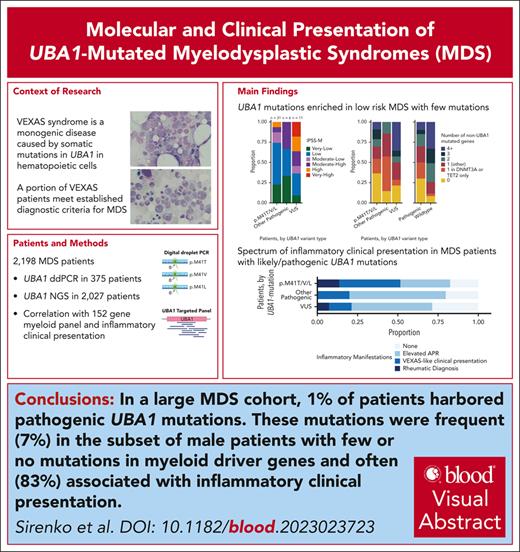
Key Points
UBA1 mutations were identified in 1% of patients with MDS and 7% of patients lacking myeloid mutations or established disease classification.
Inflammatory clinical presentation and vacuoles were observed in 83% and 71%, respectively, of patients with pathogenic UBA1 mutations.
Visual Abstract
Mutations in UBA1, which are disease-defining for VEXAS (vacuoles, E1 enzyme, X-linked, autoinflammatory, somatic) syndrome, have been reported in patients diagnosed with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Here, we define the prevalence and clinical associations of UBA1 mutations in a representative cohort of patients with MDS. Digital droplet polymerase chain reaction profiling of a selected cohort of 375 male patients lacking MDS disease-defining mutations or established World Health Organization (WHO) disease classification identified 28 patients (7%) with UBA1 p.M41T/V/L mutations. Using targeted sequencing of UBA1 in a representative MDS cohort (n = 2027), we identified an additional 27 variants in 26 patients (1%), which we classified as likely/pathogenic (n = 12) and of unknown significance (n = 15). Among the total 40 patients with likely/pathogenic variants (2%), all were male and 63% were classified by WHO 2016 criteria as MDS with multilineage dysplasia or MDS with single-lineage dysplasia. Patients had a median of 1 additional myeloid gene mutation, often in TET2 (n = 12), DNMT3A (n = 10), ASXL1 (n = 3), or SF3B1 (n = 3). Retrospective clinical review, where possible, showed that 82% (28/34) UBA1-mutant cases had VEXAS syndrome–associated diagnoses or inflammatory clinical presentation. The prevalence of UBA1 mutations in patients with MDS argues for systematic screening for UBA1 in the management of MDS.
Introduction
Patients with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) have heterogeneous clinical presentation, response to therapy, and outcomes. The recent integration of genetic alterations alongside established clinical and morphologic features in disease classification and risk stratification have informed clinical management.1-3 However, 5% to 10% of patients have no established disease defining mutations.3,4 Furthermore, inflammatory symptoms of poorly understood etiology complicate diagnosis and clinical management in 10% to 30% of patients with MDS, and are associated with high-risk disease.5-9
One such overlap between MDS and inflammatory presentation is VEXAS (vacuoles, E1 enzyme, X-linked, autoinflammatory, somatic) syndrome, a severe systemic autoinflammatory disease.10 VEXAS syndrome is linked to mutations in the UBA1 gene, which encodes the major E1-activating enzyme required for ubiquitylation. Although mutations at the p.M41 hot spot were the first to be associated with VEXAS syndrome, additional variants in UBA1 have since been characterized as pathogenic.11-17UBA1 mutations typically co-occur with common myeloid driver gene mutations including DNMT3A, TET2, and SF3B1 in VEXAS syndrome,10 clonal hematopoiesis,18 and MDS.19,20 The prevalence of MDS in patients with VEXAS syndrome is also high (25%-55%),10,12,20 however, UBA1 mutations have not been systematically screened in a representative diagnostic MDS population. In this study, we define the prevalence, comutation patterns, and clinical profiles of patients with MDS with UBA1 mutations.
Study design
Molecular data from a systematic sequencing screen of 152 myeloid driver genes used for the development of the International Prognostic Scoring System-Molecular (IPSS-M), were evaluated across a representative diagnostic and treatment-naive MDS cohort (N = 3323).3 Detailed molecular, cytogenetic, and clinical data were available. We hypothesized that UBA1 mutations would be prevalent in male patients without myeloid driver mutations or established disease classification. First, 375 cases (cohort A) with inclusion based on: (1) male sex; and (2) no identified driver mutations or mutations only in DTA (DNMT3A, TET2, ASXL1) genes; or (3) MDS unclassifiable according to the World Health Organization (WHO) revised 4th edition classification (WHO 2016)21,22 or (4) subsets of MDS/myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) overlap syndromes (MDS/MPN unclassifiable, MDS/MPN–ring sideroblasts [RS] and thrombocytosis, and atypical chronic myeloid leukemia) per WHO 2016 classification (Figure 1A) were profiled using UBA1 p.M41 digital droplet polymerase chain reaction (ddPCR). To determine the prevalence of UBA1 mutations in MDS, the cohort was then expanded to profile 2027 representative patients, both male and female across WHO 2016 subtypes (cohort B) using targeted sequencing of the UBA1 locus. UBA1 variants were called as previously described using the Isabl platform.3,23,24 In total, 204 cases were profiled with both assays. Retrospective review of inflammation-associated clinical history and morphology was performed for UBA1-mutated cases, when possible.
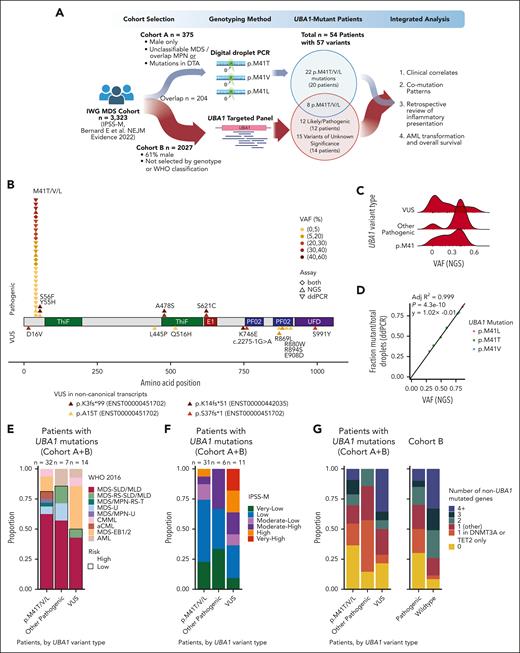
Prevalence of UBA1 mutations in MDS. (A) Schematic of study design showing cohort A (top) profiled by ddPCR and cohort B (bottom) profiled by NGS for UBA1 mutations. (B) Lollipop plot showing likely pathogenic mutations (top) and VUS (bottom) in UBA1 detected by ddPCR and/or NGS. Variants are colored by VAF and point shape indicates whether the variant was detected by ddPCR, NGS, or both. VUS in the noncanonical transcripts are reported below the x-axis. (C) VAF of UBA1 mutations detected by NGS in cohort B, adjusted for single copy of chromosome X in males. (D) Correlation of UBA1 NGS VAF and ddPCR mutant droplet fraction for patients (n = 8) with UBA1 p.M41T/V/L variants detected by both assays. (E) Stacked bar plot of WHO 2016 classification (available for n = 53/54). (F) Stacked bar plot of IPSS-M risk category (available for n = 48/54). (G) Stacked bar plot of number of co-occurring mutations in 54 patients with UBA1-mutated MDS (left) and cohort B (right).
Prevalence of UBA1 mutations in MDS. (A) Schematic of study design showing cohort A (top) profiled by ddPCR and cohort B (bottom) profiled by NGS for UBA1 mutations. (B) Lollipop plot showing likely pathogenic mutations (top) and VUS (bottom) in UBA1 detected by ddPCR and/or NGS. Variants are colored by VAF and point shape indicates whether the variant was detected by ddPCR, NGS, or both. VUS in the noncanonical transcripts are reported below the x-axis. (C) VAF of UBA1 mutations detected by NGS in cohort B, adjusted for single copy of chromosome X in males. (D) Correlation of UBA1 NGS VAF and ddPCR mutant droplet fraction for patients (n = 8) with UBA1 p.M41T/V/L variants detected by both assays. (E) Stacked bar plot of WHO 2016 classification (available for n = 53/54). (F) Stacked bar plot of IPSS-M risk category (available for n = 48/54). (G) Stacked bar plot of number of co-occurring mutations in 54 patients with UBA1-mutated MDS (left) and cohort B (right).
This study is approved under Memorial Sloan Kettering institutional review board 15-017.
Results and discussion
Profiling of UBA1 by ddPCR for cohort A identified 30 UBA1 p.M41T/V/L mutations in 7% (28/375) of patients (mutant droplet fraction median, 0.376; range, 0.00018-0.877). This included 15 patients with p.M41T (c.122T>C), 7 with p.M41V (c.121A>G), 4 with p.M41L (c.121A>C), and 2 patients with >1 mutation (1 with p.M41V/T, and 1 with p.M41L/V; Figure 1B). The median age at diagnosis in cases with UBA1 p.M41 mutation was 72 years (range, 44-89) and 71 years (range, 21-93) for cases without (supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood website). There was no significant difference in available clinical parameters (age, blast percentages, and blood counts) between UBA1-mutated and –wild-type MDS. These data demonstrate that mutations in UBA1 are frequent (7%) in male patients with MDS without established disease classification or typical disease-associated mutation patterns.
In order to (1) determine whether UBA1 mutations were indeed enriched in patients without clear MDS disease classification, (2) detect recently described mutations beyond the p.M41 locus,11-17 and (3) enable discovery of novel variants in UBA1, we sequenced the entire UBA1 gene across an expanded cohort of 2027 patients with MDS (cohort B; Figure 1A; supplemental Table 2).
By next-generation sequencing (NGS) in cohort B, we identified 35 UBA1 mutations in 34 (1.7%) patients, of which 20 (1%, all male) had likely pathogenic variants, and 14 had variants of unknown significance (VUS; 3/14 female; Figure 1B). The 20 likely pathogenic variants comprised 13 p.M41T/V/L hot-spot mutations with a broad range of variant allele fractions (VAFs; 0.013-0.94), and 7 previously described non-p.M41 mutations including 2 p.S56F (VAF of 0.87 and 0.93, respectively), 2 p.A478S (VAF of 0.72 and 0.80, respectively), 2 p.S621C (VAF of 0.80 and 0.82, respectively), and 1 p.Y55H (VAF of 0.025; Figure 1C; supplemental Table 3). The VUS are provided in supplemental Table 3 to support future studies. Within 204 cases profiled by both assays, all 8 p.M41T/V/L mutations were identified with concordant VAF estimations (R2 = 0.999; P < .0001; Figure 1D). These data demonstrate that 1% (20/2027) of patients with MDS had established pathogenic mutations in UBA1, and that UBA1 mutations are strongly enriched (7%) but not limited to males diagnosed with MDS but without disease-defining genetic alterations.
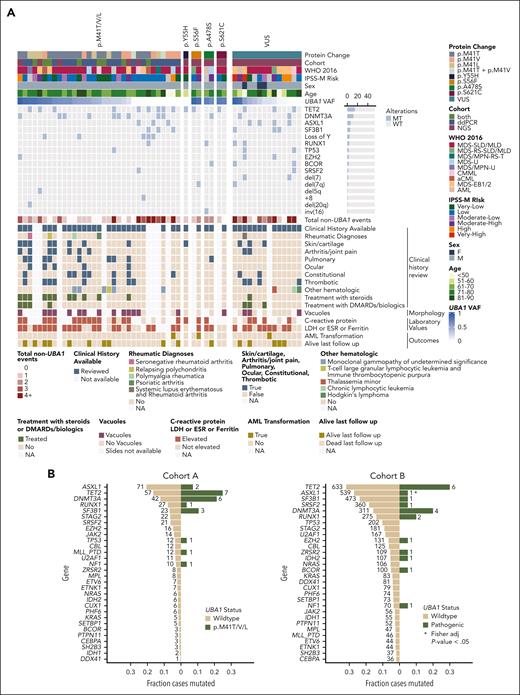
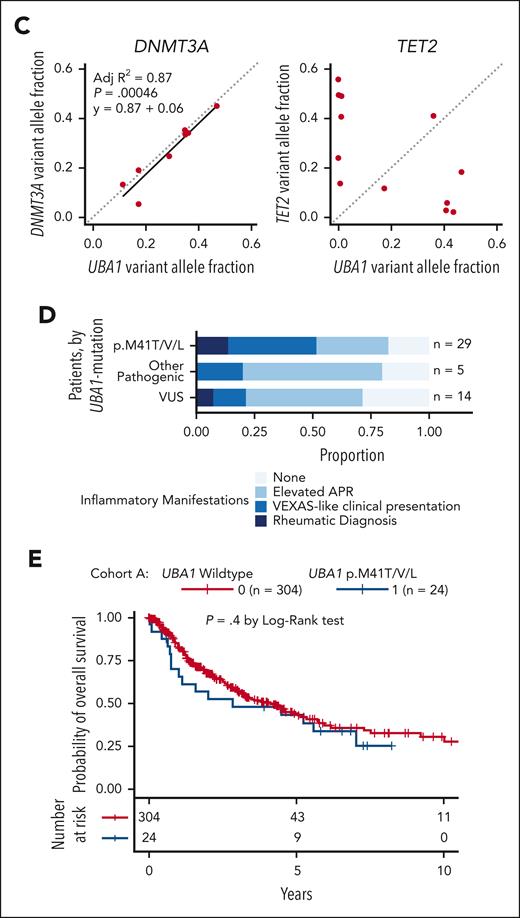
Integration of cohort A and B (n = 2198) yielded 40 patients (all male) with pathogenic UBA1 variants (Table 1). The WHO 2016 classification (available for 39) was MDS–single-lineage dysplasia/multilineage dysplasia (24), MDS–excess blasts-1 (4), MDS unclassifiable (3), chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (2), atypical chronic myeloid leukemia (2), MDS-RS–multilineage dysplasia (1), MDS/MPN-RS and thrombocytosis (1), MDS/MPN-unclassifiable (1) (Figure 1E). Two patients were reclassified as having acute myeloid leukemia (AML) after clinical review because of a history of AML diagnosis. Most patients had IPSS-M very-low/low risk (73%, 27/37; Figure 1F). These patients typically had no myeloid driver gene comutations or often only in the epigenetic regulators TET2 (n = 12) or DNMT3A (n = 10) (Figures 1G and 2A). They had fewer ASXL1 (n = 3; P = .022) and SF3B1 (n = 3) comutations (Figure 2B). Loss of the Y chromosome was frequent (13%, n = 5). In 8 patients with pathogenic UBA1 mutations with VAF of >2% and co-occurring DNMT3A mutations, DNMT3A and UBA1 VAFs were correlated (r2 = 0.87; P = .0005), suggesting that comutation leads to clonal expansion (Figure 2C). Conversely, TET2 comutations were either subclonal (n = 4) or clonally dominant (n = 8) to UBA1. The distinct clonal architectures in DNMT3A- or TET2-comutated cases suggest different mechanisms of cooperation and selection.
Characteristics of 54 patients with MDS with UBA1 mutations; table is split by UBA1 mutation: p.M41, non-p.M41 pathogenic, and VUS
| Characteristic . | p.M41T/V/L, n = 33∗ . | Other pathogenic, n = 7∗ . | VUS, n = 14∗ . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) at sample time | 73 (65-79) | 69 (64-73) | 72 (55-77) |
| WHO 2016 classification | |||
| MDS-SLD/MLD | 20 (62%) | 4 (57%) | 6 (43%) |
| MDS-RS-SLD/MLD | 0 (0%) | 1 (14%) | 1 (7.1%) |
| MDS/MPN-RS-T | 1 (3.1%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| MDS-U | 2 (6.2%) | 1 (14%) | 0 (0%) |
| MDS/MPN-U | 1 (3.1%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| MDS-EB1/2 | 4 (12%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (36%) |
| CMML | 2 (6.2%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (7.1%) |
| aCML | 2 (6.2%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| AML | 0 (0%) | 1 (14%) | 1 (7.1%) |
| Unknown | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| IPSS-M | |||
| Very-low | 7 (23%) | 2 (33%) | 1 (9.1%) |
| Low | 16 (52%) | 2 (33%) | 3 (27%) |
| Moderate-low | 4 (13%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (9.1%) |
| Moderate-high | 2 (6.5%) | 2 (33%) | 2 (18%) |
| High | 2 (6.5%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (18%) |
| Very-high | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (18%) |
| Unknown | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Sex | |||
| F | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (21%) |
| M | 33 (100%) | 7 (100%) | 11 (79%) |
| Bone marrow blast (%) | 2.00 (1.00-4.00) | 1.00 (1.00-1.00) | 4.00 (3.00-8.00) |
| Unknown | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| White blood count (×109/L) | 4.30 (3.42-7.61) | 2.45 (2.04-4.95) | 3.80 (2.59-5.23) |
| Unknown | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Absolute neutrophil count (×109/L) | 3.00 (1.80-4.66) | 1.10 (0.94-3.23) | 1.58 (1.00-2.84) |
| Unknown | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Monocytes (×109/L) | 0.31 (0.10-0.52) | 0.36 (0.20-0.65) | 0.10 (0.10-0.44) |
| Unknown | 5 | 2 | 3 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.45 (8.75-11.15) | 9.90 (8.48-11.60) | 10.35 (8.17-11.07) |
| Unknown | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Platelets (×109/L) | 118 (86-174) | 57 (25-65) | 50 (31-70) |
| Unknown | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Characteristic . | p.M41T/V/L, n = 33∗ . | Other pathogenic, n = 7∗ . | VUS, n = 14∗ . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) at sample time | 73 (65-79) | 69 (64-73) | 72 (55-77) |
| WHO 2016 classification | |||
| MDS-SLD/MLD | 20 (62%) | 4 (57%) | 6 (43%) |
| MDS-RS-SLD/MLD | 0 (0%) | 1 (14%) | 1 (7.1%) |
| MDS/MPN-RS-T | 1 (3.1%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| MDS-U | 2 (6.2%) | 1 (14%) | 0 (0%) |
| MDS/MPN-U | 1 (3.1%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| MDS-EB1/2 | 4 (12%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (36%) |
| CMML | 2 (6.2%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (7.1%) |
| aCML | 2 (6.2%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| AML | 0 (0%) | 1 (14%) | 1 (7.1%) |
| Unknown | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| IPSS-M | |||
| Very-low | 7 (23%) | 2 (33%) | 1 (9.1%) |
| Low | 16 (52%) | 2 (33%) | 3 (27%) |
| Moderate-low | 4 (13%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (9.1%) |
| Moderate-high | 2 (6.5%) | 2 (33%) | 2 (18%) |
| High | 2 (6.5%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (18%) |
| Very-high | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (18%) |
| Unknown | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Sex | |||
| F | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (21%) |
| M | 33 (100%) | 7 (100%) | 11 (79%) |
| Bone marrow blast (%) | 2.00 (1.00-4.00) | 1.00 (1.00-1.00) | 4.00 (3.00-8.00) |
| Unknown | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| White blood count (×109/L) | 4.30 (3.42-7.61) | 2.45 (2.04-4.95) | 3.80 (2.59-5.23) |
| Unknown | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Absolute neutrophil count (×109/L) | 3.00 (1.80-4.66) | 1.10 (0.94-3.23) | 1.58 (1.00-2.84) |
| Unknown | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Monocytes (×109/L) | 0.31 (0.10-0.52) | 0.36 (0.20-0.65) | 0.10 (0.10-0.44) |
| Unknown | 5 | 2 | 3 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.45 (8.75-11.15) | 9.90 (8.48-11.60) | 10.35 (8.17-11.07) |
| Unknown | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Platelets (×109/L) | 118 (86-174) | 57 (25-65) | 50 (31-70) |
| Unknown | 1 | 0 | 1 |
Characteristics of patients with UBA1-mutated MDS (n = 54).
aCML, atypical chronic myeloid leukemia; CMML, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia; EB1/2, excess blasts 1/2; F, female; M, male; MDS-U; MDS-unclassifiable; MLD, multilineage dysplasia; MPN-U, MPN-unclassifiable; SLD, single-lineage dysplasia.
Median (interquartile range); n (%)
Comutation patterns and clinical presentation of UBA1-mutated MDS. (A) Oncoprint for the total cohort of patients with UBA1-mutant MDS (n = 54) including results of retrospective review of clinical history for inflammatory features (bottom). Patients are ordered by decreasing UBA1 VAF per group (p.M41, non-p.M41 pathogenic, and VUS). (B) Frequency of comutations in patients with UBA1-mutated and –wild-type MDS. (C) VAF of pathogenic UBA1 and co-occurring DNMT3A (left) and TET2 (right) mutations. UBA1 VAF was adjusted for single copy of ChrX for comparison with heterozygous mutations in this analysis. Gray dashed line represents the identity line. Black solid line represents a linear model fit to the data. (D) Stacked bar plot of clinical inflammatory manifestations for n = 54 patients. (E) Kaplan-Meier curve for overall survival in cohort A (ddPCR) of patients with MDS with (blue) or without (red) UBA1 p.M41T/V/L mutations. Number of patients per group and P values are indicated on the plot. APR, acute phase reactants; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase.
Comutation patterns and clinical presentation of UBA1-mutated MDS. (A) Oncoprint for the total cohort of patients with UBA1-mutant MDS (n = 54) including results of retrospective review of clinical history for inflammatory features (bottom). Patients are ordered by decreasing UBA1 VAF per group (p.M41, non-p.M41 pathogenic, and VUS). (B) Frequency of comutations in patients with UBA1-mutated and –wild-type MDS. (C) VAF of pathogenic UBA1 and co-occurring DNMT3A (left) and TET2 (right) mutations. UBA1 VAF was adjusted for single copy of ChrX for comparison with heterozygous mutations in this analysis. Gray dashed line represents the identity line. Black solid line represents a linear model fit to the data. (D) Stacked bar plot of clinical inflammatory manifestations for n = 54 patients. (E) Kaplan-Meier curve for overall survival in cohort A (ddPCR) of patients with MDS with (blue) or without (red) UBA1 p.M41T/V/L mutations. Number of patients per group and P values are indicated on the plot. APR, acute phase reactants; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase.
VEXAS syndrome has been associated with a wide range of clinical characteristics and is not yet defined by specific diagnostic criteria. We conducted a detailed clinical review of UBA1-positive cases focusing on inflammatory presentation and treatment. Sufficient clinical history was available for 85% (34/40) of cases with pathogenic UBA1 variants (Figure 2A; supplemental Tables 4 and 5). Of these, 4 patients had rheumatologic diagnoses (all had p.M41T/V/L) and 12 additional patients had inflammatory symptoms associated with VEXAS-like presentation. Of 16 cases, 12 had multiorgan system involvement. Eleven patients were treated with steroids (n = 11) and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs or biologics (n = 4). An additional 9 patients had elevated acute phase reactants, suggesting subclinical levels of inflammation (Figure 2A). Inflammatory manifestations were usually reported preceding or around the time of MDS diagnosis (median time, 227 days before; range, 4.4 years before, 4.8 years after; supplemental Figure 1). Five patients had monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance. Vacuoles, a cardinal feature in VEXAS syndrome, were identified in all 13 patients with UBA1 p.M41 VAF of >2% and in 71% (15/21) of patients with available slides. Taken together, 82% (28/34) of patients with pathogenic variants had inflammatory clinical presentations (Figure 2D).
Patients with UBA1 VUS (n = 14; 3 female) had distinct comutation patterns and risk compared with those with pathogenic variants. They had more myeloid driver gene mutations, with 50% (7/14) having ≥3 comutations than the cases with pathogenic UBA1 mutations (18%; 7/40) and were more likely to harbor alterations associated with adverse prognosis3 (Figures 1G and 2A). Consequently, patients with VUS had a higher proportion of moderate or high IPSS-M risk (64%; 7/11) compared with those with pathogenic variants (27%; Figure 1F). Of 13 cases with UBA1 VUS and available clinical history, 3 patients had inflammatory presentations associated with VEXAS syndrome, and an additional 7 had elevated acute phase reactants; 3 had vacuoles. Functional validation is needed to determine whether these VUS are linked to the inflammatory clinical presentation.
AML transformation has been reported in only a few patients with UBA1-mutated MDS.25,26 Among patients with UBA1-mutated disease in cohorts A and B, 3 transformed to AML. One patient had a low VAF UBA1 p.M41V (0.0002 by ddPCR) subclonal to TET2, SF3B1, FLT3, and ASXL2 comutations. The second had UBA1 p.S56F (VAF of 0.868) and chr 7q deletion. The third had VUS UBA1 p.R869L (VAF of 0.222) and IRF1, NFE2, and RRAS comutations. Among the other patients with UBA1-mutant MDS who had died or who were censored after 1 year (n = 37), none had transformed to AML.
Next, we assessed whether UBA1 mutations carried prognostic value in cohort A, which lacked prognostic biomarkers. We did not identify a significant difference in overall survival between patients with UBA1-mutant (n = 27) and wild-type (n = 312) disease (log-rank test P = .4; Figure 2E). Further studies are required to understand whether UBA1 mutations with or without co-occurring myeloid driver mutations and/or inflammatory presentation are prognostic in low-risk MDS.
In summary, within a large representative diagnostic cohort of patients with MDS, 1% of patients harbored likely pathogenic UBA1 mutations. Notably, UBA1 mutations were frequent (7%) in the subset of male patients with few or no mutations in myeloid driver genes. Patients with UBA1-mutated MDS were predominantly IPSS-M low risk (73%) with a median of 1 additional mutation, usually in DNMT3A or TET2. UBA1 mutations were seen in both dominant clones and as subclones. Of all patients with UBA1 pathogenic variants, inflammatory presentation was seen in 83%, and vacuoles were present in 71%. Importantly, vacuoles were found in all patients with p.M41 mutations at a VAF of >2%. Our data confirm that for the majority of UBA1-mutated MDS cases there was overlapping inflammatory clinical presentation. Limitations of our study include ascertainment of the MDS cohort before the association of UBA1 mutations with VEXAS syndrome, resulting in lack of standardized inflammation assessment across the entire cohort.
Our study highlights the need to consider UBA1 mutations in the diagnostic workup for MDS and MDS/VEXAS syndrome overlap. The enrichment of UBA1 mutations in patients lacking MDS disease–defining alterations may represent a VEXAS syndrome population diagnosed as MDS, whereas others have cardinal genomic and clinical presentations of MDS along with UBA1 mutations and inflammatory phenotype, suggesting a potential VEXAS/MDS overlap syndrome. The systematic incorporation of UBA1 mutations in the diagnostic workup of MDS and inflammatory conditions will provide the necessary data to inform diagnostic criteria that may differentiate MDS to VEXAS syndrome, and/or MDS/VEXAS syndrome overlap. Future prospective studies are needed to define the clinical implications of UBA1 mutations, associated inflammatory presentation, and co-occurring myeloid driver mutations as prognostic factors.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Integrated Genomics Operation for ddPCR and sequencing services. Figure 1A was created with BioRender.com.
M.S. was supported by a National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Cancer Institute (NCI), Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award (F31-CA254130) and a National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Immunology and Inflammation Ruth L. Kirschstein Institutional National Research Service Training Award (5T32AI100853-12). E.B. was supported by the Edward P. Evans Foundation. This work was supported, in part, by a grant from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Ministerio de Economia y Competitividad, Spain (PI 20/00531 and PI 23/00007, cofunded by the European Regional Development Fund, a way to build Europe). 2017 SGR288 (GRC) and 2021 SGR 00560 (GRC) Generalitat de Catalunya; economical support from CERCA Programme/Generalitat de Catalunya, Fundació Internacional Josep Carreras. M.Y.F. was supported by grants from Italian MIUR-PRIN (grant no. 2017RKWNJT) and Fondazione Carisbo. This work was supported by the AIRC 5×1000 call “Metastatic disease: the key unmet need in oncology” to the MYNERVA project, no. 21267 (Myeloid Neoplasms Research Venture AIRC) to M.T.V. and L.M.; and by MURPNRR M4C2I1.3 PE6 project PE00000019 Heal Italia. C.G. was supported by a grant from the Edward P. Evans Foundation. V.S. was supported by Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC) IG-26537-2021 Investigator Research Grant. L.M. was supported by the Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro, Milan, Italy (Investigator Grant no. 20125; AIRC 5×1000 project no. 21267); Cancer Research UK, Fundacion Cientifica de la Asociacion Espanola Contra el Cancer, and Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro under the International Accelerator Award Program (project no. C355/A26819 and no. 22796). D.B.B. is supported by Gabrielle’s Angel Foundation, and the Department of Defense: Bone Marrow Failure Research Program Idea Development Award HT9425-23-1-0507, Edward P. Evans Foundation, and the Aplastic Anemia and MDS International Foundation. E.P. is in part supported by Edward P. Evans Foundation, the MDS Foundation, Damon Runyon Foundation, and NIH/NCI P50 CA254838-01.
Authorship
Contribution: M.S., E.B., and E.P. designed the study, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper; M. Creignou designed the retrospective clinical review form; A.F. and K.H. designed and performed the UBA1 ddPCR assays and targeted DNA sequencing for UBA1; M.S., E.B., and D.B.B. curated NGS variants and clinical annotations; D.D. and J.E.A.O. executed bioinformatics pipelines; L.M., F.S., M. Creignou, U.G., A.A.v.d.L., C. Gurnari, M.J., M.T., O.K., M.Y.F., B.S., E.O., K.Z., L.N.E., W.R.S., R.T., F.T., R.F.P., V.S., I.K., J.B., F.P.S.S., V.M.K., M.R.S., M.B., C. Ganster, L.P., L.A., M.G.D.P., P.F., A.P., U.P., M.H., P.V., C.F., M.T.V., L.-Y.S., M.F., J.H.J., J.C., N.G., M. Cazzola, E.H.-L., and S.O. provided clinical data and DNA specimens; E.B. and E.P. coordinated sample acquisition; and all authors provided feedback on the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: U.G. has received honoraria from Celgene, Novartis, Amgen, Janssen, Roche, and Jazz; and has received research funding from Celgene and Novartis. A.A.v.d.L. serves on advisory boards of Celgene, Amgen, Roche, Novartis, and Alexion; and has received research funding from Celgene. F.T. serves on the advisory boards of Jazz, Pfizer, and AbbVie; and has received research funding from Celgene. I.K. serves on the advisory board of Genesis Pharma; and has received research funding from Celgene and Janssen Hellas. F.P.S.S. has received honoraria from Janssen-Cilag, Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Amgen, AbbVie, and Pfizer; serves on the advisory boards of Novartis, Amgen, and AbbVie; and has received research funding from Novartis. M.R.S. serves on the advisory boards of AbbVie, Astex, Celgene, Karyopharm, Selvita, and TG Therapeutic; has equity in Karyopharm; and has received research funding from Astex, Incyte, Sunesis, Takeda, and TG Therapeutics. G.S. serves on the advisory boards of AbbVie, Amgen, Astellas, Böehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Helsinn Healthcare, Hoffmann-La Roche, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and Onconova; and has received research funding from Celgene, Hoffmann-La Roche, Janssen-Cilag, and Novartis. L.A. serves on the advisory boards of AbbVie, Astex, Celgene, and Novartis and has received research funding from Celgene. M.H. has received honoraria from Novartis, Pfizer, and PriME Oncology; serves on the advisory boards of AbbVie, Bayer Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo, Novartis, and Pfizer and has received institutional research funding from Astellas, Bayer Pharma, BergenBio, Daiichi Sankyo, Karyopharm, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche. P.V. has received honoraria and research funding from Celgene. C.F. serves on the advisory boards of, and has received honoraria from, Celgene, Novartis, and Janssen; and has received research funding from Celgene. M.T.V. serves on the advisory board of Celgene; has received honoraria from Celgene and Novartis; and has received research funding from Celgene. N.G. serves on the advisory board of, and has received honoraria from, Novartis; and has received research funding from Alexion. B.L.E. has received research funding from Celgene and Deerfield. R.B. serves on the advisory boards of Celgene, AbbVie, Astex, NeoGenomics, and Daiichi Sankyo; and has received research funding from Celgene and Takeda. D.B.B. receives consulting fees from Alexion Pharmaceuticals and is on the advisory boards for Novartis and Sobi. E.H.-L. has received research funding from Celgene. E.P. is a founder, equity holder, and holds fiduciary roles in Isabl Inc, a company offering analytics for cancer whole-genome sequencing data; and holds stock options in TenSixteen Bio. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Elli Papaemmanuil, Computational Oncology Service, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, 1275 York Ave, Box 20, New York, NY 10065; email: papaemme@mskcc.org.
References
Author notes
D.B.B., E.H.-L., and E.P. contributed equally to this study.
Myeloid driver gene mutations have been previously published and are available at https://doi.org/10.1056/EVIDoa2200008 and deposited to CBioPortal.
Deidentified patient data including clinical annotations and UBA1 mutations has been provided in the supplemental Tables.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal