Key Points
Pembrolizumab is effective as consolidative therapy for patients with PTCL in first remission.
Pembrolizumab administered after ASCT has an acceptable safety profile.
Abstract
Autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is often used as consolidation for several subtypes of peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) in first remission. However, many patients relapse after ASCT and have a very poor prognosis. There are no approved treatment options for posttransplantation maintenance or consolidation in PTCL. PD-1 blockade has demonstrated some efficacy for patients with PTCL. We, therefore, conducted a phase 2 multicenter study of the anti–PD-1 monoclonal antibody pembrolizumab after ASCT in patients with PTCL in first remission. Pembrolizumab was administered at 200 mg IV every 3 weeks for up to 8 cycles within 21 days from post-ASCT discharge (and within 60 days of stem cell infusion). The primary end point was progression-free survival (PFS) at 18 months after ASCT. Twenty-one patients were treated in this study and 67% (n = 14) completed 8 cycles of treatment. Among all patients who were evaluable, 13 of 21 were alive and achieved PFS at 18 months after ASCT, meeting the study’s primary end point. The estimated 18-month PFS was 83.6% (95% confidence interval [CI], 68-100), and overall survival 94.4% (95% CI, 84-100). The toxicity profile was consistent with the known toxicity profile of pembrolizumab, with no grade 5 toxicities. In conclusion, PD-1 blockade after ASCT with pembrolizumab is feasible with a favorable safety profile and promising activity, supporting further confirmatory studies. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT02362997.
Introduction
Peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCLs) carry a poor prognosis (except for ALK+ anaplastic large-cell lymphoma [ALCL]).1 For many subtypes, current guidelines recommend consideration of high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) in the first remission,2 although the benefit of ASCT has never been confirmed in randomized trials. Unfortunately, >50% of the patients will still relapse after ASCT, and most will subsequently die from their disease.3 This highlights the urgent need for further development of PTCL-specific treatments.
PD-1 inhibitors have variable activity in lymphoma, with favorable response rates in classic Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma but lower response rates in PTCL.4,5 PD-L1 is frequently expressed on the tumor and/or in the microenvironment of PTCL. The expression of PD-L1 was found to inhibit the proliferation of T cells and promote the induction of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells.6 The largest study of a PD-1 inhibitor in relapsed and refractory (R/R) PTCL is a multicenter phase 2 study of 102 patients treated with geptanolimab, which showed encouraging results. The objective response rate (ORR) was 40%, with 15% complete response (CR) and a median duration of response of 11.4 months.7 A phase 1b study evaluated nivolumab in hematologic malignancies, including 5 patients with PTCL, and showed an ORR of 40%.8 Another phase 2 study using single agent pembrolizumab in R/R PTCL showed an ORR of 33%, although this trial was stopped early after an interim futility analysis.9 Three studies of PD-1 blockade in R/R extranodal natural killer cell/T-cell lymphoma (ENKTL) also showed favorable response rates ranging from 44% to 100%.10-12
There has been a concern that PD-1 inhibitors could cause hyperprogression (HP) in certain subtypes of PTCL, consistent with the observation that PD-1 may serve as a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor.13 HP was observed in 3 patients with adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma after a single dose of nivolumab.14 Bennani et al also observed HP in 4 of 12 patients treated with nivolumab, 3 of whom had angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL).15 This study was terminated early because of concerns over HP, although 2 CRs and 2 partial responses were achieved.
Posttransplantation PD-1 blockade has shown favorable outcomes in HL and other B-cell lymphomas.16,17 However, post-ASCT consolidation with PD-1 has not been explored in PTCL, and there have been generally few studies examining the role of consolidation or maintenance in this setting. A phase 2 study evaluating brentuximab vedotin (BV) plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, etoposide, and prednisone with or without ASCT followed by BV consolidation in CD30+ PTCL showed promising results, with an ORR and a CR rate of 91% and 80%, respectively.18 A prior phase 2 study using romidepsin as consolidative therapy did not suggest this to be a beneficial treatment.19 PD-1 consolidation in the posttransplantation setting is an appealing strategy because it is a time of minimal disease burden and active immune remodeling that may be an ideal milieu to induce T-cell antitumor immunity.
In this study, we aimed to explore the efficacy of PD-1 blockade as a consolidation therapy after ASCT in patients with PTCL in first remission. We hypothesized that PD-1 blockade as consolidative therapy would improve the progression-free survival (PFS) compared with historical outcomes. This report is part of a multicohort study in which part A enrolled patients with HL and part B enrolled patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma who received consolidation with pembrolizumab after ASCT. Part A was a positive study, with an 18-month PFS rate of 82%, meeting the primary end point.20 Part B was a negative study, with no observed PFS benefit with consolidation therapy with pembrolizumab after ASCT.21
Methods
Study population
This phase 2, nonrandomized, open label, investigator-initiated, multicenter trial enrolled patients at 6 centers in the United States. This article presents the results of the PTCL cohort. Patients aged ≥18 years with PTCL in first remission (partial or complete) were included in the study. Eligible PTCL subtypes included PTCL-not otherwise specified (NOS), AITL, ALK− ALCL, enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma (EATL), monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma (MEITL), and ENKTL. Patients with other PTCL subtypes, including ALK+ PTCL and those with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma were not eligible. Major inclusion criteria were an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status ≤1, adequate hematologic and organ function, and absence of contraindication to PD-1 blockade. Patients with central nervous system involvement of lymphoma were excluded. Moreover, patients who had received prior anti–PD-1, anti–PD-L1, or anti–CTLA-4 therapy were not eligible for this study. Participants who were enrolled before ASCT were required to rescreen and meet all eligibility criteria after transplantation. The decision to offer ASCT was at the discretion of the treating physician and was not specified in the protocol. All participants included in this study provided written informed consent. The study was clinically registered as #NCT02362997, institutional review board approved, monitored by an independent data and safety monitoring board, and conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Merck & Co (Kenilworth, NJ) provided the study drug.
Treatment and assessments
Treatment was recommended to start within 21 days from the post-ASCT discharge and could commence no later than transplantation day 60. Before initiation of therapy, patients were required to have appropriate hematologic recovery (grade ≤2 per common terminology criteria for adverse events, version 4.0). Treatment consisted of pembrolizumab 200 mg administered IV every 3 weeks for up to 8 cycles. This dosing schedule was based on the dosing of pembrolizumab in the companion studies in HL and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Dose modifications were not allowed. However, subsequent dosing could be delayed up to 12 weeks to check for toxicity. Participants could not receive any additional therapy (including radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy) after ASCT. The drug was permanently held for grade 4 treatment-related adverse events (AEs) and selected grade 3 immune-related AEs (irAEs). Treatment response was assessed with positron emission tomography and computed tomography scans at baseline, immediately after ASCT (within 21 days before study treatment), and at 10 and 22 weeks and 12 and 18 months after ASCT. Radiographic assessments of treatment response were performed in accordance with the 2007 International Harmonization Project criteria.22 If radiographic progression was observed at week 10, continued treatment was allowed, if the patient was tolerating treatment without clinical deterioration.
End points and statistical analysis
Data collection and analysis were independently performed by the investigators. The primary end point was the 18-month PFS rate after ASCT in patients treated with pembrolizumab. Secondary end points included 18-month overall survival (OS), PFS, response rate to pembrolizumab in patients with measurable disease after ASCT, and safety. Extrapolating from PFS data from a large, prospective phase 2 trial of ASCT as consolidation for PTCL in first remission, the expected 18-month PFS rate after ASCT in patients with chemosensitive PTCL ranged from ∼40% to 50%.23 We hypothesized that consolidation treatment with pembrolizumab would improve the 18-month PFS rate from 45% to 70%. This was based on the assumption of a ∼40% response rate for patients with residual disease after ASCT, extrapolated from the aforementioned phase 1 and phase 2 studies, and further assumptions that patients with sensitive disease would remain free of relapse by 18 months.24 The 18-month timeframe was chosen given that a high percentage of recurrences will be observed during this time, so this was a practical timeframe for reporting the results of the trial.
With a planned sample size of 21 patients, we would consider the treatment promising if at least 13 patients remained alive and progression-free at 18 months after ASCT using the exact binomial method. With this design, the probability of considering the treatment promising in treating R/R PTCL is .09 if the true but unknown progression-free rate is 45% but .85 if the true but unknown progression-free rate is 70%. This decision rule was calculated using the exact binomial method. PFS and OS were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method, with the Greenwood formula to estimate variance. PFS was defined as the time from transplantation to death from any cause, or progression, with data of patients censored at the last time seen alive and with progression-free disease. OS was defined as the time from study entry to death from any cause, with data of patients censored at the last time seen alive. After the 18-month follow-up visit, radiographic restaging was performed at the discretion of the treating physician and was not specified in the protocol. The log-rank test was used to assess survival differences between groups.
Results
Patients
In total, 21 patients were enrolled in this study between January 2017 and July 2020. The baseline clinical characteristics of the patients are shown in Table 1. The median age was 58 years (range, 33-73 years). The most common subtype was PTCL-NOS (52%). Other subtypes were AITL (19%), ENKTL (14%), ALK–ALCL (10%), and MEITL (5%). All patients received 1 prior line of therapy. Most patients had stage IV disease (43%) before ASCT. Of all patients, 14% had a low-risk international prognostic index (IPI) score, 43% had intermediate-risk, 5% had high-risk, and 38% had unknown IPI scores. Before ASCT, 90% of the patients achieved complete metabolic response. Upon study entry, 95% of the patients achieved complete metabolic response. Of the 21 patients, 14 completed the planned 8 cycles of treatment; the other patients completed 1 (n = 4 patients), 2 (n = 1 patient), 4 (n = 1 patient), and 5 (n = 1 patient) cycles. The median number of cycles was 8. Dose delays of pembrolizumab occurred in 3 patients, whereas 1 patient had 1 missed dose. Reasons for discontinuing treatment were toxicity (n = 4), progressive disease (n = 1), withdrawal of consent (n = 1), and COVID-19 infection (n = 1). Of the 4 patients who discontinued treatment because of toxicity, 2 patients had grade 2 and 3 transaminitis, 1 patient had grade 3 diarrhea, and 1 had grade 2 arthralgias.
Patient baseline characteristics
| . | Total . |
|---|---|
| N = 21 (%) . | |
| Age at registration | |
| Median, y (range) | 58 (33-73) |
| Histology | |
| PTCL-NOS | 11 (52) |
| AITL | 4 (19) |
| ENKTL, nasal type | 3 (14) |
| ALK− ALCL | 2 (10) |
| MEITL | 1 (5) |
| Sex | |
| Female | 9 (43) |
| Male | 12 (57) |
| Race | |
| Asian | 2 (10) |
| Black or African American | 2 (10) |
| White | 11 (52) |
| Unknown | 6 (29) |
| Stage at diagnosis | |
| I | 2 (10) |
| II | 2 (10) |
| III | 3 (14) |
| IV | 9 (43) |
| Unknown | 5 (24) |
| IPI risk group | |
| 0-1 | 3 (14) |
| 2 | 6 (29) |
| 3 | 3 (14) |
| 4-5 | 1 (5) |
| Unknown | 8 (38) |
| No. of prior treatments | |
| 1 | 21 (100) |
| EBV status at diagnosis | |
| Negative | 7 (33) |
| Positive | 6 (29) |
| Not available | 8 (38) |
| Prior regimen | |
| CHOEP | 10 (48) |
| CHOEP + lenalidomide | 2 (10) |
| SMILE + RT | 2 (10) |
| Other (CHOP, CHOP + MTX, CHOP + pralatraxate, BV-CHP, SMILE and CHP) | 7 (33) |
| Conditioning regimen | |
| Carmustine/etoposide/cytarabine/melphalan (BEAM) | 19 (90) |
| Busulfan/cyclophosphamide/thiotepa | 1 (5) |
| Not reported | 1 (5) |
| Disease status before ASCT | |
| Complete metabolic response | 19 (90) |
| Partial metabolic response | 2 (10) |
| Disease status at study entry (after ASCT) | |
| Complete metabolic response | 20 (95) |
| Partial metabolic response | 1 (5) |
| . | Total . |
|---|---|
| N = 21 (%) . | |
| Age at registration | |
| Median, y (range) | 58 (33-73) |
| Histology | |
| PTCL-NOS | 11 (52) |
| AITL | 4 (19) |
| ENKTL, nasal type | 3 (14) |
| ALK− ALCL | 2 (10) |
| MEITL | 1 (5) |
| Sex | |
| Female | 9 (43) |
| Male | 12 (57) |
| Race | |
| Asian | 2 (10) |
| Black or African American | 2 (10) |
| White | 11 (52) |
| Unknown | 6 (29) |
| Stage at diagnosis | |
| I | 2 (10) |
| II | 2 (10) |
| III | 3 (14) |
| IV | 9 (43) |
| Unknown | 5 (24) |
| IPI risk group | |
| 0-1 | 3 (14) |
| 2 | 6 (29) |
| 3 | 3 (14) |
| 4-5 | 1 (5) |
| Unknown | 8 (38) |
| No. of prior treatments | |
| 1 | 21 (100) |
| EBV status at diagnosis | |
| Negative | 7 (33) |
| Positive | 6 (29) |
| Not available | 8 (38) |
| Prior regimen | |
| CHOEP | 10 (48) |
| CHOEP + lenalidomide | 2 (10) |
| SMILE + RT | 2 (10) |
| Other (CHOP, CHOP + MTX, CHOP + pralatraxate, BV-CHP, SMILE and CHP) | 7 (33) |
| Conditioning regimen | |
| Carmustine/etoposide/cytarabine/melphalan (BEAM) | 19 (90) |
| Busulfan/cyclophosphamide/thiotepa | 1 (5) |
| Not reported | 1 (5) |
| Disease status before ASCT | |
| Complete metabolic response | 19 (90) |
| Partial metabolic response | 2 (10) |
| Disease status at study entry (after ASCT) | |
| Complete metabolic response | 20 (95) |
| Partial metabolic response | 1 (5) |
BV-CHP, brentuximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin and prednisone; CHOEP, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, etoposide and prednisone; CHOP, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone; MTX, methotrexate; SMILE, dexamethasone, methotrexate, ifosfamide, l-asparaginase, and etoposide; RT, radiation therapy.
Efficacy
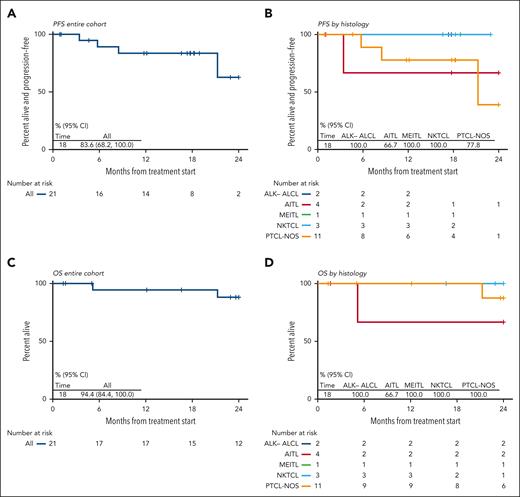
Among the 21 patients, 13 were alive and progression-free at 18 months after ASCT, thereby meeting the primary end point. Of the remaining 8 patients in the first 18 months of follow-up, 3 relapsed at 4, 12, and 12 months, and 5 did not have follow-up data at the 18-month time point. The median follow-up time was 24 months. No radiographic progression occurred at week 10. Of the 4 patients who discontinued treatment because of toxicity, 2 had continued CR up to 14 and 16 months; 1 patient only had 1 assessment, so their data were censored; and the final patient was in CR for 23 months until progressive disease occurred. The Kaplan-Meier estimates of PFS and OS are shown in Figure 1. The 18-month PFS estimate was 83.6% (95% confidence interval, 68-100), and the OS was 94.4% (95% confidence interval, 84-100). The 2 patients who died while on study had progressive disease. The PFS and OS were evaluated for the different subtypes, without a significant difference (Figure 1B,D). Of note, the 3 patients with ENKTL had no progression during the study period (Figure 1B). Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) status was available for 13 of 21 patients. There was no significant difference in the PFS (P = .55) or OS (P = .49) between the EBV-positive and -negative groups. As noted previously, we did not systematically collect data after the 18-month time point. Therefore, we do not have longer-term follow-up for these patients.
Survival curves. Kaplan-Meier curves of (A) PFS for the entire cohort; (B) PFS based on the histology; (C) OS for the entire cohort; and (D) OS based on the histology. CI, confidence interval.
Survival curves. Kaplan-Meier curves of (A) PFS for the entire cohort; (B) PFS based on the histology; (C) OS for the entire cohort; and (D) OS based on the histology. CI, confidence interval.
Toxicity
All patients who received at least 1 dose of study treatment were included in the toxicity assessments (n = 21) (Table 2). Seventeen of these 21 patients experienced at least 1 toxicity while on the study, including grade 1 (24%; n = 5), grade 2 (38%; n = 8), grade 3 (19%; n = 4), and grade 4 (5%; n = 1). The most common toxicities of any grade were nausea (24%; n = 5), alkaline phosphatase increase (19%; n = 4), diarrhea (19%; n = 4), abdominal pain (14%; n = 3), hypothyroidism (14%; n = 3), alanine aminotransferase increase (10%; n = 2), anemia (10%; n = 2), arthralgia (10%; n = 2), and aspartate aminotransferase increase (10%; n = 2). Grade 3 toxicities on study included: transaminitis (10%; n = 2), abdominal pain (n = 1), colitis (n = 1), diarrhea (n = 1), and headache (n = 1). Of the patients who had grade 3 toxicity, 1 patient had abdominal pain, watery diarrhea, and colitis. No colonoscopy was performed, but infectious studies showed negative results, and imaging was consistent with inflammatory colitis. Of the 2 patients who had transaminitis, 1 had received 1 cycle of pembrolizumab, whereas the other received 2 cycles before treatment discontinuation. Both patients received steroids for the transaminitis, and this resolved after 2 days for 1 patient and 2 months for the other. Of the 4 patients with grade 3 toxicity, 2 patients progressed, of whom 1 eventually died, and 2 patients remained in CR. None of these patients were readministered with pembrolizumab after incurring the grade 3 toxicity. One patient experienced grade 4 respiratory failure unrelated to pembrolizumab. This was because of disease progression and volume overload. No other grade 4 toxicities and no grade 5 toxicities occurred. There were 14 irAEs in the study limited to grade 1 or 3, which affected 7 of 21 (33%) patients. The most common grade ≥2 irAEs were transaminitis, diarrhea, and hypothyroidism (4 grade 2 events and 4 grade 3 events).
Summary of toxicity
| . | n (%) . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 . | Grade 2 . | Grade 3 . | Grade 4 . | |
| Severe AEs | ||||
| Transaminitis | 2 (10) | |||
| Abdominal pain | 1 (5) | |||
| Colitis | 1 (5) | |||
| Diarrhea | 1 (5) | |||
| Headache | 1 (5) | |||
| Respiratory failure | 1 (5) | |||
| trAE | ||||
| Transaminitis | 1 (5) | 2 (10) | ||
| Abdominal pain | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | ||
| Arthralgia | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | ||
| Diarrhea | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | ||
| Hypothyroidism | 1 (5) | 2 (10) | ||
| Arthralgia | 1 (5) | |||
| Colitis | 1 (5) | |||
| Dizziness | 1 (5) | |||
| Elevated ALP | 1 (5) | |||
| Flu-like symptoms | 1 (5) | |||
| Hyperthyroidism | 1 (5) | |||
| Nasal congestion | 1 (5) | |||
| Nausea | 1 (5) | |||
| Neuralgia | 1 (5) | |||
| Noncardiac chest pain | 1 (5) | |||
| Weight loss | 1 (5) | |||
| irAE | ||||
| Transaminitis | 1 (5) | 2 (10) | ||
| Hypothyroidism | 1 (5) | 2 (10) | ||
| Arthralgia | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | ||
| Diarrhea | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | ||
| Colitis | 1 (5) | |||
| Elevated ALP | 1 (5) | |||
| Hyperthyroidism | 1 (5) | |||
| . | n (%) . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 . | Grade 2 . | Grade 3 . | Grade 4 . | |
| Severe AEs | ||||
| Transaminitis | 2 (10) | |||
| Abdominal pain | 1 (5) | |||
| Colitis | 1 (5) | |||
| Diarrhea | 1 (5) | |||
| Headache | 1 (5) | |||
| Respiratory failure | 1 (5) | |||
| trAE | ||||
| Transaminitis | 1 (5) | 2 (10) | ||
| Abdominal pain | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | ||
| Arthralgia | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | ||
| Diarrhea | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | ||
| Hypothyroidism | 1 (5) | 2 (10) | ||
| Arthralgia | 1 (5) | |||
| Colitis | 1 (5) | |||
| Dizziness | 1 (5) | |||
| Elevated ALP | 1 (5) | |||
| Flu-like symptoms | 1 (5) | |||
| Hyperthyroidism | 1 (5) | |||
| Nasal congestion | 1 (5) | |||
| Nausea | 1 (5) | |||
| Neuralgia | 1 (5) | |||
| Noncardiac chest pain | 1 (5) | |||
| Weight loss | 1 (5) | |||
| irAE | ||||
| Transaminitis | 1 (5) | 2 (10) | ||
| Hypothyroidism | 1 (5) | 2 (10) | ||
| Arthralgia | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | ||
| Diarrhea | 1 (5) | 1 (5) | ||
| Colitis | 1 (5) | |||
| Elevated ALP | 1 (5) | |||
| Hyperthyroidism | 1 (5) | |||
Values are n (%), unless otherwise specified.
Therapy related AEs (trAEs): all AEs attributed as at least possibly related to study treatment. Severe AEs: all grade ≥3 AEs regardless of attribution. irAEs: all AEs considered to be immune-related by the investigator.
ALP, alkaline phosphatase.
Discussion
Patients with PTCL have a poor prognosis, especially those for whom disease recurs after frontline therapy. ASCT is commonly used as a consolidative therapy despite the lack of randomized trials evaluating its benefits. Except for BV in ALCL, existing standard-of-care treatments for relapsed PTCL such as pralatrexate and histone deacetylase inhibitors have low response rates.25,26 Although data are limited for post-ASCT consolidation in PTCL, 1 trial using romidepsin in this setting did not suggest a clinical benefit,19 although a trial looking at maintenance BV had promising results.18 Prior studies of PD-1 inhibitors in PTCL have demonstrated variable efficacy, with the most favorable outcomes noted in ENKTL.8,9 Similarly, studies investigating PD-1 blockade in the post-ASCT setting in HL have also shown favorable efficacy and safety outcomes.20 Therefore, we decided to study posttransplantation pembrolizumab consolidation in patients with PTCL in first remission after ASCT.
The side effect profile observed in this study was consistent with the known toxicity profile of pembrolizumab. No excess lung toxicity was noted, even with most of the patients receiving a carmustine-based conditioning regimen before transplantation.
This study met its primary efficacy end point, with 13 of 21 patients remaining alive and progression-free 18 months after ASCT. We did not observe a significant PFS or OS difference between PTCL subtypes. However, this may be due to the small sample size. Notably, all patients with ENKTL (n = 3) remained progression-free at last follow-up. These 3 patients had stages IE with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis at diagnosis, and stage II and IV disease. ENKTL is the PTCL subtype with the highest reported single-agent response rate with PD-1 inhibitors and is, therefore, a disease of particular interest for further study using the approach described in this article.10,11,27 Some experts suggest allogeneic SCT as an upfront consolidation in advanced-stage ENKTL.28 However, there are encouraging data on combining PD-1 inhibitors with chemotherapy in ENKTL.29,30 Therefore, a strategy of PD-1 blockade in combination with chemotherapy with or without ASCT and maintenance pembrolizumab would be worthy of study and could provide a less toxic and more efficacious alternative to allogeneic SCT or ASCT alone in ENKTL.
EBV status was available for a subset of the patients (13 of 21). EBV-driven malignancies have upregulated PD-L1 on tumor cells, making PD-1 blockade an attractive treatment strategy. However, we did not observe a difference in outcomes between the EBV-positive vs EBV-negative groups. Our analysis was hampered by missing EBV status on a significant subset of patients but is consistent with prior reports showing a lack of correlation with EBV expression and response to PD-1 inhibitors in PTCL.31-33
Our results contribute to the emerging data exploring PD-1 blockade in hematologic malignancies. HP has been a concern in some settings, and in 1 study, most of the patients who experienced HP had AITL.15 We included patients with AITL in our study because the data on HP are still limited, and we hypothesized that HP was unlikely to occur in patients who were in remission after ASCT. HP was not observed in the limited number of patients with AITL included in our study, possibly because patients were in remission at the time of pembrolizumab initiation. However, HP needs to be considered carefully in the design of any future studies of checkpoint inhibitors in PTCL, and distinguishing HP from pseudoprogression remains a challenge.
Limitations of this study include the small sample size, with a limited number of patients in each subtype, precluding adequately powered comparison of outcomes. In addition, we did not perform PD-L1 staining in this cohort, because tissue was not systematically available or collected for study; furthermore, the prognostic value of PD-L1 positivity is still unclear in PTCL with inconsistent prior reports.7,31-33 The CD30 status was not collected in this study, although the use or not of BV in induction is unlikely to have introduced a significant selection bias in this cohort. This is because our study did not include patients with ALK+ ALCL, which at the participating institutions is the only population for which ASCT is not used as the standard of care. In addition, we did not collect cytogenetics or other molecular markers on this study. Lastly, we did not evaluate how this treatment strategy may affect the quality of life of the patients. This should be examined further in future studies.
Given the limited sample size of this phase 2 study, the efficacy results should be seen as preliminary. These data do not justify this as a standard approach outside the context of a clinical trial. Randomized and placebo-controlled trials will be necessary to definitely establish whether or not this strategy improves outcomes in PTCL or in specific subsets. Treatment with PD-1 blockade before transplantation has also shown favorable outcomes in classical HL.31 Furthermore, patients with R/R HL had an improved response rate to salvage chemotherapy administered after anti–PD-1, suggest that PD-1 blockade may function as a chemosensitizing agent.32,33 ENKTL is particularly worthy of further study based upon the favorable outcomes of PD-1 inhibitors in this subtype when given alone or in combination with chemotherapy. Because the role of ASCT in ENKTL remains to be defined, future studies must examine not only the utility of PD-1 consolidation after ASCT but also whether ASCT with or without incorporation of PD-1 inhibitors in pretransplantation induction is beneficial at all. Lastly, PD-1 blockade may be combined with other immunotherapies (or BV for CD30+ disease including ALCL), which could be deployed in the pre- or post-ASCT setting, as has been done in HL.34
In conclusion, posttransplantation consolidation with pembrolizumab is feasible in patients with PTCL, with a favorable safety profile. The efficacy is promising, justifying future studies, especially in subtypes known to be sensitive to this therapy.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Pasquarello Tissue Bank in Hematologic Malignancies.
P.A. acknowledges the support of the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (Scholar in Clinical Research) as well as the long-standing generosity of the Harold and Virginia Lash Foundation. The study was supported, in part, by a research grant from Investigator-Initiated Studies Program of Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC. E.D.J. is supported by the Reid Family Fund for Lymphoma Research. P.B.D. and G.L.S. are supported, in part, by a National Institutes of Health (NIH) award P01 CA23766 and an NIH/National Cancer Institute Cancer Center support grant P30 CA008748.
The opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC.
Authorship
Contribution: M.H.M. analyzed and interpreted data and wrote the manuscript; P.A. and E.D.J. designed the research, recruited patients, analyzed and interpreted data, and helped in manuscript preparation; R.A.R. designed the research and analyzed data; and P.B.D., M.M.M., Y.-B.C., Z.D., A.F.H., D.C.F., A.S.L., O.O.O., S.Y.N., C.A.J., R.W.M., A.I.K., Y.L.N., C.S.S., G.L.S., and J.M.Z. recruited patients and approved the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: G.L.S. receives research funding from Janssen, Amgen, Beyond Spring, BMS, and DSMB for Arcellx. Y.-B.C. has served as a consultant for Magenta, Moderna, Novartis, Daiichi, Equilium, Celularity, and Incyte. A.F.H. has served as a consultant for Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, Merck, Seattle Genetics, AstraZeneca, Karyopharm, ADC Therapeutics, Takeda, Tubulis, Regeneron, Genmab, Pfizer, Caribou, Adicet Bio, and AbbVie; and has received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, Merck, Seattle Genetics, Kite Pharma, Gilead Sciences, AstraZeneca, and ADC Therapeutics. A.S.L. has served as a consultant for Kite and Seagen and is in the Research to Practice speakers’ bureau. C.A.J. has served as a consultant for Kite/Gilead, Novartis, BMS/Celgene, Abintus Bio, Instil Bio, ImmPACT Biom Miltenyi, Caribou Bio, Daiichi-Sankyo, MorphoSys, AstraZeneca, and ADC Therapeutics; and has received research funding from Pfizer and Kite/Gilead. R.W.M. has served as a consultant for Genmab, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Bristol Myers Squibb, AbbVie, Intellia, and Epizyme; and has received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, Genentech/Roche, and Genmab. Y.L.N. has received research funding from AstraZeneca, Novartis, Secura Bio, and Affimed. C.S.S. has served as a consultant for Juno Therapeutics, Sanofi-Genzyme, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Genmab, Precision Biosciences, Kite/a Gilead Company, Celgene/BMS, Gamida Cell, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Ono Pharmaceuticals, MorphoSys, CSL Behring, Syncopation Life Sciences, CRISPR Therapeutics, and GSK; and has received research funding from Juno Therapeutics, Celgene/BMS, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Precision Biosciences, Actinium Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi Genzyme, and NKARTA. J.M.Z has served as a consultant for Seattle Genetics and has received research funding from Seattle Genetics, Myeloid, CRSPR, Secure bio, AstraZeneca, Astex, and Kiowa Kirin. P.A. has served as a consultant for Merck, BMS, ADC Therapeutics, Tessa, Genmab, Enterome, Genentech/Roche, Xencor, ATB Therapeutics, and Foresight; has received research funding from Kite and institutional funding from Merck, BMS, Adaptive, Genentech, IGM, and AstraZeneca; and has received honoraria from Merck. E.D.J. has served as a consultant for Bayer, Daiichi, ADC Therapeutics, Imbrium, Merck, and Secura Bio; and has received research funding from Novartis, Pharmacyclics, Janssen, Daiichi, BeiGene, and Celgene. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Eric D. Jacobsen, Dana Farber Cancer Institute, 450 Brookline Ave, Boston, MA 02115; e-mail: eric_jacobsen@dfci.harvard.edu.
References
Author notes
Data are available on request from the corresponding author, Eric D. Jacobsen (eric_jacobsen@dfci.harvard.edu).
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal