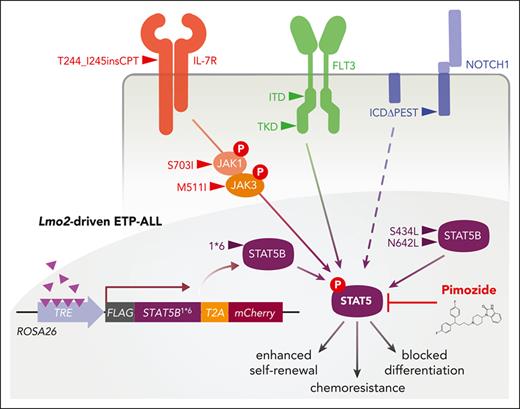
Key Points
STAT5 is sufficient for IL-7 signaling in ETP-ALL. STAT5 supports growth, self-renewal, and chemoresistance of LSCs.
Pimozide enhances eradication of LSCs by chemotherapy.
Abstract
Interleukin-7 (IL-7) supports the growth and chemoresistance of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL), particularly the early T-cell precursor subtype (ETP-ALL), which frequently has activating mutations of IL-7 signaling. Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT5) is an attractive therapeutic target because it is almost universally activated in ETP-ALL, even in the absence of mutations of upstream activators such as the IL-7 receptor (IL-7R), Janus kinase, and Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3). To examine the role of activated STAT5 in ETP-ALL, we have used a Lmo2-transgenic (Lmo2Tg) mouse model in which we can monitor chemoresistant preleukemia stem cells (pre-LSCs) and leukemia stem cells (LSCs) that drive T-ALL development and relapse following chemotherapy. Using IL-7R-deficient Lmo2Tg mice, we show that IL-7 signaling was not required for the formation of pre-LSCs but essential for their expansion and clonal evolution into LSCs to generate T-ALL. Activated STAT5B was sufficient for the development of T-ALL in IL-7R-deficient Lmo2Tg mice, indicating that inhibition of STAT5 is required to block the supportive signals provided by IL-7. To further understand the role of activated STAT5 in LSCs of ETP-ALL, we developed a new transgenic mouse that enables T-cell specific and doxycycline-inducible expression of the constitutively activated STAT5B1∗6 mutant. Expression of STAT5B1∗6 in T cells had no effect alone but promoted expansion and chemoresistance of LSCs in Lmo2Tg mice. Pharmacologic inhibition of STAT5 with pimozide-induced differentiation and loss of LSCs, while enhancing response to chemotherapy. Furthermore, pimozide significantly reduced leukemia burden in vivo and overcame chemoresistance of patient-derived ETP-ALL xenografts. Overall, our results demonstrate that STAT5 is an attractive therapeutic target for eradicating LSCs in ETP-ALL.
Introduction
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is a heterogenous cancer of T-cell progenitors that can be cured in most children and some adults with high-dose chemotherapy followed by years of maintenance chemotherapy.1 However, cure comes at the cost of significant therapy-related complications, relapse has few options and a median survival of only 8 months.2,3 The early T-cell precursor (ETP) subtype of T-ALL is a particular challenge, especially in adults who cannot tolerate pediatric-type high-dose chemotherapy regimens.4 Novel approaches are needed to significantly improve cure rates, especially with less toxic chemotherapy.
ETP-ALL has a distinct stem cell-like immunophenotype, gene expression profile, and genomic mutations involving transcription factors regulating hematopoietic development, epigenetic regulators, and cytokine signaling.5,6 The latter frequently involves the interleukin-7 (IL-7) pathway, where activating mutations of IL-7 receptor (IL-7R), or its downstream signaling components are commonly observed.5,7-10 IL-7 promotes survival and proliferation of T-ALL cells through the Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT, and RAS/MAPK pathways although their relative importance in ETP-ALL remains ill-defined. Studies using human T-ALL cell lines suggested an important role for activation of PI3K-AKT and the prosurvival factor BCL2, but more recent work revealed an essential role for the proto-oncogenes STAT5 and PIM1 in IL-7-mediated proliferation and growth of T-ALL cell lines.11-15
Irrespective of the mutational profile, STAT5 is activated in the majority of ETP-ALL.7,8 Apart from mutations of the canonical IL-7R/JAK/STAT pathway, STAT5 may be activated by increased IL-7R expression13 or loss-of-function DNM2 mutations, which enhance IL-7 signaling through perturbation of IL-7R internalization.16 In addition, cross talk from other oncogenic signaling pathways such as Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) may explain STAT5 activation.17,18 The oncogenic activity of STAT5 is best illustrated by retroviral expression of constitutively activated STAT5, which promoted hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) proliferation, self-renewal, and rapidly led to a fatal myeloid hyperproliferation or multilineage leukemia.19-24 The effects of STAT5 in leukemia stem cells (LSCs) have not been directly examined in T-ALL although studies of STAT5-deficient HSCs suggest an important role for stem cell maintenance, survival, and resistance to chemotherapy.25,26
Given that the IL-7R/JAK/STAT pathway is commonly mutated in T-ALL and other hematological malignancies, several groups have explored targeting this pathway. JAK inhibitors such as ruxolitinib had single agent activity and enhanced glucocorticoid (GC) sensitivity in ETP-ALL, even in cases that lack JAK mutations.27,28 A clinical trial is currently evaluating the value of incorporating ruxolitinib into the chemotherapy backbone for T-ALL with activation of JAK/STAT signaling (NCT03117751). However, mutations of the downstream effector STAT5B may mediate resistance to JAK inhibitors.29 Furthermore, JAK inhibitors are unlikely to be effective where STAT5 is activated through alternative signaling pathways.30,31 Therefore, STAT5 as a central signaling node represents a logical therapeutic target for ETP-ALL and other subtypes of T-ALL characterized by STAT5-activating mutations.
Using the CD2-Lmo2 transgenic (Lmo2Tg) model of T-ALL,32 we showed that aberrant overexpression of the Lmo2 oncogene induced the emergence of preleukemia stem cells (pre-LSCs) with an ETP-like gene expression profile within the CD4− CD8− CD44− CD25+ CD28low (DN3a) population of T-cell progenitors.16,33 These pre-LSCs evolved into LSCs by accumulating additional mutations that are recurrently observed in human T-ALL, including alterations of JAK-STAT and NOTCH1 signaling pathways.16,34-36 In this study we have used this model of ETP-ALL to examine the role of STAT5 in LSCs and investigate STAT5 as a therapeutic target.
Methods
ROSA26-STOPfl/fl-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6 mouse line
The ROSA26-STOPfl/fl-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6 model was generated following the previously established protocol.37 The 3X-FLAG-tagged STAT5B1∗6 transgene in fusion with the T2A linker and the mCherry fluorescent reporter was amplified from the TxTCPVIR (TRE-gene-T2A-mCherry-PGK-Venus-IRES-rtTA3) retroviral vector expressing the constitutively active STAT5BH298R+S716F mutant (STAT5B1∗6),38 which was generated as previously described.35 The polymerase chain reaction product was digested with SalI and EcoRV and cloned into the pENTRT1A plasmid, with subcloned constructs verified by DNA sequencing (Micromon, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia). We generated conditional and inducible STAT5B1∗6 knock-in G4 ROSALUC embryonic stem cells (ESCs) by targeting our pENTRT1A construct to the ROSA26 locus using the Gateway- and recombinase-mediated cassette exchange, as previously described.37 Integration was confirmed in G4 ROSALUC ESCs by in vitro Cre-mediated excision, which resulted in stable rtTA3 expression, and doxycycline treatment, which induced expression of the mCherry reporter. Finally, we generated ESC-derived highly chimeric embryonic and adult animals, which were used for establishing the ROSA26-STOPfl/fl-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6 mouse line.
Mouse experiments
All experiments were preapproved by the AMREP Animal Ethics Committee. The current study was performed with the previously described CD2-Lmo2 (Lmo2Tg) mouse model.32 Mice cohorts were generated by crossbreeding with B6.129S7-Il7rtm1/mx (IL-7R−/−),39hCD2-iCre (CD2-iCreTg),40 and ROSA26-YFP reporter (YFP)41 mouse strains purchased from Jackson Laboratories. The CD2-iCreTg; ROSA26-STOPΔ/Δ-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6 (CD2-rtTA-STAT5B1∗6) mouse model was generated by crossbreeding our ROSA26-STOPfl/fl-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6 mouse line with CD2-iCreTg and Lmo2Tg mice. All mouse lines were backcrossed onto a C57BL/6J background for 10 generations and maintained in pathogen-free conditions according to institutional animal care guidelines.
FACS analysis
In vivo drug administration
Vincristine, dexamethasone, and l-asparaginase (VXL) chemotherapy was administered by intraperitoneal injection, as previously described.43 For in vivo administration, pimozide was resuspended in 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP; Sigma-Aldrich, #328634) 1:9 poly(ethylene)glycol (PEG; Sigma-Aldrich, P3015), immediately before oral gavage at a dosage of 25 mg/kg, as previously described.44
Detailed materials and methods are included in the supplemental Methods, available on the Blood website.
Results
IL-7 signaling is required for development of Lmo2-driven T-ALL
We crossed the Lmo2Tg mouse model with IL-7R-deficient (IL-7R−/−) mice to determine the role of IL-7 signaling in ETP-ALL. We confirmed the absence of IL-7R at the surface of DN3a thymocytes (Figure 1A), the immunophenotype of the pre-LSCs in Lmo2Tg mice.16 Absence of IL-7R prevented activation of STAT5 (phosphorylated STAT5, pSTAT5; Figure 1B). Absence of IL-7R led to a 20-fold reduction in thymic cellularity irrespective of the presence of the Lmo2 transgene (Figure 1C). However, IL-7R/IL-7 signaling was not required for the development of DN3a T-cell progenitors (Figure 1D), although associated with a 25-fold reduction in DN3a absolute numbers (supplemental Figure 1A). One of the earliest phenotypic changes observed in Lmo2Tg mice is a block in T-cell differentiation at the pre-TCR DN3a stage.16 This Lmo2-induced defect in T-cell differentiation was still observed in IL-7R-deficient thymocytes (Figure 1D; supplemental Figure 1B). Thus, immunophenotypic analyses suggested that signaling through the IL-7R was not required for the formation of pre-LSCs.
IL-7/JAK/STAT5 signaling is essential for pre-LSC self-renewal and leukemogenesis. (A) Levels of IL-7R at the surface of DN3a T-cell progenitors from 6-week old mice of different genotypes, as indicated. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) ± standard deviation (SD) of N > 5 individual mice. (B) Levels of activated STAT5 (pSTAT5) in DN3a thymocytes from 6-week-old mice from the indicated genotypes treated with IL-7. MFI ± SD of N = 3 individual mice, 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey correction test; ∗∗∗P < .001. (C-D) Thymic cellularity (C), as well as representative analysis of the CD4− CD8− CD44− CD25+ (DN3) subpopulations of thymocytes (D) from 6-week-old wild-type (WT), IL-7R−/−, Lmo2Tg, and Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− mice, assessed by flow cytometry. Immature CD4−CD8− (DN), CD4+CD8+ double-positive (DP), and mature CD4+CD8− and CD4−CD8+ single-positive (SP) populations. Using CD25 and CD28 markers on DN3 thymocytes, CD25hiCD28low, CD25hiCD28hi, and CD25intermediateCD28hi immunophenotypes define DN3a, b, and c subpopulations, respectively. Median ± standard error of the mean (SEM), 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with WT; ##P < .01, ###P < .001 compared with Lmo2Tg mice. (E) Scheme for serial transplantation of thymocytes from 6-week old donor (Cd45.2+) mice of the indicated genotypes into sublethally irradiated isogenic (Cd45.1+) recipients. (F) Proportion of donor-derived thymocytes determined by flow cytometry in primary recipients, 6 weeks posttransplant. Minimal repopulation capacity (1%) is indicated by a dashed line. Median ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗P < .01 compared with WT; ##P < .01 compared with Lmo2Tg donor cells. (G) Fold expansion of donor-derived Lmo2Tg and Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− DN3a thymocytes enumerated in the thymus of primary (I), secondary (II), and tertiary (III) recipients, assessed by flow cytometry. Mean ± SEM (N = 15 and 12 recipients in the primary transplant; N = 6 in secondary and tertiary transplants, for Lmo2Tg and Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− donor cells, respectively), 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ##P < .01, ###P < .001 compared with Lmo2Tg mice. Minimal expansion for maintenance (fold of 1) is indicated by a dashed line. (H) Absolute numbers of DN3a T-cell progenitors in the thymus of WT, IL-7R−/−, Lmo2Tg, and Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− mice at 6 weeks (N = 9, 8, 9, and 10, respectively), 6 months (N = 6, 6, 4, and 3, respectively) and 12 months (N = 6, 6, 7, and 5, respectively) of age. Median ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗P < .01 compared with WT; ##P < .01 compared with Lmo2Tg donor cells. (I) Kaplan-Meier curves of the time to leukemia for mice with the indicated genotypes. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test; ∗∗∗P < .001 as compared with WT; ##P < .01, ###P < .001 compared with Lmo2Tg mice. Over T-ALL was confirmed at necropsy. (J) Experimental schematic of transplant using transduced Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPC) isolated from fetal livers at embryonic day (E) 13.5 into lethally irradiated isogenic (Cd45.1+) mice to generate thymocytes. These cells were injected into sublethally irradiated recipients, which were maintained on either doxycycline (DOX)-enriched or standard diet. (K) Levels of pSTAT5 in donor-derived Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− DN3a thymocytes transduced with TxTCPVIR-STAT5B1∗6 (STAT5B1∗6) harvested from recipients maintained on either DOX-enriched or standard diet. Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− thymocytes transduced with TxTCPVIR (vector) were used as controls. MFI ± SD of N = 5 individual mice. (L) Fold expansion of transduced Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− DN3a cells, enumerated in the thymus of recipients 6 weeks after transplantation. Dashed lines within the violin represents the 25th, 50th, and 75th quartiles, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗P < .001 to vehicle. (M) Fold expansion of transduced donor-derived Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− DN3a T-cell progenitors, enumerated in the thymus of primary (I), secondary (II), and tertiary (III) recipients maintained on DOX-enriched diet (+DOX). Mean ± SEM (N = 5 recipients in the primary and tertiary transplants; N = 6 and N = 4 in secondary transplant, for Vector and STAT5B1∗6 transduced donor cells, respectively), 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, and ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with empty vector (vector). Minimal expansion for maintenance (fold of 1) is indicated by a dashed line. (N) Kaplan-Meier curves of the leukemia onset for recipients injected with transduced Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− DN3a thymocytes, maintained on either DOX-enriched or standard diet. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test (N = 6 per cohort); ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001 as compared with littermates maintained on standard feed. All malignant thymic tumors were diagnosed at necropsy.
IL-7/JAK/STAT5 signaling is essential for pre-LSC self-renewal and leukemogenesis. (A) Levels of IL-7R at the surface of DN3a T-cell progenitors from 6-week old mice of different genotypes, as indicated. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) ± standard deviation (SD) of N > 5 individual mice. (B) Levels of activated STAT5 (pSTAT5) in DN3a thymocytes from 6-week-old mice from the indicated genotypes treated with IL-7. MFI ± SD of N = 3 individual mice, 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey correction test; ∗∗∗P < .001. (C-D) Thymic cellularity (C), as well as representative analysis of the CD4− CD8− CD44− CD25+ (DN3) subpopulations of thymocytes (D) from 6-week-old wild-type (WT), IL-7R−/−, Lmo2Tg, and Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− mice, assessed by flow cytometry. Immature CD4−CD8− (DN), CD4+CD8+ double-positive (DP), and mature CD4+CD8− and CD4−CD8+ single-positive (SP) populations. Using CD25 and CD28 markers on DN3 thymocytes, CD25hiCD28low, CD25hiCD28hi, and CD25intermediateCD28hi immunophenotypes define DN3a, b, and c subpopulations, respectively. Median ± standard error of the mean (SEM), 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with WT; ##P < .01, ###P < .001 compared with Lmo2Tg mice. (E) Scheme for serial transplantation of thymocytes from 6-week old donor (Cd45.2+) mice of the indicated genotypes into sublethally irradiated isogenic (Cd45.1+) recipients. (F) Proportion of donor-derived thymocytes determined by flow cytometry in primary recipients, 6 weeks posttransplant. Minimal repopulation capacity (1%) is indicated by a dashed line. Median ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗P < .01 compared with WT; ##P < .01 compared with Lmo2Tg donor cells. (G) Fold expansion of donor-derived Lmo2Tg and Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− DN3a thymocytes enumerated in the thymus of primary (I), secondary (II), and tertiary (III) recipients, assessed by flow cytometry. Mean ± SEM (N = 15 and 12 recipients in the primary transplant; N = 6 in secondary and tertiary transplants, for Lmo2Tg and Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− donor cells, respectively), 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ##P < .01, ###P < .001 compared with Lmo2Tg mice. Minimal expansion for maintenance (fold of 1) is indicated by a dashed line. (H) Absolute numbers of DN3a T-cell progenitors in the thymus of WT, IL-7R−/−, Lmo2Tg, and Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− mice at 6 weeks (N = 9, 8, 9, and 10, respectively), 6 months (N = 6, 6, 4, and 3, respectively) and 12 months (N = 6, 6, 7, and 5, respectively) of age. Median ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗P < .01 compared with WT; ##P < .01 compared with Lmo2Tg donor cells. (I) Kaplan-Meier curves of the time to leukemia for mice with the indicated genotypes. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test; ∗∗∗P < .001 as compared with WT; ##P < .01, ###P < .001 compared with Lmo2Tg mice. Over T-ALL was confirmed at necropsy. (J) Experimental schematic of transplant using transduced Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPC) isolated from fetal livers at embryonic day (E) 13.5 into lethally irradiated isogenic (Cd45.1+) mice to generate thymocytes. These cells were injected into sublethally irradiated recipients, which were maintained on either doxycycline (DOX)-enriched or standard diet. (K) Levels of pSTAT5 in donor-derived Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− DN3a thymocytes transduced with TxTCPVIR-STAT5B1∗6 (STAT5B1∗6) harvested from recipients maintained on either DOX-enriched or standard diet. Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− thymocytes transduced with TxTCPVIR (vector) were used as controls. MFI ± SD of N = 5 individual mice. (L) Fold expansion of transduced Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− DN3a cells, enumerated in the thymus of recipients 6 weeks after transplantation. Dashed lines within the violin represents the 25th, 50th, and 75th quartiles, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗P < .001 to vehicle. (M) Fold expansion of transduced donor-derived Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− DN3a T-cell progenitors, enumerated in the thymus of primary (I), secondary (II), and tertiary (III) recipients maintained on DOX-enriched diet (+DOX). Mean ± SEM (N = 5 recipients in the primary and tertiary transplants; N = 6 and N = 4 in secondary transplant, for Vector and STAT5B1∗6 transduced donor cells, respectively), 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, and ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with empty vector (vector). Minimal expansion for maintenance (fold of 1) is indicated by a dashed line. (N) Kaplan-Meier curves of the leukemia onset for recipients injected with transduced Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− DN3a thymocytes, maintained on either DOX-enriched or standard diet. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test (N = 6 per cohort); ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001 as compared with littermates maintained on standard feed. All malignant thymic tumors were diagnosed at necropsy.
To confirm this at a functional level,33 we transplanted thymocytes into sublethally irradiated recipients (Figure 1E). IL-7R-deficient Lmo2Tg thymocytes retained repopulating activity although 4-fold less than Lmo2Tg littermates (Figure 1F). Serial transplantation showed that repopulating activity of Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− thymocytes was impaired, thereby suggesting that IL-7 signaling was important for self-renewal of pre-LSCs (Figure 1G; supplemental Figure 1C). To determine if this defect in self-renewal impacted on the evolution of pre-LSCs with aging, we compared the numbers of DN3a thymocytes in 6-week, 6- and 12-month-old Lmo2Tg mice. As previously reported,36 we observed a progressive accumulation of DN3a thymocytes in aged Lmo2Tg mice (Figure 1H; supplemental Figure 1D). In contrast, there was no expansion of the DN3a population in Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− mice. Furthermore, there was reduced monoclonality as assessed by Tcrβ rearrangement (supplemental Figure 1E), suggesting a defect in clonal evolution of pre-LSCs. Finally, we aged a cohort of mice to determine if IL-7 signaling was important for the development of T-ALL. Unlike most Lmo2Tg mice that developed T-ALL within 12 months of age, IL-7R-deficient Lmo2Tg mice did not develop T-ALL (Figure 1I). Furthermore, there was evidence of a dose effect of IL-7 signaling as the absence of one IL-7R allele significantly decreased penetrance and delayed the development of T-ALL (Figure 1I). Altogether, our results suggest that IL-7 signaling was dispensable for the formation of pre-LSCs but required for their long-term self-renewal, clonal expansion, and progression to T-ALL.
Activation of STAT5 rescued loss of IL-7R
IL-7 stimulates the JAK/STAT, RAS/MAPK, and PI3K/AKT pathways in T-ALL.11,12 To determine if activation of STAT5 could rescue the absence of IL-7R, we infected embryonic day (E) 13.5 Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− fetal liver cells with a doxycycline-inducible constitutively active STAT5B mutant (STAT5B1∗6) which mimics cytokine-mediated activation of wild-type STAT5B38,45,46 (Figure 1J). Infected cells were transplanted into lethally irradiated mice to establish Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− thymocytes with doxycycline-inducible STAT5B1∗6. Treatment of mice with doxycycline led to STAT5 activation in IL-7R-deficient DN3a thymocytes (Figure 1K). Transplantation assays showed that expression of STAT5B1∗6 significantly increased expansion of Lmo2Tg; IL-7R−/− DN3a thymocytes (Figure 1L) and restored their self-renewal capacity (Figure 1M; supplemental Figure 1F). Moreover, transplanted mice maintained on a doxycycline-containing diet developed overt T-ALL whereas transplanted mice on normal diet remained leukemia-free for >12 months (Figure 1N). Thus, aberrant STAT5 activation was sufficient to overcome the loss of IL-7R.
STAT5 promotes proliferation and survival of LSCs
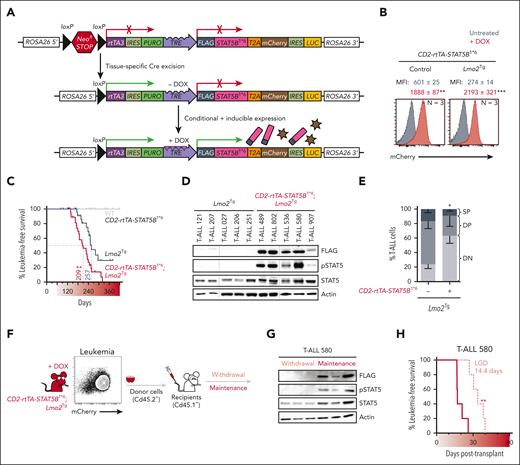
We generated a conditional and doxycycline-inducible mouse line with the STAT5B1∗6 transgene inserted into the ROSA26 locus (ROSA26-STOPfl/fl-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6) to enable T-cell specific activation of STAT5 (Figure 2A). We bred our ROSA26-STOPfl/fl-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6 model with CD2-iCreTg or CD2-iCreTg; Lmo2Tgmice and confirmed doxycycline-induced expression in the DN3a population of T-cell progenitors (Figure 2B; supplemental Figure 2A-D). In CD2-iCreTg;ROSA26-STOPΔ/Δ-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6 mice (CD2-rtTA-STAT5B1∗6), expression of STAT5B1∗6 did not induce T-ALL (Figure 2C; supplemental Figure 2D). In contrast, expression of STAT5B1∗6 in Lmo2Tg mice accelerated T-ALL development and increased penetrance. Increased pSTAT5 was confirmed in T-ALL developing in CD2-rtTA-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg mice maintained on doxycycline-enriched diet (Figure 2D). Leukemias arising in doxycycline-treated CD2-rtTA-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg mice were more immature than T-ALL not expressing STAT5B1∗6 (Figure 2E). To address the importance of maintaining activated STAT5 in T-ALL, STAT5B1∗6-expressing Lmo2Tg leukemias were injected into recipient mice maintained (maintenance) or not (withdrawal) on doxycycline (Figure 2F). Loss of STAT5B1∗6 expression following withdrawal of doxycycline delayed but did not prevent the growth of T-ALL (Figure 2G-H; supplemental Figure 2E).
Constitutively active STAT5 promotes T-ALL progression and maintenance. (A) Schematic overview of the conditional and inducible STAT5B1∗6–targeted ROSA26 locus. Cre-mediated removal of the conditional NeoR STOP cassette leads to ROSA26-based reverse tetracycline-transactivator 3 (rtTA3) expression and availability of the tetracycline response element (TRE). Doxycycline (DOX) administration leads to inducible expression of the FLAG-tagged STAT5B1∗6 oncogene, which can be monitored by mCherry reporter expression. (B) Representative flow cytometric analysis of mCherry expression in DN3a thymocytes from 6-week-old CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6 (Control) and CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg (Lmo2Tg) mice maintained or not on doxycycline-enriched diet (DOX; red). MFI ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with untreated (gray). (C) Kaplan-Meier curves of the time to leukemia for WT, CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6, Lmo2Tg, and CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg mice maintained on DOX-enriched diet (). Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test; ∗∗P < .01 as compared with Lmo2Tg littermates. All malignant thymic tumors were diagnosed at necropsy median time to leukemia (days) is indicated. All malignant thymic tumors were diagnosed at necropsy. (D-E) Levels of the FLAG-tagged STAT5B1∗6 oncoprotein, phosphorylated STAT5 (pSTAT5), and total STAT5 (D), as well as proportion of T-cell populations (%; E), in T-ALL cells harvested from the thymus of Lmo2Tg and CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg mice at the onset of disease. Actin was used as a loading control. Immature CD4−CD8− (DN), CD4+CD8+ DP, and mature CD4+CD8− and CD4−CD8+ SP populations are indicated. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05 compared with mice maintained on standard diet. (F) Flow cytometry analysis and schematic representation of the transplantation strategy of primary STAT5B1∗6–expressing Lmo2Tg (Cd45.2+) leukemia cells into sublethally irradiated Cd45.1+ recipients maintained or not on DOX-enriched diet. (G) Expression of the FLAG-tagged STAT5B1∗6 oncoprotein and resulting pSTAT5 in leukemic cells from the thymus of 3 recipients per cohort was confirmed by western blot. Actin was used as a loading control. (H) Kaplan-Meier curves of the time to leukemia for recipients transplanted with primary CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg T-ALL 580, with leukemia growth delay (LGD; days) indicated between cohorts of mice maintained (maintenance; dark red) or not (withdrawal; light red) on DOX-enriched feed. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test (N = 6 per cohort); ∗∗P < .01 as compared with maintenance recipients. IRES: internal ribosome entry site; LUC: luciferase; PURO: puromycin resistance sequence; T2A: Thosea asigna virus 2A self-cleaving peptide sequence.
Constitutively active STAT5 promotes T-ALL progression and maintenance. (A) Schematic overview of the conditional and inducible STAT5B1∗6–targeted ROSA26 locus. Cre-mediated removal of the conditional NeoR STOP cassette leads to ROSA26-based reverse tetracycline-transactivator 3 (rtTA3) expression and availability of the tetracycline response element (TRE). Doxycycline (DOX) administration leads to inducible expression of the FLAG-tagged STAT5B1∗6 oncogene, which can be monitored by mCherry reporter expression. (B) Representative flow cytometric analysis of mCherry expression in DN3a thymocytes from 6-week-old CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6 (Control) and CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg (Lmo2Tg) mice maintained or not on doxycycline-enriched diet (DOX; red). MFI ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with untreated (gray). (C) Kaplan-Meier curves of the time to leukemia for WT, CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6, Lmo2Tg, and CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg mice maintained on DOX-enriched diet (). Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test; ∗∗P < .01 as compared with Lmo2Tg littermates. All malignant thymic tumors were diagnosed at necropsy median time to leukemia (days) is indicated. All malignant thymic tumors were diagnosed at necropsy. (D-E) Levels of the FLAG-tagged STAT5B1∗6 oncoprotein, phosphorylated STAT5 (pSTAT5), and total STAT5 (D), as well as proportion of T-cell populations (%; E), in T-ALL cells harvested from the thymus of Lmo2Tg and CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg mice at the onset of disease. Actin was used as a loading control. Immature CD4−CD8− (DN), CD4+CD8+ DP, and mature CD4+CD8− and CD4−CD8+ SP populations are indicated. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05 compared with mice maintained on standard diet. (F) Flow cytometry analysis and schematic representation of the transplantation strategy of primary STAT5B1∗6–expressing Lmo2Tg (Cd45.2+) leukemia cells into sublethally irradiated Cd45.1+ recipients maintained or not on DOX-enriched diet. (G) Expression of the FLAG-tagged STAT5B1∗6 oncoprotein and resulting pSTAT5 in leukemic cells from the thymus of 3 recipients per cohort was confirmed by western blot. Actin was used as a loading control. (H) Kaplan-Meier curves of the time to leukemia for recipients transplanted with primary CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg T-ALL 580, with leukemia growth delay (LGD; days) indicated between cohorts of mice maintained (maintenance; dark red) or not (withdrawal; light red) on DOX-enriched feed. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test (N = 6 per cohort); ∗∗P < .01 as compared with maintenance recipients. IRES: internal ribosome entry site; LUC: luciferase; PURO: puromycin resistance sequence; T2A: Thosea asigna virus 2A self-cleaving peptide sequence.
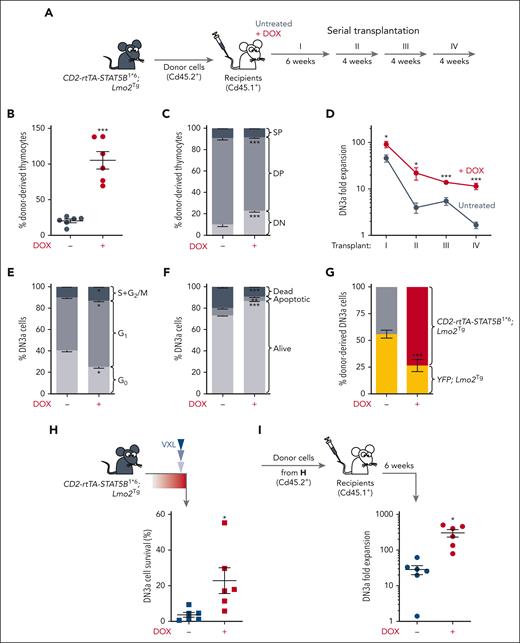
To examine the effect of activated STAT5 in LSCs, we performed serial thymocyte transplantation assays, using DN3a numbers as a measure of pre-LSC numbers. (Figure 3A). Expression of STAT5B1∗6 enhanced repopulation capacity and expansion of DN3a thymocytes (Figure 3B), and limited the differentiation of pre-LSCs in the thymus of recipient mice (Figure 3C). Furthermore, serial transplantation assays demonstrated enhanced self-renewal (Figure 3D; supplemental Figure 3A). Expansion of DN3a cells by STAT5B1∗6 was associated with increased cell cycle and reduced apoptosis (Figure 3E-F), suggesting that constitutive activation of STAT5 conferred a competitive advantage to LSCs. To address this, we performed competitive transplant assays with a 1:1 mixture of pre-LSCs from 6-week-old YFP; Lmo2Tg and CD2-rtTA-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg mice. In the presence of doxycycline, pre-LSCs with constitutively active STAT5 had a 3-fold competitive advantage over pre-LSCs with wild-type STAT5 (Figure 3G). As expected, pre-LSCs from YFP; Lmo2Tg and CD2-rtTA-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg thymocytes displayed a similar capacity to generate DN3a cells in sublethally irradiated recipients in the absence of doxycycline (Figure 3G). Thus, activation of STAT5 conferred a cell-intrinsic advantage for LSCs.
Functional characterization of STAT5B1∗6-expressing Lmo2Tg pre-LSCs. (A) Scheme for serial transplantation into primary (I), secondary (II), tertiary (III), and quaternary (IV) recipients, using CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg thymocytes. (B) Proportion of donor-derived (Cd45.2+) cells enumerated in the thymus of primary recipient mice. Mean ± SEM, Student t test, ∗∗∗P < .001. (C) Immunophenotype of donor-derived cells in the thymus of primary recipients. DN, DP, and SP represent the CD4−CD8− double-negative, CD4+CD8+ DP, and CD4+CD8− single-positive with CD4−CD8+ single-positive populations, respectively. Mean ± SEM, Student t test (N = 6), ∗∗∗P < .001. (D) Fold expansion of donor-derived CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg DN3a cells in the thymus of serially injected recipients maintained (+DOX) or not (untreated) on DOX-enriched feed. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05, ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with mice maintained on standard diet. (E-F) Cell-cycle (E) and apoptosis (F) analysis in DN3a thymocytes from CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg mice after 7 days administration of DOX. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05, ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with mice maintained on standard diet. (G) Competitive assay of LSCs assessed by flow cytometry 4 weeks after transplantation of equal numbers of CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg, and YFP; Lmo2Tg (yellow) thymocytes into sublethally irradiated recipients. Proportion of donor-derived CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg (gray or red) and YFP; Lmo2Tg (yellow) DN3a thymocytes from recipients maintained (+DOX) or not maintained on doxycycline-enriched feed. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01 compared with YFP; Lmo2Tg cells. (H) Survival of DN3a thymocytes from CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg mice treated with induction-like therapy for T-ALL (VXL43) after 7 days administration of DOX. Numbers of DN3a thymocytes in mice treated with vehicle (supplemental Figure 3B) was used as reference and defined as 100%. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, and ∗∗∗P < .001. (I) Fold expansion of donor-derived DN3a cells enumerated in the thymus of recipients injected with CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg thymocytes from panel H. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05.
Functional characterization of STAT5B1∗6-expressing Lmo2Tg pre-LSCs. (A) Scheme for serial transplantation into primary (I), secondary (II), tertiary (III), and quaternary (IV) recipients, using CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg thymocytes. (B) Proportion of donor-derived (Cd45.2+) cells enumerated in the thymus of primary recipient mice. Mean ± SEM, Student t test, ∗∗∗P < .001. (C) Immunophenotype of donor-derived cells in the thymus of primary recipients. DN, DP, and SP represent the CD4−CD8− double-negative, CD4+CD8+ DP, and CD4+CD8− single-positive with CD4−CD8+ single-positive populations, respectively. Mean ± SEM, Student t test (N = 6), ∗∗∗P < .001. (D) Fold expansion of donor-derived CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg DN3a cells in the thymus of serially injected recipients maintained (+DOX) or not (untreated) on DOX-enriched feed. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05, ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with mice maintained on standard diet. (E-F) Cell-cycle (E) and apoptosis (F) analysis in DN3a thymocytes from CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg mice after 7 days administration of DOX. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05, ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with mice maintained on standard diet. (G) Competitive assay of LSCs assessed by flow cytometry 4 weeks after transplantation of equal numbers of CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg, and YFP; Lmo2Tg (yellow) thymocytes into sublethally irradiated recipients. Proportion of donor-derived CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg (gray or red) and YFP; Lmo2Tg (yellow) DN3a thymocytes from recipients maintained (+DOX) or not maintained on doxycycline-enriched feed. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01 compared with YFP; Lmo2Tg cells. (H) Survival of DN3a thymocytes from CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg mice treated with induction-like therapy for T-ALL (VXL43) after 7 days administration of DOX. Numbers of DN3a thymocytes in mice treated with vehicle (supplemental Figure 3B) was used as reference and defined as 100%. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, and ∗∗∗P < .001. (I) Fold expansion of donor-derived DN3a cells enumerated in the thymus of recipients injected with CD2-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg thymocytes from panel H. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05.
To determine whether constitutively active STAT5 promotes chemoresistance of LSCs, we enumerated DN3a thymocytes remaining 24 hours after treatment with a combination of VXL.43 Consistent with STAT5-driven chemoresistance, the proportion of cells surviving 24 hours after chemotherapy was 6-fold higher in CD2-rtTA-STAT5B1∗6; Lmo2Tg mice maintained on a doxycycline-enriched diet (Figure 3H; supplemental Figure 3B). Transplant of these surviving thymocytes showed significantly increased repopulating activity of STAT5B1∗6-expressing pre-LSCs (Figure 3I). Thus, activation of STAT5 promoted chemoresistance of LSCs.
Pimozide inhibits pSTAT5 activation by canonical and noncanonical pathways
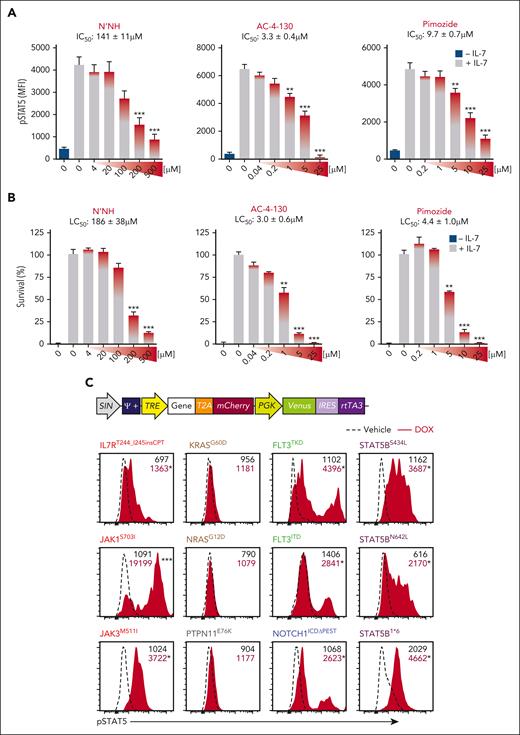
Given the ability of STAT5 to promote growth and chemoresistance of LSCs, we examined the therapeutic potential of STAT5 inhibitors.47 We first compared the ability of 3 STAT5 inhibitors to inhibit pSTAT5 using the IL-7 dependent Ba/F3 cells line: pimozide, AC-4-130, and N′-((4-Oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl) methylene) nicotinohydrazide (N’NH).48-52 All 3 small molecules showed a dose-dependent inhibition of IL-7-induced pSTAT5 (Figure 4A). Cytotoxicity of these agents correlated with their ability to inhibit pSTAT5 (Figure 4B; supplemental Figure 4A). Given similar potency of all 3 STAT5 inhibitors, further studies focused on the efficacy of pimozide, an antipsychotic drug with many years of use in humans.
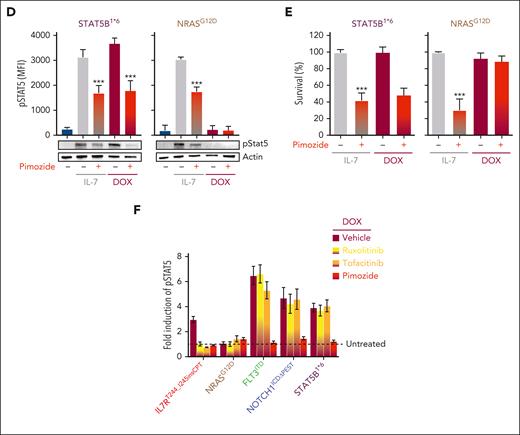
STAT5 is the common effector downstream multiple oncogenic signaling pathways. (A-B) Levels of pSTAT5 (A) and survival (B) of BaF3-IL7R cells treated with increasing doses of the STAT5 inhibitors N’NH, AC-4-130, and pimozide assessed by flow cytometry. MFI ± SD of n = 3 biological replicates are shown, 1-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with vehicle + IL-7 (gray). Basal levels of pSTAT5 were measured in unstimulated BaF3-IL7R cells (− IL-7; teal). Median inhibitory concentration (IC50) and lethal concentration (LC50) of N’NH, AC-4-130, and pimozide are indicated. (C) Schematic representation of the TxTCPVIR retroviral vector used for the doxycycline-inducible expression of the listed oncogenic mutants in Ba/F3-IL7R cells (top). Inducible expression of the oncogenic mutants in transduced cells can be assessed by measuring levels of the mCherry reporter by flow cytometry, as previously described.35 Representative flow cytometric analysis of pSTAT5 levels in transduced Ba/F3-IL7R cells after 4 hours of stimulation with doxycycline (DOX; red area), which induced overexpression of oncogenic signaling pathways frequently mutated in T-ALL.5,6 MFI, Student t test (N = 3); ∗P < .05, ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with cells treated with vehicle (dashed line). (D-E) Levels of pSTAT5 (D) and survival (E) of transduced BaF3-IL7R cells expressing STAT5B1∗6 and NRASG12D mutants, cultured in the presence (gray) or absence of IL-7 (teal) and DOX (red), assessed by flow cytometry (top) and western blots (bottom). MFI ± SD of n = 2 biological replicates are shown, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with untreated cells; gray bars. For western blots, actin was used as a loading control. (F) Fold induction of pSTAT5 in transduced Ba/F3-IL7R cells stimulated with DOX for inducing expression of the oncogenic mutants, in the presence of the indicated inhibitors. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001 as compared with untreated cells (dashed line, reported as 1).
STAT5 is the common effector downstream multiple oncogenic signaling pathways. (A-B) Levels of pSTAT5 (A) and survival (B) of BaF3-IL7R cells treated with increasing doses of the STAT5 inhibitors N’NH, AC-4-130, and pimozide assessed by flow cytometry. MFI ± SD of n = 3 biological replicates are shown, 1-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with vehicle + IL-7 (gray). Basal levels of pSTAT5 were measured in unstimulated BaF3-IL7R cells (− IL-7; teal). Median inhibitory concentration (IC50) and lethal concentration (LC50) of N’NH, AC-4-130, and pimozide are indicated. (C) Schematic representation of the TxTCPVIR retroviral vector used for the doxycycline-inducible expression of the listed oncogenic mutants in Ba/F3-IL7R cells (top). Inducible expression of the oncogenic mutants in transduced cells can be assessed by measuring levels of the mCherry reporter by flow cytometry, as previously described.35 Representative flow cytometric analysis of pSTAT5 levels in transduced Ba/F3-IL7R cells after 4 hours of stimulation with doxycycline (DOX; red area), which induced overexpression of oncogenic signaling pathways frequently mutated in T-ALL.5,6 MFI, Student t test (N = 3); ∗P < .05, ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with cells treated with vehicle (dashed line). (D-E) Levels of pSTAT5 (D) and survival (E) of transduced BaF3-IL7R cells expressing STAT5B1∗6 and NRASG12D mutants, cultured in the presence (gray) or absence of IL-7 (teal) and DOX (red), assessed by flow cytometry (top) and western blots (bottom). MFI ± SD of n = 2 biological replicates are shown, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with untreated cells; gray bars. For western blots, actin was used as a loading control. (F) Fold induction of pSTAT5 in transduced Ba/F3-IL7R cells stimulated with DOX for inducing expression of the oncogenic mutants, in the presence of the indicated inhibitors. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001 as compared with untreated cells (dashed line, reported as 1).
Pimozide binds to Asn642 of STAT5 and suppresses its function without completely preventing its phosphorylation.51 However, it remains unclear if the cytotoxicity of pimozide is specifically because of inhibition of pSTAT5. To address this question, we infected IL-7 dependent Ba/F3 cells with a doxycycline-inducible vector expressing mutations of signaling genes found in human T-ALL (Figure 4C). As expected, mutations in the IL-7/JAK/STAT signaling pathway (IL-7R, JAK1, JAK3, and STAT5B) induced STAT5 activation and enabled Ba/F3 cells to survive in the absence of IL-7 (Figure 4C-D; supplemental Figure 4B). Inducible expression of FLT3 internal tandem duplication (FLT3ITD) and tyrosine kinase domain (FLT3TKD) mutants also induced pSTAT5. Interestingly, NOTCH1 gain-of-function mutant (NOTCH1ICDΔPEST)53,54 also triggered STAT5 activation. Conversely, mutants of KRAS, NRAS, and PTPN115,6,55 did not activate STAT5. In STAT5B1∗6-expressing cells, pimozide inhibited pSTAT5 and induced cell death similar to its effects in cells grown in IL-7 (Figure 4D-E). In contrast, pimozide had no effect on the survival of NRASG12D Ba/F3 cells, which can maintain IL-7 independent survival without activating pSTAT5 (Figure 4E). Thus, pimozide-induced cytotoxicity was STAT5-dependent. Finally, we compared pimozide with JAK inhibitors to inhibit pSTAT5. Similar to the effects observed in cells dependent on IL-7 and STAT5B1∗6, pimozide was able to inhibit pSTAT5 in cells expressing IL-7R, FLT3, and NOTCH1 mutants (Figure 4F). In contrast, the specific JAK inhibitors ruxolitinib and tofacitinib inhibited pSTAT5 in cells expressing mutant IL-7R (IL7RT244_I245insCPT) but not in cells overexpressing mutants of STAT5B, FLT3, or NOTCH1. Thus, pimozide inhibited pSTAT5 induced by a broader range of signaling mutants than JAK inhibitors.
Pimozide targets pre-LSCs in vivo by inhibiting pSTAT5
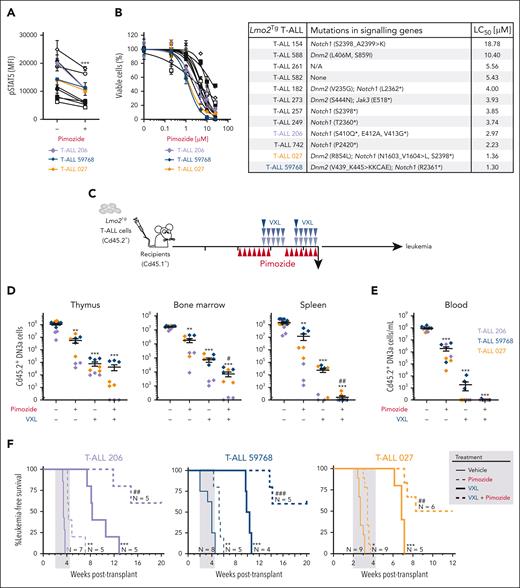
To examine the in vivo effects of pimozide on pre-LSCs, 6-week-old Lmo2Tg mice were treated for 2 weeks and thymocytes harvested the next day for analyses. Pimozide led to a 4-fold reduction in numbers of DN3a thymocytes (Figure 5A), and a significant decrease in pSTAT5 levels (Figure 5B). Pimozide showed preferential killing of immature CD4−CD8− (DN) thymocytes in Lmo2Tg mice (Figure 5C), without any effect on normal thymopoiesis (supplemental Figure 5). To determine if pimozide targets functional pre-LSCs, a limit dilution analysis was performed using thymocytes from vehicle or pimozide treated mice. Pimozide induced a 30-fold decrease in pre-LSC frequency (Figure 5D). Thus, pimozide could suppress STAT5 activation and reduce numbers of functional pre-LSCs.
Inhibition of STAT5 targets Lmo2Tg pre-LSCs. (A-C) Treatment schematic and absolute numbers of DN3a T-cell progenitors (A), levels of activated STAT5 (pSTAT5) in DN3a cells (B) and representative flow cytometry analysis of T-cell populations (C) in the thymus of 6-week old Lmo2Tg mice following treatment with vehicle or pimozide. Mean ± SEM, Student t test; ∗∗P < .01 and ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with vehicle. (D) Pre-LSC frequency within the DN3a thymocyte population of Lmo2Tg mice treated with vehicle or pimozide assessed by limiting dilution assays. Mice were scored positive when T-cell lineage reconstitution was more than 1%, as previously described.56 Pre-LSC frequencies (95% confidence intervals) were calculated from 2 biological replicates. (E) Treatment schematic and absolute numbers of DN3a cells in the thymus of 6-week-old Lmo2Tg mice following administration of 2 rounds of vehicle and pimozide, alone or combined with VXL chemotherapy. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with vehicle; ###P < .001, as compared with VXL. (F-G) Fold expansion of DN3a thymocytes (F) and immunophenotype of donor-derived (Cd45.2+) thymocytes (G) from Lmo2Tg mice treated with either vehicle, pimozide, VXL, or combination therapy, analyzed 8 weeks posttransplant into sublethally irradiated Cd45.1+ recipients. Immature CD4−CD8− (DN), CD4+CD8+ DP, and mature CD4+CD8− and CD4−CD8+ SP populations are indicated. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction test; ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, and ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with vehicle; ##P < .001 compared with VXL.
Inhibition of STAT5 targets Lmo2Tg pre-LSCs. (A-C) Treatment schematic and absolute numbers of DN3a T-cell progenitors (A), levels of activated STAT5 (pSTAT5) in DN3a cells (B) and representative flow cytometry analysis of T-cell populations (C) in the thymus of 6-week old Lmo2Tg mice following treatment with vehicle or pimozide. Mean ± SEM, Student t test; ∗∗P < .01 and ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with vehicle. (D) Pre-LSC frequency within the DN3a thymocyte population of Lmo2Tg mice treated with vehicle or pimozide assessed by limiting dilution assays. Mice were scored positive when T-cell lineage reconstitution was more than 1%, as previously described.56 Pre-LSC frequencies (95% confidence intervals) were calculated from 2 biological replicates. (E) Treatment schematic and absolute numbers of DN3a cells in the thymus of 6-week-old Lmo2Tg mice following administration of 2 rounds of vehicle and pimozide, alone or combined with VXL chemotherapy. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with vehicle; ###P < .001, as compared with VXL. (F-G) Fold expansion of DN3a thymocytes (F) and immunophenotype of donor-derived (Cd45.2+) thymocytes (G) from Lmo2Tg mice treated with either vehicle, pimozide, VXL, or combination therapy, analyzed 8 weeks posttransplant into sublethally irradiated Cd45.1+ recipients. Immature CD4−CD8− (DN), CD4+CD8+ DP, and mature CD4+CD8− and CD4−CD8+ SP populations are indicated. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction test; ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, and ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with vehicle; ##P < .001 compared with VXL.
We next tested the ability of pimozide to overcome chemoresistance of pre-LSCs by treating 6-week-old Lmo2Tg mice with chemotherapy (VXL). The combination of pimozide and chemotherapy reduced DN3a numbers 140-fold than 8-fold for pimozide alone and 20-fold for chemotherapy alone (Figure 5E; supplemental Figure 6A). We observed reduced monoclonality in DN3a cells from Lmo2Tg mice treated with pimozide and loss of preleukemic clones with the combination therapy (supplemental Figure 6B). Thymocytes from these treated mice were transplanted to measure the ability of DN3a cells to expand in recipient mice (Figure 5F). In this assay, the combination therapy suppressed DN3a expansion 1000-fold than untreated cells. Furthermore, pimozide alone or in combination with VXL promoted T-cell differentiation of DN cells to more mature double-positive and single-positive cells (Figure 5G). Importantly, the combination therapy was well tolerated with no detrimental effect on mouse weight (supplemental Figure 6C) or the numbers of bone marrow stem and progenitor cells (supplemental Figure 6D).
Pimozide improves efficacy of chemotherapy in T-ALL
We then tested the efficacy of pimozide in Lmo2-induced T-ALL. In vitro treatment resulted in decreased pSTAT5 levels (Figure 6A) and dose-dependent killing of leukemic DN3a cells in coculture experiments, irrespective of the mutational profile and constitutive STAT5 activation (Figure 6B; supplemental Figure 7A). We evaluated the in vivo therapeutic potential of pimozide as a single agent, or in combination with chemotherapy using sublethally irradiated mice injected with primary Lmo2Tg leukemias (Figure 6C; supplemental Figure 7B). Compared with chemotherapy, pimozide as a single agent had modest activity in 3 independent T-ALL, with up to 100-fold reduction in leukemia cells 24 hours after the final dose of pimozide (Figure 6D-E). In addition, pimozide promoted differentiation of leukemic DN3a T-cell progenitors to more mature double-positive and single-positive cells (supplemental Figure 7C). This effect on differentiation of DN3a cells contrasts with chemotherapy, which had a 10-fold greater reduction in leukemic cells but no effect on T-cell differentiation (Figure 7D-E; supplemental Figure 7C). The combination of pimozide and chemotherapy was most striking, with up to 100 000-fold reduction in DN3a leukemic cells. Consequently, pimozide combined with chemotherapy resulted in up to 50% of mice leukemia-free for up to 20 weeks after treatment (Figure 6F; supplemental Figure 7D-E). Altogether, pimozide had single agent activity and enhanced the effectiveness of chemotherapy in Lmo2-induced T-ALL.
Efficacy of STAT5 inhibition against LSCs from primary Lmo2Tg T-ALL. (A) Relative levels of activated STAT5 (pSTAT5) in leukemic DN3a cells from primary Lmo2Tg T-ALL treated with pimozide (1 μM), after in vitro stimulation of the IL-7 signaling pathway. Primary leukemias are indicated; unstimulated leukemic DN3a cells treated with vehicle were used as control. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction test; ∗∗∗P < .001 as compared with vehicle. (B) Relative viability (%) of primary Lmo2Tg leukemic cells treated with increasing concentration of pimozide for 48 hours (left). Viability was normalized to vehicle-treated cells with experiments performed in duplicates or triplicates. Mutations of growth factor-induced signaling pathways and median LC50 of pimozide for each primary Lmo2Tg T-ALL (right). (C) Experimental schematic for testing the efficacy of pimozide, VXL, and combination therapy in sublethally irradiated Cd45.1+ recipients injected with Lmo2Tg primary leukemias. (D-E) Absolute numbers of leukemic DN3a cells in the thymus, bone marrow, and spleen (D), as well as in the peripheral blood (E) of recipients, 24 hours after the last administration of pimozide, VXL, and combination therapy. Primary leukemias are indicated on the right. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with vehicle; #P < .05 and ##P < .01 compared with VXL. (F) Kaplan-Meier curves of sublethally irradiated recipients injected with Lmo2Tg primary T-ALL, treated with pimozide, VXL, or combination therapy. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test; ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, and ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with vehicle; ##P < .01 and ###P < .001 compared with VXL. The period of administration is indicated in light gray.
Efficacy of STAT5 inhibition against LSCs from primary Lmo2Tg T-ALL. (A) Relative levels of activated STAT5 (pSTAT5) in leukemic DN3a cells from primary Lmo2Tg T-ALL treated with pimozide (1 μM), after in vitro stimulation of the IL-7 signaling pathway. Primary leukemias are indicated; unstimulated leukemic DN3a cells treated with vehicle were used as control. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction test; ∗∗∗P < .001 as compared with vehicle. (B) Relative viability (%) of primary Lmo2Tg leukemic cells treated with increasing concentration of pimozide for 48 hours (left). Viability was normalized to vehicle-treated cells with experiments performed in duplicates or triplicates. Mutations of growth factor-induced signaling pathways and median LC50 of pimozide for each primary Lmo2Tg T-ALL (right). (C) Experimental schematic for testing the efficacy of pimozide, VXL, and combination therapy in sublethally irradiated Cd45.1+ recipients injected with Lmo2Tg primary leukemias. (D-E) Absolute numbers of leukemic DN3a cells in the thymus, bone marrow, and spleen (D), as well as in the peripheral blood (E) of recipients, 24 hours after the last administration of pimozide, VXL, and combination therapy. Primary leukemias are indicated on the right. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with vehicle; #P < .05 and ##P < .01 compared with VXL. (F) Kaplan-Meier curves of sublethally irradiated recipients injected with Lmo2Tg primary T-ALL, treated with pimozide, VXL, or combination therapy. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test; ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, and ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with vehicle; ##P < .01 and ###P < .001 compared with VXL. The period of administration is indicated in light gray.
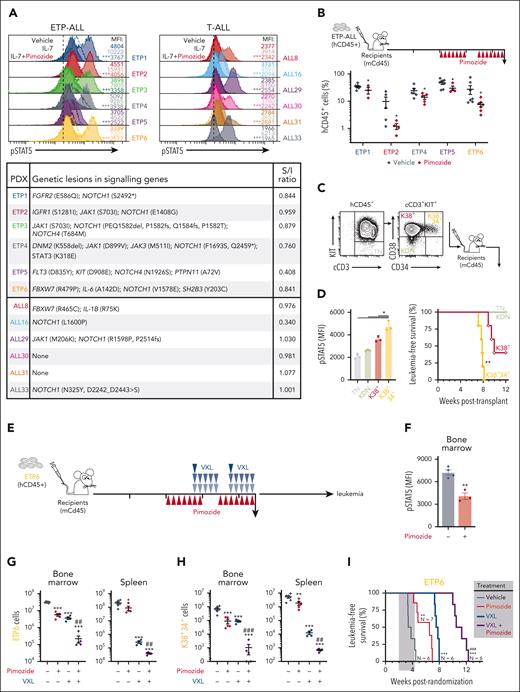
Antileukemic activity of pimozide in human T-ALL. (A) Levels of STAT5 activity (pSTAT5) in ETP-ALL and mature T-ALL cells from human xenografts (top) treated with vehicle and pimozide, after in vitro stimulation with IL-7 (light area). Levels in unstimulated xenograft cells treated with vehicle were used as control (solid contour line). MFI from 3 technical replicates, Student t test; ∗∗∗P < .001 as compared with stimulated cells. Mutations of growth factor-induced signaling pathways and stimulation-inhibition (S/I) ratio of pimozide for each patient-derived ETP-ALL and mature T-ALL xenografts (bottom). The amino acid position for each mutation is shown, fs means frameshift, del means deletion. For the complete list of mutations in each patient-derived xenograft (PDX) refer to the supplemental Table 1. (B) Experimental schematic for testing the efficacy of pimozide in different ETP-ALL PDX models. Sublethally irradiated NSG recipients were randomized and subsequently treated when the average proportion of human leukemic cells reached 1% in the peripheral blood. Proportion of patient-derived leukemic cells (%hCD45+) in the peripheral blood of recipients at 24 hours after the last dose of pimozide was administered. 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05 as compared with vehicle. (C) Flow sorting strategy for transplantation of purified leukemic KIT−CD38−CD34− (TN), KIT+CD38−CD34− (KDN), KIT+CD38+CD34− (K38+), and KIT+CD38+CD34+ (K38+34+) populations of ETP6 xenograft cells. Indicated leukemic populations were purified and injected (3 × 104 cells) into sublethally irradiated immunocompromised NSG recipients. Kaplan-Meier curves of mice injected with purified TN, KDN, K38+, and K38+34+ populations (N = 5) from ETP6 human xenografts. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test; ∗∗P < .01 compared with K38+. (D) Levels of pSTAT5 in TN, KDN, K38+, and K38+34+ populations from ETP6 cells. MFI ± SD, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05. (E) Experimental schematic for testing the efficacy of pimozide, VXL, and combination therapy in the ETP6 xenograft model of human ETP-ALL. Sublethally irradiated NSG recipients were randomized after engraftment was confirmed in the peripheral blood, and subsequently treated when the average proportion of human leukemic cells in the peripheral blood reached 1%. (F) Levels of pSTAT5 in ETP6 patient-derived cells, harvested from the bone marrow of recipients 24 hours after the last administration of pimozide, assessed by flow cytometry. MFI ± SEM, Student t test; ∗∗P < .01. (G-H) Absolute number of ETP6 (G) and K38+34+ (H) leukemic cells in the bone marrow and spleen of recipients analyzed 24 hours after the last drug injection. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗P < .01 and ∗∗∗P < .001 as compared with vehicle; ##P < .01 and ###P < .001 compared with VXL. (I) Kaplan-Meier curves of sublethally irradiated recipients injected with ETP6, administered with either vehicle or pimozide, as a single agent or in combination with VXL chemotherapy. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test; ∗∗P < .01 and ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with vehicle; ###P < .001 compared with VXL. The period of administration is indicated in light gray, with the number of recipients for each cohort indicated.
Antileukemic activity of pimozide in human T-ALL. (A) Levels of STAT5 activity (pSTAT5) in ETP-ALL and mature T-ALL cells from human xenografts (top) treated with vehicle and pimozide, after in vitro stimulation with IL-7 (light area). Levels in unstimulated xenograft cells treated with vehicle were used as control (solid contour line). MFI from 3 technical replicates, Student t test; ∗∗∗P < .001 as compared with stimulated cells. Mutations of growth factor-induced signaling pathways and stimulation-inhibition (S/I) ratio of pimozide for each patient-derived ETP-ALL and mature T-ALL xenografts (bottom). The amino acid position for each mutation is shown, fs means frameshift, del means deletion. For the complete list of mutations in each patient-derived xenograft (PDX) refer to the supplemental Table 1. (B) Experimental schematic for testing the efficacy of pimozide in different ETP-ALL PDX models. Sublethally irradiated NSG recipients were randomized and subsequently treated when the average proportion of human leukemic cells reached 1% in the peripheral blood. Proportion of patient-derived leukemic cells (%hCD45+) in the peripheral blood of recipients at 24 hours after the last dose of pimozide was administered. 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05 as compared with vehicle. (C) Flow sorting strategy for transplantation of purified leukemic KIT−CD38−CD34− (TN), KIT+CD38−CD34− (KDN), KIT+CD38+CD34− (K38+), and KIT+CD38+CD34+ (K38+34+) populations of ETP6 xenograft cells. Indicated leukemic populations were purified and injected (3 × 104 cells) into sublethally irradiated immunocompromised NSG recipients. Kaplan-Meier curves of mice injected with purified TN, KDN, K38+, and K38+34+ populations (N = 5) from ETP6 human xenografts. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test; ∗∗P < .01 compared with K38+. (D) Levels of pSTAT5 in TN, KDN, K38+, and K38+34+ populations from ETP6 cells. MFI ± SD, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗P < .05. (E) Experimental schematic for testing the efficacy of pimozide, VXL, and combination therapy in the ETP6 xenograft model of human ETP-ALL. Sublethally irradiated NSG recipients were randomized after engraftment was confirmed in the peripheral blood, and subsequently treated when the average proportion of human leukemic cells in the peripheral blood reached 1%. (F) Levels of pSTAT5 in ETP6 patient-derived cells, harvested from the bone marrow of recipients 24 hours after the last administration of pimozide, assessed by flow cytometry. MFI ± SEM, Student t test; ∗∗P < .01. (G-H) Absolute number of ETP6 (G) and K38+34+ (H) leukemic cells in the bone marrow and spleen of recipients analyzed 24 hours after the last drug injection. Mean ± SEM, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey correction test; ∗∗P < .01 and ∗∗∗P < .001 as compared with vehicle; ##P < .01 and ###P < .001 compared with VXL. (I) Kaplan-Meier curves of sublethally irradiated recipients injected with ETP6, administered with either vehicle or pimozide, as a single agent or in combination with VXL chemotherapy. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test; ∗∗P < .01 and ∗∗∗P < .001 compared with vehicle; ###P < .001 compared with VXL. The period of administration is indicated in light gray, with the number of recipients for each cohort indicated.
STAT5 inhibition delays leukemia onset in xenograft models of ETP-ALL
To examine the relevance to human T-ALL, we tested the efficacy of pimozide in 6 ETP and 6 mature T-ALL patient-derived xenografts.57 Like mouse Lmo2Tg T-ALL cells, pimozide abrogated IL-7-induced pSTAT5 levels in both ETP and mature T-ALL irrespective of the presence of STAT5-activating mutations, as measured by a stimulation/inhibition (S/I) ratio <1 (Figure 7A; supplemental Figure 8A). Pimozide was superior to JAK inhibitors for decreasing IL-7-induced pSTAT5 in ETP-ALL harboring STAT5-activating mutations, and as effective in other ETP-ALL and mature T-ALL (supplemental Figure 8B). To assess in vivo efficacy of pimozide in ETP-ALL, we examined the impact of 2 weeks treatment with pimozide in mice engrafted with 5 different xenografts (Figure 7B). Analysis 24 hours after the final dose of pimozide showed decreased leukemic cell burden in all 5 ETP-ALL xenografts.
To examine the ability of pimozide to synergize with chemotherapy, we focused on ETP6, which has mutations of both the JAK/STAT (SH2B3) and NOTCH1 (NOTCH1 and FBXW7) pathways and responds to pimozide with inhibition of IL-7-induced pSTAT5 (Figure 7A). We first subfractionated ETP6 (hCD45+cCD3+) blasts according to expression of KIT, CD34, and CD38 (Figure 7C) to seek for populations the most enriched in LSCs, as previously described.58 Transplantation of KIT−CD38−CD34− (TN), KIT+CD38−CD34− (KDN), KIT+CD38+CD34− (K38+), and KIT+CD38+CD34+ (K38+34+) populations revealed that LSC activity was most enriched in the K38+34+ population (Figure 7C), which had the highest levels of pSTAT5 (Figure 7D).
Mice engrafted with ETP6 (>1% hCD45+ in the peripheral blood) were randomized, and subsequently administered with pimozide, VXL, or combination therapy (Figure 7E). Analysis at the end of treatment showed that pimozide reduced pSTAT5 in leukemic cells within the bone marrow and spleen (Figure 7F; supplemental Figure 8C). At this timepoint, single agent pimozide reduced leukemic cell burden 6-fold in the bone marrow, and 2-fold in the peripheral blood and spleen (Figure 7G; supplemental Figure 8D-E). The combination of pimozide and chemotherapy was synergistic, with the most striking effect on the leukemic cell burden in bone marrow (Figure 7G). The combinatorial effect was even more pronounced on the LSC-enriched K38+34+ cell fraction, where pimozide added to chemotherapy reduced cell numbers by 8000-fold in the spleen and 1000-fold in the bone marrow. In 2 out of 5 animals, this population was no longer detectable (Figure 7H). Cohorts of treated mice were followed to assess the impact on survival. Consistent with the effects on K38+34+ cells, single agent pimozide significantly improved survival but not as effectively as chemotherapy alone. However, the addition of pimozide to chemotherapy provided a further 23 days benefit over chemotherapy alone (Figure 7I; supplemental Figure 8F-G). Thus, inhibition of STAT5 by pimozide targeted LSCs and enhanced response to chemotherapy in human ETP-ALL.
Discussion
IL-7 is an important cytokine for the growth and survival of T-ALL cells, especially the high-risk ETP-ALL subtype, where activating mutations of IL-7R are frequently observed.5,6 Use of IL-7R knockout mice in the Lmo2Tg provides new insights for the role of IL-7 in pre-LSCs and LSCs. In this mouse model of ETP-ALL, we show that IL-7 signaling was not required for the establishment of pre-LSCs (Figure 1C-F). This indicates that the stem-cell reprograming of T-cell progenitors by Lmo2 was IL-7 independent. Although we cannot exclude other thymic niche signals, the ability of transcription factors including LMO2 to reprogram committed blood cells into HSCs59 suggests that perturbation of the transcriptional program is sufficient to initiate the stem-cell program in T-cell progenitors. However, IL-7 signaling was essential for the clonal expansion of pre-LSCs and evolution into LSCs that drive the development of T-ALL (Figure 1G-I). The observation that loss of a single allele of IL-7R delayed T-ALL development (Figure 1I) indicates that this pathway is limiting for LSCs, which strengthens the rationale for targeting the IL-7 pathway. An important role for expansion but not initiation of pre-LSCs supports the concept that signaling mutations such as those activating the IL-7 pathway occur later during T-cell leukemogenesis.
In normal and malignant T-cell progenitors, IL-7 stimulation triggers downstream activation of the canonical JAK/STAT pathway and the MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways.11-13,60 Although all 3 pathways are mutated in T-ALL, mutations of the JAK/STAT and RAS pathways are more common than PI3K/AKT in ETP-ALL.5,6 Rescue of leukemia development by constitutively active STAT5 in Lmo2Tg mice lacking IL-7R (Figure 1N) provides the first direct evidence that activation of STAT5 is sufficient to mediate the critical signals downstream of IL-7 in ETP-ALL. We did not test the ability of oncogenic RAS (eg, NRASG12D) to rescue T-ALL development in IL-7R-deficient Lmo2Tg mice although our studies in Ba/F3 cells (Figure 4C-F) suggest rescue by RAS mutants would be through a STAT5-independent pathway. Irrespective, the observation that activated STAT5 is sufficient for growth and survival of LSCs has very important implications: inhibition of STAT5 may be needed for effectively eliminating relapse-inducing cells in ETP-ALL.
Development of a STAT5B1∗6 conditional and inducible transgenic mouse provides a new tool enabling cell-type specific expression of activated STAT5, which is more reflective of cancer. In addition to T-ALL, this mouse model could be used to study the role of aberrant STAT5 activation in other types of cancers using tissue-specific Cre lines. Previous studies using retroviral expression of constitutively active STAT5 in HSCs led to multilineage leukemia.19,45 In contrast, inducible expression of STAT5B1∗6 in T-cell progenitors was not sufficient for generating T-ALL (Figure 2C). This lack of oncogenic effect may relate to more physiologic levels of activated STAT5 driven by the ROSA26 locus or expression restricted to a cell type that lacks long-term self-renewal. The cellular effects of STAT5B1∗6 in pre-LSCs (increased cell proliferation, survival, and chemoresistance; Figure 3) suggest that the effects previously reported for IL-7 stimulation in unfractionated T-ALL cell populations are also true for LSCs. Gene expression profiling of T-ALL cells has defined the transcriptional changes induced by STAT5 activation, including downregulation of the cell-cycle regulator p27kip1, as well as upregulation of BCL6, PIM1, MYC, and the prosurvival factor BCL2L1/BCL-xL.14,61-65 Possible downstream targets of STAT5 that may mediate proliferation and survival in LSCs include the oncogenic serine/threonine kinase PIM1, which is expressed highly in ETP-ALL and upregulated following chemotherapy.66,67 Future studies will be required to elucidate which associated factors are recruited by activated STAT5 to regulate transcription of cell-type-specific genes driving progression and relapse in ETP-ALL.
Aberrant activation of the IL-7/JAK/STAT5 signaling pathway has been shown to promote GC resistance, which is a major hurdle for patients with T-ALL.68-70 JAK inhibitors have efficacy in IL-7-responsive T-ALL and can synergize with dexamethasone to overcome GC resistance.28,70 However, activation of STAT5 is associated with resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors.49,50,71,72 Furthermore, JAK inhibitors were unable to prevent STAT5 activation by oncogenic mutants of STAT5B, FLT3, and NOTCH1 that are frequently found in T-ALL (Figure 4F). This suggests that alternate pathways of STAT5 activation may enable resistance to JAK inhibitors. The elevated STAT5 activity in LSCs and its role in the expansion and chemoresistance of LSCs further strengthens this rationale. We focused on pimozide because this small molecule was as effective as the STAT5 inhibitor AC-4-130 (Figure 4A-B) and has in vivo efficacy in BCR-ABL and FLT3-ITD mutant acute myeloid leukemia.44,48 Our studies with pimozide extend the therapeutic landscape of direct STAT5 inhibitors to ETP-ALL, where it can sensitize LSCs to chemotherapy (Figures 5E-F, 6D-F, and 7G-I). One of the caveats of pimozide has been the lack of a clear mechanism of action, with cytotoxic effects not only through inhibition of STAT5 but also calcium channel blockade.51,73 However, the observation that pimozide was cytotoxic to STAT5-dependent (expressing STAT5B1∗6) but not STAT5-independent (expressing NRASG12D) Ba/F3 cells (Figure 4E) argues that inhibition of STAT5 the likely mechanism of cytotoxicity in leukemia cells. Although our data strongly support the pharmacological inhibition of STAT5 as an effective therapeutic strategy in ETP-ALL, these preclinical experiments are not compatible with repurposing pimozide for clinical trials given the dose of pimozide required to suppress STAT5 significantly exceeds the recommended daily dose in patients. Several direct and indirect STAT5 inhibitors are currently under development for the treatment of autoimmune diseases or myeloproliferative neoplasms.47 Potential uses of pharmacological inhibition of STAT5 in ETP-ALL include addition to high-dose chemotherapy or during maintenance therapy, where the LSC-targeting activity of STAT5 inhibitors may help improve the overall survival of patients.
Conclusion
This study provides the first in vivo evidence that STAT5 activity controls self-renewal, clonal evolution, expansion, and chemoresistance of LSCs in ETP-ALL, thereby contributing to leukemia aggressiveness and relapse. Collectively, our data suggest that direct STAT5 inhibitors could be used in ETP-ALL to improve cure rates and potentially limit the need for toxic chemotherapy.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank David A. Frank from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Geza Paukovics, Eva Orlowski-Oliver, Magdaline Costa, and Jeanne LeMasurier from the AMREP Flow Cytometry Facility, as well as Prue O’Hare, Kylie Spark, and Stephanie Jansen from the Alfred Medical Research & Educational Precinct Animal Services (AMREP AS). The authors also thank Jessica M. Salmon and Loretta Cerruti for technical assistance.
This work was supported by a Research Fellowship (#700153) from the Terry Fox Foundation (C.S.T.), a grant-in-aid from the Leukaemia Foundation of Australia (C.S.T.), a Fellowship from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (R.B.L.) and a Senior Medical Research Fellowship from the Sylvia and Charles Viertel Foundation (D.J.C.).
Authorship
Contribution: C.S.T. designed, supervised, led, and performed research, coordinated the interactions between the authors, interpreted the results, and wrote the manuscript; J.S. performed in vitro experiments, processed samples from in vivo studies, and analyzed data; J.A.B. and V.L. performed in vivo studies and analyzed data; C.S.T., K.H., and J.J.H. developed and established the ROSA26-STOPfl/fl-rtTA3-STAT5B1∗6 mouse line; H.M., K.E., and R.B.L. provided whole-exome sequencing data and biological samples of patient-derived xenografts, and wrote the manuscript; and S.M.J., J.J.H., and D.J.C. provided reagents, supported research, contributed to research design, and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Cedric S. Tremblay, CancerCare Manitoba, 675 McDermot Ave, ON5022, Winnipeg, MB R3E 0V9, Canada; e-mail: cedric.tremblay@umanitoba.ca.
References
Author notes
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the article and/or its supplemental Data.
Information about experimental procedures and data analysis is available on request from the corresponding author, Cedric S. Tremblay (cedric.tremblay@unanitoba.ca).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal