to assumptions that might not be reproducible. Baseline factors, including treatment group, age, sex, Rai stage, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status, white blood cell count, beta-2 microglobulin (B2M), lactate dehydrogenase, splenomegaly, del(11q), TP53 abnormality (mutation or deletion), number of karyotype abnormalities, and ZAP-70 methylation (<20% methylated [unmethylated] vs ≥20% methylated [methylated]), were assessed using univariable Cox proportional hazards models. Factors with P < .20 from univariable models were included in the full multivariable Cox proportional hazards model. The main effects model was determined from the full model using backward selection until the remaining variables had P < .05. Furthermore, the interaction terms for the treatment arms and each prognostic factor from the main effects model were fitted. Interaction terms with a P < .05 were selected using the backward selection method to determine the final model.
The safety analyses included randomized patients who began treatment. Adverse events (AEs) were recorded by investigators using CTCAE v4.0. Competing risk models were estimated to calculate the cumulative incidence rates for treatment discontinuation due to AEs, specifically atrial fibrillation or flutter (afib) and hypertension, in arms 2 (I) and 3 (IR) vs arm 1 (BR). For these AEs, the time to occurrence of the AE was measured from the start of treatment until the start date of the AE assessment, during which an AE event was first documented for atrial fibrillation analysis, or until a new or worsening AE relative to the baseline was first documented for hypertension analysis. Patients without AE of interest were censored at the end date of last AE assessment. For patients in the BR arm, this included discontinuation during the observation phase before crossing over to ibrutinib. The Fine-Gray method11 was used for comparisons and death without an AE of interest was considered a competing risk. Data collection and statistical analyses were conducted by the Alliance Statistics and Data Management Center. Data quality was ensured by review of data by the Alliance Statistics and Data Management Center and the study chairperson following Alliance policies.
We recognize that these subgroup analyses are post hoc and hypothesis generating and have not been adjusted for multiple testing. In addition to rigor in the selection of factors in univariable and multivariable models, we also reported 95% CI for the estimates, in addition to P values.
Results
Patient characteristics and follow-up
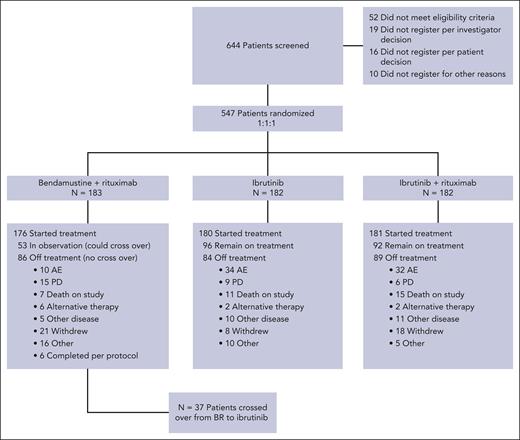
Between 9 December 2013 and 16 May 2016, 547 patients were randomized to therapy with BR (arm 1 = 183), ibrutinib (arm 2 = 182), or IR (arm 3 = 182). A CONSORT diagram is shown in Figure 1. For this analysis, the data were frozen in February 2021, representing all patient visits and data collection through April 2020. The baseline characteristics have been reported previously1 and are listed in supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood website. The median age of the study was 71 years (range, 65-89), 53% had unmethylated ZAP-70, 9% had del(17p), 19% had del(11q) by local fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and 10% had mutated TP53. IGHV sequencing was performed in 66% of patients, and 61% were IGHV-unmutated. Central FISH was performed, which revealed del(17p) in 6% and del(11q) in 20%. The overall agreement between central and local FISH was 86% for del(11q) and 83% for del(17p). Stimulated karyotyping was performed centrally and revealed ≥3 abnormalities in 27% and ≥5 abnormalities in 11% of the patients.
CONSORT diagram. Here, we demonstrate the disposition of all patients screened for A041202 during the current follow-up period.
CONSORT diagram. Here, we demonstrate the disposition of all patients screened for A041202 during the current follow-up period.
Progression-free survival and OS
With a median follow-up of 55 months, the median PFS for patients treated with BR was 44 months (95% CI, 38-54) and was not reached for patients treated with I or IR (Figure 2A) (I vs BR hazard ratio [HR], 0.36; 95% CI, 0.26-0.52; P < .0001; IR vs BR: HR, 0.36; 95% CI, 0.25-0.51; P < .0001). There was no difference in PFS between the 2 ibrutinib arms (IR vs I: HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.66-1.48; P = .96). Forty-eight-month PFS estimates were 47%, 76%, and 76% in the BR, I, and IR arms, respectively. At this time, there were no statistically significant differences in OS among the arms (P = .49). OS estimates at 48 months were 84%, 85%, and 86% in BR, I, and IR, respectively (Figure 2B).
Progression-free survival and OS. Kaplan-Meier curves demonstrating improvement in PFS (A) and OS (B) with ibrutinib and ibrutinib plus rituximab compared with bendamustine plus rituximab.
Progression-free survival and OS. Kaplan-Meier curves demonstrating improvement in PFS (A) and OS (B) with ibrutinib and ibrutinib plus rituximab compared with bendamustine plus rituximab.
Seventy-five patients treated with I and 83 with IR discontinued for reasons other than disease progression, whereas only 9 and 6 have discontinued progression in the 2 arms, respectively. In the 2 I and IR arms combined, the most common reasons for discontinuation other than progression included AEs (n = 66; 18%), death in the study (n = 26; 7%), other diseases (n = 21; 6%), and other reasons (n = 45; 12%). In the 2 arms combined, only 4% of patients experienced progressive disease while on treatment and 10% experienced disease progression after discontinuation of therapy, with a median time to progression after discontinuation of 24 months (supplemental Figure 1).
Clinical and genomic characteristics influencing PFS
Because there were no statistically significant differences in PFS between the 2 ibrutinib–based therapy arms, I and IR were combined for all modeling analyses.
When looking across specific patient subgroups, all subgroups favored ibrutinib-based therapy over BR (supplemental Figure 2). The only subgroup in which the advantage was not significant was patients with IGHV-mutated disease, which was only analyzed in 67% of patients (baseline characteristics for this group are listed in supplemental Table 2).
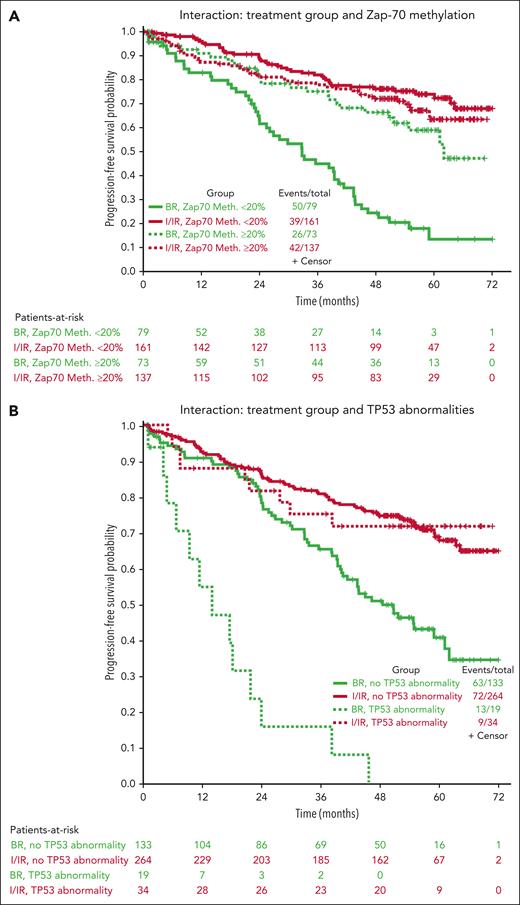
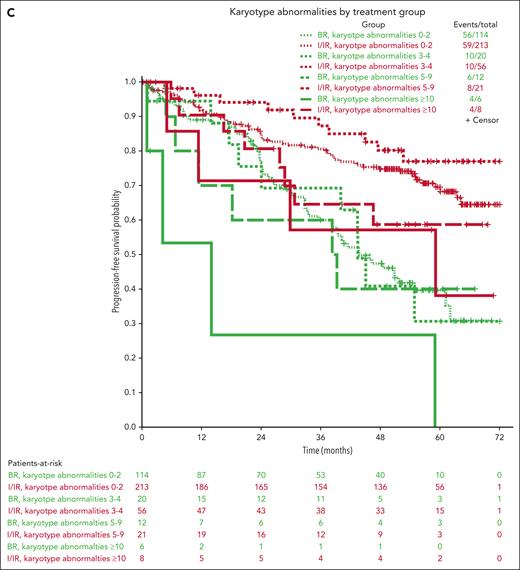
Multivariable models for PFS were created using 450 patients with complete data (not including IGHV mutational status), combining the ibrutinib and IR arms. Other than treatment group, increasing age, B2M > 5 mg/dL, presence of TP53 abnormalities, increasing number of karyotype abnormalities, and ZAP-70 unmethylated disease (used as a surrogate for IGHV unmutated disease12) were all associated with inferior PFS in all arms (Table 1). However, because it is likely that the treatment effect could be different for each prognostic factor, we tested for interaction effects between the treatment group and previously identified significant prognostic factors (Table 1; Figure 3). No significant interaction effects were observed between the treatment arm and B2M levels or karyotype abnormalities, but this was significantly different for age, TP53 abnormalities, and ZAP-70 methylation. Although the protective effects of the ibrutinib-based regimens were evident across subgroups, we found some evidence that ibrutinib regimens are even more protective for younger patients (HR for ibrutinib, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.11-0.37 for those 65 years old vs 0.55; 95% CI, 0.31-0.98 for those 80 years old) and those with high-risk TP53 abnormalities (HR for ibrutinib, 0.07; 95% CI, 0.03-0.18) or ZAP-70 unmethylated disease (HR for ibrutinib, 0.18; 95% CI, 0.12-0.28) (Figure 3).
Multivariable model for progression-free survival (N = 450∗)
| Comparison . | Hazard ratio . | 95% CI . | P value (Pr > χ-square) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multivariable main effects model† | |||
| Treatment group, I / IR vs BR | 0.32 | 0.23-0.45 | <.0001 |
| Age, 5-year increase | 1.26 | 1.08-1.47 | .0036 |
| Beta-2 microglobulin, >5 vs <5 | 1.84 | 1.33-2.55 | .0002 |
| TP53 abnormality, yes vs no | 1.65 | 1.01-2.69 | .0447 |
| Karyotype abnormalities, 1 unit increase | 1.07 | 1.02-1.14 | .0124 |
| ZAP-70 methylation, >20% vs <20% | 0.68 | 0.5-0.94 | .0208 |
| Multivariable model, with interaction terms | |||
| Beta-2 microglobulin, >5 vs <5 | 1.82 | 1.31-2.52 | .0003 |
| Karyotype abnormalities, 1 unit increase | 1.07 | 1.01-1.13 | .0280 |
| Treatment group∗ at age of interaction | .0408 | ||
| I/IR vs BR at age = 65 | 0.20 | 0.11-0.37 | |
| I/IR vs BR at age = 70 | 0.28 | 0.20-0.41 | |
| I/IR vs BR at age = 75 | 0.40 | 0.27-0.57 | |
| I/IR vs BR at age = 80 | 0.55 | 0.31-0.98 | |
| Treatment group∗TP53 abnormality interaction | .0006 | ||
| I/IR vs BR, no TP53 abnormality | 0.39 | 0.27-0.55 | |
| I/IR vs BR, TP53 abnormality | 0.07 | 0.03-0.18 | |
| Treatment group∗ZAP-70 methylation interaction | .0002 | ||
| I/IR vs BR, ZAP-70 methylation <20% | 0.18 | 0.12-0.28 | |
| I/IR vs BR, ZAP-70 methylation >20% | 0.61 | 0.37-1.01 |
| Comparison . | Hazard ratio . | 95% CI . | P value (Pr > χ-square) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multivariable main effects model† | |||
| Treatment group, I / IR vs BR | 0.32 | 0.23-0.45 | <.0001 |
| Age, 5-year increase | 1.26 | 1.08-1.47 | .0036 |
| Beta-2 microglobulin, >5 vs <5 | 1.84 | 1.33-2.55 | .0002 |
| TP53 abnormality, yes vs no | 1.65 | 1.01-2.69 | .0447 |
| Karyotype abnormalities, 1 unit increase | 1.07 | 1.02-1.14 | .0124 |
| ZAP-70 methylation, >20% vs <20% | 0.68 | 0.5-0.94 | .0208 |
| Multivariable model, with interaction terms | |||
| Beta-2 microglobulin, >5 vs <5 | 1.82 | 1.31-2.52 | .0003 |
| Karyotype abnormalities, 1 unit increase | 1.07 | 1.01-1.13 | .0280 |
| Treatment group∗ at age of interaction | .0408 | ||
| I/IR vs BR at age = 65 | 0.20 | 0.11-0.37 | |
| I/IR vs BR at age = 70 | 0.28 | 0.20-0.41 | |
| I/IR vs BR at age = 75 | 0.40 | 0.27-0.57 | |
| I/IR vs BR at age = 80 | 0.55 | 0.31-0.98 | |
| Treatment group∗TP53 abnormality interaction | .0006 | ||
| I/IR vs BR, no TP53 abnormality | 0.39 | 0.27-0.55 | |
| I/IR vs BR, TP53 abnormality | 0.07 | 0.03-0.18 | |
| Treatment group∗ZAP-70 methylation interaction | .0002 | ||
| I/IR vs BR, ZAP-70 methylation <20% | 0.18 | 0.12-0.28 | |
| I/IR vs BR, ZAP-70 methylation >20% | 0.61 | 0.37-1.01 |
Patients with complete prognostic data not including IGHV data.
Variables considered for multivariable modeling were treatment group, age, sex, Rai stage, ECOG performance status, white blood cell count, beta-2 macroglobulin, lactate dehydrogenase, splenomegaly, del(11q), TP53 abnormality, number of karyotype abnormalities, and ZAP-70 methylation. Only significant variables (P < .05) are shown in this table.
Interaction of treatment groups and specific baseline characteristics. Kaplan-Meier curves showing the interaction of the treatment groups with ZAP-70 methylation (A), TP53 abnormalities (B), and karyotype (C).
Interaction of treatment groups and specific baseline characteristics. Kaplan-Meier curves showing the interaction of the treatment groups with ZAP-70 methylation (A), TP53 abnormalities (B), and karyotype (C).
Because IGHV mutational status is more standardly evaluated than ZAP-70 methylation, we also performed multivariable modeling in the 319 patients in whom complete data, including IGHV mutational status, were available, using IGHV instead of ZAP-70 methylation. The previous factors of age, B2M, TP53 abnormalities, and IGHV mutational status were significant overall, but karyotypic complexity was no longer observed. A significant interaction between the treatment arm and outcome was only observed for TP53 abnormalities, in which the protective effect of ibrutinib was enhanced for patients with TP53 abnormalities (HR for ibrutinib with TP53 abnormalities, 0.13; 95% CI, 0.05-0.35 vs HR, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.31-0.70 without TP53 abnormalities).
A total of 387 bone marrow samples were submitted for central minimal residual disease (MRD) analysis using flow cytometry on day 1 of cycle 9 of therapy.1 Four percent of patients treated with BR had undetectable bone marrow MRD compared with 0.3% of ibrutinib and 2% of IR-treated patients. Of the 108 MRD samples in arm 1 (BR) patients, a higher 3-year PFS was observed for patients with undetectable MRD (HR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.59-0.99) compared with those with detectable MRD (HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.39-0.60) (supplemental Figure 3).
Long-term AEs and deaths on treatment
Because there were no statistically significant differences in PFS between the 2 ibrutinib–based therapy arms, I and IR were combined for safety analyses. A total of 537 and 520 patients were included in the analyses of afib and hypertension (HTN), respectively.
Sixty-six patients (34 in arm 2 [I] and 32 in arm 3 [IR]) discontinued ibrutinib therapy for AEs. Discontinuation due to AEs was higher in the BR arm than in the I/IR during the first 6 months when therapy was planned for all arms, although by 12 months, the rate of discontinuation due to AEs with I/IR surpassed the rate of discontinuation due to AEs for patients treated with BR (supplemental Figure 4).
Notable AEs that can occur for patients treated long-term with ibrutinib include afib and HTN. All-grade atrial fibrillation was observed in 6 patients treated with BR (3%) and 66 patients treated with ibrutinib (18%) (Figure 4A). The incidence continues to increase with the time of treatment at a higher rate for patients treated in the I/IR arm.
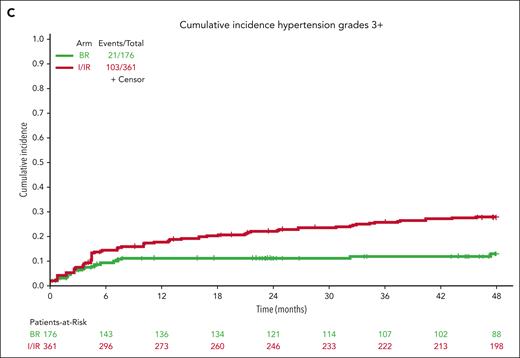
Cumulative incidence of AEs. Extended follow-up demonstrates continued incidence of all-grade atrial fibrillation (A), all-grade hypertension (B), and grade 3 or higher hypertension (C) for patients treated with ibrutinib compared with those treated with bendamustine plus rituximab.
Cumulative incidence of AEs. Extended follow-up demonstrates continued incidence of all-grade atrial fibrillation (A), all-grade hypertension (B), and grade 3 or higher hypertension (C) for patients treated with ibrutinib compared with those treated with bendamustine plus rituximab.
For hypertension, baseline hypertension assessments were not available for 17 patients who were not included in this analysis. Hypertension (any grade) was reported in 47 patients on BR (27%) and 198 patients on ibrutinib (55%) during treatment (Figure 4B). Grade 3 or higher hypertension (requiring >1 medication for management, systolic blood pressure ≥160 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure ≥100 mm Hg) was reported in 21 patients on BR (12%) and 103 patients on ibrutinib (29%) during treatment (Figure 4C).
Secondary cancers are common occurrence for patients with CLL. New primary malignancies were reported in 14 patients on arm 1 (BR), 14 on arm 2 (I), and 17 on arm 3 (IR). Accounting for more than 1 malignancy in individual patients, there were 26, 14, and 23 malignancies, respectively (supplemental Table 3).
For patients who died during treatment or within 30 days after discontinuation, the cause of death was manually reviewed and the sites were queried for detailed information. The causes of death are listed in Table 2. After manual review, unexplained, unwitnessed death was noted in 3 patients treated with BR who did not cross over to ibrutinib, 8 patients on the I arm, and 5 patients on the IR arm.
Causes of death
| Cause of death . | Total . | BR . | Ibrutinib . | IR . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Death following progressive disease∗ | 29 | 15 | 7 | 7 |
| Disease progression | 8 | 5 | 1 | 2 |
| Secondary cancer | 21 | 10 | 6 | 5 |
| Infection | 13 | 3 | 4 | 6 |
| Myocardial infarction | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Hemorrhage | 4 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Other† | 10 | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| Unexplained/unwitnessed | 16 | 3 | 8 | 5 |
| Cause of death . | Total . | BR . | Ibrutinib . | IR . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Death following progressive disease∗ | 29 | 15 | 7 | 7 |
| Disease progression | 8 | 5 | 1 | 2 |
| Secondary cancer | 21 | 10 | 6 | 5 |
| Infection | 13 | 3 | 4 | 6 |
| Myocardial infarction | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Hemorrhage | 4 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Other† | 10 | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| Unexplained/unwitnessed | 16 | 3 | 8 | 5 |
Sites were not required to report details surrounding deaths for patients after progression; these categories were merged unless death was reported as secondary cancer.
Other causes of death on the BR arm include chronic kidney disease (1) and site unable to provide further information (1). Other causes of death on the ibrutinib arm include multiple comorbidities (1), multiorgan failure (1), and site inability to provide further information (1). Other causes of death on the IR arm include dementia (1), obstructive uropathy (1), suicide (1), complications of endoscopy (1), and complications of splenectomy (1).
Discussion
Here, we showed with a longer follow-up of a pivotal phase 3 study that ibrutinib-containing regimens continue to show improved PFS compared with BR in previously untreated older patients with CLL. We continue to see that it is feasible to treat patients with indefinite ibrutinib, and even those patients who ultimately discontinue due to AE or other reasons have durable remissions. However, safety considerations with this agent remain, and we see here that cumulative rates of afib and HTN increase with increasing duration of therapy.
The efficacy of ibrutinib and indeed of BTK inhibitors in frontline treatment of older patients with CLL is remarkable. With a follow-up of >4 years, only 15 patients treated with ibrutinib arms experienced disease progression while receiving therapy. This showed that patients who continued frontline treatment had an extremely small chance of disease progression—within this time frame, it is much more common to discontinue therapy and then experience disease progression than to experience disease progression while receiving ibrutinib. Although patients have a median of 24 months from discontinuation to disease progression, this is likely to be a shorter PFS than those who would experience continuous therapy. This finding underscores the importance of continued efforts to administer ibrutinib as safely as possible so that patients can remain on this effective therapy.
Importantly, our multivariable analyses showed that even patients with high-risk disease can have prolonged PFS with ibrutinib, and patients with TP53 abnormalities (deletion or mutation) did not show inferior PFS compared with those with functional TP53. This is a distinction for this class of drugs vs venetoclax + obinutuzumab and indicates that continuous BTK inhibitors should be the standard of care frontline treatment for these high-risk patients. These data are supported by other studies on frontline BTK inhibitors, which also show similar PFS regardless of TP53 status.13,14 However, higher degrees of karyotypic complexity indicated that patients were less likely to have an extended PFS with both ibrutinib and BR. In this study, a complex karyotype (≥3 abnormalities) was observed in 29% of the patients by a centralized stimulated karyotype. Although most of these complex karyotypes had <5 abnormalities, we observed that a small number of patients with high-complexity karyotypes had shorter PFS. This is a subgroup of patients who still have unmet clinical needs from current therapies, and it continues to be important to identify these patients by pretreatment karyotype and continue to evaluate novel strategies for treatment of this group.
Although, overall, this study showed that ibrutinib regimens are superior to standard chemoimmunotherapy, there are patients in this study who have extended PFS with BR. The only subgroup of patients who may not have improved PFS with ibrutinib compared with BR is those with IGHV-mutated disease, although it does appear that the difference between BR and ibrutinib regimens in IGHV-mutated CLL increases with time. Because this study was not powered to detect differences between regimens within these subgroups, it is difficult to conclude that BR is equivalent to ibrutinib-based regimens in this subgroup. Patients treated with BR who have undetectable MRD after treatment will have prolonged remission compared with those with detectable MRD. Unfortunately, this is still a small subgroup of patients, and we do not have a way to identify a priori which patients are likely to develop undetectable MRD. Therefore, these data still support that ibrutinib should be preferred over BR.
OS in this trial remained similar among the 3 arms. Because there are multiple treatment options for patients whose CLL has relapsed after frontline therapy, it has historically been difficult to detect a difference in OS with initial treatment, especially with early follow-up. Although the E1912 study, which tested ibrutinib plus rituximab vs fludarabine/cyclophosphamide/rituximab detected a survival advantage for ibrutinib plus rituximab,4 the FLAIR trial, which used the same treatment regimens, did not detect a survival advantage.15 Adding to the difficulty in using this study to evaluate survival, this trial was designed with a crossover, so there was no intent to prove a survival advantage. The current data would suggest that, within the time frame evaluated, patients initially treated with BR can be successfully salvaged with additional treatment, including ibrutinib. However, longer-term follow-up will be helpful to determine whether there are survival advantages to using ibrutinib in the first-line rather than second-line setting.
The safety profile of ibrutinib has been established through multiple clinical trials with prolonged follow-ups. Unique to this cohort, however, was the older age of the patients. Here, we observed that the incidence of atrial fibrillation and hypertension continues to rise throughout the course of therapy, which is expected based on prior studies,6,16 although the rate of incidence of these toxicities has decreased over time. In addition to atrial arrhythmias, ventricular arrhythmias have also been a concerning toxicity with ibrutinib. In the initial publication of this trial, unexplained/unwittnessed deaths, presumed to have been due to ventricular arrhythmias, were observed in 2, 7, and 4 patients on BR, I, and IR, respectively.1 With 17 months of follow-up, unexplained/unwitnessed deaths were observed in 1 additional patient per arm, continuing to support that sudden death is an uncommon side effect of ibrutinib and also suggests that this is primarily an early event that patients might have an intrinsic predisposition to.
Although we observed that most patients will perform well over many years on frontline ibrutinib, the cardiac toxicities associated with this therapy warrant consideration, especially in this older population. Before initiation of ibrutinib, it would be reasonable to evaluate the medical risk factors for atrial fibrillation (hypertension, obesity, sleep apnea, and prolonged PR interval on EKG)17 and lifestyle factors (alcohol and smoking).18 Patients deemed to be at a higher risk for atrial fibrillation might benefit from consultation with a cardio-oncologist before the initiation of therapy. Additionally, once therapy has commenced, careful evaluation of cardiac toxicities is important so that complications of untreated hypertension and atrial fibrillation can be avoided. Finally, weighing the risk benefit is necessary for each individual patient to determine whether the potential toxicity outweighs the efficacy of this regimen. This risk-benefit analysis is especially relevant for those at high risk of cardiac toxicity, where an alternative regimen might be preferred, or for those with high genomic risk disease, in which the efficacy of the regimen likely outweighs the potential risk.
Overall, this trial continues to provide valuable insights into the safety and efficacy of ibrutinib and IR as frontline therapy for older adults with CLL. Although the second-generation BTK inhibitors acalabrutinib and zanubrutinib have gained popularity due to their favorable safety and efficacy profiles compared with ibrutinib,19,20 ibrutinib remains a standard of care for frontline CLL therapy, and these data support its continued use in this setting.
Acknowledgments
Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Cancer Institute under award numbers U10CA180821 and U10CA180882 (to the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology), UG1CA189858, UG1CA233178, UG1CA233180, UG1CA233253, UG1CA232760, UG1CA233320, UG1CA233327, UG1CA233331, UG1CA233339; U10CA180863, CCS 707213 (Canadian Cancer Trials Group), U10CA180820 (Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group-American College of Radiology Imaging Network), and U10CA180888 (Southwest Oncology Cooperative Group). K.A.R. and J.A.W. are clinical scholars of the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society. Fluorescence in situ hybridization probes were provided by Abbott Molecular and Kreatech Biotechnology. The trial was sponsored in part by Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie company.
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
A full listing of acknowledgments of the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology can be found at https://acknowledgments.alliancefound.org.
Authorship
Contribution: J.A.W., A.S.R., R.F.L., S.J.M., and J.C.B. designed the research; J.A.W., C.M., N.A.H., W.Z., W.D., N.L.B., D.M.B., P.M.B., K.A.R., S.A.P., D.M.S., J.R.B., G.L., J.B., S.N., R.A.L., H.E., M.L., S.L., C.O., C.K., J.S.A., S.D., R.M.S., G.U., W.S., and J.C.B. performed the research; and G.P.B., A.S.R., A.W., and S.J.M. analyzed the data.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: J.A.W. received research funding from AbbVie, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, and Schrodinger and consulted for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Genentech, Loxo/Lilly, Janssen, Merck, Newave, Pharmacyclics, and Schrodinger. A.S.R. is an employee of Eli Lilly but worked at The Ohio State University without conflicts at the time of this work. C.M. received research funding from AbbVie. K.A.R. received research funding from Genentech, AbbVie, Janssen, and Novartis, consulted for AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, Genentech, LOXO@Lilly, and received travel funding from AstraZeneca. S.A.P. received research funding from Janssen, AstraZeneca, Merck, and Genentech and consults for Pharmacyclics, Merck, AstraZeneca, Janssen, BeiGene, Genentech, Amgen, Mingsight, TG Therapeutics, Novalgen Limited, Kite Pharma, and AbbVie. R.M.S. consults for AbbVie, Actinium, Amgen, Aptevo, Arog, AvenCell, BerGenBio, Bristol Myers Squib, Boston Pharmaceuticals, Cellularity, CTI pharma, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Hermavant, Janssen, Jazz, Kura Onc, Ligand Pharma, Novartis, Rigel, Syros, and Takeda. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Jennifer A. Woyach, The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, 400 W 12th Ave, Columbus, OH 43210; email: jennifer.woyach@osumc.edu.
References
Author notes
Deidentified patient data may be requested from the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology (concepts@alliancenctn.org), if the data are not publicly available. The formal review process includes verifying the availability of data, conducting a review of any existing agreements that may have implications for the project, and ensuring that any transfer is in compliance with the institutional review board. The investigator will be required to sign a data release form before transfer.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal