Key Points
Multihit TP53MT represents a novel very high-risk group in patients with myelofibrosis undergoing HSCT.
Multihit TP53MT was particularly associated with high rates of leukemic transformation early after transplantation.
Abstract
TP53 mutations (TP53MTs) have been associated with poor outcomes in various hematologic malignancies, but no data exist regarding its role in patients with myelofibrosis undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Here, we took advantage of a large international multicenter cohort to evaluate the role of TP53MT in this setting. Among 349 included patients, 49 (13%) had detectable TP53MT, of whom 30 showed a multihit configuration. Median variant allele frequency was 20.3%. Cytogenetic risk was favorable (71%), unfavorable (23%), and very high (6%), with complex karyotype present in 36 patients (10%). Median survival of patients with TP53MT was 1.5 vs 13.5 years for those with wild-type TP53 (TP53WT; P < .001). Outcome was driven by multihit TP53MT constellation (P < .001), showing 6-year survival of 56% for individuals with single-hit vs 25% for those with multihit TP53MT vs 64% for those with TP53WT. Outcome was independent of current transplantation-specific risk factors and conditioning intensity. Similarly, cumulative incidence of relapse was 17% for single-hit vs 52% for multihit vs 21% for TP53WT. Ten patients with TP53MT (20%) presented as leukemic transformation vs only 7 (2%) in the TP53WT group (P < .001). Out of the 10 patients with TP53MT, 8 showed multihit constellation. Median time to leukemic transformation was shorter for multihit and single-hit TP53MT (0.7 and 0.5 years, respectively) vs 2.5 years for TP53WT. In summary, multihit TP53MT represents a very high-risk group in patients with myelofibrosis who are undergoing HSCT, whereas single-hit TP53MT alone showed similar outcome to patients with nonmutated TP53, informing prognostication for survival and relapse together with current transplantation-specific tools.
Introduction
In the past 40 years, researchers have described the protein structure, functions, and regulation mechanism of TP53.1-3 The use of alternate promoters and alternate splicing of introns result in multiple transcript variants in a tissue-dependent manner.4 In addition, the dominant-negative and gain-of-function effects are associated with specific mutations.5 Hence, ascertaining the tumorigenic mechanism of TP53 is essential for developing a precise treatment regimen in specific tumors.3
As the most frequently mutated gene, the frequency of TP53 mutations (TP53MTs) is highly variable in different types and different stages of (hematologic) cancers. For instance, in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes, TP53MTs are associated with high-risk disease, rapid transformation to acute myeloid leukemia (AML), resistance to conventional therapies and dismal outcomes, even after intensive treatment with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT).6,7
Myelofibrosis is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm that develops either de novo (as primary myelofibrosis) or that evolves from essential thrombocythemia or polycythemia vera (as secondary myelofibrosis).8 Although significant progress has been achieved over recent years in understanding the effects of mutation profiles,9-12 the role of TP53MT in the prognosis of myelofibrosis is still poorly understood and has not yet been reported in the setting of curative treatment using HSCT.13
Here, we aim to investigate the impact of TP53MT and cytogenetics on the outcomes of patients with myelofibrosis undergoing HSCT by using a large collaborative international cohort.
Methods
Patients
A total of 349 patients with primary or post–essential thrombocythemia/polycythemia vera myelofibrosis undergoing first HSCT between 1997 and 2021 with information available on mutation profile and cytogenetics were included in this study. Patient data were collected from the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (Hamburg, Germany); the West German Cancer Center (Essen, Germany); Hôpital Saint-Louis (Paris, France); the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center (Seattle, WA); Leukemia Program, Department of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Cleveland Clinic, (Cleveland, OH); Department of Hematology, Brabois Hospital, Centre Hospitalier Régional Universitaire (Nancy, France); and Hannover Medical School (Hannover, Germany). Patients with myelofibrosis in progression to acute leukemia at the time of HSCT were excluded. All relevant clinical and transplantation-specific variables and samples for sequencing and cytogenetic analyses were collected at time of HSCT. Conditioning regimens and dose intensities have been reported previously.14,15 The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and all patients provided informed consent for analysis of the data.
Mutational and cytogenetic analysis
Bone marrow or peripheral blood samples were obtained before transplantation (start of conditioning), and mutations were detected using next-generation sequencing, as previously described.18-21 Cytogenetic analysis and reporting were performed in accordance with the international system for human cytogenetic nomenclature criteria, using standardized techniques. Cytogenetic risk classifications were applied in accordance with previous reports.22 High-molecular risk mutations were categorized in accordance with that proposed by Vannucchi et al.11,17
Most samples were analyzed using targeted sequencing of TP53, for which 20-ng samples were used for manual library preparation with Ion AmpliSeq Library Kit Plus in 3 steps (amplifies the DNA target, partially digs amplicons, and ligates adapters to the amplicons and purifies them). The Ion AmpliSeq TP53 panel was a 2-pool panel with 24 amplicons designed to analyze all coding exons of the TP53 gene as a community panel by Thermo Fisher. The library was amplified via quantitative polymerase chain reaction. A 50-pM sample of library was used for templating via Ion Chef, using Ion 540 Kit-Chef. The sequencing run was done on Ion S5 Plus with 540-Chip. The amplicon length was between 125 and 175 bp. On average, the coverage ranged from 8000× to 10 000×, with uniformity of 95%, achieving 97% on target reads, and with an average depth of coverage of 92%. The analysis workflow was specific for this panel and has been developed with Ion Reporter software. The detection threshold was 2%, and detailed information of all analyses are described in the supplemental Material, available on the Blood website.
To analyze the role of TP53MT in more detail, we categorized patients with single-hit or multihit constellation and defined this in accordance with the international consensus classification (multihit constellation: the presence of ≥2 distinct mutations in TP53 with a variant allele frequency of ≥10%, 1 mutation plus 1 deletion involving the TP53 locus at 17p, 1 mutation with a variant allele frequency ≥50%, or 1 mutation plus complex karyotype, and single-hit constellation as the absence of multihit with a variant allele frequency <50%).23
End points and statistical analysis
The primary end point of the study was overall survival, which was defined as the time from HSCT to last follow-up or death from any cause. Secondary end points were leukemic transformation, nonrelapse mortality, progression-free survival, and overall cumulative incidence of relapse. Progression-free survival was defined as the time from transplantation to either relapse or death from any cause. Nonrelapse mortality was defined as death from any cause as a cumulative incidence estimate, with relapse as the competing risk.
Probabilities of survival were calculated using Kaplan-Meier estimates. Probabilities of nonrelapse mortality and relapse were calculated using the cumulative incidence function, accounting for competing risks. Multivariable analyses were performed to evaluate associations among TP53MT; cytogenetics; patient-related, disease-related, donor-related, and HSCT-related variables; and outcomes of interest using a Cox proportional hazards regression model for survival and a Fine and Gray model for competing risk outcomes. Hazard ratios (HRs) with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated. Backward stepwise selection was used to identify significant covariates that influenced outcomes. Interaction analyses were performed for univariate and multivariate analysis. The utility of prediction was evaluated by estimating the model’s discrimination measured with the concordance index as well as the time-dependent area under the curve.24 A threshold of P < .05 was considered significantly different. In case of missing information, multiple imputation was used. All analyses were performed using R statistical software version 4.0.5.
Results
Patients
This study collected data from 349 patients with myelofibrosis undergoing first HSCT from a multicenter international cohort, of whom 49 patients (14%) had TP53MT. When analyzing patient and transplantation characteristics at baseline, patients with TP53MT who more frequently harbored complex karyotype and unfavorable cytogenetic risk were less likely to receive pretransplantation ruxolitinib and more frequently underwent high-intensity conditioning regimens as compared with individuals in the TP53WT group. The median age of patients was 58 years and was similar in both groups. The remaining patient and transplantation characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
Patient characteristics
| Characteristic . | TP53WT (n = 300) . | TP53MT single-hit (n = 19) . | TP53MT multihit (n = 30) . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y, median (range) | 58 (22-75) | 52 (44-74) | 58 (24-75) | .62 |
| Female sex, n (%) | 99 (40) | 8 (47) | 14 (48) | .58 |
| Diagnosis, n (%) | .23 | |||
| Primary myelofibrosis | 214 (71) | 14 (74) | 17 (57) | |
| Secondary myelofibrosis | 86 (29) | 5 (26) | 13 (43) | |
| Circulating blasts, %, median (range) | 1 (0-19) | 1 (0-12) | 1 (0-19) | .85 |
| Platelets, ×109/L, median (range) | 144 (4-2437) | 160 (20-975) | 90 (5-623) | .02 |
| WBC, ×109/L, median (range) | 7.0 (0.1-107.1) | 9.8 (0.2-43.0) | 6.2 (0.2-168.8) | .44 |
| Hb, g/dL, median (range) | 9.4 (5.6-17.9) | 9.3 (7.3-13.6) | 8.4 (6.8-11.9) | .03 |
| KPS <90%, n (%) | 115 (39) | 10 (53) | 18 (60) | .04 |
| Constitutional symptoms, n (%) | 168 (56) | 11 (42) | 14 (47) | .33 |
| Driver mutation, n (%) | .16 | |||
| CALR | 61 (20) | 8 (42) | 5 (17) | |
| JAK2 | 175 (58) | 7 (37) | 17 (57) | |
| MPL | 16 (5) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | |
| Triple negative | 48 (16) | 3 (16) | 8 (27) | |
| High molecular risk, n (%) | 104 (44) | 6 (35) | 10 (35) | .54 |
| Cytogenetic risk, n (%) | .004 | |||
| Favorable | 220 (73) | 13 (68) | 15 (50) | |
| Unfavorable | 60 (20) | 4 (21) | 15 (50) | |
| Very high risk | 20 (7) | 2 (11) | 0 (0) | |
| Complex karyotype, n (%) | 22 (7) | 0 (0) | 14 (47) | <.001 |
| Ruxolitinib pre-HSCT, n (%) | 124 (42) | 6 (32) | 6 (20) | .05 |
| Donor relation, n (%) | .15 | |||
| MRD | 68 (23) | 9 (48) | 6 (20) | |
| MUD | 161 (54) | 7 (37) | 13 (43) | |
| MMRD | 9 (3) | 0 (0) | 2 (7) | |
| MMUD | 62 (21) | 3 (16) | 9 (30) | |
| Conditioning intensity, n (%) | <.001 | |||
| Reduced | 261 (87) | 9 (47) | 15 (50) | |
| Myeloablative | 39 (13) | 10 (53) | 15 (50) | |
| ATG for GVHD prophylaxis, n (%) | 206 (69) | 12 (63) | 20 (67) | .87 |
| Time to HSCT in months, median (range) | 26 (0.5-567) | 33 (4.6-266.3) | 14.2 (2.0-356.6) | .58 |
| Characteristic . | TP53WT (n = 300) . | TP53MT single-hit (n = 19) . | TP53MT multihit (n = 30) . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y, median (range) | 58 (22-75) | 52 (44-74) | 58 (24-75) | .62 |
| Female sex, n (%) | 99 (40) | 8 (47) | 14 (48) | .58 |
| Diagnosis, n (%) | .23 | |||
| Primary myelofibrosis | 214 (71) | 14 (74) | 17 (57) | |
| Secondary myelofibrosis | 86 (29) | 5 (26) | 13 (43) | |
| Circulating blasts, %, median (range) | 1 (0-19) | 1 (0-12) | 1 (0-19) | .85 |
| Platelets, ×109/L, median (range) | 144 (4-2437) | 160 (20-975) | 90 (5-623) | .02 |
| WBC, ×109/L, median (range) | 7.0 (0.1-107.1) | 9.8 (0.2-43.0) | 6.2 (0.2-168.8) | .44 |
| Hb, g/dL, median (range) | 9.4 (5.6-17.9) | 9.3 (7.3-13.6) | 8.4 (6.8-11.9) | .03 |
| KPS <90%, n (%) | 115 (39) | 10 (53) | 18 (60) | .04 |
| Constitutional symptoms, n (%) | 168 (56) | 11 (42) | 14 (47) | .33 |
| Driver mutation, n (%) | .16 | |||
| CALR | 61 (20) | 8 (42) | 5 (17) | |
| JAK2 | 175 (58) | 7 (37) | 17 (57) | |
| MPL | 16 (5) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | |
| Triple negative | 48 (16) | 3 (16) | 8 (27) | |
| High molecular risk, n (%) | 104 (44) | 6 (35) | 10 (35) | .54 |
| Cytogenetic risk, n (%) | .004 | |||
| Favorable | 220 (73) | 13 (68) | 15 (50) | |
| Unfavorable | 60 (20) | 4 (21) | 15 (50) | |
| Very high risk | 20 (7) | 2 (11) | 0 (0) | |
| Complex karyotype, n (%) | 22 (7) | 0 (0) | 14 (47) | <.001 |
| Ruxolitinib pre-HSCT, n (%) | 124 (42) | 6 (32) | 6 (20) | .05 |
| Donor relation, n (%) | .15 | |||
| MRD | 68 (23) | 9 (48) | 6 (20) | |
| MUD | 161 (54) | 7 (37) | 13 (43) | |
| MMRD | 9 (3) | 0 (0) | 2 (7) | |
| MMUD | 62 (21) | 3 (16) | 9 (30) | |
| Conditioning intensity, n (%) | <.001 | |||
| Reduced | 261 (87) | 9 (47) | 15 (50) | |
| Myeloablative | 39 (13) | 10 (53) | 15 (50) | |
| ATG for GVHD prophylaxis, n (%) | 206 (69) | 12 (63) | 20 (67) | .87 |
| Time to HSCT in months, median (range) | 26 (0.5-567) | 33 (4.6-266.3) | 14.2 (2.0-356.6) | .58 |
High molecular risk was defined as the presence of mutations in ASXL1, SRSF2, EZH2, or IDH1/2.17
ATG, antithymocyte globulin; GVHD, graft-versus-host disease; Hb, hemoglobin; KPS, Karnofsky Performance Status; MMRD, mismatched related donor; MMUD, mismatched unrelated donor; MRD, matched related donor; MUD, matched unrelated donor; WBC, white blood cell.
Bold font indicates statistical significance.
Molecular-genetic landscape of patients with TP53MT undergoing HSCT
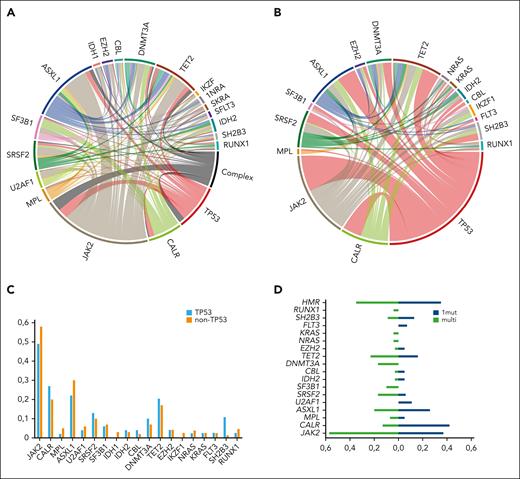
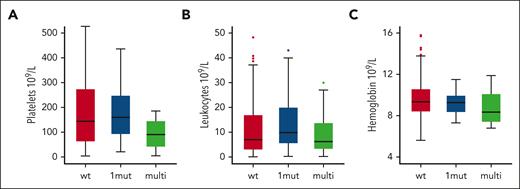
The median variant allele frequency was 20.3% (range, 2.9%-97.6%), and 30 patients with TP53MT showed a multihit configuration. Patients with TP53MT showed similar cooccurrence of driver mutations compared with those with TP53WT, with JAK2 being the most frequent, followed by CALR and triple negative driver mutation genotype. The remaining distribution of cooccurring additional mutations was generally balanced between both groups, except for SH2B3, which occurred in 11% of patients with TP53MT vs 1% of those with TP53WT (P = .01). In addition, we found enrichment of TP53MT in patients with mutated SH2B3 (n = 2, 50%) vs patients with nonmutated SH2B3 (n = 17; 19%; P = .04). In addition, no significant differences between patients with TP53MT and TP53WT were observed for cooccurrence of ASXL1 or other high-molecular risk mutations (Table 1; Figure 1A-C). In terms of mutation patterns within the TP53MT group, patients with multihit constellation more frequently presented with JAK2 driver mutation genotype, SRSF2, SF3B1, DNMT3A, NRAS, and KRAS mutations (Figure 1D). In terms of phenotype, patients with TP53MT multihit presented with more severe anemia and thrombocytopenia at the time of HSCT (Table 1; Figure 2).
Distribution of mutations in the total cohort based on TP53MT status. (A) The mutation landscape and network with complex karyotype of the total cohort (n = 349). (B) The mutation landscape in a chord diagram for all patients with TP53MT (n = 49). (C) Frequencies of cooccurring driver and other mutations in patients with TP53MT and TP53WT. (D) Frequencies of cooccurring driver and other mutations in patients with TP53MT with single- vs multihit constellations.
Distribution of mutations in the total cohort based on TP53MT status. (A) The mutation landscape and network with complex karyotype of the total cohort (n = 349). (B) The mutation landscape in a chord diagram for all patients with TP53MT (n = 49). (C) Frequencies of cooccurring driver and other mutations in patients with TP53MT and TP53WT. (D) Frequencies of cooccurring driver and other mutations in patients with TP53MT with single- vs multihit constellations.
TP53MT state is associated with distinct clinical phenotypes at time of HSCT. The graphs show levels of platelets (A), leukocytes (B), and hemoglobin (C) in patients with wild-type (wt), single-hit (1mut), and multihit TP53MT.
TP53MT state is associated with distinct clinical phenotypes at time of HSCT. The graphs show levels of platelets (A), leukocytes (B), and hemoglobin (C) in patients with wild-type (wt), single-hit (1mut), and multihit TP53MT.
In terms of cytogenetics, risk classification in the total cohort (in accordance with that by Tefferi et al22) was favorable (n = 248; 71%), unfavorable (n = 79; 23%), and very high risk (n = 22; 6%). The median number of cytogenetic aberrations was 0 (range, 0-6 aberrations). Complex karyotype (defined as presence of at least 3 aberrations) was present in a total of 36 patients (10%), and significantly more patients in the unfavorable risk group had complex karyotype (43%) vs patients in the favorable risk (0%) and very high-risk (9%; P < .001) groups. Furthermore, when compared with TP53WT cases, TP53MT cases were enriched in the unfavorable cytogenetic risk category (20% vs 39%, P = .01) and, importantly, in patients with complex karyotype (7% vs 29%; P < .001).
Impact of TP53MT on post-HSCT outcome
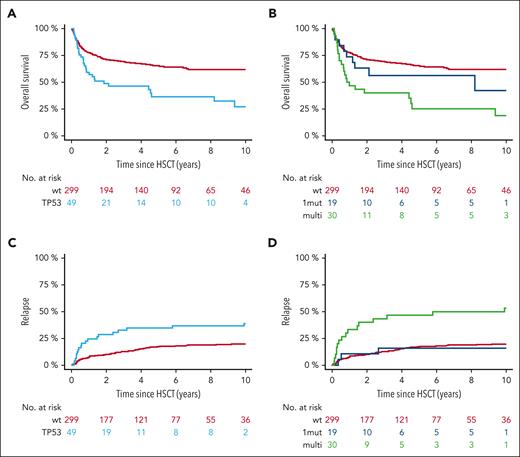
With a median follow-up from HSCT of 5.8 years for the TP53MT group and 9.2 years for the non-TP53MT group, the 6-year overall survival was 36% (95% CI, 20-50) vs 64% (95% CI, 58-70), respectively (P < .001; Figure 3A). As a result, median overall survival was 1.5 years (95% CI, 0.3-2.8 years) for the TP53MT group vs 13.5 years (95% CI, 9.2-17.8) for the TP53WT group (HR, 2.08; 95% CI, 1.37-3.15).
TP53MT state is associated with distinct outcomes after HSCT. (A,C) Overall survival (A) and relapse incidence (C) for the comparison of patients with wt TP53MT and all patients. (B,D) Overall survival (B) and relapse incidence (D) for the comparison of patients with wt TP53MT, TP53MT single-hit (1mut), and TP53MT multihit (multi).
TP53MT state is associated with distinct outcomes after HSCT. (A,C) Overall survival (A) and relapse incidence (C) for the comparison of patients with wt TP53MT and all patients. (B,D) Overall survival (B) and relapse incidence (D) for the comparison of patients with wt TP53MT, TP53MT single-hit (1mut), and TP53MT multihit (multi).
When stratified based on TP53MT status, 6-year overall survival was 56% (95% CI, 33-79) for individuals with single-hit vs 25% for those with multihit TP53MT (vs 64% for those with TP53WT; P < .001; Figure 3B). Stratified only based on variant allele frequency, 6-year overall survival was 46% vs 27% for variant allele frequency <20% vs ≥20%, respectively (P = .21). Furthermore, no significant impact of variant allele frequency as continuous variable was observed, independent of multihit constellation.
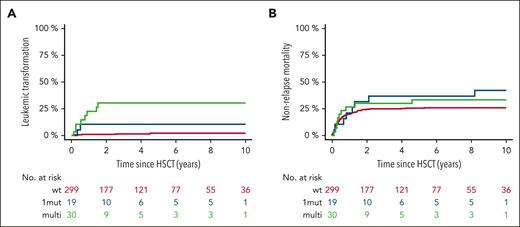
In terms of relapse, individuals with TP53MT also showed significantly higher 6-year cumulative incidence of relapse (39% [95% CI, 25-54] vs 21% [95% CI, 17-25]) when compared with individuals in the TP53WT group (P = .001; Figure 3C). Digging into TP53MT configurations, this outcome was specifically driven by multihit constellation (Figure 3D), resulting in cumulative incidence of relapse of 17% (95% CI, 1-34) for single-hit and 52% (95% CI, 34-70) for multihit (HR, 1.42; 95% CI, 1.16-14.56; P = .03). A total of 81 patients (19 [39%] with TP53MT, 62 [21%] with TP53WT) experienced disease relapse; notably, 17 presented as leukemic transformation, of whom 10 were carried TP53MT (20% of all patients) vs only 7 (2%) who carried TP53WT (P < .001). When considering only cases presenting with leukemic transformation, multihit TP53MT were observed in 80% of patients compared with 29% in TP53WT cases. The median time to leukemic transformation was significantly shorter for multi-and single-hit TP53MT (0.7 and 0.5 years, respectively) vs 2.5 years for TP53WT (Figure 4A). Furthermore, nonrelapse mortality was not significantly different between all groups (P = .54; Figure 4B).
Leukemic transformation and nonrelapse mortality according to TP53 status. Cumulative incidence of leukemic transformation (A) and nonrelapse mortality (B) based on single-hit or multihit constellation vs TP53WT.
Leukemic transformation and nonrelapse mortality according to TP53 status. Cumulative incidence of leukemic transformation (A) and nonrelapse mortality (B) based on single-hit or multihit constellation vs TP53WT.
Impact of cytogenetics alone and in the presence of TP53MT
Current cytogenetic risk stratification showed no discrete survival differences (P = .40), with a 6-year overall survival of 63% (95% CI, 57-69) for favorable, 53% (95% CI, 41-65) for unfavorable, and 62% (95% CI, 41-83) for very high-risk groups. Conversely, complex karyotype still affected post-HSCT outcomes, with a median overall survival of 1.9 years (95% CI, 0-4.2) in such a setting vs 13.5 years in cases with other karyotypes (P < .001), which translates into 6-year overall survival rates of 34% vs 63%, respectively. The impact of complex karyotype was verified by analyzing the number of cytogenetic aberrations, showing superimposable overall survival of 63% and 65% for 0 and 1 aberration, 56% for 2 aberrations, 45% for 3 aberrations, and 0% for >3 aberrations (P = .001). The presence of trisomy 8 showed significantly worse survival compared with cases without such alteration (P = .02). However, we noticed that trisomy 8 cooccurred with complex karyotype in the majority of cases (54% vs 7%; P < .001), and the interaction test for trisomy 8 and complex karyotype in terms of outcome was significant (P < .001), suggesting that the outcome is driven by a complex karyotype. The remaining impact of other cytogenetic features on overall survival is shown in Table 2. There was a significant interaction between complex karyotype and TP53MT, and the outcome was driven by mutation status, especially multihit constellation (P < .001).
Univariate analysis of the impact of cytogenetics on overall survival
| Characteristic . | Overall survival at 6 y (%) . | 95% CI . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cytogenetic risk | .40 | ||
| Low | 63 | 57-69 | |
| Unfavorable | 53 | 41-65 | |
| Favorable | 62 | 41-83 | |
| Number of aberrations | .001 | ||
| 0 | 63 | 56-70 | |
| 1 | 65 | 54-76 | |
| 2 | 56 | 36-76 | |
| 3 | 45 | 23-67 | |
| >3 | 0 | ||
| Complex karyotype | <.001 | ||
| No | 63 | 57-69 | |
| Yes | 34 | 16-52 | |
| Trisomy 8 | .02 | ||
| No | 61 | 55-67 | |
| Yes | 52 | 33-71 | |
| Trisomy 9 | .68 | ||
| No | 61 | 55-67 | |
| Yes | 54 | 27-81 |
| Characteristic . | Overall survival at 6 y (%) . | 95% CI . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cytogenetic risk | .40 | ||
| Low | 63 | 57-69 | |
| Unfavorable | 53 | 41-65 | |
| Favorable | 62 | 41-83 | |
| Number of aberrations | .001 | ||
| 0 | 63 | 56-70 | |
| 1 | 65 | 54-76 | |
| 2 | 56 | 36-76 | |
| 3 | 45 | 23-67 | |
| >3 | 0 | ||
| Complex karyotype | <.001 | ||
| No | 63 | 57-69 | |
| Yes | 34 | 16-52 | |
| Trisomy 8 | .02 | ||
| No | 61 | 55-67 | |
| Yes | 52 | 33-71 | |
| Trisomy 9 | .68 | ||
| No | 61 | 55-67 | |
| Yes | 54 | 27-81 |
n = 28 with trisomy 8 and n = 13 with trisomy 9.
Bold font indicates statistical significance.
The current cytogenetic risk stratification also failed to separate patients with different relapse risks (P = .73), whereas the 6-year cumulative incidence of relapse was 31% in cases harboring complex karyotype as compared with 19% in patients with other cytogenetic configurations (P = .03).
Other factors influencing the posttransplantation outcome
In terms of molecular markers, driver mutation genotype and ASXL1 mutations were the only other variables affecting post-HSCT overall survival. The complete univariate analysis of patient-, HSCT-, and molecular-related factors is shown in the supplemental Table 1. Regarding currently adopted risk stratification, the 6-year overall survival per DIPSS was 64% for low risk, 64% for intermediate-1 risk, 57% for intermediate-2 risk, and 57% for high-risk (P = .83) cases. For the MIPSS70, the overall survival was 100% for low risk, 64% for intermediate risk, and 57% for high-risk (P = .09) categories. The MTSS also showed significant association with overall survival (P < .001), with 6-year overall survival rates of 88% for low, 69% for intermediate, 46% for high, and 31% for very high risk. The concordance index was 0.52 for the DIPSS, 0.55 for the MIPSS70, and 0.69 for the MTSS. The time-dependent area under the curve for the 3 scoring systems was 0.60, 0.55, and 0.72, respectively. In terms of relapse, neither the DIPSS nor the MIPSS70 showed prognostic utility, whereas the MTSS appeared to separate groups with discrete relapse rates, showing 18%, 22%, 27%, and 31% for low, intermediate, high, and high-risk groups, respectively (P = .08). Concordance index was 0.57 for the DIPSS, 0.57 for the MIPSS70, and 0.67 for the MTSS; and the time-dependent area under the curve was 0.51, 0.57, and 0.67, respectively.
Multivariable adjustment
Lastly, we analyzed the multivariable effect on the outcomes, selecting previously established transplantation-specific risk stratification (namely, the MTSS) and other potentially confounding characteristics that were unequally distributed between the mutation groups (ie, conditioning intensity). Overall, the model combining MTSS, TP53MT, and conditioning intensity (controlling for more frequent use of higher intensity conditioning in TP53MT) confirmed the significant impact of a multihit constellation on the overall survival after HSCT, whereas single-hit showed a similar outcome compared with TP53WT. In addition, the impact of MTSS on the overall survival was maintained, whereas no significant difference in survival was observed for different conditioning intensities. Moreover, multihit TP53MT confirmed its association with worse outcomes when analyzing relapse risk. For MTSS, the very high risk group was associated with significantly higher risk of relapse when compared with the low risk group. No influence of conditioning intensity was observed. (Table 3). The influence of each variable within the MTSS in addition to TP53 status was confirmed in a separate analysis, adjusting for all variables (supplemental Table 2). No interaction was observed for TP53 status and platelet count.
Multivariable adjustment for overall survival per current risk stratification
| Characteristic . | HR . | 95% CI . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model for survival | |||
| Concordance index: 0.71 | |||
| AIC: 979.11 | |||
| TP53status | |||
| WT | Reference | ||
| Single-hit | 1.44 | 0.69-3.01 | .33 |
| Multihit | 2.12 | 1.29-3.49 | .003 |
| MTSS | |||
| Low | Reference | ||
| Intermediate | 2.44 | 1.25-4.79 | .01 |
| High | 5.11 | 2.60-10.03 | <.001 |
| Very high | 7.53 | 3.85-14.74 | <.001 |
| Myeloablative conditioning | 1.35 | 0.88-2.09 | .17 |
| Model for relapse | |||
| Concordance index: 0.68 | |||
| AIC: 1252.43 | |||
| TP53status | |||
| WT | Reference | ||
| Single-hit | 0.85 | 0.26-2.81 | .79 |
| Multihit | 3.30 | 1.78-6.09 | <.001 |
| MTSS | |||
| Low | Reference | ||
| Intermediate | 1.25 | 0.64-2.44 | .51 |
| High | 1.55 | 0.76-3.18 | .23 |
| Very high | 2.26 | 1.10-4.67 | .03 |
| Myeloablative conditioning | 1.10 | 0.62-1.94 | .75 |
| Characteristic . | HR . | 95% CI . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model for survival | |||
| Concordance index: 0.71 | |||
| AIC: 979.11 | |||
| TP53status | |||
| WT | Reference | ||
| Single-hit | 1.44 | 0.69-3.01 | .33 |
| Multihit | 2.12 | 1.29-3.49 | .003 |
| MTSS | |||
| Low | Reference | ||
| Intermediate | 2.44 | 1.25-4.79 | .01 |
| High | 5.11 | 2.60-10.03 | <.001 |
| Very high | 7.53 | 3.85-14.74 | <.001 |
| Myeloablative conditioning | 1.35 | 0.88-2.09 | .17 |
| Model for relapse | |||
| Concordance index: 0.68 | |||
| AIC: 1252.43 | |||
| TP53status | |||
| WT | Reference | ||
| Single-hit | 0.85 | 0.26-2.81 | .79 |
| Multihit | 3.30 | 1.78-6.09 | <.001 |
| MTSS | |||
| Low | Reference | ||
| Intermediate | 1.25 | 0.64-2.44 | .51 |
| High | 1.55 | 0.76-3.18 | .23 |
| Very high | 2.26 | 1.10-4.67 | .03 |
| Myeloablative conditioning | 1.10 | 0.62-1.94 | .75 |
MTSS was in accordance with that given by Gagelmann et al.12
AIC, Akaike information criterion.
Discussion
In this large international collaborative study delving into the outcomes of patients with myelofibrosis undergoing their first HSCT with information on their mutation status and cytogenetics available, we, to the best of our knowledge, for the first time, specifically evaluated the role of TP53MT in myelofibrosis. We showed that individuals with TP53MT had an inferior an overall survival compared with those with TP53WT, and this was mainly driven by multihit constellation. Furthermore, dismal outcome seemed to be triggered by leukemic transformation, which occurred significantly more often, and sooner, after HSCT in patients with multihit TP53MT.
Our data, in line with those of previous reports in the nontransplantation setting investigating patients with myelodysplastic syndromes and AML,7,25,26 clearly show that (multihit) TP53MT significantly increases the risk of relapse and, more importantly, leukemic relapse in patients with myelofibrosis receiving HSCT. Reportedly, TP53MTs often occur later in the disease course but dominate the genomic and clinical features of such patients regardless of the initial driver of the myeloproliferative neoplasm.27 In addition, previous work in patients with myelofibrosis and a non-HSCT setting confirmed that, as in patients with other blood cancers with TP53MT, these patients also have a dismal prognosis, with an especially high risk of transformation to AML in myelofibrosis.27,28
When looking at baseline clinical features of patients with TP53MT, those with multihit constellations were more likely to present with more severe anemia and thrombocytopenia compared with patients with TP53WT or TP53MT single-hit, whereas most disease-specific and patient-specific characteristics were generally balanced. In terms of mutation patterns, patients with multihit constellation more frequently presented with JAK2 driver mutation genotype, SRSF2, SF3B1, DNMT3A, NRAS, and KRAS mutations. However, comparisons regarding other previously established high-molecular risk constellations showed similar distributions between both groups. In our study, the only mutation that was significantly more frequent in both TP53MT groups compared with TP53WT was SH2B3, whose role is still ill defined and warrants further confirmation. SH2B adapter protein 3 is a protein that is encoded by the SH2B3 gene on chromosome 12 in humans.29 It is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types, functioning as a regulator in signaling pathways related to hematopoiesis, inflammation, and cell migration. As a result, it is involved in several hematologic malignancies,29 autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular disease (including associations with coronary artery disease).30 It has also been reported specifically in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms, indicating that changes in its expression and JAK2 binding may control JAK2-mediated signaling.31 In such a context, the finding of an enrichment of TP53MTJAK2− status in the SH2B3-mutant group in our study may not be surprising but may be limited because of the small sample of mutated cases and, thus, warrants further investigation in more patients to give more insights into molecular and clinical correlates.
Regarding cytogenetics, the high frequency of complex karyotype among patients with TP53MT with myelofibrosis may reflect a higher cytogenetic instability and higher tolerance to gross karyotypic aberrancies in preleukemic cells lacking functional TP53WT protein. Indeed, the combined poor prognostic impact of a complex karyotype and TP53MT has been observed in the setting of other myeloid neoplasms, especially in cases arising from prior hematologic disorders because acquisition of TP53MT drives clonal evolution and is associated with disease ontogeny.26,32-34 For all these reasons, TP53 mutational status and allelic state are currently taken into account in both classification and prognostic schemes of myeloid neoplasia.23,26,32,35
The importance of multihit TP53MT configuration has been shown for AML after an allograft, a scenario in which concomitant 17p abnormalities constitute additional poor prognostic factors among patients with TP53MT AML.26 More recently, in a largely non-HSCT setting, the biallelic loss of TP53 activity and its allelic state have been shown to be important for outcomes of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes.6 In 2 additional studies, variant allele frequency was an independent prognostic factor in predicting the response to hypomethylating agents among patients with TP53MT myelodysplastic syndromes,36 whereas its role was dependent on the treatment intensity among patients with AML.37 Other evidence, however, show contradicting results as to the role of TP53 clonal burden in patients with AML.25,38 Of note, none of these studies were powered to specifically determine the interaction between variant allele frequency and outcomes after HSCT. Moreover, in our study, we clearly demonstrate a significant role of multihit TP53MT in the setting of myelofibrosis, suggesting that screening for TP53MT might be essential for patients eligible for HSCT. More patients with multihit TP53MT received myeloablative conditioning (65% vs 44%), potentially reflecting physicians’ choice for more intensive treatment in a high-risk population in this retrospective multicenter cohort. Overall, our results emphasize the need for more basic, translational, and clinical research in patients with myelofibrosis carrying TP53MT and its role in various treatment environments, including HSCT and beyond.
For patients with myelodysplastic syndromes and acute leukemia harboring TP53MT, lower intensity therapeutic strategies, such as venetoclax-based regimens, may have at least comparable responses to intensive treatment. In such a context, the decision to proceed to HSCT entails many factors, with consideration of fitness in a dynamic fashion upon completion of the first treatment cycles.39 In myelofibrosis, the combination of venetoclax with hypomethylating agents has been shown to produce robust responses in the blast phase and may serve as a potential strategy to bridge patients with (particularly multihit) TP53MT or complex karyotype to HSCT.40
Posttransplantation relapse remains a major cause of treatment failure in patients with myelofibrosis carrying TP53MT, warranting further investment of effort to determine the exact role of post-HSCT next-generation sequencing monitoring and treatment strategies. Indeed, previous work showed the importance of molecular monitoring for driver mutations and highly sensitive chimerism, predicting post-HSCT outcomes.41 The feasibility of molecular monitoring has been proven among patients with AML, using a targeted gene panel at diagnosis and before and early after HSCT (at day 21).42 In a subset of patients, mutations were observed in both the pre- and post-HSCT sampling, and the assessment of variant allele frequency showed that an overall threshold of >0.2% post-HSCT was associated with an increased risk of relapse and worse overall survival. The use of post-HSCT sequencing for nondriver mutations was not used in most patients in our cohort, thereby precluding the exploration of its role in our study. However, its sensitivity and relevance in a more chronic disease such as myelofibrosis is an important subject of future research, especially for certain subgroups of cases such as those harboring TP53MT. With respect to post-HSCT treatments, donor lymphocyte infusions are the current standard of care for post-HSCT relapse in myelofibrosis,43 showing relatively high and deep responses with excellent long-term outcome in comparison to other myeloid malignancies such as AML or myelodysplastic syndromes.44,45 Our study was not designed to evaluate the role of donor lymphocyte infusions.7 Other preemptive or maintenance strategies after HSCT using hypomethylating agents or even newly introduced TP53MT-targeted therapy may provide other options for this group of patients without the risk of graft-versus-host disease and should be a question for further work.46
We did not identify a significant HSCT-related variable, including conditioning intensity, graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis, or T-cell depletion, which could have altered post-HSCT outcomes of patients with TP53MT myelofibrosis. Furthermore, assuming a priori that TP53MT myelofibrosis might have a more aggressive disease phenotype, clinicians may choose pretreatment before transplantation to reduce the disease burden. None of the patients with TP53MT in our study received chemotherapy or other agents as a bridge to HSCT, and further research is needed to investigate whether particularly patients with a multihit constellation could benefit from such an approach, given the promising results of new drugs and the observed dismal outcomes. Conversely, patients with single-hit TP53MT showed results comparable with WT cases, suggesting prioritizing the timely recourse to HSCT in this setting. Recent studies of AML suggested that TP53MT may be associated with an immunosuppressive milieu in the bone marrow microenvironment.47 This may open new therapeutic possibilities with the application of existing treatments that can remodel the immune environment, potentially reinducing a graft-versus-leukemia (or graft-versus-myelofibrosis) effect, for example, PD-1 blockade.48 However, a recent study reported that use of pembrolizumab showed improved T-cell responses but did not lead to clinical responses among patients with myelofibrosis.49
Lastly, we acknowledge several limitations. We cannot exclude the possibility of selection bias, mostly because of the retrospective design of our study. In order to fully capture the complex role of TP53, we focused our study on patients with available information of mutation profile and cytogenetics. The selection bias might have been specifically introduced by a focus of patients undergoing HSCT, which is indicated more frequently in patients at higher risk and thus might have resulted in higher frequency of patients with TP53MT than that in other published cohorts, which were all done in the non-HSCT setting.50,51 To control for this, we applied multivariable adjustment, which confirms other risk factors that have previously shown to predict worse outcomes after HSCT (including performance status, age, driver mutation genotype, donor relation, leukocyte, and platelet counts), suggesting comparability of the present cohort.12 Furthermore, physicians who are aware of the TP53 status at time of HSCT might have opted for higher intensity conditioning to address a more aggressive disease. However, we could show that conditioning intensity did not significantly influence post-HSCT outcomes, which is in line with previous results from our group and others.14,52
In summary, this report provides, to our knowledge, the first comprehensive analysis of the role of TP53MT in myelofibrosis in the setting of HSCT. These data suggest that specific counseling regarding HSCT is necessary for patients with myelofibrosis and TP53MT with and without complex karyotypes. Despite the worse overall survival observed for this high-risk group, which seems to be inherent to the biology of the disease and independent of transplantation-specific variables, HSCT still remains the only cure for these patients. Our data are not only of immediate clinical relevance for the transplantation and nontransplantation community but also highlight the need for translational and clinical studies focused on understanding the mechanism of TP53MT specifically in patients with myelofibrosis.
Authorship
Contribution: N.G. and N.K. conceived the study, collected and analyzed data, interpreted results, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript; A.B. collected and analyzed data, interpreted results, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript; R.B.S., T.S., C.G., S.P., V.P., C.R., B.C., F.T., C.W., M.R., M.H., M.-T.R., J.P.M., H.C.R., and B.L.S. collected data, interpreted results, and wrote the manuscript; and all authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Nicolaus Kröger, Department of Stem Cell Transplantation, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Martinistr 52, 20246 Hamburg, Germany; e-mail: nkroeger@uke.uni-hamburg.de.
References
Author notes
∗N.G. and A.B. contributed equally to this study.
The authors deposited the code used to generate the results to github for open-source access at https://github.com/ngagelmann/TP53inMFandHSCT.
Genomic data of the study participants are available upon request from the corresponding author, Nicolaus Kröger (nkroeger@uke.de).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal