A single-chain CD38 T-cell engager targets CD38-negative LSCs activated by IFN-γ and induces CD38 expression on AML blasts.
CD38 T-cell engager activates T cells against autologous leukemia cells and in AML mouse models.
Visual Abstract
Treatment resistance of leukemia stem cells (LSCs) and suppression of the autologous immune system represent major challenges to achieve a cure in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Although AML blasts generally retain high levels of surface CD38 (CD38pos), LSCs are frequently enriched in the CD34posCD38neg blast fraction. Here, we report that interferon gamma (IFN-γ) reduces LSCs clonogenic activity and induces CD38 upregulation in both CD38pos and CD38neg LSC-enriched blasts. IFN-γ–induced CD38 upregulation depends on interferon regulatory factor 1 transcriptional activation of the CD38 promoter. To leverage this observation, we created a novel compact, single-chain CD38-CD3 T-cell engager (BN-CD38) designed to promote an effective immunological synapse between CD38pos AML cells and both CD8pos and CD4pos T cells. We demonstrate that BN-CD38 engages autologous CD4pos and CD8pos T cells and CD38pos AML blasts, leading to T-cell activation and expansion and to the elimination of leukemia cells in an autologous setting. Importantly, BN-CD38 engagement induces the release of high levels of IFN-γ, driving the expression of CD38 on CD34posCD38neg LSC-enriched blasts and their subsequent elimination. Critically, although BN-CD38 showed significant in vivo efficacy across multiple disseminated AML cell lines and patient-derived xenograft models, it did not affect normal hematopoietic stem cell clonogenicity and the development of multilineage human immune cells in CD34pos humanized mice. Taken together, this study provides important insights to target and eliminate AML LSCs.
Introduction
Despite therapeutics recently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration, only 30% of adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) are alive at 5 years from diagnosis.1,2 Both initial treatment refractoriness and postremission relapse remain major challenges.3,4 Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) transplantation is the only curative approach for most patients with AML, but treatment-related morbidity and mortality limit its use to clinically fit and younger patients.5,6 As such, a significant number of patients with AML are in dire need for more effective and less toxic therapies.
In AML, leukemia stem cells (LSCs) are primitive clonal cells capable of self-renewal and disease initiation and maintenance.7 These cells are highly treatment resistant,8 and therefore are likely responsible for disease refractoriness and relapse. Compared with their “bulk blast” progeny, AML LSCs are characterized by quiescence, distinct metabolism, and phenotypic plasticity.9 They are, however, difficult to identify because they can reside in immunophenotypic-diverse leukemic cell subpopulations10 and share common antigens with both bulk blasts and normal HSCs.11 In human patients with AML, LSCs are frequently enriched in the CD34posCD38neg fraction, whereas more differentiated AML progenitors and bulk AML blasts reside in the CD34posCD38pos fraction.9
Bispecific T-cell engager antibodies that redirect T cells to killing of cancer cells by simultaneously binding a tumor associated antigen (TAA) on cancer cells and the CD3 receptor on T-cells have shown robust clinical activity in hematological cancers.12 Several AML-associated TAAs have been targeted by T-cell engagers, including CD33, CD123, CD13, and C-type lectin-like molecule-1 (CLL-1).13 Although these targets are ubiquitously expressed on AML blasts and LSCs, they are also highly expressed by normal HSCs,14 leading to off-target activity and reducing their clinical efficacy.
CD38 is an ectoenzyme transmembrane glycoprotein involved in the metabolism of extracellular nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.15 This antigen has successfully been exploited as a therapeutic target in multiple myeloma (MM) and T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.16,17 However, because LSCs are mainly CD38neg, the therapeutic targeting of CD38 is of secondary interest in AML.18 We show, however, when targeted by a novel compact single-chain T-cell engager, CD38 is a very promising therapeutic target in AML. Specifically, CD38 expression is induced by interferon gamma (IFN-γ), which converts CD34posCD38neg into CD34posCD38pos blasts and marks the AML cell population for elimination using a CD38-directed immunotherapeutic. To exploit this feed-forward mechanism, we developed a novel single-domain, CD38-targeting T-cell engager (hereafter called CD38 biologic nested inside chains [CD38-BIONIC]). We demonstrate that, once engaged with CD38pos AML cells, CD38-BIONIC (BN-CD38) induces T cells to release IFN-γ and convert bystander CD38neg cells (including LSCs) into CD38pos blasts. Consequently, BN-CD38 eliminates both CD38pos and CD38neg leukemic blasts and offers an attractive therapeutic approach for AML.
Materials and methods
Samples from patients with primary AML
Samples from patients with AML were obtained from the City of Hope Hematopoietic Tissue Biorepository according to institutional review board–approved protocols and after written informed consent from all participants before inclusion in the study.
Single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) was conducted in primary AML bone marrow (BM) mononuclear cells (MNCs) treated either with vehicle or IFN-γ for 5 hours at 10 ng/mL. Bulk RNAseq was conducted in CD34pos blasts purified from patients with AML, and exposed overnight to either vehicle or 10 ng/mL IFN-γ. Library preparation, sequencing methods, and data analyses are detailed in supplemental Materials, available on the Blood website.
Generation of BN-CD38
Supplemental Materials detail the conceptualization, generation, and characterization of the single-chain T-cell engager called CD38-CD3 BIONIC (BN-CD38) and the control that is CD38-mutated BN-CD38 (BN-CD38Mut).
Mass cytometry (cytometry by time of flight [CyTOF]) staining and acquisition
Primary peripheral blood (PB) or BM MNCs from patients with AML were treated with 1.0 ng/mL of BN-CD38 or controls that included BN-CD38Mut, CD38 nanobody, or human immunoglobulin G (IgG) for 5 days and stained with a customized 36–surface marker panel according to Standard BioTools standard cell surface staining protocol.
In vivo studies
AML cell lines (THP1 and U937) xenografts and patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models were generated and handled under approved City of Hope institutional animal care and use committee protocols. Once engraftment was confirmed, the mice were injected with either BIONICs or control IgG (2.5 mg/kg per mouse) along with healthy donor–derived pan T cells (3 million T cells), as described in supplemental Materials and supplemental Figures.
Results
IFN-γ induces CD38 expression in AML cells through IRF-1 transcriptional regulation
CD38 expression is induced in response to T helper type 1 cell–derived IFN-γ.19 To gain insights in CD38 mechanisms of regulation in AML cells, we exposed primary BM AML blasts to IFN-γ. We observed a significant dose-dependent increase in surface CD38 in both CD34pos and CD34neg AML blasts (Figure 1A-C). In colony forming unit assays, IFN-γ treatment significantly decreased the clonogenic activities of AML cells (Figure 1D; P = .002), independent of their cytogenetic and molecular features (supplemental Table 1). To understand how IFN-γ induces CD38 expression, we treated total BM MNCs from a patient with relapsed AML with IFN-γ or vehicle and carried out scRNAseq. We observed significant transcriptional changes involving >1000 distinct genes in IFN-γ–treated cells compared with in the vehicle-treated AML cells. Among the most upregulated genes in the IFN-γ–treated cells (>2.5 log2 fold change; P = 0; false discovery rate [FDR] = 0), we found CD38 and 2 previously reported transcriptional regulators of CD38 expression, interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 120-23 (Figure 1E; supplemental Table 2).
IFN-γ induces CD38 expression in AML cells through IRF-1 transcriptional regulation. (A) Representative flow cytometry dot plots for 2 AML BM samples comparing percent of CD38High population in IFN-γ–treated group vs vehicle-treated group. IFN-γ was added overnight at a concentration of 10 ng/mL to total BM MNCs and gated for CD45DimCD34CD38 population. (B) Violin plot comparing percent of CD38High population between vehicle- and IFN-γ–treated groups for patients with AML (n = 5; 4 BM and 1 PB). Each shape represents a different patient with AML. Each patient sample was analyzed in duplicate except for 1 patient. Unpaired Student t test was used to calculate statistical significance between vehicle- and IFN-γ–treated groups; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. (C) AML BM MNCs were treated overnight with different doses of IFN-γ (1.0, 10.0, and 50.0 ng/mL), and CD38 surface expression was determined in CD45Dim population with flow cytometry. Overlaid dot plots show shift in CD38 expression with IFN-γ treatment, and the table to the right lists mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) for each dose and control. (D) Representative images of colony forming cell (CFC) assay for patient with AML after treatment with IFN-γ (10 ng/mL) or vehicle. Images were acquired in tiles to cover complete well and stitched. Violin plot comparing colony forming units (CFUs) between vehicle- and IFN-γ–treated (10 ng/mL) groups for patients with AML (n = 4: 3 PB and 1 BM). Each shape represents a different patient with AML. Samples from each patient was analyzed in duplicate. Unpaired Student t test was used to calculate statistical significance between vehicle- and IFN-γ–treated groups; ∗∗P < .01. (E) 3D uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) depicting effect of IFN-γ treatment (10 ng/mL, 5 hours) on AML total BM MNCs of 1 patient with relapsed AML. (F) CD34pos cells were purified from 3 patients’ BM MNCs (relapsed AML) and equally divided for vehicle and IFN-γ (10 ng/mL) treatment groups. After overnight treatment, cells were collected, and RNA was extracted and subjected to bulk RNAseq. z score–based hierarchical clustering heat map showing top 75 upregulated genes and 5 downregulated genes in 3 patients with AML upon IFN-γ treatment. (G) Venn diagram analysis showing the highest upregulated genes upon IFN-γ treatment that were commonly found between scRNAseq and bulk RNAseq analysis. (H) CD34pos cells were selected from BM MNCs of 3 patients with relapsed AML and treated overnight with vehicle or 10 ng/mL of IFN-γ, followed by CD38 and IRF-1 quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). CD38 and IRF-1 messenger RNA (mRNA) expression is shown as fold change (F.C.) relative to vehicle control. Each sample was normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and analyzed in triplicate. Paired Student t test was used to calculate significance. (I) Schematic cartoon showing cloned CD38 promoter in pGL3 plasmid, which encompassed IRF-1 consensus sequences (CS) and transcription start site (TSS) and shows location of IRF-1 CS relative to TSS. Also, mutagenesis strategy used to delete the IRF-1 binding sites in CD38 promoter is shown. (J-K) THP1 and HEK293 cells were cotransfected with CD38 wild-type (WT) promoter vector and empty expression vector, CD38 WT promoter vector and IRF-1 expression vector, and CD38 mutant promoter vector and empty expression vector, and CD38 mutant promoter vector and IRF-1 expression vector for 24 hours for HEK293 and 48 hours for THP1 cells. All the samples were also cotransfected with pRL-TK as internal control. All the samples were subjected to dual luciferase assay and luciferase/renilla ratio was calculated for each sample. Bar graphs show luciferase activity of CD38 promoter. Each group (WT and mutant CD38 promoter) with IRF-1 expression vector was normalized with its respective control expression vectors. Three independent experiments containing 2 technical duplicates were performed. Paired Student t test was used to compare groups. (L) THP1 cells were transfected twice with 50 nM siRNA control (siCtrl) or siRNA IRF-1 (siIRF-1) at time 0 and 24 hours. At 24 hours after transfection, cells were equally divided between wells for siCtrl and siIRF-1 and half the wells for each siRNA were either subjected to vehicle or IFN-γ (10 ng/mL) treatment overnight. Surface staining was performed for CD38 and subjected to flow cytometry. Histograms represented in MFI show IFN-γ–induced CD38 surface expression, which was rescued by IRF-1 knock down. Violin plot is representation of 3 independent experiments. Ordinary 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with multiple comparisons was used as statistical test.
IFN-γ induces CD38 expression in AML cells through IRF-1 transcriptional regulation. (A) Representative flow cytometry dot plots for 2 AML BM samples comparing percent of CD38High population in IFN-γ–treated group vs vehicle-treated group. IFN-γ was added overnight at a concentration of 10 ng/mL to total BM MNCs and gated for CD45DimCD34CD38 population. (B) Violin plot comparing percent of CD38High population between vehicle- and IFN-γ–treated groups for patients with AML (n = 5; 4 BM and 1 PB). Each shape represents a different patient with AML. Each patient sample was analyzed in duplicate except for 1 patient. Unpaired Student t test was used to calculate statistical significance between vehicle- and IFN-γ–treated groups; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. (C) AML BM MNCs were treated overnight with different doses of IFN-γ (1.0, 10.0, and 50.0 ng/mL), and CD38 surface expression was determined in CD45Dim population with flow cytometry. Overlaid dot plots show shift in CD38 expression with IFN-γ treatment, and the table to the right lists mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) for each dose and control. (D) Representative images of colony forming cell (CFC) assay for patient with AML after treatment with IFN-γ (10 ng/mL) or vehicle. Images were acquired in tiles to cover complete well and stitched. Violin plot comparing colony forming units (CFUs) between vehicle- and IFN-γ–treated (10 ng/mL) groups for patients with AML (n = 4: 3 PB and 1 BM). Each shape represents a different patient with AML. Samples from each patient was analyzed in duplicate. Unpaired Student t test was used to calculate statistical significance between vehicle- and IFN-γ–treated groups; ∗∗P < .01. (E) 3D uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) depicting effect of IFN-γ treatment (10 ng/mL, 5 hours) on AML total BM MNCs of 1 patient with relapsed AML. (F) CD34pos cells were purified from 3 patients’ BM MNCs (relapsed AML) and equally divided for vehicle and IFN-γ (10 ng/mL) treatment groups. After overnight treatment, cells were collected, and RNA was extracted and subjected to bulk RNAseq. z score–based hierarchical clustering heat map showing top 75 upregulated genes and 5 downregulated genes in 3 patients with AML upon IFN-γ treatment. (G) Venn diagram analysis showing the highest upregulated genes upon IFN-γ treatment that were commonly found between scRNAseq and bulk RNAseq analysis. (H) CD34pos cells were selected from BM MNCs of 3 patients with relapsed AML and treated overnight with vehicle or 10 ng/mL of IFN-γ, followed by CD38 and IRF-1 quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). CD38 and IRF-1 messenger RNA (mRNA) expression is shown as fold change (F.C.) relative to vehicle control. Each sample was normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and analyzed in triplicate. Paired Student t test was used to calculate significance. (I) Schematic cartoon showing cloned CD38 promoter in pGL3 plasmid, which encompassed IRF-1 consensus sequences (CS) and transcription start site (TSS) and shows location of IRF-1 CS relative to TSS. Also, mutagenesis strategy used to delete the IRF-1 binding sites in CD38 promoter is shown. (J-K) THP1 and HEK293 cells were cotransfected with CD38 wild-type (WT) promoter vector and empty expression vector, CD38 WT promoter vector and IRF-1 expression vector, and CD38 mutant promoter vector and empty expression vector, and CD38 mutant promoter vector and IRF-1 expression vector for 24 hours for HEK293 and 48 hours for THP1 cells. All the samples were also cotransfected with pRL-TK as internal control. All the samples were subjected to dual luciferase assay and luciferase/renilla ratio was calculated for each sample. Bar graphs show luciferase activity of CD38 promoter. Each group (WT and mutant CD38 promoter) with IRF-1 expression vector was normalized with its respective control expression vectors. Three independent experiments containing 2 technical duplicates were performed. Paired Student t test was used to compare groups. (L) THP1 cells were transfected twice with 50 nM siRNA control (siCtrl) or siRNA IRF-1 (siIRF-1) at time 0 and 24 hours. At 24 hours after transfection, cells were equally divided between wells for siCtrl and siIRF-1 and half the wells for each siRNA were either subjected to vehicle or IFN-γ (10 ng/mL) treatment overnight. Surface staining was performed for CD38 and subjected to flow cytometry. Histograms represented in MFI show IFN-γ–induced CD38 surface expression, which was rescued by IRF-1 knock down. Violin plot is representation of 3 independent experiments. Ordinary 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with multiple comparisons was used as statistical test.
Total RNAseq from isolated CD34pos AML blasts of patients with relapsed AML (n = 3) confirmed that upregulation of CD38 and IRF-1 but not of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (>2.5 log2 fold change FDR of <0.25; P = .0007) in the IFN-γ–treated cells (Figure 1F-G; supplemental Figure 1A; supplemental Table 3). These results were further confirmed by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and flow cytometry assays (Figure 1H; supplemental Figure 1B-D). Gene set enrichment analysis showed that IFN-γ treatment also induced a significant (FDR = 0) upregulation of genes involved in apoptosis, DNA repair, reactive oxygen species regulation, and inflammation (ie, tumor necrosis factor α), among others (supplemental Figure 1E), and significant suppression of genes involved in the pro-oncogenic Wnt β catenin pathways (supplemental Figure 1F) and cell survival (eg, CD109,24 KDM6B,25 and MYCN26; supplemental Table 3).
To investigate the role of IRF-1 in IFN-γ–induced CD38 transcription, we analyzed the CD38 promoter using the JASPAR 2022 database.27 We found 2 partially overlapping and highly conserved IRF-1 consensus sequences in the CD38 promoter starting at −6 and −27 nucleotides from the transcriptional starting site (supplemental Figure 1G). To verify these experimentally, we developed a luciferase-based reporter system to measure CD38 promoter (WT-CD38) activation. We transfected the CD38 luciferase-based reporter construct into CD38-negative HEK-293 cells along with a vector expressing IRF-1. Ectopic expression of IRF-1 significantly increased CD38 promoter luciferase activity (P < .0001) compared with cells transfected with the CD38 reporter vector and a vector-null control (Ctrl; Figure 1J). To assess the specificity of the IRF-1 transcription reporter assay, we also generated a second CD38 promoter reporter system lacking the IRF-1 consensus sequences only (−6 to −27, Mut-CD38; Figure 1I) and transfected with this construct in CD38-negative (HEK-293) and CD38-positive THP-1 cells. The ectopic IRF-1 expression, in contrast, failed to induce any luciferase activity (Figure 1J-K). In addition, we knocked down IRF-1 expression with small interfering RNAs (siRNA) in AML cells treated with IFN-γ and observed a significant downregulation of both CD38 messenger RNA and surface protein compared with cells transfected with nontargeting siRNA (Ctrl-siRNA; Figure 1L; supplemental Figure 1H-I).
The single-chain CD38 T-cell engager (CD38-CD3 BIONIC) shows potent antileukemic efficacy in vitro and ex vivo
CD4pos T helper type 1 and CD8pos cytotoxic T cells release IFN-γ once engaged on their target(s).28 Thus, we hypothesized that a CD38-directed T-cell engager would not only kill CD34posCD38pos AML blasts but also convert CD34posCD38neg LSCs into CD34posCD38pos blasts via the secreted IFN-γ, thereby expanding the targetable AML cell population also to the CD38neg blasts (Figure 2A). To this end, we hypothesized that a compact T-cell engager, mimicking the distance between the T-cell receptor (TCR) and the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) while limiting steric hindrance, would produce an optimal immunological synapse.29,30 To achieve a compact structure while simultaneously addressing challenges in generating immune engagers (eg, light chain pairing), we created a single-chain construct, inserting a CD38 nanobody (CD38-NB) between the light and heavy chains of an anti-CD3 Fab using 2 short peptide linkers. The net result is a compact, single-chain molecule we have named a CD38-CD3 BIONIC (BN-CD38; Figure 2B). As a point of comparison, superposition of the cryoelectron microscope structure of the TCR (PDB:6JXR) and the MHC structure (PDB:4GRL) indicates the distance between T-cell membrane and antigen presenting cells is ∼140 Å (Figure 2C), which is consistent with previously reported values.31 Simple modeling indicates that BN-CD38 closely matches the TCR-MHC distance (Figure 2D).
BN-CD38 shows potent antileukemic efficacy in vitro and ex vivo. (A) Schematic illustration of the therapeutic rationale to target CD38neg LSCs with T-cell engagers against CD38 to eradicate AML by uncovering the IFN-γ/CD38 regulatory loop. Graphical representation of (B) BN-CD38 projected structure; (C) distance between T cell and tumor cell membranes upon TCR-MHC interaction; and (D) spatial prediction of how BN-CD38 interaction with T cell (CD3) and tumor cell (CD38) is similar to the interaction observed in the MHC-TCR complex. (E) Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensorgrams for CD38 and CD3 binding with different concentrations of BN-CD38. (F) THP1 green fluorescent protein–positive (GFPpos) cells were cocultured with healthy donor T cells at an E:T ratio of 1:1 overnight (16 hours) in the presence of increasing doses of BN-CD38 active (A) and BN-CD38Mut. THP1 cell killing was determined with 7-aminoactinomycin D staining and gating on GFPpos cells by flow cytometry. IC50 curves are shown for BN-CD38 and BN-CD38Mut, and data are represented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of 5 independent healthy donors. (G-H) Samples in panel F were also used to assess the induction of early (CD69) and late (CD25) T-cell activation markers in the total CD4 or CD8 T cells. Dose-dependent T-cell activation curves are represented as mean ± SEM of 3 healthy donors. Ordinary 1-way ANOVA test was used for calculation of statistical significance. (I-K) Total AML cells (n = 7) were treated with 1.0 ng/mL IgG, CD38-NB, BN-CD38 Mut, or BN-CD38 for 5 days and subjected to cell surface staining for CD34 and CD38. (I) Representative flow cytometry contour plots of 2 representative patient-derived AML samples and (J-K) violin plots show elimination of total AML cells (CD34posCD38pos blasts and CD34posCD38neg LSCs) with BN-CD38 compared with control treatments (IgG, CD38-NB, and BN-CD38Mut). Cell frequencies were normalized to the paired control human IgG treatment and shown as F.C. Overall, 2 of 7 patients were not assessed with BN-CD38Mut and CD38 NB. (L) Total AML cells were treated with 1.0 ng/mL control human IgG, CD38NB, BN-CD38 Mut, or BN-CD38 and plated in CFC assay for 14 days. Violin plot illustrates the normalized CFU F.C. for each treatment group compared with the paired IgG (CD38 NB, n = 4 PB; BN-CD38 Mut, n = 4 PB; BN-CD38, n = 11 [9 PB and 2 BM]). Each dot in each treatment group represents 1 individual patient. (M) Schematic cartoon and representative flow cytometry contour plot of the experimental design and gating strategy used to assess apoptosis of CD38neg AML blasts by autologous T cells. (N) Contour plots of 2 representative patients with AML showing annexin-V/4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining of the CD38neg gated population after treatment with IgG, BN-CD38Mut, or BN-CD38 SNs in the presence of autologous T cells. (O) Violin plot showing changes in induced apoptosis in each treatment group. Unpaired Student t test was used to calculate statistical significance in n = 4 patients with AML; ∗∗∗P < .001, n = 4. For panels G-H,J-L, 1-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance between different groups; ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; and ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. E, effector T cells; ns, not significant; T, target cancer cells.
BN-CD38 shows potent antileukemic efficacy in vitro and ex vivo. (A) Schematic illustration of the therapeutic rationale to target CD38neg LSCs with T-cell engagers against CD38 to eradicate AML by uncovering the IFN-γ/CD38 regulatory loop. Graphical representation of (B) BN-CD38 projected structure; (C) distance between T cell and tumor cell membranes upon TCR-MHC interaction; and (D) spatial prediction of how BN-CD38 interaction with T cell (CD3) and tumor cell (CD38) is similar to the interaction observed in the MHC-TCR complex. (E) Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensorgrams for CD38 and CD3 binding with different concentrations of BN-CD38. (F) THP1 green fluorescent protein–positive (GFPpos) cells were cocultured with healthy donor T cells at an E:T ratio of 1:1 overnight (16 hours) in the presence of increasing doses of BN-CD38 active (A) and BN-CD38Mut. THP1 cell killing was determined with 7-aminoactinomycin D staining and gating on GFPpos cells by flow cytometry. IC50 curves are shown for BN-CD38 and BN-CD38Mut, and data are represented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of 5 independent healthy donors. (G-H) Samples in panel F were also used to assess the induction of early (CD69) and late (CD25) T-cell activation markers in the total CD4 or CD8 T cells. Dose-dependent T-cell activation curves are represented as mean ± SEM of 3 healthy donors. Ordinary 1-way ANOVA test was used for calculation of statistical significance. (I-K) Total AML cells (n = 7) were treated with 1.0 ng/mL IgG, CD38-NB, BN-CD38 Mut, or BN-CD38 for 5 days and subjected to cell surface staining for CD34 and CD38. (I) Representative flow cytometry contour plots of 2 representative patient-derived AML samples and (J-K) violin plots show elimination of total AML cells (CD34posCD38pos blasts and CD34posCD38neg LSCs) with BN-CD38 compared with control treatments (IgG, CD38-NB, and BN-CD38Mut). Cell frequencies were normalized to the paired control human IgG treatment and shown as F.C. Overall, 2 of 7 patients were not assessed with BN-CD38Mut and CD38 NB. (L) Total AML cells were treated with 1.0 ng/mL control human IgG, CD38NB, BN-CD38 Mut, or BN-CD38 and plated in CFC assay for 14 days. Violin plot illustrates the normalized CFU F.C. for each treatment group compared with the paired IgG (CD38 NB, n = 4 PB; BN-CD38 Mut, n = 4 PB; BN-CD38, n = 11 [9 PB and 2 BM]). Each dot in each treatment group represents 1 individual patient. (M) Schematic cartoon and representative flow cytometry contour plot of the experimental design and gating strategy used to assess apoptosis of CD38neg AML blasts by autologous T cells. (N) Contour plots of 2 representative patients with AML showing annexin-V/4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining of the CD38neg gated population after treatment with IgG, BN-CD38Mut, or BN-CD38 SNs in the presence of autologous T cells. (O) Violin plot showing changes in induced apoptosis in each treatment group. Unpaired Student t test was used to calculate statistical significance in n = 4 patients with AML; ∗∗∗P < .001, n = 4. For panels G-H,J-L, 1-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance between different groups; ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; and ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. E, effector T cells; ns, not significant; T, target cancer cells.
Surface plasmon resonance and analytical cytometry studies show that BN-CD38 retained binding affinity to both CD38 and CD3 antigens (Figure 2E). Moreover, the CD38-NB alone and BN-CD38 also show comparable binding kinetics to CD38 (supplemental Figure 2A). We also generated a BN-CD38Mut as a negative control. Replacing serine with histidine at residue 57 (Ser57His) within the anti-CD38 nanobody (based on nanobody numbering), located within the CD38-CD38 nanobody interface (supplemental Figure 2B) abrogated the binding to CD38. Binding to T-cell surface CD3 remained unaffected (supplemental Figure 2B-C).
To test the activity of BN-CD38, we cocultured T cells (hereafter called “effector”) with CD38pos (hereafter called “target”) AML cells (ie, THP1, MV-4;11, HL-60, U937, NOMO1, and SKM1) and MM cells (ie, MM.1S) at an effector-to-target (E:T) ratio of 1:1 in the presence of BN-CD38. We observed significant killing activity (P < .0001), which correlated with the levels of CD38 expression (supplemental Figure 2D-E). No significant killing was observed in CD38neg cells, that is, the AML SKM1 cells or CD38-knockout HL-60 AML cells, in which the CD38 was silenced via CRISPR (supplemental Figure 2D-E). Killing activity was also not observed in the presence of BN-CD38Mut or nonspecific human IgG, instead of BN-CD38 (supplemental Figure 2F). The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) for BN-CD38 was calculated to be within the 0.01 to 0.1 ng/mL range, whereas the IC50 of BN-CD38Mut was at least 100-fold higher (Figure 2F; supplemental Figure 2G). Significant increases in expression of early (CD69) and late (CD25) T-cell activation markers was observed both on CD4pos and CD8pos T cells cocultured with CD38pos THP1 cells (P < .0001) in the presence of BN-CD38, and not in those cocultures with control treatments (human IgG or BN-CD38Mut; Figure 2G-H; supplemental Figure 2H-I). Furthermore, a significant increase in secretion levels of IFN-γ, tumor necrosis factor α, and interleukin-2, among others, by T cells was observed in cocultures of T cells and CD38pos THP1 cells treated with BN-CD38 (supplemental Figure 3A-B). No cytokine secretion was detected in the absence of CD38pos THP1 cells (supplemental Figure 3C) or in T cells cocultured with CD38neg target cells (ie, CD38-knockout HL-60 cells; supplemental Figure 3D). Of particular interest, levels of BN-CD38 that induced engagement and activation for CD4pos and CD8pos T cells were comparable (supplemental Figure 3E-F).32
To assess whether BN-CD38 could effectively engage blasts and activate autologous T cells, we cocultured total BM or PB blasts and autologous T cells from the same patients with AML in the presence of 1 ng/mL of BN-CD38 or controls (ie, IgG, CD38-NB, or BN-CD38Mut). Compared with controls, exposure to BN-CD38 resulted in a significant decrease of both CD38pos and CD38neg blasts and their clonogenic activity (P < .01; Figure 2I-L; supplemental Table 1). Consistently, we observed upregulation of early (CD69) and late (CD25) T-cell activation markers (P < .0001; supplemental Figure 2J-K) and, after 5 days from the initial treatment, a significant expansion of patient-derived CD4pos and CD8pos T cells (P < .01; supplemental Figure 2L). To further investigate whether BN-CD38 induces specific killing of the CD38neg LSC–enriched population as well, we purified these cells from the total AML MNCs. Specifically, as shown in the graphical experimental design in Figure 2M, we first treated the CD38pos enriched blast population with their autologous effector cells and either BN-CD38, BN-CD38Mut, or control IgG for 24 hours. We then collected the CD38pos supernatant (SN) from each experimental group and used it to treat the CD38neg population cocultured with autologous T cells (E:T, 1:1), for 24 hours. We observed significant apoptotic induction of the CD38neg blasts treated with BN-CD38–enriched SN, compared with levels in blasts treated with BN-CD38Mut SN (51.4% ± 7.4% vs 2.1% ± 2.6%; P = .0001; n = 4 normalized for the respective Ctrl IgG SN), as assessed by annexin-V/propidium iodide staining (Figure 2N-O).
IFN-γ plays a pivotal role in BN-CD38 antileukemic activity
To investigate how exposure to BN-CD38 modifies distinct cellular components of the BM from patients with AML, we assembled a 36-metal mass cytometry (CyTOF) panel enabling us to discriminate AML and immune cell subpopulations (supplemental Tables 4 and 5).
Using supervised gating on vi_SNE (FlowSOM), we showed that BN-CD38 but not IgG, BN-CD38Mut, or CD38-NB significantly reduced the viability of both CD34posCD38pos and CD34posCD38neg AML blasts (Figure 3A-C; supplemental Figure 4A). BN-CD38 treatment was also associated with a significant expansion of CD8pos effector memory cells (P < .01), terminally differentiated effector memory CD45RApos cells (P < .05; Figure 3D), central memory regulatory T cells (P < .0001), and natural killer (NK) T cells (P < .01; Figure 3E-F). Consistent with these results, IFN-γ induction was also observed in the SNs of total AML cells treated with BN-CD38 (P = .04; supplemental Figure 4B). B cells were not significantly affected by exposure to BN-CD38, whereas NK cell expansion was observed in 5 of 6 primary samples with detectable NK cells (supplemental Figure 4C). Data-driven self-stratifying clustering CITRUS (cluster identification, characterization, and regression) analysis also shows that BN-CD38 significantly induces leukemic cytoreduction, while expanding T cells and phagocytic CD14posCD16neg classical monocytes (Figure 3G-I).33 Furthermore, BN-CD38 induced a significant increase in CD38 messenger RNA and protein expression (P < .0001) in primary AML samples, which was effectively reverted when 2 μg/mL anti-human IFN-γ neutralizing antibody was added to the culture (Figure 3J-K). We then treated PB MNCs from patients with AML for 5 days with 1 ng/mL BN-CD38 and 2 μg/mL anti-human IFN-γ neutralizing antibody; we confirmed that blocking IFN-γ significantly reversed the BN-CD38 killing activity for CD34posCD38neg cells (P < .05; Figure 3L-M), without affecting T-cell expansion. Because IFN-γ can impair T-cell killing activity through the induction of programmed cell death protein 1,34 as also observed in the T cells of AML MNCs treated ex vivo with BN-CD38 compared with the relative controls (P = .02; n = 7; supplemental Figure 4D-E), we investigated whether those T cells maintained their killing capabilities once re-exposed to the tumor cells. Despite programmed cell death protein 1 upregulation, BN-CD38–treated T cells eliminated autologous AML cells and THP1 cells upon rechallenge, to a level that was comparable with that of the first exposure (supplemental Figure 4F-G).
IFN-γ plays a pivotal role in BN-CD38 antileukemic activity. (A-I,L-M) Total MNCs of 7 patients with AML (see supplemental Table 1) were treated with 1.0 ng/mL of BN-CD38, BN-CD38Mut, or control human IgG for 5 days. Moreover, cells from 4 of the patients were also treated with BN-CD38 (1.0 ng/mL) and 2.0 μg of αIFN-γ antibody for 5 days. The treated MNCs were subjected to CyTOF immunophenotyping comprising 36 surface markers tailored to detect AML primary cells and different immune subsets. Analysis was performed with the Cytobank platform. (A) Supervised high-fidelity FlowSOM (“self-organizing maps”) based on vi-SNE 2D analysis for 2 representative patients with AML (1 PB and 1 BM) showing that BN-CD38 reduces CD38pos and CD38neg AML cells and expands T-cell subsets. Equal number of events were analyzed for each treatment group for each patient, and bulk MNCs were gated. (B-C) Violin plots showing BN-CD38 but not BN-CD38Mut significantly decreases CD38pos and CD38neg AML cells event count. (D-F) Violin plots showing BN-CD38 and not BN-CD38Mut expands CD8pos effector memory (EM) and terminally differentiated EM CD45RApos cells (TEMRA), memory T regulatory cells (Tregs), and NK T cells. (G-H) Data-driven self-stratifying CITRUS (cluster identification, characterization, and regression) analysis of 5 CD34pos AML PB samples subjected to CyTOF immunophenotyping revealed that 7 clusters (red circles) were significantly changed (FDR < 0.01) between BN-CD38 and control groups (IgG and BN-CD38Mut). Clusters (599995, 599997, and 599998) were significantly less abundant with BN-CD38 treatment and were enriched with AML specific markers CD34, CD33, and CD117 (c-Kit), and negative for CD3 T-cell marker. Clusters (599990, 599993, 599994, and 599996) were significantly abundant with BN-CD38 treatment and are enriched with T-cell surface markers and phagocytic classical monocytes (CD14+CD16negHLA-DR+). (I) Bar graphs of 7 clusters differentially and significantly (FDR < 0.01) changed with BN-CD38 compared with control human IgG and BN-CD38Mut. (J) Total AML cells of 4 patients with AML were treated with 1.0 ng/mL BN-CD38, BN-CD38Mut, CD38 NB, and control human IgG in combination with 2.0 μg rat control IgG or 2.0 μg rat anti-human IFN-γ antibody for 48 hours. RNA was extracted and subjected to CD38 qRT-PCR. Each sample was normalized to GAPDH followed by normalization to control human IgG for each patient and shown as F.C. over IgG. Two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance between different groups; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. (K) Cells treated in panel J were also collected and subjected to flow cytometry surface staining of CD45, CD34, and CD38. CD38 expression was determined in CD45DIM AML population. Two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance between different groups; ∗∗∗P < .001 and ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. (L) Four of the patient samples (4 PB samples from patients with CD34pos) were also treated with BN-CD38 (A; 1.0 ng/mL) and 2.0 μg of αIFN-γ antibody for 5 days. The treated MNCs were subjected to CyTOF immunophenotyping. Unsupervised high-fidelity FlowSOM (self-organizing maps) based on vi-SNE 2D analysis for PB-derived MNCs of 3 representative patients with AML showing that anti-human IFN-γ antibody restores AML cells, specifically LSCs in the presence of BN-CD38. (M) Violin plot representation showing that anti-human IFN-γ antibody in the presence of BN-CD38 rescues CD34posCD38neg LSCs compared with BN-CD38 alone. For panels B through F and panel M, event counts of BN-CD38 (A) and BN-CD38Mut were normalized to control human IgG and normalization was converted to log scale F.C. The paired Student t test was used to calculate statistical significance; ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; and ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
IFN-γ plays a pivotal role in BN-CD38 antileukemic activity. (A-I,L-M) Total MNCs of 7 patients with AML (see supplemental Table 1) were treated with 1.0 ng/mL of BN-CD38, BN-CD38Mut, or control human IgG for 5 days. Moreover, cells from 4 of the patients were also treated with BN-CD38 (1.0 ng/mL) and 2.0 μg of αIFN-γ antibody for 5 days. The treated MNCs were subjected to CyTOF immunophenotyping comprising 36 surface markers tailored to detect AML primary cells and different immune subsets. Analysis was performed with the Cytobank platform. (A) Supervised high-fidelity FlowSOM (“self-organizing maps”) based on vi-SNE 2D analysis for 2 representative patients with AML (1 PB and 1 BM) showing that BN-CD38 reduces CD38pos and CD38neg AML cells and expands T-cell subsets. Equal number of events were analyzed for each treatment group for each patient, and bulk MNCs were gated. (B-C) Violin plots showing BN-CD38 but not BN-CD38Mut significantly decreases CD38pos and CD38neg AML cells event count. (D-F) Violin plots showing BN-CD38 and not BN-CD38Mut expands CD8pos effector memory (EM) and terminally differentiated EM CD45RApos cells (TEMRA), memory T regulatory cells (Tregs), and NK T cells. (G-H) Data-driven self-stratifying CITRUS (cluster identification, characterization, and regression) analysis of 5 CD34pos AML PB samples subjected to CyTOF immunophenotyping revealed that 7 clusters (red circles) were significantly changed (FDR < 0.01) between BN-CD38 and control groups (IgG and BN-CD38Mut). Clusters (599995, 599997, and 599998) were significantly less abundant with BN-CD38 treatment and were enriched with AML specific markers CD34, CD33, and CD117 (c-Kit), and negative for CD3 T-cell marker. Clusters (599990, 599993, 599994, and 599996) were significantly abundant with BN-CD38 treatment and are enriched with T-cell surface markers and phagocytic classical monocytes (CD14+CD16negHLA-DR+). (I) Bar graphs of 7 clusters differentially and significantly (FDR < 0.01) changed with BN-CD38 compared with control human IgG and BN-CD38Mut. (J) Total AML cells of 4 patients with AML were treated with 1.0 ng/mL BN-CD38, BN-CD38Mut, CD38 NB, and control human IgG in combination with 2.0 μg rat control IgG or 2.0 μg rat anti-human IFN-γ antibody for 48 hours. RNA was extracted and subjected to CD38 qRT-PCR. Each sample was normalized to GAPDH followed by normalization to control human IgG for each patient and shown as F.C. over IgG. Two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance between different groups; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. (K) Cells treated in panel J were also collected and subjected to flow cytometry surface staining of CD45, CD34, and CD38. CD38 expression was determined in CD45DIM AML population. Two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance between different groups; ∗∗∗P < .001 and ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. (L) Four of the patient samples (4 PB samples from patients with CD34pos) were also treated with BN-CD38 (A; 1.0 ng/mL) and 2.0 μg of αIFN-γ antibody for 5 days. The treated MNCs were subjected to CyTOF immunophenotyping. Unsupervised high-fidelity FlowSOM (self-organizing maps) based on vi-SNE 2D analysis for PB-derived MNCs of 3 representative patients with AML showing that anti-human IFN-γ antibody restores AML cells, specifically LSCs in the presence of BN-CD38. (M) Violin plot representation showing that anti-human IFN-γ antibody in the presence of BN-CD38 rescues CD34posCD38neg LSCs compared with BN-CD38 alone. For panels B through F and panel M, event counts of BN-CD38 (A) and BN-CD38Mut were normalized to control human IgG and normalization was converted to log scale F.C. The paired Student t test was used to calculate statistical significance; ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; and ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
BN-CD38 displays a strong antileukemic efficacy in vivo
To study the antileukemic activity of BN-CD38 in vivo, we IV injected 1 × 106 luciferase-positive CD38pos THP1 cells into nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficiency (NOD-SCID) IL2Rgnull (NSG) mice (Figure 4A). On day 19 after injection, mice were randomized into 2 groups and treated with either 2.5 mg/kg BN-CD38 (n = 8) or human IgG (n = 10), and 3 × 106 human T cells were given IV weekly. The mice receiving BN-CD38 plus T cells were treated for a total of 4 weeks, whereas control mice were treated for 2 weeks, because the control animals had all died by day 32. A significant decrease in leukemic burden was observed in the BN-CD38–treated mice compared with human IgG–treated controls as early as 1 week after treatment initiation (day 25; P = .003; Figure 4B-C). Although lymphoproliferation and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) were expected side-effects associated with allogeneic T-cell infusion, 38% of BN-CD38–treated mice remained AML- and GVHD-free and remained this way for 120 days after the last treatment until they were humanely euthanized and no signs of disease were found, whereas the median survival for control mice was 29 days (Figure 4D). The antileukemic activity of BN-CD38 was also tested in mice xenografted with U937 cells, which have lower CD38 expression (CD38dim) and are less susceptible to BN-CD38 T-cell killing compared with THP-1 cells (supplemental Figure 5A-B). Mice treated with BN-CD38 and human T cells and not those treated with BN-CD38Mut or Ctrl-IgG under the same experimental setting, showed near-complete disease eradication (supplemental Figure 5C-F).
BN-CD38 displays a strong antileukemic efficacy in vivo. (A) Schematic representation of the experimental design and treatment for in vivo studies in NSG mice xenografted with 1 million GFPposLucposTHP-1 cells. On day 18, engraftment was confirmed with bioluminescence imaging (BLI), and mice were randomized. Treatment was started on day 19, and mice were administered control human IgG or BN-CD38 (2.5 mg/kg per mouse), together with 3 million healthy donor–derived human T cells per mouse weekly by IV. Mice in the treatment group were treated once a week for 4 weeks with BN-CD38 plus T cells, whereas mice in the control group received only 2 treatments, because all control mice had died by day 32, before the next planned treatment (day 33). Mice were monitored weekly by BLI for tumor burden assessment. (B) BLI images showing tumor engraftment in the different treatment groups. (C) Bar graph showing the BLI average radiance for control human IgG– and BN-CD38–treated mice on days 25 and 29. Error bars are represented as mean ± SEM. Unpaired Student t test was used for statistical significance calculation. (D) Kaplan-Meier survival curve showing increased survival in BN-CD38–treated mice (n = 8) compared with control IgG–treated mice (n = 10). Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test was used to determine statistical significance. (E) Kaplan-Meier survival curve showing increased survival in PDX-1 (AML-15) mice transplanted with the BM of BN-CD38–treated animals as reported in the schematic representation and treatment design in supplemental Figure 5G-J. Briefly, 1 million MNCs from a patient with AML with complex karyotype (PDX-1, AML-15) were injected by IV into irradiated NSG, and once engraftment was confirmed in the PB, mice were randomized and weekly cotreated with BN-CD38 (A, 2.5 mg/kg per mouse; n = 5), BN-CD38Mut (n = 5), or control IgG (n = 5), and 3 million healthy donor purified T cells by IV. A total of 3 treatments were administered, and mice BM cells were collected on day 42 and subjected to subsequent secondary and tertiary transplantations. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test was used to determine statistical significance; ∗∗∗P < .001. (F) Kaplan-Meier survival curve showing increased survival in PDX-2 (AML-22) mice engrafted with 1 million of total AML MNCs and treated with BN-CD38. Briefly, once engraftment was confirmed in week 8, mice were randomized into 4 groups: control human IgG (n = 5), BN-CD38Mut (n = 5), CD38 NB (n = 4), and BN-CD38 (n = 6). Each group received 2.5 mg/kg of respective treatment and 3 million healthy donor–derived T cells weekly at week 8, 9, 10, and 11 by IV. In week 12 and 13, mice of each group received only respective treatment and no T cells. Survival was monitored, and on week 20, BN-CD38 (A) treated mice were rechallenged with 1 million paired AML blasts (AML-22). In week 29, mice remained healthy and were humanely euthanized to assess tumor burden. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test was used to determine statistical significance. (G) Schematic representation of the experimental design and treatment for PDX-3 (AML-4); this model was administered with autologous T cells. Once engraftment was confirmed by flow cytometry on day 14, mice were randomized into 2 groups: BN-CD38Mut (n = 4) and BN-CD38 (n = 5). Each week mice were treated with 2.5 mg/kg of respective BIONICs and 1 million autologous T cells enriched fraction by IV. A total of 4 treatments (once a week) were administered. Mice were humanely euthanized on day 71 and assessed for tumor engraftment and T cells. (H-I) Contour plots of 1 representative mouse for each treatment group illustrate percentages of human CD33pos AML cells and human CD3pos T cells in the total BM and spleen (SP) cellular population. AML-to–T cells ratio was calculated for each mouse in 2 treatment groups, and violin plots show that BN-CD38Mut–treated mice had higher tumor burden than levels in BN-CD38–treated mice that showed T-cell expansion. Unpaired Student t test was used to calculate statistical significance; ∗∗P < .01 and ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
BN-CD38 displays a strong antileukemic efficacy in vivo. (A) Schematic representation of the experimental design and treatment for in vivo studies in NSG mice xenografted with 1 million GFPposLucposTHP-1 cells. On day 18, engraftment was confirmed with bioluminescence imaging (BLI), and mice were randomized. Treatment was started on day 19, and mice were administered control human IgG or BN-CD38 (2.5 mg/kg per mouse), together with 3 million healthy donor–derived human T cells per mouse weekly by IV. Mice in the treatment group were treated once a week for 4 weeks with BN-CD38 plus T cells, whereas mice in the control group received only 2 treatments, because all control mice had died by day 32, before the next planned treatment (day 33). Mice were monitored weekly by BLI for tumor burden assessment. (B) BLI images showing tumor engraftment in the different treatment groups. (C) Bar graph showing the BLI average radiance for control human IgG– and BN-CD38–treated mice on days 25 and 29. Error bars are represented as mean ± SEM. Unpaired Student t test was used for statistical significance calculation. (D) Kaplan-Meier survival curve showing increased survival in BN-CD38–treated mice (n = 8) compared with control IgG–treated mice (n = 10). Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test was used to determine statistical significance. (E) Kaplan-Meier survival curve showing increased survival in PDX-1 (AML-15) mice transplanted with the BM of BN-CD38–treated animals as reported in the schematic representation and treatment design in supplemental Figure 5G-J. Briefly, 1 million MNCs from a patient with AML with complex karyotype (PDX-1, AML-15) were injected by IV into irradiated NSG, and once engraftment was confirmed in the PB, mice were randomized and weekly cotreated with BN-CD38 (A, 2.5 mg/kg per mouse; n = 5), BN-CD38Mut (n = 5), or control IgG (n = 5), and 3 million healthy donor purified T cells by IV. A total of 3 treatments were administered, and mice BM cells were collected on day 42 and subjected to subsequent secondary and tertiary transplantations. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test was used to determine statistical significance; ∗∗∗P < .001. (F) Kaplan-Meier survival curve showing increased survival in PDX-2 (AML-22) mice engrafted with 1 million of total AML MNCs and treated with BN-CD38. Briefly, once engraftment was confirmed in week 8, mice were randomized into 4 groups: control human IgG (n = 5), BN-CD38Mut (n = 5), CD38 NB (n = 4), and BN-CD38 (n = 6). Each group received 2.5 mg/kg of respective treatment and 3 million healthy donor–derived T cells weekly at week 8, 9, 10, and 11 by IV. In week 12 and 13, mice of each group received only respective treatment and no T cells. Survival was monitored, and on week 20, BN-CD38 (A) treated mice were rechallenged with 1 million paired AML blasts (AML-22). In week 29, mice remained healthy and were humanely euthanized to assess tumor burden. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test was used to determine statistical significance. (G) Schematic representation of the experimental design and treatment for PDX-3 (AML-4); this model was administered with autologous T cells. Once engraftment was confirmed by flow cytometry on day 14, mice were randomized into 2 groups: BN-CD38Mut (n = 4) and BN-CD38 (n = 5). Each week mice were treated with 2.5 mg/kg of respective BIONICs and 1 million autologous T cells enriched fraction by IV. A total of 4 treatments (once a week) were administered. Mice were humanely euthanized on day 71 and assessed for tumor engraftment and T cells. (H-I) Contour plots of 1 representative mouse for each treatment group illustrate percentages of human CD33pos AML cells and human CD3pos T cells in the total BM and spleen (SP) cellular population. AML-to–T cells ratio was calculated for each mouse in 2 treatment groups, and violin plots show that BN-CD38Mut–treated mice had higher tumor burden than levels in BN-CD38–treated mice that showed T-cell expansion. Unpaired Student t test was used to calculate statistical significance; ∗∗P < .01 and ∗∗∗∗P < .0001.
Next, we prepared 3 PDXs using AML MNCs from 2 patients with refractory disease with complex karyotypes (patient identifiers: AML-4 and AML-15) and 1 patient with relapsed disease with a normal karyotype in which the CD34posCD38neg fraction in the total blast was >20% (AML-22; supplemental Table 1). One million AML MNCs from each patient were injected into 3 independent cohorts of irradiated NSG mice. To assess LSC eradication upon BN-CD38 treatment, we first performed a multiple transplantation study using the PDX-1 model (AML-15). Specifically, as shown in supplemental Figure 5G, on day 20, upon confirmation of successful engraftment (>1% circulating human AML blasts in the PB), PDX-1 engrafted mice were randomized into 3 groups to receive BN-CD38, BN-CD38Mut, or IgG (2.5 mg/kg per week) respectively, together with healthy donor human T cells (3 × 106 cells per week). After 3 treatments, mice were humanely euthanized, and leukemia burden was assessed. We observed significant decreases in AML cell engraftment in BN-CD38–treated animals (supplemental Figure 5H). We then transplanted BM MNCs of each donor into secondary NSG recipients. After 10 days, the secondary recipient mice were given the same treatment, and at the end of treatment, we observed that BN-CD38–treated mice had near disease eradication, both in the spleen and the BM, compared with mice treated with BN-CD38Mut or IgG (P < .0001; supplemental Figure 5I-K). To assess the long-term effect of BN-CD38–induced T-cell killing on AML cells, we performed a tertiary transplantation and followed-up for survival. Mice transplanted with BM MNCs from BN-CD38Mut– or IgG-treated mice had significantly lower survival (median survival, 28 days) than those transplanted with the BM MNCs from BN-CD38–treated mice (P = .002), which were followed-up to 256 days (Figure 4E); no signs of disease were observed before euthanasia. To assess the BN-CD38–directed antileukemic effect, we used a different PDX model (PDX-2, AML-22) with limited GVHD complications and conducted multiple treatments without multiple transplantation. Specifically, mice after engraftment were treated for 4 weeks with BN-CD38 or relative controls in combination with 3 × 106 T cells, and when T-cell engraftment was assessed, the same mice were treated only with BN-CD38 or relative controls once a week for 2 subsequent weeks (Figure 4F). Almost 70% of the BN-CD38–treated mice remained disease free, compared with the relative control groups, which showed a median survival of 12 weeks (P = .0007), even when the BN-CD38–treated mice at week 20 were rechallenged with autologous AML cells (Figure 4F). Although the mice did not show signs of distress by week 29 (201 days), they were euthanized, and flow cytometry analysis showed absence of leukemia engraftment, and human T cells were still detected (supplemental Figure 5L). Because we observed ex vivo that BN-CD38 can redirect patient-derived AML T cells against autologous AML blasts, we investigated whether similar effects occurred in vivo. For this purpose, we used the complex karyotype TP53-mutated PDX-3 (AML-4; Figure 4G). Using a lower number of autologous T cells (1 × 106 cells) once a week for 3 subsequent weeks because of sample limitation, we observed T-cell expansion and significant reduction in BM and spleen tumor engraftment only in the mice treated with BN-CD38 (BN-CD38 vs BN-CD38Mut: P = .002, BM; P < .0001, spleen; Figure 4H-I), further supporting the therapeutic potential of BN-CD38 to induce T-cell activation in autologous conditions.
BN-CD38 spares HSCs and noncancer immune cells
A concern with therapeutically targeting CD38 is CD38 antigen expression on the surface of normal HSC precursor cells. Thus, depletion of normal CD38pos HSC precursor cells could result in long-term hematological toxicity. To this end, our data indicate that in colony forming unit, flow cytometry, and mass cytometry assays, BN-CD38 and/or IFN-γ did not perturb the clonogenic potential or the total number of the uncommitted CD34posCD38low/neg HSCs obtained from healthy donors (Figure 5A-D; supplemental Figure 6A-D). Moreover, BN-CD38 and/or IFN-γ induced variable, not statistically significant reduction of the committed CD38pos normal hematopoietic progenitors (Figure 5E; supplemental Figure 6B-D). A trend toward upregulation of CD4posCD69pos and CD8posCD69pos T cells was observed (Figure 5F) but at a level significantly lower than that observed with AML blasts (supplemental Figure 6E) or CD38pos cell lines (supplemental Figure 6F). Of note, we did not observe a fratricidal effect of BN-CD38 on mature BM or PB noncancer cells expressing CD38 (T, B, and NK cells, and monocytes) compared with each internal control (Figure 5G-I; supplemental Figure 6G-H). In contrast to AML blasts, no significant CD38 upregulation was observed in normal BM MNCs exposed to BN-CD38 for 48 hours (Figure 5J-K; supplemental Figure 6I). To further address this subject, we performed a killing assay in which we cocultured the total CD34pos normal population, which contains both HSCs (∼7%) and CD38+ hematopoietic progenitors (∼92%; supplemental Figure 6J-K), together with CD38posCD34neg AML cells (1:10 ratio) and T cells (E:T ratio 1:1) and assessed the BN-CD38 T-cell killing activity of both total healthy CD34pos and AML cells at different concentrations. We did not observe dose-dependent killing of normal HSCs as instead found in the cocultured AML cells (P = .01; Figure 5L). To further investigate the impact of BN-CD38 on normal hematopoietic cells, we treated human CD34pos HSC–engrafted NSG mice (hu-CD34), which produce multilineage human immune cells, with BN-CD38 or controls, weekly for 3 consecutive weeks. Under these conditions, we did not observe differences in BM engraftment or in lineage development between BN-CD38–treated or control-treated mice (supplemental Figure 7A-C). We also did not observe, among the different treatment groups, differences in human HSCs engraftment or hematopoietic lineage development when we used a second CD34pos humanized animal model in which BN-CD38 was administrated together with 3 × 106 autologous T cells (Figure 5M-O; supplemental Figure 7D-F) obtained from the same donor from which the CD34pos cells used for engraftment were isolated.
BN-CD38 spares HSCs and noncancer immune cells. (A) Healthy donor (HD)-derived total BM MNCs were treated with 1.0 ng/mL control human IgG (n = 7), CD38 NB (n = 3), BN-CD38Mut (n = 7), and BN-CD38 (n = 7) and plated in CFC assay for 14 days. Representative images of CFC assay for 2 representative HDs’ BM MNCs showing effect of 4 treatments. Images were acquired in tiles by the City of Hope microscopy core facility using ZEN 3.1 (blue edition, Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH). (B) Violin plot comparing CFU of each treatment group. CFU of each treatment group was normalized to control human IgG for each HD and shown as F.C. over IgG. One-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance. (C-E) Three HD-derived total BM MNCs were treated with 1.0 ng/mL control human IgG, CD38 NB, BN-CD38Mut, or BN-CD38. BM MNCs were collected at 48 and 120 hours after treatment and subjected to surface staining with CD45, CD34, and CD38. (C) Representative dot plot of 2 HDs’ BM MNCs showing effect of control human IgG, CD38NB, BN-CD38Mut, and BN-CD38 treatment on CD34posCD38pos healthy progenitors and CD34posCD38neg HSCs. (D-E) Violin plots compare the effect of different treatment groups on CD34posCD38pos healthy progenitors and CD34posCD38neg HSCs after treatment. The percent CD34posCD38pos and percent CD34posCD38neg of each treatment group was normalized to control human IgG and shown as F.C. over IgG. One-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance. (F-H) HDs’ total BM MNCs (n = 3) treated in panel B were gated in total CD4 or CD8 T cells and each population was assessed for CD69 expression. (F) Violin plots compare the percent CD4posCD69pos and percent CD8posCD69pos activated T cells at 48 hours. One-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance for T-cell activation. (G-H) Violin plots compare percent CD4pos and percent CD8pos T cells over the total cellular population between different treatment groups at 48 and 120 hours. Paired Student t test was used to compare percent frequencies of T cells between treatment groups. (I) HD-derived total PB MNCs were treated with 1.0 ng/mL control human IgG, CD38 NB, BN-CD38Mut, or BN-CD38 for 72 hours and gated for monocytes (n = 5), NK cells (n = 4), B cells (n = 4), and CD4pos and CD8pos T cells (n = 4), followed by gating with DAPI to assess percent killing. Violin plots compare percent killing (DAPI positivity) between different treatment groups. One-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance. (J) Representative dot plot showing CD38 expression in CD45Dim population after treatment of bulk MNCs with 1.0 ng/mL of BN-CD38, BN-CD38Mut, and control human IgG. (K) Violin plot comparing CD38 surface expression in CD45Dim population of AML (n = 7: 5 PB, 1 BM, and 1 leukapheresis [LP]) and HD (n = 3 BM) MNCs treated with 1.0 ng/mL of control human IgG, BN-CD38Mut, or BN-CD38 for 48 hours. BN-CD38 and BN-CD38Mut CD38 surface expression measured by flow cytometry in MFI were normalized to control human IgG. Ordinary 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett multiple comparisons test was used to calculate significance; ∗P < .05. (L) Total CD34pos cells (HSCs and CD38+ progenitors) were isolated from HDs and cocultured with THP1 GFPpos cells (CD34neg; supplemental Figure 6J-K) at a HSCs:THP1 ratio of 1:10, and T cells were added at an E:T (T cells:THP1) of 1:1 overnight in the presence of increasing doses of BN-CD38. The experiment was repeated using n = 2 donors for a total of 4 independent replicates for each point. DAPIneg THP1 GFP and CD34pos alive cell frequencies were determined by gating in the GFP or CD34pos populations, respectively. Each dose frequency was normalized to vehicle control, and simple linear regression analyses were used to determine the BN-CD38 dose effect on THP1 and total CD34pos cells. (M) Schematic representation of the generation and treatment of CD34pos humanized NSG mouse model. Specifically, 5 × 105 CD34pos selected cells from HDs were IV injected into irradiated NSG mice. Once engraftment of human CD45pos cells was confirmed on day 150, mice were randomized into 3 groups: control human IgG (n = 4), BN-CD38Mut (n = 4), and BN-CD38 (n = 5). Each mouse was IV treated with 2.5 mg/kg and 3 million autologous T cells, as indicated. Following 3 treatments, mice were euthanized on day 173, and total BM cells were isolated and subjected to flow cytometry analysis for human immune cell engraftment (hCD45+). (N) Representative contour plots of hCD34 in hCD45pos selected cells. One representative mouse is shown for each treatment group. (O) Bar graph comparing percent of different immune subsets in human CD45pos selected cells in BM, as indicated. Ordinary 1-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used as statistical test. ns, not significant.
BN-CD38 spares HSCs and noncancer immune cells. (A) Healthy donor (HD)-derived total BM MNCs were treated with 1.0 ng/mL control human IgG (n = 7), CD38 NB (n = 3), BN-CD38Mut (n = 7), and BN-CD38 (n = 7) and plated in CFC assay for 14 days. Representative images of CFC assay for 2 representative HDs’ BM MNCs showing effect of 4 treatments. Images were acquired in tiles by the City of Hope microscopy core facility using ZEN 3.1 (blue edition, Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH). (B) Violin plot comparing CFU of each treatment group. CFU of each treatment group was normalized to control human IgG for each HD and shown as F.C. over IgG. One-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance. (C-E) Three HD-derived total BM MNCs were treated with 1.0 ng/mL control human IgG, CD38 NB, BN-CD38Mut, or BN-CD38. BM MNCs were collected at 48 and 120 hours after treatment and subjected to surface staining with CD45, CD34, and CD38. (C) Representative dot plot of 2 HDs’ BM MNCs showing effect of control human IgG, CD38NB, BN-CD38Mut, and BN-CD38 treatment on CD34posCD38pos healthy progenitors and CD34posCD38neg HSCs. (D-E) Violin plots compare the effect of different treatment groups on CD34posCD38pos healthy progenitors and CD34posCD38neg HSCs after treatment. The percent CD34posCD38pos and percent CD34posCD38neg of each treatment group was normalized to control human IgG and shown as F.C. over IgG. One-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance. (F-H) HDs’ total BM MNCs (n = 3) treated in panel B were gated in total CD4 or CD8 T cells and each population was assessed for CD69 expression. (F) Violin plots compare the percent CD4posCD69pos and percent CD8posCD69pos activated T cells at 48 hours. One-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance for T-cell activation. (G-H) Violin plots compare percent CD4pos and percent CD8pos T cells over the total cellular population between different treatment groups at 48 and 120 hours. Paired Student t test was used to compare percent frequencies of T cells between treatment groups. (I) HD-derived total PB MNCs were treated with 1.0 ng/mL control human IgG, CD38 NB, BN-CD38Mut, or BN-CD38 for 72 hours and gated for monocytes (n = 5), NK cells (n = 4), B cells (n = 4), and CD4pos and CD8pos T cells (n = 4), followed by gating with DAPI to assess percent killing. Violin plots compare percent killing (DAPI positivity) between different treatment groups. One-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance. (J) Representative dot plot showing CD38 expression in CD45Dim population after treatment of bulk MNCs with 1.0 ng/mL of BN-CD38, BN-CD38Mut, and control human IgG. (K) Violin plot comparing CD38 surface expression in CD45Dim population of AML (n = 7: 5 PB, 1 BM, and 1 leukapheresis [LP]) and HD (n = 3 BM) MNCs treated with 1.0 ng/mL of control human IgG, BN-CD38Mut, or BN-CD38 for 48 hours. BN-CD38 and BN-CD38Mut CD38 surface expression measured by flow cytometry in MFI were normalized to control human IgG. Ordinary 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett multiple comparisons test was used to calculate significance; ∗P < .05. (L) Total CD34pos cells (HSCs and CD38+ progenitors) were isolated from HDs and cocultured with THP1 GFPpos cells (CD34neg; supplemental Figure 6J-K) at a HSCs:THP1 ratio of 1:10, and T cells were added at an E:T (T cells:THP1) of 1:1 overnight in the presence of increasing doses of BN-CD38. The experiment was repeated using n = 2 donors for a total of 4 independent replicates for each point. DAPIneg THP1 GFP and CD34pos alive cell frequencies were determined by gating in the GFP or CD34pos populations, respectively. Each dose frequency was normalized to vehicle control, and simple linear regression analyses were used to determine the BN-CD38 dose effect on THP1 and total CD34pos cells. (M) Schematic representation of the generation and treatment of CD34pos humanized NSG mouse model. Specifically, 5 × 105 CD34pos selected cells from HDs were IV injected into irradiated NSG mice. Once engraftment of human CD45pos cells was confirmed on day 150, mice were randomized into 3 groups: control human IgG (n = 4), BN-CD38Mut (n = 4), and BN-CD38 (n = 5). Each mouse was IV treated with 2.5 mg/kg and 3 million autologous T cells, as indicated. Following 3 treatments, mice were euthanized on day 173, and total BM cells were isolated and subjected to flow cytometry analysis for human immune cell engraftment (hCD45+). (N) Representative contour plots of hCD34 in hCD45pos selected cells. One representative mouse is shown for each treatment group. (O) Bar graph comparing percent of different immune subsets in human CD45pos selected cells in BM, as indicated. Ordinary 1-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used as statistical test. ns, not significant.
Discussion
Unlike MM or T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the clinical relevance of CD38 as a target in AML remains to be clearly demonstrated. Of note, CD38 expression in AML cell lines and patients with primary AML can be induced by all-trans retinoic acid.35,36 Consistent with previous studies,17,18,32 we show here that IFN-γ induces CD38 upregulation in AML blasts,37 through the activation of IRF-1, a transcription factor that plays a pivotal role in IFN-γ intracellular signaling, as demonstrated by promoter analysis and functional experiments.23,38 IRF-1 is a tumor suppressor gene39-41 located in the long arm of chromosome 5. Interestingly, we observed IRF-1 upregulation in all AML cell lines and primary samples, including those carrying monoallelic 5q deletion, a chromosomal aberration found in ∼15% of patients with AML and myelodysplastic syndromes.42
Consistent with recent results demonstrating that mouse immune cells produce high levels of IFN-γ that block AML growth,43 we show the anticlonogenic activity of IFN-γ on AML LSCs but not on normal HSCs. Gene expression profiling highlighted that primary AML blasts exposed to IFN-γ upregulate genes involved in apoptosis, DNA repair, and reactive oxygen species, and downregulate genes involved in Wnt signaling that supports LSCs clonogenicity and AML survival.44-46
Considering these results, we reasoned that we could target not only CD38pos but also CD38neg AML blasts with immunotherapeutics that induce IFN-γ degranulation from T cells, and thus we designed and produced the BN-CD38 chain T-cell engager. We demonstrated that not only did the BN-CD38 directly kill CD38pos AML blasts but also activated engaged T cells to produce IFN-γ. We further showed that this approach successfully converted CD38neg into CD38pos blasts, thereby expanding the BN-CD38–targetable AML cell population.
Le Dieu et al have characterized an aberrant T-cell activation signature in patients with AML47 and demonstrated that although T cells isolated from patients with AML are phenotypically effector cytotoxic T lymphocytes, they exhibit impairment in effectively forming immune synapses.47,48 We demonstrate in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo that BN-CD38 produced an effective synapse between T cells and CD38pos AML cells. Importantly, the BN-CD38–engaged T cells efficiently degranulated and released measurable levels of IFN-γ, which proceeded to induce high CD38 expression on both CD38pos and CD38neg AML blasts. Using CyTOF immunophenotyping assays, we demonstrated that BN-CD38 significantly reduced AML blasts concurrently with expansion of autologous CD4pos and CD8pos T cells and lack of a fratricide effect toward other CD38pos mature cells (ie, NK cells, NK T cells, or B cells). Interestingly, in the BM samples obtained from patients with AML, BN-CD38 not only spares CD38pos noncancer immune subsets but expanded NK T cells, NK cells, and CD14posCD16neg classical monocytes, which have high capacity for phagocytosis, migration, and innate immune responses.33 Moreover, in healthy donor BM samples, BN-CD38 did not compromise engraftment and normal hematopoiesis in 2 independent models of CD34pos humanized animals, supporting lack of hematological toxicity that could prevent the broad use of this molecule. Although the mechanisms of CD38 regulation in normal HSCs upon IFN-γ treatment will need further investigation, we suggest that this effect may be because of a different epigenetic and transcriptional signature of HSCs compared with LSCs, as previously reported.49,50
In AML, CD33, CD123, CLEC12A, and FLT3 represent suitable targets for T-cell engagers51 but, to date, the clinical benefits have been limited. The limitation to successfully use these engagers ranges from the immunophenotypic heterogeneity of AML cells, to the overlap of TAAs with those on normal HSCs, to the limited immune activity of T cells present in patients with AML.52 BN-CD38 exhibits a potent cytotoxicity profile with an IC50 ranging from 0.01 to 0.1 ng/mL after overnight incubation at an E:T ratio of 1:1, compared with other T-cell engagers, which have an IC50 range of 0.01 to 68 ng/mL at an E:T of 5:1 or 10:1 after 48 hours of AML cell lines and effectors coculture.53-56 We also show that BN-CD38 exhibits potent cytotoxicity in in vivo models without the need of using preactivated T cells as reported with many other engagers including those targeting CD33, FLT3, and BCMA.53,56-58
CD38-directed chimeric antigen receptor T cells have also been developed and tested as a potential AML therapy.59-62 In preclinical experiments, CD38-directed chimeric antigen receptor T cells mediated killing against CD38pos blasts, but the ability of these cells to eliminate LSCs was not fully characterized.59 In contrast, we show that BN-CD38 can target LSCs, through mechanisms that are IFN-γ dependent, further supporting that CD38-BN can induce the release of effective levels of IFN-γ even in the context of the AML immune suppressive environment concomitantly blocking LSCs clonogenicity and enhancing their direct targeting, an observation that, to the best of our knowledge, has not been reported before.
Although BN-CD38 increased the survival of mice xenografted with different AML cell lines and primary leukemia cells, it is reasonable to assume that patients with AML with a higher frequency of CD38− LSCs may require a longer treatment schedule to achieve remission, a question that we are planning to address in the clinical setting.
Taken together, here we report a novel strategy to specifically target LSCs, and in doing so, we demonstrate that the biologic activities of BN-CD38 overcome the AML tumor suppressive environment and potentiate the efficacy of CD38-directed T-cell therapy, providing the scientific rationale for rapidly translating BN-CD38 into the clinic as an effective therapeutic approach for AML.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Tinisha McDonald, Kelly Synold, and Elena Pulkinen for technical support in this work. The authors also thank Hyeran Choi for assisting with fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis of BIONICs constructs. The authors thank Yuriy Shostak and Christoph Pittius for the scientific and administrative support in this work.
Research reported in this publication was, in part, supported by the generous contributions of the Nason-Hollingsworth Project for Multiple Myeloma (A.K., F.P.). This research was also supported by the City of Hope Preclinical Drug Development Venture Program Award (F.P., J.C.W., G.M.), and partially supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Cancer Institute (NCI) grants R01-CA238429 (F.P.) and R50-CA252135 (E.C.). Research reported in this publication included work performed at the City of Hope X-ray, Liquid Tissue Bank, Analytical Cytometry, and Integrative Genomics, and Small Imaging cores supported by the NIH, NCI under award number P30CA033572.
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not represent the official views of the National Cancer Institute or the National Institutes of Health.
Authorship
Contribution: M. Murtadha, M.P., L.L., B.Z., G.M., J.C.W., and F.P. designed the research; M. Murtadha, M.P., Y.Z., E.C., O.N., A.A.D., M.S., H.V., T.T., M. Moloudizargari, A.G., K.L., C.O., L.N., and A.D. performed research; L.G. provided support with selection of the patient samples for the PDX models; M. Murtadha, M.P., and J.F.S. analyzed data; A.P. and A.C. provided biostatistical support; A.P. provided bioinformatics support; M. Murtadha, M.P., J.F.S., G.M., J.C.W., and F.P. wrote the manuscript; A.K. scientifically edited the manuscript; and all authors reviewed and approved of the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: M. Murtadha, M.P., G.M., J.C.W., and F.P. have pending patents covering certain aspects of this technology in anticipation of commercialization. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Flavia Pichiorri, Department of Hematology and Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation, Judy and Bernard Briskin Center for Multiple Myeloma Research, Department of Hematologic Malignancies Translational Science, Beckman Research Institute, City of Hope, 1500 Duarte Rd, Duarte, CA 91010; email: fpichiorri@coh.org; John C. Williams, Department of Cancer Biology and Molecular Medicine, Beckman Research Institute, City of Hope, 1500 Duarte Rd, Duarte, CA 91010; email: jcwilliams@coh.org; and Guido Marcucci, Department of Hematologic Malignancies Translational Science, Beckman Research Institute, 1500 Duarte Rd, Duarte, CA 91010; email: gmarcucci@coh.org.
References
Author notes
M. Murtadha, M.P., and Y.Z. contributed equally to this work.
The complete microarray data set has been deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) at the National Center for Biotechnology Information and is accessible through GEO Series accession number GSE253922.
The mass cytometry data and the imaging data in Figure 5A are publicly available through Precision Oncology Software Environment Interoperable Data Ontologies Network (POSEIDON) cloud storage; https://app.globus.org/file-manager?origin_id=80eb4c76-b7fe-4b04-96c9-121ac058cc6a&origin_path=%2Fflavia%2Fcd38dire%2F.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

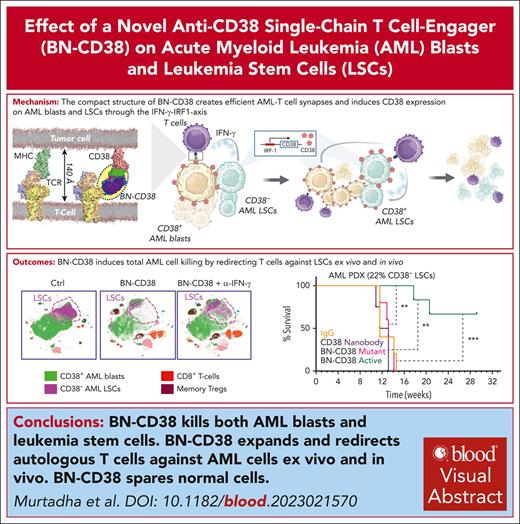
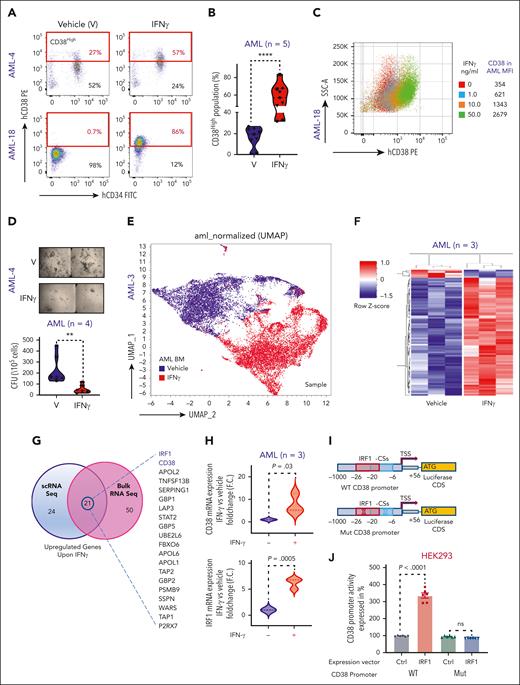
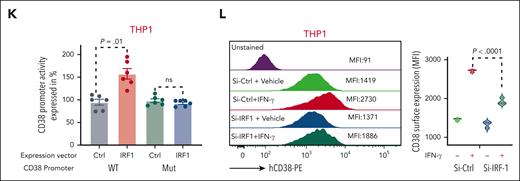
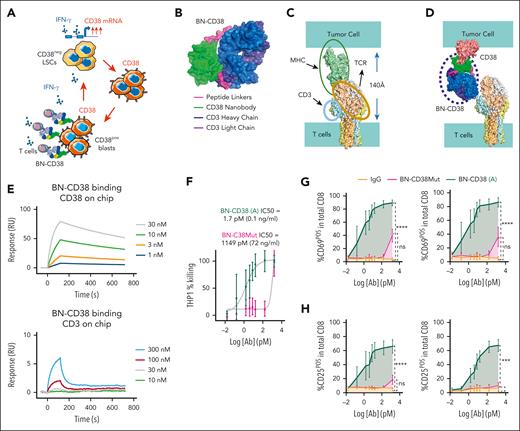
![BN-CD38 shows potent antileukemic efficacy in vitro and ex vivo. (A) Schematic illustration of the therapeutic rationale to target CD38neg LSCs with T-cell engagers against CD38 to eradicate AML by uncovering the IFN-γ/CD38 regulatory loop. Graphical representation of (B) BN-CD38 projected structure; (C) distance between T cell and tumor cell membranes upon TCR-MHC interaction; and (D) spatial prediction of how BN-CD38 interaction with T cell (CD3) and tumor cell (CD38) is similar to the interaction observed in the MHC-TCR complex. (E) Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensorgrams for CD38 and CD3 binding with different concentrations of BN-CD38. (F) THP1 green fluorescent protein–positive (GFPpos) cells were cocultured with healthy donor T cells at an E:T ratio of 1:1 overnight (16 hours) in the presence of increasing doses of BN-CD38 active (A) and BN-CD38Mut. THP1 cell killing was determined with 7-aminoactinomycin D staining and gating on GFPpos cells by flow cytometry. IC50 curves are shown for BN-CD38 and BN-CD38Mut, and data are represented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of 5 independent healthy donors. (G-H) Samples in panel F were also used to assess the induction of early (CD69) and late (CD25) T-cell activation markers in the total CD4 or CD8 T cells. Dose-dependent T-cell activation curves are represented as mean ± SEM of 3 healthy donors. Ordinary 1-way ANOVA test was used for calculation of statistical significance. (I-K) Total AML cells (n = 7) were treated with 1.0 ng/mL IgG, CD38-NB, BN-CD38 Mut, or BN-CD38 for 5 days and subjected to cell surface staining for CD34 and CD38. (I) Representative flow cytometry contour plots of 2 representative patient-derived AML samples and (J-K) violin plots show elimination of total AML cells (CD34posCD38pos blasts and CD34posCD38neg LSCs) with BN-CD38 compared with control treatments (IgG, CD38-NB, and BN-CD38Mut). Cell frequencies were normalized to the paired control human IgG treatment and shown as F.C. Overall, 2 of 7 patients were not assessed with BN-CD38Mut and CD38 NB. (L) Total AML cells were treated with 1.0 ng/mL control human IgG, CD38NB, BN-CD38 Mut, or BN-CD38 and plated in CFC assay for 14 days. Violin plot illustrates the normalized CFU F.C. for each treatment group compared with the paired IgG (CD38 NB, n = 4 PB; BN-CD38 Mut, n = 4 PB; BN-CD38, n = 11 [9 PB and 2 BM]). Each dot in each treatment group represents 1 individual patient. (M) Schematic cartoon and representative flow cytometry contour plot of the experimental design and gating strategy used to assess apoptosis of CD38neg AML blasts by autologous T cells. (N) Contour plots of 2 representative patients with AML showing annexin-V/4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining of the CD38neg gated population after treatment with IgG, BN-CD38Mut, or BN-CD38 SNs in the presence of autologous T cells. (O) Violin plot showing changes in induced apoptosis in each treatment group. Unpaired Student t test was used to calculate statistical significance in n = 4 patients with AML; ∗∗∗P < .001, n = 4. For panels G-H,J-L, 1-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance between different groups; ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001; and ∗∗∗∗P < .0001. E, effector T cells; ns, not significant; T, target cancer cells.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/143/16/10.1182_blood.2023021570/2/m_blood_bld-2023-021570-gr2io.jpeg?Expires=1769301402&Signature=2XTtEHWm8~TAZpPefuQ~EiQEFm8Jscu583l2bamjV4mLweTk0fh6pcme9mP168GbxgQG6JjyNaghNP67ClmtQ0DMj~19m3k1ZZA8Xmk0OabPX5oi5Vdz3BuLLuEVjGB8NZ5j7j3Zgie2PtZhIBYqgy1eXbnSPQDP4V3u-a4bU84l1bGCjOQ-J~cAvGy7TJ~wuQahFAkbM6gtclkkLOZc9~GpGvIFOSQl2HjFgk9ldRtPTeOKyOJowgpzHED6ebDF~h0kFGbP8ySzsHMDdBXUuFV8iwmv31kPJTFrdOOuPxS97ytV8JvVR8XMxo7uDlxhlO8nnW2WLJofryBxjk165g__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
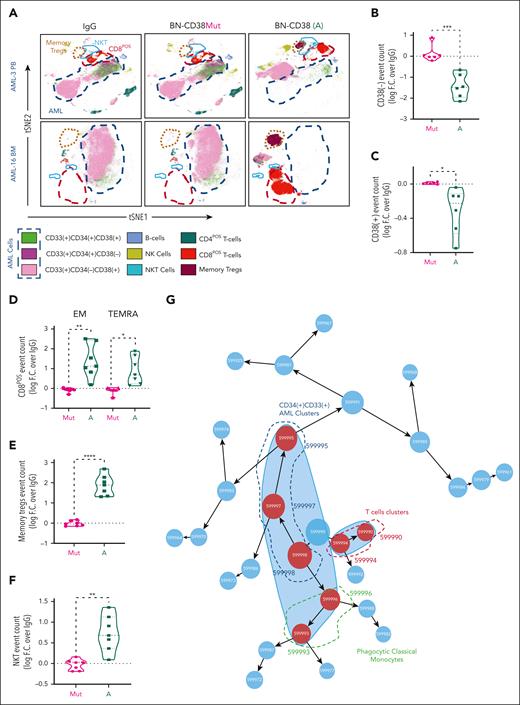
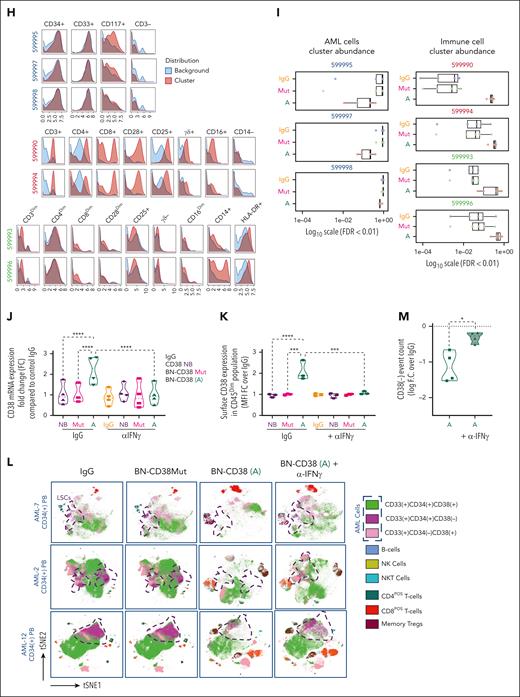
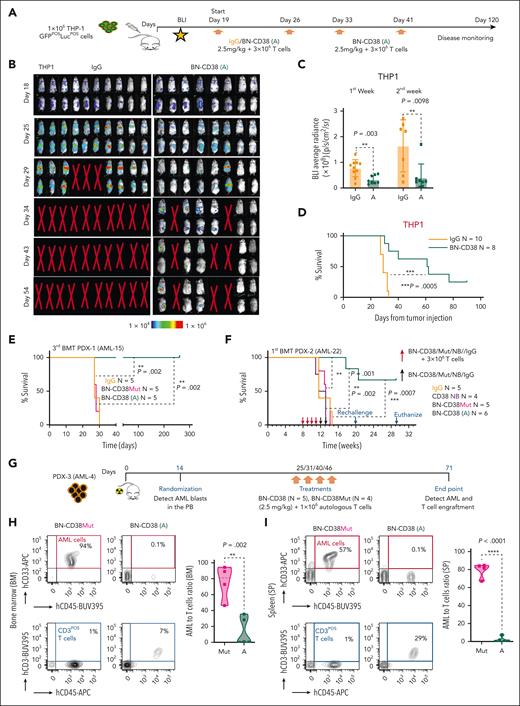
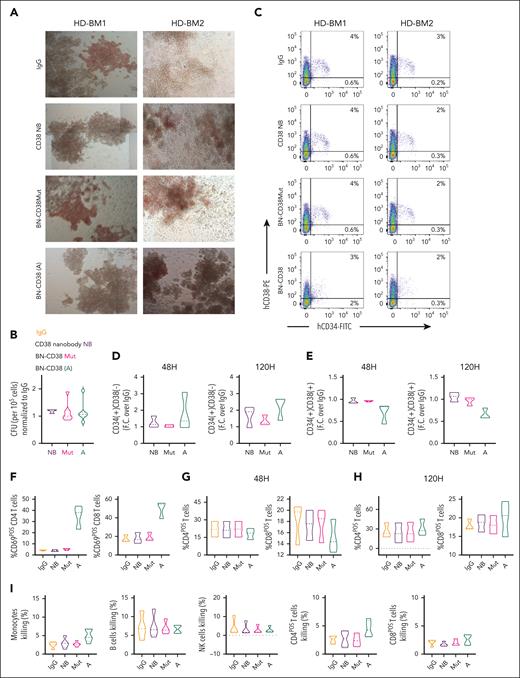
![BN-CD38 spares HSCs and noncancer immune cells. (A) Healthy donor (HD)-derived total BM MNCs were treated with 1.0 ng/mL control human IgG (n = 7), CD38 NB (n = 3), BN-CD38Mut (n = 7), and BN-CD38 (n = 7) and plated in CFC assay for 14 days. Representative images of CFC assay for 2 representative HDs’ BM MNCs showing effect of 4 treatments. Images were acquired in tiles by the City of Hope microscopy core facility using ZEN 3.1 (blue edition, Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH). (B) Violin plot comparing CFU of each treatment group. CFU of each treatment group was normalized to control human IgG for each HD and shown as F.C. over IgG. One-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance. (C-E) Three HD-derived total BM MNCs were treated with 1.0 ng/mL control human IgG, CD38 NB, BN-CD38Mut, or BN-CD38. BM MNCs were collected at 48 and 120 hours after treatment and subjected to surface staining with CD45, CD34, and CD38. (C) Representative dot plot of 2 HDs’ BM MNCs showing effect of control human IgG, CD38NB, BN-CD38Mut, and BN-CD38 treatment on CD34posCD38pos healthy progenitors and CD34posCD38neg HSCs. (D-E) Violin plots compare the effect of different treatment groups on CD34posCD38pos healthy progenitors and CD34posCD38neg HSCs after treatment. The percent CD34posCD38pos and percent CD34posCD38neg of each treatment group was normalized to control human IgG and shown as F.C. over IgG. One-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance. (F-H) HDs’ total BM MNCs (n = 3) treated in panel B were gated in total CD4 or CD8 T cells and each population was assessed for CD69 expression. (F) Violin plots compare the percent CD4posCD69pos and percent CD8posCD69pos activated T cells at 48 hours. One-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance for T-cell activation. (G-H) Violin plots compare percent CD4pos and percent CD8pos T cells over the total cellular population between different treatment groups at 48 and 120 hours. Paired Student t test was used to compare percent frequencies of T cells between treatment groups. (I) HD-derived total PB MNCs were treated with 1.0 ng/mL control human IgG, CD38 NB, BN-CD38Mut, or BN-CD38 for 72 hours and gated for monocytes (n = 5), NK cells (n = 4), B cells (n = 4), and CD4pos and CD8pos T cells (n = 4), followed by gating with DAPI to assess percent killing. Violin plots compare percent killing (DAPI positivity) between different treatment groups. One-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used to calculate statistical significance. (J) Representative dot plot showing CD38 expression in CD45Dim population after treatment of bulk MNCs with 1.0 ng/mL of BN-CD38, BN-CD38Mut, and control human IgG. (K) Violin plot comparing CD38 surface expression in CD45Dim population of AML (n = 7: 5 PB, 1 BM, and 1 leukapheresis [LP]) and HD (n = 3 BM) MNCs treated with 1.0 ng/mL of control human IgG, BN-CD38Mut, or BN-CD38 for 48 hours. BN-CD38 and BN-CD38Mut CD38 surface expression measured by flow cytometry in MFI were normalized to control human IgG. Ordinary 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett multiple comparisons test was used to calculate significance; ∗P < .05. (L) Total CD34pos cells (HSCs and CD38+ progenitors) were isolated from HDs and cocultured with THP1 GFPpos cells (CD34neg; supplemental Figure 6J-K) at a HSCs:THP1 ratio of 1:10, and T cells were added at an E:T (T cells:THP1) of 1:1 overnight in the presence of increasing doses of BN-CD38. The experiment was repeated using n = 2 donors for a total of 4 independent replicates for each point. DAPIneg THP1 GFP and CD34pos alive cell frequencies were determined by gating in the GFP or CD34pos populations, respectively. Each dose frequency was normalized to vehicle control, and simple linear regression analyses were used to determine the BN-CD38 dose effect on THP1 and total CD34pos cells. (M) Schematic representation of the generation and treatment of CD34pos humanized NSG mouse model. Specifically, 5 × 105 CD34pos selected cells from HDs were IV injected into irradiated NSG mice. Once engraftment of human CD45pos cells was confirmed on day 150, mice were randomized into 3 groups: control human IgG (n = 4), BN-CD38Mut (n = 4), and BN-CD38 (n = 5). Each mouse was IV treated with 2.5 mg/kg and 3 million autologous T cells, as indicated. Following 3 treatments, mice were euthanized on day 173, and total BM cells were isolated and subjected to flow cytometry analysis for human immune cell engraftment (hCD45+). (N) Representative contour plots of hCD34 in hCD45pos selected cells. One representative mouse is shown for each treatment group. (O) Bar graph comparing percent of different immune subsets in human CD45pos selected cells in BM, as indicated. Ordinary 1-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was used as statistical test. ns, not significant.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/143/16/10.1182_blood.2023021570/2/m_blood_bld-2023-021570-gr5jo.jpeg?Expires=1769301402&Signature=QM1RJpd0TVHX3Vs6MjBbK0CeZuV1vMN51hTAWc6Ss3oYDBQdYMEIIuv5XvTYmfALQRpV8dSi-xrDt7oR8qt6HUoHbgv-ZhyUChWpDf18z3VOfkRF-x7yOYja0KWOmJ2muWbbBJ0q3FJ7~0V9E6LI9EKHjTh29OEpLT3FIfFI4goblegeLiJ11DtD-DZb-0Amq0O3~pIaI2Sz4DjqwyQBpNiTlEwFdqVnySQmGuHNrRxsf-8BEmaZlJS9RZCk3L~PbK-gXW0CDMjKVRRhKK3FjLgBG4AEhLmpGiaIGezteoqXAUB8zbl8OM1wt7SecjxRxb~o96BflQmv2Owh4mcavw__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal