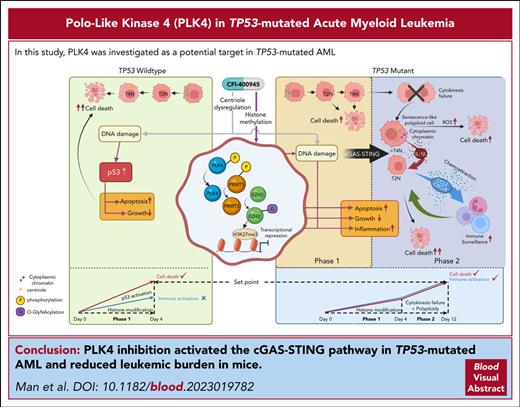
Key Points
A novel PLK4/PRMT5/EZH2/H3K27me3 axis was demonstrated upon PLK4 inhibition in both TP53 wild-type and mutated AML.
PLK4 inhibition activated the cGAS-STING pathway in TP53-mutated AML.
Abstract
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with TP53 mutation is one of the most lethal cancers and portends an extremely poor prognosis. Based on in silico analyses of druggable genes and differential gene expression in TP53-mutated AML, we identified pololike kinase 4 (PLK4) as a novel therapeutic target and examined its expression, regulation, pathogenetic mechanisms, and therapeutic potential in TP53-mutated AML. PLK4 expression was suppressed by activated p53 signaling in TP53 wild-type AML and was increased in TP53-mutated AML cell lines and primary samples. Short-term PLK4 inhibition induced DNA damage and apoptosis in TP53 wild-type AML. Prolonged PLK4 inhibition suppressed the growth of TP53-mutated AML and was associated with DNA damage, apoptosis, senescence, polyploidy, and defective cytokinesis. A hitherto undescribed PLK4/PRMT5/EZH2/H3K27me3 axis was demonstrated in both TP53 wild-type and mutated AML, resulting in histone modification through PLK4-induced PRMT5 phosphorylation. In TP53-mutated AML, combined effects of histone modification and polyploidy activated the cGAS-STING pathway, leading to secretion of cytokines and chemokines and activation of macrophages and T cells upon coculture with AML cells. In vivo, PLK4 inhibition also induced cytokine and chemokine expression in mouse recipients, and its combination with anti-CD47 antibody, which inhibited the “don’t-eat-me” signal in macrophages, synergistically reduced leukemic burden and prolonged animal survival. The study shed important light on the pathogenetic role of PLK4 and might lead to novel therapeutic strategies in TP53-mutated AML.
Introduction
TP53-mutated acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome portend an extremely grave prognosis and are refractory to conventional chemotherapy and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cells transplantation.1,2 A 10-day course of decitabine,3 APR246,4 and magrolimab5 might induce remission, which is characteristically transient, and its benefit to patients remains to be determined.
Pololike kinases (PLKs) are serine/threonine kinases essential for cell cycle progression, mitosis, and cytokinesis.6 Five mammalian PLKs have been identified, and in particular, PLK4 was known as the master regulator of centriole duplication and positive modulator of cell cycle progression by phosphorylating key effectors including STIL, FBXW5, and ECT2.7-9 During oncogenesis, increased PLK4 expression resulted in an abnormal increase in centriole number and centrosome amplification, leading to chromosomal instability and aneuploidy.10 PLK4 also promoted tumorigenesis through multiple pathways such as ATR/CHEK1, PI3K/AKT, and the NF-κB axis.11-13
p53 has been shown to suppress PLK4 expression via methylation of the PLK4 promoter and histone demethylation in liver and lung cancer.14,15 Aberrant regulation of PLK4 due to defective p53 signaling has been associated with a wide spectrum of TP53-mutated cancers,16 underscoring the pathogenetic role of PLK4 in TP53-mutated cancers.16 PLK4 inhibition generated supernumerary centrioles and multipolar mitotic spindles that perpetuated errors of DNA replication during chromosome segregation.7 These cells could progress through the cell cycle, leading to polyploidy and eventually mitotic catastrophe.17
In this study, we identified PLK4 as a potential target in AML and hypothesized that its inhibition might have antileukemia effects and distinct therapeutic mechanisms in TP53 wild-type and mutant AML. The information arising from this study might result in novel therapeutic strategies against these AML subtypes.
Methods
Detailed descriptions of materials and methods, including phagocytosis and T cell coculture assays, xenotransplantation studies, and statistical analyses, are given in supplemental Methods, available at the Blood website.
Time-lapse live cell imaging
AML cell lines were treated with PLK4 inhibitor CFI-400945 for 18 hours, and time-lapsed live cell images were taken using Nikon Ti2-E Widefield Microscope at 37°C, 5% CO2. Brightfield and fluorescent images (magnification x20) were taken every 3 minutes at 4 predetermined fields for 16 hours. Images were processed using MetaMorph 7.8.0.0 software.
Cell senescence assay
Cell lines were cultured at 0.2 × 106 cells per mL, treated with CFI-400945 for 2 days, washed with phosphate-buffered saline, fixed with 1X fixative solution (provided in the CellEvent Senescence Green Flow Cytometry Assay Kit) for 15 minutes at room temperature, and incubated with senescence β-galactosidase staining solution at 37°C overnight in a dry incubator. The cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline and overlaid with 70% glycerol.
RNA sequencing and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
RNA sequencing analysis was performed as previously reported.18 Reads passing quality control were mapped to reference human genome (GRCh38) with GENCODE19 annotation (release 38) using STAR. Differential gene expression analysis was implemented based on raw counts matrix by DESeq2 with default parameters. ClusterProfiler R package20 was used for gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) based on gene set collections in Molecular Signatures Database (MsigDB). ChIP assay has been described previously.21 Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (QPCR) analysis was performed using specific primers (supplemental Table 5). Input genomic DNA was used as the reference. Human SP8 was included as a negative control.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Human cytokines and chemokines were quantified using Legendplex Multi-Analyte Flow Assay Kit Human Inflammation Panel 1. Cell lysates were prepared using Mammalian Protein Extraction Reagent (M-PER), and cGAMP in cytosol was measured using a 2’3’-cGAMP ELISA Kit.
Experiments involving mice were approved by the Committee of the Use of Laboratory Animals for Teaching and Research of the University of Hong Kong. Primary AML samples and cord blood CD34+ progenitors were obtained from patients and healthy donors with consent, in accordance to the Declaration of Helsinki (Institutional Review Board reference number UW 05-183 T/846).
Results
PLK4 expression and dependence in TP53 wild-type and mutated AML
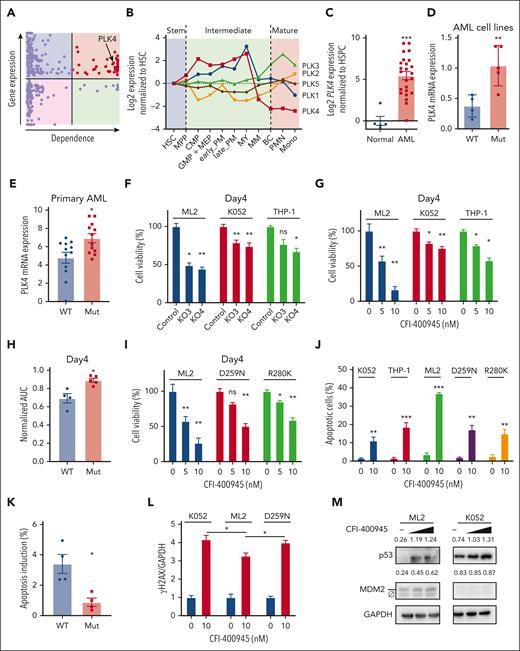
To identify novel therapeutic targets in TP53-mutated AML, we performed in silico analyses to examine druggable genes that were preferentially expressed in this AML subtype with reference to the Beat AML and Leucegene databases. Their potential pathogenetic role was examined based on data from CRISPR/Cas9 dropout screen that were provided by the Dependency Map (DepMap) portal. Of the 3953 druggable genes identified from the DGldb database, 310 were differentially expressed between TP53-mutated and normal karyotype AML. These differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were analyzed using the DepMap database with a focus on 6 TP53-mutated AML cell lines (HEL, HEL9217, SET-2, F36P, KO52, and MONOMAC1), excluding those with characteristic driver fusion genes. A total of 45 genes were shown to have essential functions in these cell lines (Figure 1A, supplemental Figure 1A, and supplemental Table 1). In particular, PLK4 was shown to be highly expressed in TP53-mutated AML compared with other AML subtypes (supplemental Figure 1B). Moreover, in human and mouse, PLK4 was highly expressed in early hematopoietic progenitors and down-regulated along differentiation (Figure 1B and supplemental Figure 1C). The conserved expression profile of PLK4 in hematopoiesis was unique among other PLK isoforms, and its high expression in proliferative progenitors suggested it might be a potential therapeutic target in leukemogenesis. In fact, PLK4 showed significantly higher expression in primary bone marrow samples from patients with AML than those from healthy donors (Figure 1C).
Differential effects of PLK4 inhibition on TP53 wild-type and mutated AML. (A) The expression (Beat AML and Leucegene databases) and dependency (Depmap database) profile of 310 druggable genes (DGIdb), which were differentially expressed in TP53-mutated AML when compared with those with normal karyotype. Each dot represents 1 gene. Red color indicates genes that were upregulated and essential in TP53-mutated AML, and PLK4 was 1 of them. (B) In humans, public database (Bloodspot) showed the lowest PLK4 messenger RNA (mRNA) expression in mature cells compared with hematopoietic stem and intermediate cells, whereas other PLK proteins showed fluctuating expression during hematopoietic differentiation. (C) Reverse transcription QPCR (RT-QPCR) analysis showed upregulated PLK4 expression in human AML (n = 24) compared with normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells (n = 5). (D-E) Higher PLK4 mRNA expression in TP53-mutated human AML cell line (D) (n = 9) and primary AML cell line (E) (n = 24). (F-G) On day 4, PLK4-knockout by CRISPR/Cas9 (F) or PLK4 inhibitor (CFI-400945) (G) significantly suppressed leukemia growth in TP53 wild-type AML cell line ML2 but less so in TP53-mutated AML cell line K052 and THP1 (n = 3). (H) On day 4 of treatment, CFI-400945 (10 nM) treatment induced more suppression in wild-type (WT) than the TP53 mutant (Mut) AML cell lines (n = 9) as shown by a small area under curve (AUC). (I) CFI-400945 treatment induced more suppression in ML-2 than the TP53-mutant derivatives. (J) CFI-400945 treatment induced more apoptosis in ML-2 compared with K052, THP1, and TP53-mutant knockin ML2 on day 1 (n = 3). (K) CFI-400945 treatment (20 nM) induced higher level of apoptosis in TP53 WT primary AML compared with TP53 Mut primary AML on day 1 (n = 8). (L) DNA damage, as enumerated by γH2AX based on western blot and ImageJ analysis, was observed in both TP53 wild-type and mutated ML2 cell line (n = 3). (M) Representative western blot showing CFI-400945 (10-20 nM) activated p53 signaling in ML2 but not in K052. The number above the blots indicate the quantification of p53 and MDM2 normalized by GAPDH protein. Ø indicates a nonspecific band of MDM2. HSC, hematopoietic stem cell.
Differential effects of PLK4 inhibition on TP53 wild-type and mutated AML. (A) The expression (Beat AML and Leucegene databases) and dependency (Depmap database) profile of 310 druggable genes (DGIdb), which were differentially expressed in TP53-mutated AML when compared with those with normal karyotype. Each dot represents 1 gene. Red color indicates genes that were upregulated and essential in TP53-mutated AML, and PLK4 was 1 of them. (B) In humans, public database (Bloodspot) showed the lowest PLK4 messenger RNA (mRNA) expression in mature cells compared with hematopoietic stem and intermediate cells, whereas other PLK proteins showed fluctuating expression during hematopoietic differentiation. (C) Reverse transcription QPCR (RT-QPCR) analysis showed upregulated PLK4 expression in human AML (n = 24) compared with normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells (n = 5). (D-E) Higher PLK4 mRNA expression in TP53-mutated human AML cell line (D) (n = 9) and primary AML cell line (E) (n = 24). (F-G) On day 4, PLK4-knockout by CRISPR/Cas9 (F) or PLK4 inhibitor (CFI-400945) (G) significantly suppressed leukemia growth in TP53 wild-type AML cell line ML2 but less so in TP53-mutated AML cell line K052 and THP1 (n = 3). (H) On day 4 of treatment, CFI-400945 (10 nM) treatment induced more suppression in wild-type (WT) than the TP53 mutant (Mut) AML cell lines (n = 9) as shown by a small area under curve (AUC). (I) CFI-400945 treatment induced more suppression in ML-2 than the TP53-mutant derivatives. (J) CFI-400945 treatment induced more apoptosis in ML-2 compared with K052, THP1, and TP53-mutant knockin ML2 on day 1 (n = 3). (K) CFI-400945 treatment (20 nM) induced higher level of apoptosis in TP53 WT primary AML compared with TP53 Mut primary AML on day 1 (n = 8). (L) DNA damage, as enumerated by γH2AX based on western blot and ImageJ analysis, was observed in both TP53 wild-type and mutated ML2 cell line (n = 3). (M) Representative western blot showing CFI-400945 (10-20 nM) activated p53 signaling in ML2 but not in K052. The number above the blots indicate the quantification of p53 and MDM2 normalized by GAPDH protein. Ø indicates a nonspecific band of MDM2. HSC, hematopoietic stem cell.
To confirm these observations, PLK4 expression was examined in different AML cell lines (Figure 1D) and primary AML samples (Figure 1E and supplemental Table 2), showing higher levels in AML carrying TP53 mutations. Correlation between p53 signaling and PLK4 expression was further examined in an isogenic system in which TP53 was knocked out in hitherto wild-type MOLM13, MV4-11, and ML2 cell lines (supplemental Figure 1D-E). Induction of CDKN1A expression by etoposide was used as a surrogate of p53 signaling in these experiments (supplemental Figure 1E lower panel). In wild-type TP53 AML, induction of p53 signaling was associated with downregulation of PLK4 expression (supplemental Figure 1E upper panel). Knockout (KO) of TP53 ameliorated the latter responses and paradoxically induced a significant increase in PLK4 expression in ML2 cell line. There was no significant change in PLK4 expression upon etoposide treatment in TP53-mutated AML cell lines, consistent with the notion that PLK4 expression was suppressed upon the activation of the p53 signaling pathway.
PLK4 inhibition induced early inhibitory response in TP53 wild-type AML
To ascertain the pathogenetic role of PLK4 in AML, PLK4 functions were perturbed by genetic knockout using CRISPR/Cas9 (supplemental Figure 1F), knockdown using short hairpin RNA (shRNA) (supplemental Figure 1G), or pharmacologic inhibition by CFI-400945, CFI-400437, and centrinone-B. Antileukemia effects were examined at different time points. On day 4 of treatment, PLK4 inhibition significantly suppressed the growth of TP53 wild-type AML cell lines but only mildly affected that of TP53-mutant lines (Figure 1F-H and supplemental Figure 1H-J). The observation was confirmed in an isogenic system, in which PLK4 inhibition showed less suppressive effects on TP53 mutation knockin derivative line compared with the parental cell line (Figure 1I and supplemental Figure 1I-J). Furthermore, PLK4 inhibition by CFI-400945 for day 1 was associated with a preferential increase in apoptosis in TP53 wild-type over mutant AML cell lines and primary samples (Figure 1J-K). PLK4 inhibition resulted in DNA damage in both TP53 wild-type and mutated AML (Figure 1L), reminiscent of its effects on diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.22 In TP53-mutated AML, CFI-400945 induced DNA damage (Figure 1L) but without significant increase in p53 signal (Figure 1M). The latter was associated with the suppression of AML growth.23
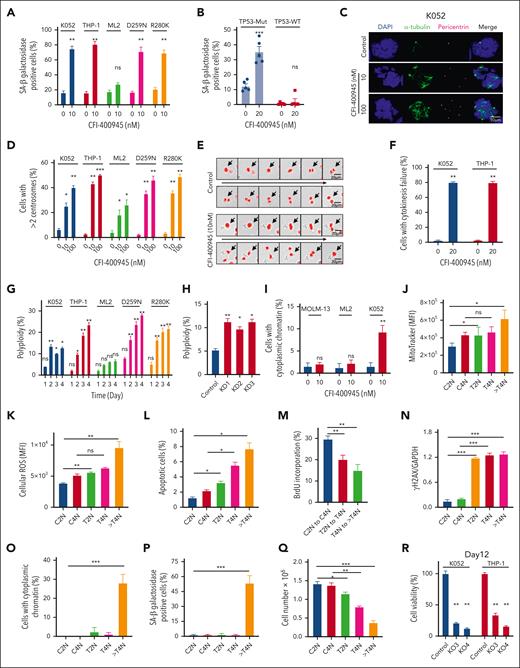
PLK4 inhibition induced senescence and cytokinesis failure in TP53-mutated AML
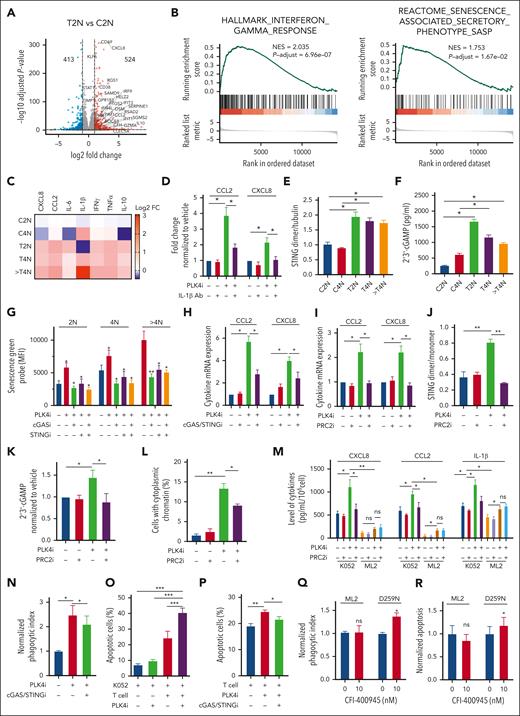
Whereas CFI-400945 preferentially activated p53 signaling and induced apoptosis in TP53 wild-type AML, senescence-associated β-galactosidase positive cells were seen exclusively in TP53-mutated but not wild-type AML (Figure 2A and supplemental Figure 2A) on day 2 of CFI-400945 treatment. Senescence was also seen in TP53-mutated but not wild-type primary AML samples (Figure 2B). Furthermore, CFI-400945 induced increase in centrioles and microtubule organizing centers after 2 days of treatment, suggestive of cytokinesis failure (Figure 2C-D and supplemental Figure 2B). The latter was confirmed by time-lapse microscopy (Figure 2E-F and supplemental Video 1A-B). Defective cytokinesis was associated with generation of polyploid cells, specifically in TP53-mutated AML (Figure 2G). Polyploidy in TP53-mutated AML could be similarly induced by PLK4-KD using shRNA (Figure 2H). The formation of cytoplasmic chromatin was preferentially observed in TP53-mutated AML (Figure 2I and supplemental Figure 2C). Increase in DNA ploidy was associated with progressive increase in mitochondrial mass (Figure 2J and supplemental Figure 2D), increased reactive oxygen species production (Figure 2K), apoptosis induction (Figure 2L), reduced proliferation (Figure 2M), increased γH2AX staining (Figure 2N and supplemental Figure 2E), generation of cytoplasmic chromatin (Figure 2O and supplemental Figure 2F), and induction of cellular senescence as shown by senescence-associated β-galactosidase staining (Figure 2P and supplemental Figure 2G). Interestingly, TP53-mutated AML cells that were treated with CFI-400945 for 2 days but remained diploid were isolated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting and cultured in the absence of CFI-400945 (supplemental Figure 2H). They started to regress in cell number (Figure 2Q) and progressed to polyploidy (supplemental Figure 2I-J), supporting the proposition that PLK4 inhibition led to growth inhibition in premitotic cells and the progression to polyploidy was an irreversible process.
Inhibition of PLK4 triggered cytokinesis failure and polyploidy in TP53-mutated AML. (A) CFI-400945 treatment induced senescence (increased staining of senescence-associated [SA] β-galactosidase) in K052, THP-1, and TP53-mutant knockin ML2 but not ML2 on day 2 (n = 3). (B) CFI-400945 treatment induced senescence in primary TP53-mutated AML, compared with vehicle control on day 6 (n = 5). (C) Representative immunofluorescence images of DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; blue), α-tubulin (green), and pericentrin (purple) staining in K052 upon CFI-400945 treatment on day 2. (D) CFI-400945 treatment increased the number of centrosomes in K052, THP-1, ML-2, and TP53-mutant knockin ML2 on day 2 (n = 3). (E) Representative time-lapse microscopy images showing defective cell division of K052 upon CFI-400945 treatment on day 2. (F) CFI-400945 treatment increased the number of cells with cytokinesis failure in K052 and THP-1 on day 2 from time-lapsed microscopy for 18 hours (n = 3). (G) CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) induced polyploidy in K052, THP-1, and TP53-mutant knockin ML2 but not in ML2 (n = 3). (H) PLK4-knockdown by shRNA resulted in polyploidy in K052 (n = 3). (I) CHI-400945 treatment (10 nM) induced the formation of cytoplasmic chromatin in K052 but not in MOLM-13 or ML2 (n = 3). (J-N) CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) increased the mitochondrial mass (J), reactive oxygen species production (K), and apoptosis (L); reduced proliferation (M); and induced DNA damage (by western blot) (N) in both T2N and polyploidy subpopulation of K052 at day 2 (n = 3). (O-P) CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) increased the formation of cytoplasmic chromatin (O) and senescence in polyploidy subpopulation of K052 (P) on day 2 (n = 3). (Q) T2N, T4N, and treated polyploidy cell of K052 failed to proliferate compared with control arms (n = 3). (R) On day 12, PLK4-knockout by CRISPR/Cas9 significantly suppressed leukemia growth in K052 and THP-1 (n = 3). (S) On day 12, CFI-400945 treatment significantly suppressed leukemia growth in K052, THP-1, and TP53-mutant knockin ML2 (n = 3). (T) CFI-400945 reduced clonogenicity of K052 and THP-1 on day 14 (n = 3). (U) CFI-400945 treatment reduced leukemia growth in TP53-mutated primary AML (n = 10) but not normal human cord blood CD34+ cells on day 6 (n = 5). (V) CFI-400945 had no effect on clonogenicity of normal human cord blood CD34+ cells on day 14 (n = 3). D259N: knockin of TP53-D259N mutant. R280K: knockin of TP53-R280K mutant. In panels A-I, cell numbers were obtained by manual counting based on stained images or videos or by flow cytometry. In panels J-Q, 2N, 4N, and > 4N refer to diploid (2N), tetraploid (4N), and polyploid (> 4N) cells in the control (C) or treatment (T) arm. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001. ns, nonsignificant.
Inhibition of PLK4 triggered cytokinesis failure and polyploidy in TP53-mutated AML. (A) CFI-400945 treatment induced senescence (increased staining of senescence-associated [SA] β-galactosidase) in K052, THP-1, and TP53-mutant knockin ML2 but not ML2 on day 2 (n = 3). (B) CFI-400945 treatment induced senescence in primary TP53-mutated AML, compared with vehicle control on day 6 (n = 5). (C) Representative immunofluorescence images of DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; blue), α-tubulin (green), and pericentrin (purple) staining in K052 upon CFI-400945 treatment on day 2. (D) CFI-400945 treatment increased the number of centrosomes in K052, THP-1, ML-2, and TP53-mutant knockin ML2 on day 2 (n = 3). (E) Representative time-lapse microscopy images showing defective cell division of K052 upon CFI-400945 treatment on day 2. (F) CFI-400945 treatment increased the number of cells with cytokinesis failure in K052 and THP-1 on day 2 from time-lapsed microscopy for 18 hours (n = 3). (G) CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) induced polyploidy in K052, THP-1, and TP53-mutant knockin ML2 but not in ML2 (n = 3). (H) PLK4-knockdown by shRNA resulted in polyploidy in K052 (n = 3). (I) CHI-400945 treatment (10 nM) induced the formation of cytoplasmic chromatin in K052 but not in MOLM-13 or ML2 (n = 3). (J-N) CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) increased the mitochondrial mass (J), reactive oxygen species production (K), and apoptosis (L); reduced proliferation (M); and induced DNA damage (by western blot) (N) in both T2N and polyploidy subpopulation of K052 at day 2 (n = 3). (O-P) CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) increased the formation of cytoplasmic chromatin (O) and senescence in polyploidy subpopulation of K052 (P) on day 2 (n = 3). (Q) T2N, T4N, and treated polyploidy cell of K052 failed to proliferate compared with control arms (n = 3). (R) On day 12, PLK4-knockout by CRISPR/Cas9 significantly suppressed leukemia growth in K052 and THP-1 (n = 3). (S) On day 12, CFI-400945 treatment significantly suppressed leukemia growth in K052, THP-1, and TP53-mutant knockin ML2 (n = 3). (T) CFI-400945 reduced clonogenicity of K052 and THP-1 on day 14 (n = 3). (U) CFI-400945 treatment reduced leukemia growth in TP53-mutated primary AML (n = 10) but not normal human cord blood CD34+ cells on day 6 (n = 5). (V) CFI-400945 had no effect on clonogenicity of normal human cord blood CD34+ cells on day 14 (n = 3). D259N: knockin of TP53-D259N mutant. R280K: knockin of TP53-R280K mutant. In panels A-I, cell numbers were obtained by manual counting based on stained images or videos or by flow cytometry. In panels J-Q, 2N, 4N, and > 4N refer to diploid (2N), tetraploid (4N), and polyploid (> 4N) cells in the control (C) or treatment (T) arm. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001. ns, nonsignificant.
PLK4 inhibition induced late inhibitory response in TP53-mutant AML
The occurrence of senescence and defective cytokinesis upon CFI-400945 treatment in TP53-mutated AML suggested the possibility of a late leukemia-suppressive effect in this AML subtype. Therefore, we treated TP53-mutated AML with CFI-400945 for a prolonged period of time. Genetic or therapeutic inhibition of PLK4 significantly reduced cell growth (Figure 2R-S and supplemental Figure 2K-L) and abolished clonogenic activities (Figure 2T and supplemental Figure 2M) of TP53-mutated AML on day 12. Moreover, CFI-400945 had significant cytotoxic effects on primary TP53-mutated AML samples but not normal cord blood CD34+ progenitor cells (Figure 2U-V).
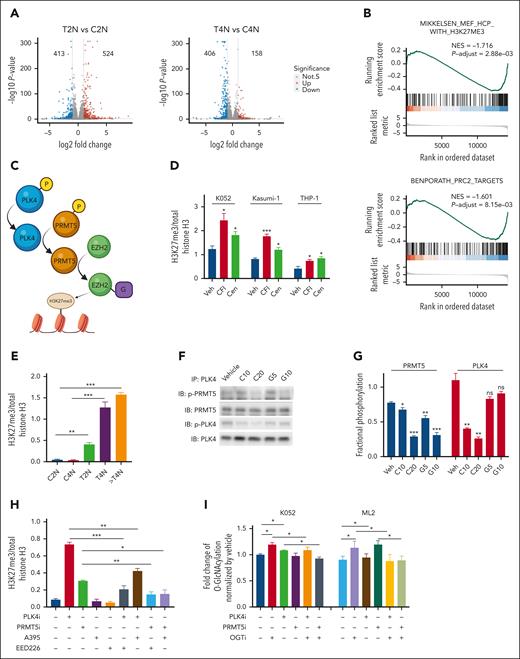
Histone modification in AML upon PLK4 inhibition
To examine the molecular mechanisms, transcriptomic analysis was performed in K052 cells treated with CFI-400945 and vehicle control. To avoid confounding effects of polyploidy induced by CFI-400945, K052 cells were purified based on ploidy before RNA sequencing (supplemental Figure 3A). Principle component analysis based on gene expression showed that each ploidy group (2N, 4N, and polyploidy) of treatment and control arms were distinctly clustered (supplemental Figure 3B). A total of 937 and 564 DEGs were identified when 2N and 4N cells in CFI-400945–treated cells and vehicle controls were compared (Figure 3A). To investigate the functional pathways enriched by the DEG, GSEA was carried out. The sets of genes whose promoters possess the H3K27me3 mark or are bound by polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2 complex) were negatively enriched upon CFI-400945 treatment (Figure 3B and supplemental Figure 3C). A comparison of our transcriptome data with public data sets (GSE142764 and GSE132407) showed that the DEG upon PLK4 inhibition was significantly correlated with those genes perturbed by protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) inhibition (supplemental Figure 3D).24 These observations suggested that PLK4 inhibition might be associated with increase in histone methylation through inhibiting PRMT5 and increasing PRC2 activity (Figure 3C). In fact, CFI-400945 treatment of TP53-mutated AML cell lines K052, Kasumi-1, and THP-1 increased their global H3K27me3 expression (Figure 3D and supplemental Figure 3E). Similar effects were seen upon treatment with another PLK4 inhibitor, centrinone-B (Figure 3D). The increase in global H3K27me3 was seen in both 2N and 4N populations (Figure 3E and supplemental Figure 3F).
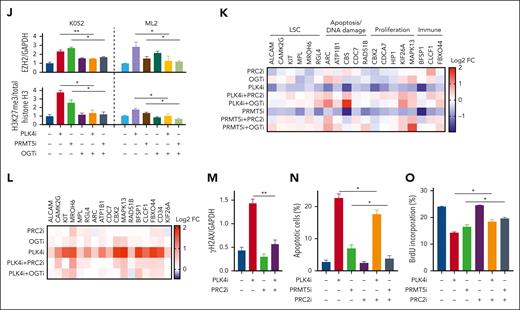
Histone modification in TP53-mutated AML upon PLK4 inhibition. (A) Volcano plots indicating differentially expressed genes (DEG: log2FC > 1 or < −1, adjusted P value < .05) for each sample pair on day 2 post CFI-400945 treatment (20 nM). 524/413 and 158/406 DEGs were found upregulated/downregulated upon CFI-400945 treatment at T2N vs C2N and T4N vs C4N comparison, respectively. (B) GSEA showed negative enrichment of H3K27me3 and PRC2 targets upon CFI-400945 treatment (20 nM) compared with vehicle control on day 2, when 2N populations were analyzed. (C) Schematic diagram on the interaction between PLK4 and PRMT5 and the subsequent histone methylation via EZH2. (D) CFI-400945 (CFI, 10 nM) and centrinone-B (Cen, 10 nM) increased global H3K27me3 normalized to total histone H3 on day 2, compared with vehicle control (supplemental Figure 3E) (n = 3). (E) CFI-400945 (10 nM) increased global H3K27me3 normalized to total histone H3 in T2N, T4N, and polyploidy subpopulation of K052 on day 2, compared with vehicle control (supplemental Figure 3F) (n = 3). (F-G) Representative immunoblot images (F) and statistics (G) showing the coimmunoprecipitation of PLK4 and PRMT5. CFI-400945 (10-20 nM) (C10 and C20) suppressed the phosphorylation of both PLK4 and PRMT5, whereas the PRMT5 inhibitor, GSK591 (5-10 μM) (G5 and G10), only suppressed the phosphorylation of PRMT5, compared with vehicle control (n = 3). (H) Increase in global H3K27me3 upon CFI-400945 (PLK4i, 10 nM) or GSK591 (PRMT5i, 5 μM) treatment was rescued by PRC2 inhibitors, A395 (200 nM) or EED226 (500 nM) (n = 3). (I) CFI-400945 (PLK4i, 10 nM) or GSK591 (PRMT5i, 5 μM) treatment increased O-GlcNAcylation in K052 on day 2, compared with vehicle control. CFI-400945 and GSK591 treatment increased O-GlcNAcylation in ML2 on day 1 and day 4, respectively. The increase was rescued by OGT inhibitor, OSMI-1 (10 μM) (OGTi) (n = 4). (J) CFI-400945 (PLK4i, 10 nM) or GSK591 (PRMT5i, 5 μM) treatment increased the protein expression of EZH2, normalized by GAPDH. Increases in EZH2 and H3K27me3 were rescued by OSMI-1 (OGTi, 10 μM) (supplemental Figure 3H) (n = 3). (K) Heat map summarizing the RT-QPCR analysis upon CFI-400945 treatment in K052. It showed downregulation of gene expression in K052 upon CFI-400945 treatment (PLK4i, 10 nM) or GSK591 (PRMT5i, 5 μM) on day 2, compared with vehicle control. The downregulation of gene expression was rescued by EED226 (PRC2i, 500 nM) or OSMI-1 (OGTi, 10 μM) (supplemental Figure 3I) (n = 5). (L) Heat map summarizing the H3K27me3 ChIP-PCR analysis upon CFI-400945 treatment (PLK4i, 10 nM) in K052. It showed increased H3K27me3 enrichment of the promoter regions of the downregulated genes on day 2, normalized to vehicle control. The increase in H3K27me3 could be rescued by EED226 (PRC2i, 500 nM) or OSMI-1 (OGTi, 10 μM) (supplemental Figure 3J) (n = 3). (M) CFI-400945 (PLK4i, 10 nM) treatment increased DNA damage in K052 that could be rescued by EED226 (PRC2i, 500 nM) (supplemental Figure 3K) (n = 3). (N) CFI-400945 (PLK4i, 10 nM) or GSK591 (PRMT5i, 5 μM) treatment induced apoptosis in K052 that could be rescued by EED226 (PRC2i, 500 nM) (n = 3). (O) CFI-400945 (PLK4i, 10 nM) or GSK591 (PRMT5i, 5 μM) treatment suppressed proliferation in K052 that could be rescued by EED226 (PRC2i, 500 nM) (n = 3). D259N: knockin of TP53-D259N mutant. R280K: knockin of TP53-R280K mutant. ∗P <.05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
Histone modification in TP53-mutated AML upon PLK4 inhibition. (A) Volcano plots indicating differentially expressed genes (DEG: log2FC > 1 or < −1, adjusted P value < .05) for each sample pair on day 2 post CFI-400945 treatment (20 nM). 524/413 and 158/406 DEGs were found upregulated/downregulated upon CFI-400945 treatment at T2N vs C2N and T4N vs C4N comparison, respectively. (B) GSEA showed negative enrichment of H3K27me3 and PRC2 targets upon CFI-400945 treatment (20 nM) compared with vehicle control on day 2, when 2N populations were analyzed. (C) Schematic diagram on the interaction between PLK4 and PRMT5 and the subsequent histone methylation via EZH2. (D) CFI-400945 (CFI, 10 nM) and centrinone-B (Cen, 10 nM) increased global H3K27me3 normalized to total histone H3 on day 2, compared with vehicle control (supplemental Figure 3E) (n = 3). (E) CFI-400945 (10 nM) increased global H3K27me3 normalized to total histone H3 in T2N, T4N, and polyploidy subpopulation of K052 on day 2, compared with vehicle control (supplemental Figure 3F) (n = 3). (F-G) Representative immunoblot images (F) and statistics (G) showing the coimmunoprecipitation of PLK4 and PRMT5. CFI-400945 (10-20 nM) (C10 and C20) suppressed the phosphorylation of both PLK4 and PRMT5, whereas the PRMT5 inhibitor, GSK591 (5-10 μM) (G5 and G10), only suppressed the phosphorylation of PRMT5, compared with vehicle control (n = 3). (H) Increase in global H3K27me3 upon CFI-400945 (PLK4i, 10 nM) or GSK591 (PRMT5i, 5 μM) treatment was rescued by PRC2 inhibitors, A395 (200 nM) or EED226 (500 nM) (n = 3). (I) CFI-400945 (PLK4i, 10 nM) or GSK591 (PRMT5i, 5 μM) treatment increased O-GlcNAcylation in K052 on day 2, compared with vehicle control. CFI-400945 and GSK591 treatment increased O-GlcNAcylation in ML2 on day 1 and day 4, respectively. The increase was rescued by OGT inhibitor, OSMI-1 (10 μM) (OGTi) (n = 4). (J) CFI-400945 (PLK4i, 10 nM) or GSK591 (PRMT5i, 5 μM) treatment increased the protein expression of EZH2, normalized by GAPDH. Increases in EZH2 and H3K27me3 were rescued by OSMI-1 (OGTi, 10 μM) (supplemental Figure 3H) (n = 3). (K) Heat map summarizing the RT-QPCR analysis upon CFI-400945 treatment in K052. It showed downregulation of gene expression in K052 upon CFI-400945 treatment (PLK4i, 10 nM) or GSK591 (PRMT5i, 5 μM) on day 2, compared with vehicle control. The downregulation of gene expression was rescued by EED226 (PRC2i, 500 nM) or OSMI-1 (OGTi, 10 μM) (supplemental Figure 3I) (n = 5). (L) Heat map summarizing the H3K27me3 ChIP-PCR analysis upon CFI-400945 treatment (PLK4i, 10 nM) in K052. It showed increased H3K27me3 enrichment of the promoter regions of the downregulated genes on day 2, normalized to vehicle control. The increase in H3K27me3 could be rescued by EED226 (PRC2i, 500 nM) or OSMI-1 (OGTi, 10 μM) (supplemental Figure 3J) (n = 3). (M) CFI-400945 (PLK4i, 10 nM) treatment increased DNA damage in K052 that could be rescued by EED226 (PRC2i, 500 nM) (supplemental Figure 3K) (n = 3). (N) CFI-400945 (PLK4i, 10 nM) or GSK591 (PRMT5i, 5 μM) treatment induced apoptosis in K052 that could be rescued by EED226 (PRC2i, 500 nM) (n = 3). (O) CFI-400945 (PLK4i, 10 nM) or GSK591 (PRMT5i, 5 μM) treatment suppressed proliferation in K052 that could be rescued by EED226 (PRC2i, 500 nM) (n = 3). D259N: knockin of TP53-D259N mutant. R280K: knockin of TP53-R280K mutant. ∗P <.05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
PLK4 activated PRMT5 and stabilized EZH2 by mediating O-GlcNAcylation
To ascertain the interaction between PLK4 and PRMT5, coimmunoprecipitation was performed. PLK4 was found to bind with PRMT5 (Figure 3F). CFI-400945 significantly suppressed PRMT5 phosphorylation, whereas PRMT5 inhibitor GSK591 had no effect on PLK4 phosphorylation, indicating PLK4 was the upstream activator of PRMT5 (Figure 3F-G). CFI-400945 or GSK591 per se had no effect on the interaction between PLK4 and PRMT5. Inhibition of PRC2 by A395 and EED226 had no effect on basal level of H3K27me3. However, they ameliorated the increase in H3K27me3 upon PLK4 or PRMT5 inhibition (Figure 3H and supplemental Figure 3G).
As PRMT5 inhibition might activate the protein O-GlcNAcylation,25 which stabilizes EZH2 and facilitates the formation of H3K27me3,26 we tested whether CFI-400945 or GSK591 might increase O-GlcNAcylation and EZH2 protein expression in TP53-mutated AML. PLK4 and PRMT5 inhibition induced global increases in O-GlcNAcylation, EZH2 protein expression, and H3K27me3 enrichment, whereas the inductions were ameliorated by O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase (OGT) inhibitor (OGTi) (Figure 3I-J and supplemental Figure 3H). Similar observations were noted in the ML2 cell line carrying wild-type TP53. The results suggested that stabilization of EZH2 and increase in H3K27me3 upon PLK4 or PRMT5 inhibition could be mediated by O-GlcNAcylation irrespective of TP53 mutation status.
PLK4 and PRMT5 inhibition suppressed leukemic growth through PRC2-mediated histone modification
To examine the relevance of histone modification in gene expression in AML, we selected a panel of genes for further examination based on 3 criteria. First, they were downregulated by CFI-400945 in K052; second, their promoters possessed H3K27me3 mark (GSE142764); third, they were reported to play key roles in carcinogenesis, including cancer stem cell signature, apoptosis, DNA damage, cellular proliferation, and immune surveillance (Figure 3K and supplemental Figure 3I). Downregulation of these gene expressions by CFI-400945 was ameliorated by PRC2 or OGT inhibition. H3K27me3 ChIP PCR targeting their promoter regions showed that PLK4 inhibition induced increase in H3K27me3 enrichment, which was also ameliorated by PRC2 or OGT inhibition (Figure 3L and supplemental Figure 3J). Furthermore, increased DNA damage, apoptosis induction, and proliferation suppression upon PLK4 or PRMT5 inhibition were partially ameliorated by PRC2 inhibitor (Figure 3M-O and supplemental Figure 3K). The results supported the proposition that the antileukemic effect of CFI-400945 might be achieved by PRMT5/PRC2-mediated histone methylation and the resulting changes in gene expression.
Histone modification induced by PLK4 inhibition in TP53 wild-type AML
To examine whether the PLK4/PRMT5/EZH2/H3K27me3 axis was operative in AML subtype without TP53 mutations, the effects of PLK4 and PRMT5 inhibition on H3K27me3 in TP53 wild-type AML cell line ML2 were examined. PLK4 or PRMT5 inhibition induced similar increases in global H3K27me3 (supplemental Figure 3L). The results suggested that the histone modification upon PLK4 inhibition also occurred in TP53 wild-type AML. However, in contrast to TP53-mutated AML, apoptosis induced by CFI-400945 in ML2 was unaffected by PRC2 inhibitor, suggesting that the response was independent of histone modification (supplemental Figure 3M).
Activation of proinflammatory program upon PLK4 inhibition in AML
In addition to histone methylation, expression of genes associated with interferon alfa (IFN-α) and IFN-γ, inflammatory pathways, and senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) (Figure 4A-B and supplemental Figure 4A-B) were also upregulated and positively enriched upon CFI-400945 treatment, supporting the proposition of a noncell intrinsic therapeutic mechanism of PLK4 inhibition in TP53-mutated AML. Specific DEGs induced by CFI-400945 were examined with particular reference to the interferon and inflammatory pathways. Genes encoding for various cytokines and their receptors, such as CXCL8, CCL2, IL6, IFN-γ, tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), and interleukin-10 (IL-10) were significantly increased in 2N, 4N, and polyploidy populations, as validated by RT-QPCR of the leukemic cells and ELISA of the media culturing these cells, whereas IL-1β, the SASP activator,27 was uniquely upregulated in polyploidy cells (Figure 4C and supplemental Figure 4C-D). Interestingly, CCL2 and CXCL8 expression in K052 cells were upregulated by exogenous IL-1β in a dose-dependent manner (supplemental Figure 4E), whereas IL-1β–neutralizing antibody significantly suppressed their expression (Figure 4D), suggesting paracrine regulation of SASP.28,29
Activation of SASP and interplay with immune cells upon PLK4 inhibition in AML. (A) Volcano plots showing differentially expressed cytokines (log2FC > 1 or < −1, false discovery rate < 0.05) for each sample pair on day 2 post CFI-400945 treatment (20 nM). (B) GSEA showed positive enrichment of IFN-γ and SASP upon CFI-400945 treatment (20 nM) compared with vehicle control on day 2. (C) Heat map summarizing the ELISA results upon CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) in K052. The concentration of CXCL8, CCL2, IL-6, IFN-γ, and TNF-α in media cultured with T2N, T4N, and polyploidy of K052 were upregulated, whereas IL-1β was only upregulated in the media from polyploidy cells (supplemental Figure 5D) (n = 3). (D) Addition of IL-1β–neutralizing antibody (0.3 μg/mL) could ameliorate CFI-400945–induced CCL2 and CXCL8 in K052 (n = 3). (E-F) CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) increased STING dimerization (E) and 2’3’-cGAMP levels (F) in K052 at day 2 (n = 3). (G-H) CFI-400945 (10 nM) increased senescence (G) and expression of CCL2 and CXCL8 (H) on day 2, and the response was ameliorated by cGAS (RU521, 1.6 μM) or STING inhibitors (H-151, 800 nM) (n = 3). (I-K) CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) increased expression of CCL2 and CXCL8 (I), STING dimerization (J), and cGAMP (K) on day 2, which was rescued by EED226 (PRC2i, 500 nM) (n = 3). (L) CFI-400945 increased the formation of cytoplasmic chromatin in K052 that could be ameliorated by PRC2 inhibitor (supplemental Figure 4I) (n = 3). (M) CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) increased the secretion of CCL2, CXCL8, and IL-1β in K052 but less in ML2 (n = 3), which was rescued by EED226 (PRC2i, 500 nM). (N) THP-1–derived macrophage showed higher phagocytosis against 2-day CFI-400945–pretreated (10 nM) K052 compared with vehicle-treated K052, which could be ameliorated by RU521 (cGASi, 1.6 μM) and H-151 (STINGi, 800 nM) (n = 3). (O) Activated T cells induced more apoptosis in CFI-400945–pretreated (10 nM) K052 compared with vehicle-treated K052 at day 2 (n = 3). (P) Therapeutic inhibition of RU521 (cGASi, 1.6 μM) and H-151 (STINGi, 800 nM) diminished the CFI-400945 (10 nM) and T cell–induced apoptosis in K052 (n = 3). (Q-R) ML2 isogenic system showed that TP53-knockin line showed relatively higher phagocytosis and (R) T-cell–mediated apoptosis (Q). Phagocytosis and AML cell apoptosis were normalized with respect to those in coculture of ML2 cells with macrophages (Q) and T cells (R) in the vehicle control. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
Activation of SASP and interplay with immune cells upon PLK4 inhibition in AML. (A) Volcano plots showing differentially expressed cytokines (log2FC > 1 or < −1, false discovery rate < 0.05) for each sample pair on day 2 post CFI-400945 treatment (20 nM). (B) GSEA showed positive enrichment of IFN-γ and SASP upon CFI-400945 treatment (20 nM) compared with vehicle control on day 2. (C) Heat map summarizing the ELISA results upon CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) in K052. The concentration of CXCL8, CCL2, IL-6, IFN-γ, and TNF-α in media cultured with T2N, T4N, and polyploidy of K052 were upregulated, whereas IL-1β was only upregulated in the media from polyploidy cells (supplemental Figure 5D) (n = 3). (D) Addition of IL-1β–neutralizing antibody (0.3 μg/mL) could ameliorate CFI-400945–induced CCL2 and CXCL8 in K052 (n = 3). (E-F) CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) increased STING dimerization (E) and 2’3’-cGAMP levels (F) in K052 at day 2 (n = 3). (G-H) CFI-400945 (10 nM) increased senescence (G) and expression of CCL2 and CXCL8 (H) on day 2, and the response was ameliorated by cGAS (RU521, 1.6 μM) or STING inhibitors (H-151, 800 nM) (n = 3). (I-K) CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) increased expression of CCL2 and CXCL8 (I), STING dimerization (J), and cGAMP (K) on day 2, which was rescued by EED226 (PRC2i, 500 nM) (n = 3). (L) CFI-400945 increased the formation of cytoplasmic chromatin in K052 that could be ameliorated by PRC2 inhibitor (supplemental Figure 4I) (n = 3). (M) CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) increased the secretion of CCL2, CXCL8, and IL-1β in K052 but less in ML2 (n = 3), which was rescued by EED226 (PRC2i, 500 nM). (N) THP-1–derived macrophage showed higher phagocytosis against 2-day CFI-400945–pretreated (10 nM) K052 compared with vehicle-treated K052, which could be ameliorated by RU521 (cGASi, 1.6 μM) and H-151 (STINGi, 800 nM) (n = 3). (O) Activated T cells induced more apoptosis in CFI-400945–pretreated (10 nM) K052 compared with vehicle-treated K052 at day 2 (n = 3). (P) Therapeutic inhibition of RU521 (cGASi, 1.6 μM) and H-151 (STINGi, 800 nM) diminished the CFI-400945 (10 nM) and T cell–induced apoptosis in K052 (n = 3). (Q-R) ML2 isogenic system showed that TP53-knockin line showed relatively higher phagocytosis and (R) T-cell–mediated apoptosis (Q). Phagocytosis and AML cell apoptosis were normalized with respect to those in coculture of ML2 cells with macrophages (Q) and T cells (R) in the vehicle control. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
As SASP can be induced by the cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase-Stimulator of interferon genes (cGAS-STING) pathway in association with DNA damage,30 cGAS-STING was examined in K052 upon PLK4 inhibition. Activation of the cGAS-STING was confirmed by the increase in STING dimerization and 2’3’-cGAMP production after 2-day treatment with CFI-400945 (Figure 4E-F and supplemental Figure 4F). Inhibition of cGAS (RU.521) or STING (H-151) ameliorated the increases in senescence and cytokine upregulation upon CFI-400945 treatment (Figure 4G-H). Based on immunofluorescence, the increase in cGAS upon PLK4 inhibition was found in close proximity to cytoplasmic chromatin (supplemental Figure 4G). PRC2 inhibitor also reduced cytokine expression, STING dimerization, and 2’3’-cGAMP production in response to PLK4 inhibition, consistent with the contribution of histone modification to DNA damage, formation of cytoplasmic chromatin, cGAS-STING activation, and SASP (Figure 4I-L and supplemental Figure 4H-4I). To investigate whether SASP induced by CFI-400945 was preferentially enhanced in TP53-mutated AML, the cytokine levels in the conditioned media from K052 (TP53-mutated) and ML2 (TP53 wild-type) upon CFI-400945 treatment were examined. Conditioned media from K052 at baseline and upon CFI-400945 treatment contained higher levels of CCL2, CXCL8, and IL-1β than those from ML2 (Figure 4M). Similar observations were encountered in the TP53-mutated isogenic AML cell line (supplemental Figure 4), supporting the proposition that SASP was preferentially induced in this AML subtype. Similar results were seen when only the diploid populations (2N) were examined (supplemental Figure 4K).
To examine the mechanistic link between PLK4 inhibition and immune activation, genes that were associated with immune regulation and were downregulated by PLK4 inhibition (BFSP131 and CLCF132) (Figure 3K) were knocked down by shRNA. There was a significant increase in SASP cytokines upon gene knockdown, the effects of which could be ameliorated by cGAS inhibitor (supplemental Figure 4L). The results suggested that PLK4 inhibition might downregulate the expression of these genes and induce SASP expression via the cGAS-STING pathway.
PLK4 inhibition potentiated the anti-AML effects of macrophages and T cells
To examine the functional significance of these cytokines in mediating blast clearance upon PLK4 inhibition, K052 cells were cocultured with human macrophages or T cells and the effects of CFI-400945 were examined. CFI-400945 induced phagocytic activity of M1 macrophages against K052 cells, and the response could be ameliorated by cGAS and STING inhibitors (Figure 4N). CD3+ T cells from healthy donors with prior activation by anti-CD3/CD28 beads were cocultured with K052 cells. The presence of activated T cells substantially induced apoptosis of cocultured K052 cells, which was accentuated by CFI-400945 (Figure 4O). The latter response was diminished by cGAS-STING inhibition (Figure 4P). Induction of apoptosis in leukemia cells was associated with corresponding increases in intracellular IFN-γ and TNF-α levels in cocultured T cells (supplemental Figure 4M). In TP53 wild-type ML2 cell line, CFI-400945 had no effect on phagocytic activity of cocultured macrophages or T cell–mediated AML apoptosis, whereas TP53-mutant knockin in the ML2 cell line showed a significant increase in phagocytosis (coculture with macrophages) and apoptosis (coculture with T cells) upon CFI-400945 treatment (Figure 4Q-R). The results suggested that the activation of immune response against AML was specific to TP53-mutated AML and dependent on the cGAS-STING pathway.
To examine the significance of secreted cytokines in mediating immune activation by PLK4 inhibition, media culturing K052 or ML2 upon 2-day treatment with CFI-400945 or dimethyl sulfoxide control, known as conditioned medium (CM), were harvested (supplemental Figure 4N). Coculture experiments of AML cells with macrophage or T cells in different CM were performed. Basal CM from K052 induced a greater immune response than ML2, and CFI-400945–treated CM from K052 induced the strongest activation of macrophages and T cells against both K052 and ML2 (supplemental Figure 4O-P). The results suggested that chemokines secreted from K052, potentiated by CFI-400945, were important mediators of the activated immune response. Moreover, CCL2, CXCL8, and IL-1β neutralizing antibodies were shown to suppress CFI-400945–induced phagocytosis by macrophages (supplemental Figure 4Q) and apoptosis by T cells (supplemental Figure 4R) in TP53-mutated AML, attesting to the functional significance of these cytokines.
In vivo effects of PLK4 inhibition
Finally, we examined the efficacy of CFI-400945 in targeting TP53-mutated AML in vivo. K052 cells were transplanted into NSG mice and the in vivo effects of CFI-400945 were evaluated (supplemental Figure 5A). CFI-400945 was well tolerated (supplemental Figure 5B), and it significantly reduced the leukemic burden of K052 (Figure 5A and supplemental Figure 5C) and improved animal survival compared with vehicle control (Figure 5B). In addition, CFI-400945 also suppressed the leukemic burden of ML2 in vivo and was associated with significant apoptosis induction upon 3-day in vivo treatment (supplemental Figure 5D-F). The antileukemic effect of CFI-400945 was further demonstrated in patient-derived xenograft model from primary TP53-mutated AML (Figure 5C-D and supplemental Figure 5G). In vivo interaction between AML cells and macrophages in recipient animals was examined. CFI-400945 induced cytokine expression in engrafting K052 cells (Figure 5E) and increased the abundance of mouse macrophages in the recipient bone marrow (Figure 5F). We further examined the relationship between PLK4 inhibition, polyploidy, apoptosis, and cGAS-STING activation in an immune-competent C57BL/6 mouse model using MLL-AF9 murine AML cell line with Tp53-KO.33 CFI-400945 induced apoptosis in both Tp53 wild-type and KO AML, but only the response in the latter could be ameliorated by cGAS-STING inhibition (supplemental Figure 5H). Furthermore, CFI-400945 induced polyploidy and SASP expression and increased macrophage and CD4+ T cell populations in Tp53-KO but not wild-type MLL-AF9 AML (supplemental Figure 5I-5L), and these responses could also be ameliorated by STING inhibition. These observations supported the proposition that cGAS-STING activation mediated the immune activation upon CFI-400945 treatment.
In vivo antiproliferative effect of PLK4 inhibition. (A) In vivo CFI-400945 treatment (20 mg/kg per day) suppressed the growth, examined by in vivo bioluminescence assay, of K052 engrafted in sublethally irradiated NSG mice, compared with vehicle control. Chemotherapy (cytarabine 25 mg/kg per day + doxorubicin 1.5 mg/kg per day) did not affect the growth of K052 in mice (n = 18). Fold change of total flux refers to the flux intensity at a specific time point normalized to the flux intensity measured on day 0 of treatment. (B) Survival analysis of NSG mice engrafted with K052 showed longer survival upon in vivo CFI-400945 treatment, compared with vehicle control (n = 12). (C) In vivo CFI-400945 treatment (20 mg/kg per day) reduced the human engraftment (percentage of human CD45+, CD33+, and mouse CD45− cells in the total [human and mouse] CD45+ population) of primary TP53-mutated AML in NSG bone marrow at 28-day posttransplantation (n = 14). (D) Survival analysis of NSG mice engrafted with primary TP53-mutated AML upon in vivo CFI-400945 treatment (20 mg/kg per day) compared with vehicle control (n = 8). (E) RT-QPCR analysis showed increases in cytokines mRNA expressions in K052 upon in vivo CFI-400945 treatment (20 mg/kg per day) for 14 days (n = 12). (F) In vivo CFI-400945 treatment increased the number of macrophages (F4/80+) in NSG bone marrow compared with vehicle control (n = 12). (G) In vivo CFI-400945 (20 mg/kg per day) and anti-CD47 antibody treatment (8 mg/kg per day) showed the greatest inhibition of K052 growth, examined by in vivo bioluminescence assay, in nonirradiated NSG mice, compared with vehicle control or single treatment (CFI-400945 or anti-CD47 antibody only) (n = 40). (H) Survival analysis of NSG mice engrafted with K052 showed the longest survival upon in vivo combination treatment of CFI-400945 (20 mg/kg per day) and anti-CD47 antibody (8 mg/kg per day), compared with vehicle control or single treatment (CFI-400945 or anti-CD47 antibody only) (n = 40). (I-J) The combination treatment induced significant leukemia suppression as compared with single-arm treatment in the TP53-mutated (N = 22 mice) but not wild-type AML samples (N = 33 mice). ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
In vivo antiproliferative effect of PLK4 inhibition. (A) In vivo CFI-400945 treatment (20 mg/kg per day) suppressed the growth, examined by in vivo bioluminescence assay, of K052 engrafted in sublethally irradiated NSG mice, compared with vehicle control. Chemotherapy (cytarabine 25 mg/kg per day + doxorubicin 1.5 mg/kg per day) did not affect the growth of K052 in mice (n = 18). Fold change of total flux refers to the flux intensity at a specific time point normalized to the flux intensity measured on day 0 of treatment. (B) Survival analysis of NSG mice engrafted with K052 showed longer survival upon in vivo CFI-400945 treatment, compared with vehicle control (n = 12). (C) In vivo CFI-400945 treatment (20 mg/kg per day) reduced the human engraftment (percentage of human CD45+, CD33+, and mouse CD45− cells in the total [human and mouse] CD45+ population) of primary TP53-mutated AML in NSG bone marrow at 28-day posttransplantation (n = 14). (D) Survival analysis of NSG mice engrafted with primary TP53-mutated AML upon in vivo CFI-400945 treatment (20 mg/kg per day) compared with vehicle control (n = 8). (E) RT-QPCR analysis showed increases in cytokines mRNA expressions in K052 upon in vivo CFI-400945 treatment (20 mg/kg per day) for 14 days (n = 12). (F) In vivo CFI-400945 treatment increased the number of macrophages (F4/80+) in NSG bone marrow compared with vehicle control (n = 12). (G) In vivo CFI-400945 (20 mg/kg per day) and anti-CD47 antibody treatment (8 mg/kg per day) showed the greatest inhibition of K052 growth, examined by in vivo bioluminescence assay, in nonirradiated NSG mice, compared with vehicle control or single treatment (CFI-400945 or anti-CD47 antibody only) (n = 40). (H) Survival analysis of NSG mice engrafted with K052 showed the longest survival upon in vivo combination treatment of CFI-400945 (20 mg/kg per day) and anti-CD47 antibody (8 mg/kg per day), compared with vehicle control or single treatment (CFI-400945 or anti-CD47 antibody only) (n = 40). (I-J) The combination treatment induced significant leukemia suppression as compared with single-arm treatment in the TP53-mutated (N = 22 mice) but not wild-type AML samples (N = 33 mice). ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.
The effects of interrupting the “don’t eat me” signal on leukemic cells by monoclonal anti-CD47 antibody, which could enhance macrophage-mediated phagocytosis, were examined. Upon leukemic engraftment, anti-CD47 antibody monotherapy showed only modest suppression of leukemic burden and extension of animal survival (mean survival, 73.5 days) as compared with vehicle control (50 days). Combination of CFI-400945 with anti-CD47 antibody significantly suppressed leukemic burden and prolonged animal survival (146 days), underscoring the role of innate immunity in potentiating the leukemic-clearing effect of CFI-400945 in vivo (Figure 5G-H and supplemental Figure 5M-N). To demonstrate the in vivo effect of CFI-400945 and anti-CD47 antibody combination on primary AML samples, we evaluated the difference in engraftment before and after single or combination treatment for 2 weeks. The wide variation in engraftment of individual AML samples notwithstanding, the combination treatment induced significant leukemia suppression as compared with single-arm treatment in the TP53-mutated but not wild-type AML samples (Figure 5I-J).
Discussion
In this study, inhibition of PLK4 induced a biphasic response in AML: early growth inhibition was seen in TP53 wild-type AML and was associated with an increase in apoptosis due to DNA damage and subsequent p53 activation before defective cytokinesis and polyploidy could manifest. In TP53-mutated AML, apoptosis did not occur due to defective p53 function so that cytokinesis failure, polyploidy, and cellular senescence with prolonged PLK4 inhibition could be detected (see the visual abstract in the online article). A novel PLK4/PRMT5/EZH2/H3K27me3 axis was operative in both TP53 wild-type and mutated AML that drove the antileukemic effect of PLK4 inhibition on proliferation, apoptosis, and DNA damage. The notions of DNA damage, senescence, and defective cytokinesis upon PLK4 inhibition has been reported in other cancer models.7,22,28,34 On the other hand, our observations have shed important light on the pathogenetic role of PLK4 in AML with particular reference to TP53 mutation and provided new opportunities to develop therapeutic interventions for this AML subtype.
First, PLK4 inhibition induced cell-intrinsic effects, ie, cellular senescence and defective cytokinesis, specifically in TP53-mutated AML cell lines. These cellular effects have also been reported in TP53-mutated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma22 and prostate cancer.35 The observations were consistent with the reciprocal relationship between PLK4 expression and TP53 deletion and the reported mechanistic link between TP53 mutation and PLK4 in lung cancers, in which PLK1/4 expression was increased in TP53-mutant cases.36PLK4 overexpression has also been shown to induce supernumerary centrosome, aneuploidy, and genome instability in p53-deficient cells, leading to oncogenesis.16 CFI-400945 has shown off-target effects on Aurora B kinase,37 which plays a pivotal role in cytokinesis.7 However, the cytokinesis defects induced by CFI-400945 were seen at as low as 10 nM, which had no effect on Aurora B phosphorylation (supplemental Figure 6A). The observation corroborated with that of a previous study showing the dose of CFI-400945 against Aurora B kinase was nearly 10-fold higher.38 Moreover, specific knockdown of PLK4 similarly induced polyploidy. Therefore, the defects in cytokinesis were specifically caused by perturbation of PLK4 function.22
Second, we reported the hitherto undescribed effects of PLK4 inhibition on histone modification. The mechanistic link was first suggested by the negative enrichment of genes associated with H3K27me3 and PRC2 in AML treated with CFI-400945. In silico analysis showed that the DEG profile of PLK4 inhibition was significantly correlated with those of PRMT5 inhibition, associated with stabilization of H3K27me3 via the PRC2 axis.24,39 Interaction between PLK4 and PRMT5 and a novel PLK4/PRMT5/EZH2/H3K27me3 axis operative in both TP53-mutated and wild-type AML were subsequently demonstrated. To our knowledge, this is the first report linking PLK4 inhibition to histone modification, and the results corroborated with the reports on PRMT5/EZH2 axis in colorectal cancer40 and the effects of increased EZH2/H3K27me3 on DNA damage, growth inhibition, and sensitization toward genotoxic treatment.41-44 Histone methylation and the reported dysregulated centriole biogenesis upon PLK4 inhibition might cooperatively suppress leukemia growth and account for the therapeutic effects.
Third, we demonstrated the non–cell intrinsic effects of PLK4 inhibition on TP53-mutated AML. cGAS-STING pathway was activated as evidenced by the increase in STING dimerization and cGAMP upon PLK4 inhibition, and the responses could be ameliorated by cGAS and STING inhibitors. Activation of cGAS-STING pathway was associated with increase in cytokines and chemokines and might result from the combined effect of the PLK4/PRMT5/EZH2/H3K27me3 axis,45,46 hence the associated DNA damage, and the distinct increase in IL-1β secretion in polyploid leukemia cells. In fact, PRC2 inhibitor was shown to ameliorate CFI-400945–induced SASP cytokine expression, suggesting activation of the proinflammatory program was, at least partially, regulated by histone methylation. IL-1β has been shown to activate cGAS and induce cytokine and chemokine expression in neighboring diploid cells via paracrine fashion.27,30,47-49 SASPs, including CXCL8 and CCL2, have been shown to attract activated effector CD8+ T cells based on their expression of the cognate receptors.50 CCL2 is known to be a strong chemoattractant of macrophages and a powerful initiator of inflammation.51,52
Our observations were clinically relevant. PLK4 inhibition suppressed leukemia growth in xenotransplantation model and induced activation of cGAS-STING pathway and phagocytosis of leukemia cells by macrophages in vivo. This process might be limited by the CD47-SIRPα axis, in which CD47 on leukemia cells interacts with SIRPα on macrophages to convey the “don’t eat me” signal.53 The proposition was supported by the observations that addition of monoclonal anti-CD47 antibody to PLK4 inhibition potentiated the antileukemia effect of the latter and prolonged animal survival. In a phase II clinical trial, anti-CD47 monoclonal antibody magrolimab combined with azacitidine appeared safe and effective in TP53-mutated AML.54 Information arising from the present study may provide important leads for future trials.
In conclusion, we demonstrated anti-AML effects of PLK4 inhibition via a novel PRMT5/EZH2/H3K27me3 axis. In TP53-mutated AML, the cumulative DNA damage led to senescence and activation of cGAS-STING pathway, which subsequently induced SASP, resulting in activation of macrophage and T cells. The information provides the foundation for the development of novel therapeutic strategies targeting both cell intrinsic and non–cell intrinsic mechanisms in AML.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Derek Wong, Michelle Chen, and Emily Liu from the Centre for PanorOmic Sciences, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong, for technical assistance.
This research was supported by the Centre for Oncology and Immunology under the Health@InnoHK Initiative funded by the Innovation and Technology Commission, The Government of Hong Kong SAR, China (A.Y.-H.L.), Theme-based Research Scheme (T12-702/20-N) (A.Y.-H.L.), Health and Medical Research Fund (08191906) (K.-L.N.), Li Shu Fan Medical Foundation (A.Y.-H.L.), Ying Wan Leung Research Fund (A.Y.-H.L.), Collaborative Research Fund (C7028-19G) (A.Y.-H.L.), Tang King Ying Research Fund (A.Y.-H.L.), and Madam Madeline Tong Lai-Sheung Cancer Research Fund (A.Y.-H.L.).
Authorship
Contribution: conceptualization, C.-C.D., C.-H.M., T.W.M., and A.Y.-H.L.; methodology, C.-C.D., C.-H.M., K.-L.N., L.-C.Z., Z.D, and A.Y.-H.L.; investigation, C.-C.D., C.-H.M., K.-L.N., N.N.-M.C., W.L., X.-y.Z., L.-C.Z., T.-H.K, K.-C.C, T.C.-C.N., and W.-Y.L.; resources, K.-L.N., C.-H.M., S.G., T.W.M., and A.Y.-H.L.; data curation, C.-C.D., C.-H.M., and A.Y.-H.L.; writing of original draft, C.-H.M. and A.Y.-H.L.; review and editing, C.-H.M., M.S.-Y.H., C.C.-L.W., C.W.E.S., Z.D., M.R.B., T.W.M., and A.Y.-H.L.; funding acquisition, C.-H.M., K.-L.N., T.W.M., and A.Y.-H.L.; and supervision, C.-H.M. and A.Y.-H.L.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: M.R.B. and T.W.M. are the shareholders of Treadwell Therapeutics. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Cheuk-Him Man, Room 816, Laboratory Block, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, 21 Sassoon Road, Hong Kong SAR, China; e-mail: csman729@hku.hk; and Anskar Yu-Hung Leung, Room K418, K Block, Department of Medicine, Queen Mary Hospital, Pok Fu Lam Road, Hong Kong SAR, China; e-mail: ayhleung@hku.hk.
Supplementary Materials
References
Author notes
∗C.-H.M., W.L., and C.-C.D. contributed equally to this study.
Transcriptome data are available at Sequenced Read Archive at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra under project number PRJNA925822. For original data, contact the corresponding author, Anskar Yu-Hung Leung (ayhleung@hku.hk).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

![Inhibition of PLK4 triggered cytokinesis failure and polyploidy in TP53-mutated AML. (A) CFI-400945 treatment induced senescence (increased staining of senescence-associated [SA] β-galactosidase) in K052, THP-1, and TP53-mutant knockin ML2 but not ML2 on day 2 (n = 3). (B) CFI-400945 treatment induced senescence in primary TP53-mutated AML, compared with vehicle control on day 6 (n = 5). (C) Representative immunofluorescence images of DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; blue), α-tubulin (green), and pericentrin (purple) staining in K052 upon CFI-400945 treatment on day 2. (D) CFI-400945 treatment increased the number of centrosomes in K052, THP-1, ML-2, and TP53-mutant knockin ML2 on day 2 (n = 3). (E) Representative time-lapse microscopy images showing defective cell division of K052 upon CFI-400945 treatment on day 2. (F) CFI-400945 treatment increased the number of cells with cytokinesis failure in K052 and THP-1 on day 2 from time-lapsed microscopy for 18 hours (n = 3). (G) CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) induced polyploidy in K052, THP-1, and TP53-mutant knockin ML2 but not in ML2 (n = 3). (H) PLK4-knockdown by shRNA resulted in polyploidy in K052 (n = 3). (I) CHI-400945 treatment (10 nM) induced the formation of cytoplasmic chromatin in K052 but not in MOLM-13 or ML2 (n = 3). (J-N) CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) increased the mitochondrial mass (J), reactive oxygen species production (K), and apoptosis (L); reduced proliferation (M); and induced DNA damage (by western blot) (N) in both T2N and polyploidy subpopulation of K052 at day 2 (n = 3). (O-P) CFI-400945 treatment (10 nM) increased the formation of cytoplasmic chromatin (O) and senescence in polyploidy subpopulation of K052 (P) on day 2 (n = 3). (Q) T2N, T4N, and treated polyploidy cell of K052 failed to proliferate compared with control arms (n = 3). (R) On day 12, PLK4-knockout by CRISPR/Cas9 significantly suppressed leukemia growth in K052 and THP-1 (n = 3). (S) On day 12, CFI-400945 treatment significantly suppressed leukemia growth in K052, THP-1, and TP53-mutant knockin ML2 (n = 3). (T) CFI-400945 reduced clonogenicity of K052 and THP-1 on day 14 (n = 3). (U) CFI-400945 treatment reduced leukemia growth in TP53-mutated primary AML (n = 10) but not normal human cord blood CD34+ cells on day 6 (n = 5). (V) CFI-400945 had no effect on clonogenicity of normal human cord blood CD34+ cells on day 14 (n = 3). D259N: knockin of TP53-D259N mutant. R280K: knockin of TP53-R280K mutant. In panels A-I, cell numbers were obtained by manual counting based on stained images or videos or by flow cytometry. In panels J-Q, 2N, 4N, and > 4N refer to diploid (2N), tetraploid (4N), and polyploid (> 4N) cells in the control (C) or treatment (T) arm. ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001. ns, nonsignificant.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/142/23/10.1182_blood.2023019782/1/m_blood_bld-2023-019782-gr2sv.jpeg?Expires=1769800999&Signature=1rMScCTwNLiUnFmDTrufUO9DiyY-r7q0IKdDuyHF6L1T6XqJIZ2ppfccorOsjQC4U5I8YegYVLh7gotRIMaY0DirrL3dSHFwEzXVeiqqVecXE4Bdyjp79WOB0G7qoc~IdEz-Rtct39EXV0A0DPZYNzlRakfMObx-zXKvuZeksIQ-mtzdU7TD5HysE-UK4PwO3hc655c94y9VCMvXK-1atZjEUH~Z0l0RNn~x4XPz28ysx-9qlXOwcXv5p4ELvwXLMuXx2yFNMgaw0gZNJ1OVUNoqd1g~sRDI61nC66C9xRTKRgwSeH6a2JCrkr5VTz~1osy589vfsLhcWbQyg4Aq6Q__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
![In vivo antiproliferative effect of PLK4 inhibition. (A) In vivo CFI-400945 treatment (20 mg/kg per day) suppressed the growth, examined by in vivo bioluminescence assay, of K052 engrafted in sublethally irradiated NSG mice, compared with vehicle control. Chemotherapy (cytarabine 25 mg/kg per day + doxorubicin 1.5 mg/kg per day) did not affect the growth of K052 in mice (n = 18). Fold change of total flux refers to the flux intensity at a specific time point normalized to the flux intensity measured on day 0 of treatment. (B) Survival analysis of NSG mice engrafted with K052 showed longer survival upon in vivo CFI-400945 treatment, compared with vehicle control (n = 12). (C) In vivo CFI-400945 treatment (20 mg/kg per day) reduced the human engraftment (percentage of human CD45+, CD33+, and mouse CD45− cells in the total [human and mouse] CD45+ population) of primary TP53-mutated AML in NSG bone marrow at 28-day posttransplantation (n = 14). (D) Survival analysis of NSG mice engrafted with primary TP53-mutated AML upon in vivo CFI-400945 treatment (20 mg/kg per day) compared with vehicle control (n = 8). (E) RT-QPCR analysis showed increases in cytokines mRNA expressions in K052 upon in vivo CFI-400945 treatment (20 mg/kg per day) for 14 days (n = 12). (F) In vivo CFI-400945 treatment increased the number of macrophages (F4/80+) in NSG bone marrow compared with vehicle control (n = 12). (G) In vivo CFI-400945 (20 mg/kg per day) and anti-CD47 antibody treatment (8 mg/kg per day) showed the greatest inhibition of K052 growth, examined by in vivo bioluminescence assay, in nonirradiated NSG mice, compared with vehicle control or single treatment (CFI-400945 or anti-CD47 antibody only) (n = 40). (H) Survival analysis of NSG mice engrafted with K052 showed the longest survival upon in vivo combination treatment of CFI-400945 (20 mg/kg per day) and anti-CD47 antibody (8 mg/kg per day), compared with vehicle control or single treatment (CFI-400945 or anti-CD47 antibody only) (n = 40). (I-J) The combination treatment induced significant leukemia suppression as compared with single-arm treatment in the TP53-mutated (N = 22 mice) but not wild-type AML samples (N = 33 mice). ∗P < .05; ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗P < .001.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/142/23/10.1182_blood.2023019782/1/m_blood_bld-2023-019782-gr5.jpeg?Expires=1769800999&Signature=Vlo134Xkw2s8uWyOOiN0nkCA8r7m~44OKDJiluWOnS5hiJhLPycE2DDRkUtaZsgNavzhtZ5TQ8gVQAeW0XQc0Poz559C-dL5LLa7DIqc~vbdrCGyjybNpkfk2MNyehBVb4ZQ9vSzK4Oio2f8kOn1q-EfZ2UzhxApR-gB6VxRpYmsgplz2JRHeYgIfGuSCJvxCOf5-tgCHGLyNaHLpVyKDfPfZm6Xv7iPmzYufA5DUfhYrTdRzOBPT1kDnNEdLo6vvfr0kmWyV9XtFsbotDQUH4ftV0IvHP48ILMTpiDYoApPBfBaYG7udA5Qba~urkedocL4~TPrG4thOeQ1OcRGJw__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal