Key Points
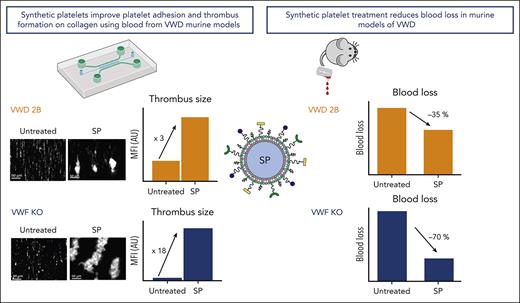
SP nanoparticles improve thrombus formation on collagen using blood from VWD murine models.
Treatment with SP nanoparticles reduces blood loss in murine models of VWD.
Abstract
The lack of innovation in von Willebrand disease (VWD) originates from many factors including the complexity and heterogeneity of the disease but also from a lack of recognition of the impact of the bleeding symptoms experienced by patients with VWD. Recently, a few research initiatives aiming to move past replacement therapies using plasma-derived or recombinant von Willebrand factor (VWF) concentrates have started to emerge. Here, we report an original approach using synthetic platelet (SP) nanoparticles for the treatment of VWD type 2B (VWD-2B) and severe VWD (type 3 VWD). SP are liposomal nanoparticles decorated with peptides enabling them to concomitantly bind to collagen, VWF, and activated platelets. In vitro, using various microfluidic assays, we show the efficacy of SPs to improve thrombus formation in VWF-deficient condition (with human platelets) or using blood from mice with VWD-2B and deficient VWF (VWF-KO, ie, type 3 VWD). In vivo, using a tail-clip assay, SP treatment reduced blood loss by 35% in mice with VWD-2B and 68% in mice with VWF-KO. Additional studies using nanoparticles decorated with various combinations of peptides demonstrated that the collagen-binding peptide, although not sufficient by itself, was crucial for SP efficacy in VWD-2B; whereas all 3 peptides appeared necessary for mice with VWF-KO. Clot imaging by immunofluorescence and scanning electron microscopy revealed that SP treatment of mice with VWF-KO led to a strong clot, similar to those obtained in wild-type mice. Altogether, our results show that SP could represent an attractive therapeutic alternative for VWD, especially considering their long half-life and stability.
Introduction
The treatment of von Willebrand disease (VWD) has remained basically unchanged for the past 30 years.1 It rests on 3 pillars: antifibrinolytics, desmopressin, and von Willebrand factor (VWF) concentrates. However, these different approaches do not consider the heterogeneity of VWD and so far, no type or subtype-specific treatment option has been developed.
In this regard, VWD-type 2B (VWD-2B) could represent an attractive target because of its very specific nature. Indeed, VWD-2B is characterized by gain-of-function mutations in the VWF A1 domain, which increase VWF binding to its platelet receptor, glycoprotein (GP) Ibα. Consequently, it is the only VWD subtype associated with a platelet phenotype including the presence of circulating platelet aggregates, giant platelets, a fluctuating thrombocytopenia, and a platelet function defect.2-4 These distinctive features raise the question of whether correcting the platelet defect could improve hemostasis in VWD-2B. Thrombocytopenia can be addressed with platelet transfusions5 or even with thrombopoietin receptor agonists6,7 but these approaches do not solve the thrombocytopathy because the mutant VWF will still bind spontaneously to platelet GPIbα. Strategies that can bypass the VWF-GPIbα axis while supporting platelet adhesion and aggregation may offer new possibilities to treat VWD-2B. In this regard, platelet-inspired synthetic hemostatic nanoparticles represent a very attractive alternative. These “synthetic platelet” (SP) nanoparticles are made of a phospholipid-based liposomal template that is surface-decorated with 3 different peptides: a fibrinogen mimetic peptide (FMP) that can bind to the active form of platelet integrin αIIbβ3, a collagen-binding peptide (CBP) that can bind to exposed subendothelial fibrillar collagen, and a VWF-binding peptide (VBP) derived from the C2 domain of Factor VIII that can bind to the D′-D3 domain of VWF.8-10 SP have been shown to collaborate with residual platelets to restore hemostatic efficacy in tail-clip model in severely thrombocytopenic mice.11-13 Their hemostatic efficacy was also demonstrated in several animal models of traumatic injury, including a murine model of hepatic laceration,14 a porcine model of traumatic arterial hemorrhage,15 and a rodent model of traumatic liver resection injury.12 Because of their promising hemostatic performance efficiency in these models and their unique mode of action toward VWF, that is, binding to the D′-D3 region and not to the A1-domain like platelets, we hypothesized that SP could be used to improve hemostasis in VWD-2B. Furthermore, because SP maintains the ability to bind to collagen irrespective of VWF presence8 and still coaggregate with active platelets to reduce bleeding, we postulated that they might also provide hemostatic support in a situation where native platelet adhesion to VWF is lacking because of the absence of VWF. Therefore, we also tested the hemostatic capability of SP in a VWF-knockout (KO) murine model.
Methods
Additional description of the experimental procedures can be found in the supplemental Material (available on the Blood website).
Animals and ethics statement
Mice with VWD-2B harboring the p.V1316M mutation in murine VWF and mice with VWF deficiency (VWF-KO) have been described previously.16,17 Male and female mice were used throughout the study (8-24 weeks old). This project was approved by the ethical committee CEEA26 (number APAFIS#27290-2020091714275854 v1).
Particle manufacturing methods
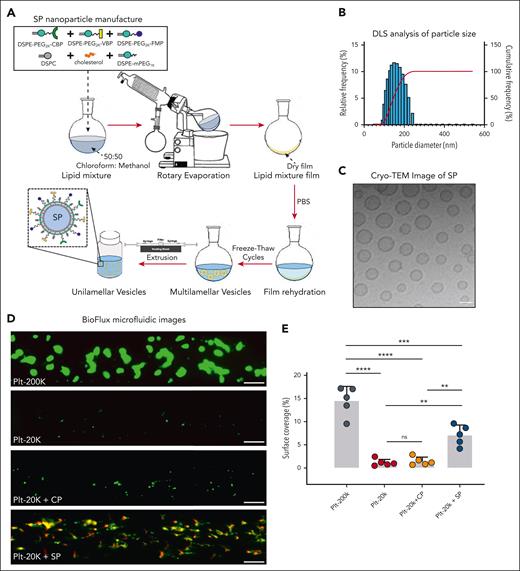
VBP and CBP were conjugated to DSPE-PEG2K-Mal via thiol-maleimide coupling to form DSPE-PEG2K-VBP and DSPE-PEG2K-CBP and FMP was conjugated to DSPE-PEG2K-azide via copper-catalyzed alkyne-azide cycloaddition (CuCAAC) or ‘click chemistry’ to form DSPE-PEG2K-FMP. All lipid-peptide conjugates were purified by dialysis and characterized by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. For manufacturing liposome-based SP nanoparticles surface-decorated with all 3 peptides, DSPE-PEG-VBP and DSPE-PEG-CBP were combined at 1 mol% each with DSPE-PEG-FMP (15 mol%), DSPC (40 mol%), cholesterol (40 mol%), DSPE-mPEG1K (2 mol%), and DHPE-RhB (1 mol%) in 1:1 chloroform:methanol. They were then subjected to solvent evaporation under reduced pressure to form thin lipid films, rehydrated with 0.9% NaCl, then subjected to 10 freeze-thaw cycles using alternating exposure to liquid nitrogen and 60°C water bath, and finally extruded 5 times through a 200 nm pore size polycarbonate filter (thin film rehydration and extrusion method) (Figure 1A).18 For nanoparticles with 2, 1, or no peptides, the specific lipid-peptide conjugates were replaced with an equivalent mol% of DSPE-mPEG2000 and subjected to the same process of liposomal nanoparticle fabrication as described above. Before use, nanoparticle size was characterized by dynamic light scattering (Figure 1B) and cryo-transmission electron microscopy (Figure 1C).
Physical and functional characterization of the SP nanoparticles. (A) Schematic of the manufacturing process for SP nanoparticle with lipids and lipid-peptide conjugates using the thin film rehydration followed by extrusion methodology. (B) Dynamic Light Scattering characterization and (C) Cryo-transmission electron microscopy (Cryo-TEM) imaging of SP nanoparticles indicates a diameter of approximately 150 to 200 nm. (D-E) Representative fluorescence microscopy images and quantitative analysis of imaging data from BioFlux microfluidics studies with platelet suspensions indicate that depletion of platelets from 200 000 per μL (Plt-200K) to 20 000 per μL (Plt-20K) results in drastic reduction of platelet coverage of collagen-coated microfluidic channel surface. Treatment of Plt-20K with CP does not rescue this whereas the treatment of Plt-20K with SP nanoparticles significantly rescues platelet recruitment and coverage on the collagen-coated channel surface (colocalization of Rhodamine B-labeled red fluorescent SP with calcein-stained green fluorescent platelets appear yellow). The particle/platelet ratio was 1000:1. Means ± SD are represented. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey's correction. ∗∗P ≤ .01; ∗∗∗P ≤ .001; ∗∗∗∗P ≤ .0001. ns, not significant.
Physical and functional characterization of the SP nanoparticles. (A) Schematic of the manufacturing process for SP nanoparticle with lipids and lipid-peptide conjugates using the thin film rehydration followed by extrusion methodology. (B) Dynamic Light Scattering characterization and (C) Cryo-transmission electron microscopy (Cryo-TEM) imaging of SP nanoparticles indicates a diameter of approximately 150 to 200 nm. (D-E) Representative fluorescence microscopy images and quantitative analysis of imaging data from BioFlux microfluidics studies with platelet suspensions indicate that depletion of platelets from 200 000 per μL (Plt-200K) to 20 000 per μL (Plt-20K) results in drastic reduction of platelet coverage of collagen-coated microfluidic channel surface. Treatment of Plt-20K with CP does not rescue this whereas the treatment of Plt-20K with SP nanoparticles significantly rescues platelet recruitment and coverage on the collagen-coated channel surface (colocalization of Rhodamine B-labeled red fluorescent SP with calcein-stained green fluorescent platelets appear yellow). The particle/platelet ratio was 1000:1. Means ± SD are represented. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey's correction. ∗∗P ≤ .01; ∗∗∗P ≤ .001; ∗∗∗∗P ≤ .0001. ns, not significant.
BioFlux microfluidic assay to study effect of SP on human platelets in absence of VWF
Human platelet suspensions in buffer, containing 200 000 platelets per μL (Plt-200k), 50 000 platelets per μL (Plt-50K) or 20 000 platelets per μL (Plt-20k) were perfused on collagen-coated channels at 60 dyn/cm2 for 10 minutes and the green fluorescence (calcein) for surface-adhered and aggregated platelets was imaged in real time. Next, rhodamine-B labeled (red fluorescence) control nanoparticles (CP) or SP nanoparticles at a particle:platelet ratio of 1000:1 were added to Plt-50K and Plt-20K conditions, to evaluate the ability of CP vs SP in rescuing platelet recruitment on the collagen-coated surface.
Total thrombus formation analysis system (T-TAS) perfusions
The T-TAS Plus (Zacros Fujimori Kogyo, Tokyo, Japan) is an automated microchip-based flow chamber system developed for assessment of platelet thrombus formation under flow conditions.19-21 Murine blood was collected under general anesthesia (isoflurane) by retro-orbital puncture within a nonheparinized glass capillary, in one-tenth volume trisodium citrate (13.8 mM final concentration). Blood was half-diluted in citrate solution (3.2% trisodium citrate solution/ 0.9% NaCl at the ratio of 1:9) and complemented with undecorated (control) nanoparticles or SP at a ratio of 50 particles per platelet. T-TAS Plus perfusions were performed on AR chips coated with collagen and tissue factor at a shear rate of 600 s−1 for up to 30 minutes. Area under the curve (AUC), representative of the increase in pressure which relates to thrombus formation, was calculated, or extrapolated at 30 minutes.
Parallel plate flow chamber
Murine blood half-diluted in Tyrode’s buffer was labeled with rhodamine 6G and complemented with CP or SP at a ratio of 50 particles per platelet. Thrombus formation was evaluated after perfusion assay on a fibrillar collagen matrix under arterial shear conditions (shear rate of 1500 s−1).22
Tail-clip bleeding assay
After general anesthesia with ketamine and xylazine, the mice received different formulations of particles via intravenous injection (2 mg/kg, in a final volume of 100 μL NaCl 0.9%, leading to a platelet: particle ratio between 1:5 to 1:10). Ten minutes later, 3 mm of the distal tip of the tail was amputated. Blood collection and blood loss measurement were performed as previously described.23 Of note, bleeding was assessed over 30 minutes for mice with VWD-2B and 20 minutes for VWF-KO mice.
Immunofluorescence imaging of amputated tails
At the end of the tail-clip bleeding assay, 1 cm of the distal tip of tails from wild-type (WT) mice with VWF or VWF-KO mice injected with SP was amputated and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 24 hours. Sections were stained for platelets using an antimouse CD41 antibody and for fibrin. Analysis was done in a selected region of interest which was defined inside the vessel. Sections were imaged using epifluorescent microscopy and analyzed using ImageJ software.
Scanning electron microscopy observation of clot morphology after tail vein transection
Untreated VWF-KO mice or VWF-KO mice injected with SP underwent a tail vein transection procedure as previously described.24 After 10 minutes, the tail was immersed in 4% PFA/1% glutaraldehyde and cut. The sample was then immediately immersed in 10 mL 4% PFA/1% glutaraldehyde and fixed overnight at 4°C. Then, a 1 cm tail section was cut, centered on injury. A “nanosuit” was used to protect the samples from electron beam and hard drying.25 The tails were dipped 3 times during 1 minute in the nanosuit and then preirradiated by a sputtering device without the metal emitter. Finally, silver metallization (setting: 10 nm of silver, 120 seconds at 5 cm and 30 mA) of the complete tail section was performed, and the samples were observed with scanning electron microscopy at different magnifications.
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) unless indicated otherwise. Mann-Whitney test was performed for 2 groups comparison. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test was performed when comparing multiple groups. P < .05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 7 software (La Jolla, CA).
Results
SP enhances platelet surface coverage in BioFlux microfluidics in VWF-deficient condition
Figure 1D shows representative fluorescence images of platelet surface coverage in Plt-200k vs Plt-20k vs “Plt-20k + CP” vs “Plt-20k + SP” conditions on collagen-coated BioFlux microfluidic channels in the absence of any plasma VWF. As is evident from the images, the surface coverage was drastically reduced in Plt-20K condition compared with Plt-200K condition. Adding CP in Plt-20K condition did not rescue or improve platelet surface coverage. In contrast, adding SP in Plt-20K condition substantially improved platelet surface coverage, and a high colocalization of red SP nanoparticles with green platelets was observed (appearing yellow in the merged image), suggesting that SP nanoparticles were able to rapidly bind to the exposed collagen even in the absence of VWF and enable concomitant binding of active platelets onto them to render enhanced recruitment and coverage of platelets on the surface. Figure 1E shows quantitative analysis of the results from these studies (n = 5 per condition), confirming that surface coverage of platelets on collagen-coated microchannels is significantly reduced (P < .0001) in Plt-20K condition (1.2% ± 0.8%) compared to Plt-200K condition (14.5% ± 3.2%), and the addition of SP significantly rescued (7.0% ± 2.2%, P = .0014) this surface coverage compared with the addition of CP (1.4% ± 0.9%). Surface-averaged platelet fluorescence intensity (green fluorescence, arbitrary units) from the same conditions, normalized to Plt-200K condition, are shown in supplemental Figure 1. Supplementary Movies A, B, C, and D show representative microfluidic imaging of Plt-200K, Plt-20K, Plt-20K + CP, and Plt-20K + SP conditions. In addition, supplemental Figure 2 shows representative fluorescence images and quantitative analysis data for SP treatment of Plt-50K condition, once again indicating the ability of SP to rescue platelet coverage on collagen-coated microfluidic surface. Altogether, these results indicate that SP nanoparticles can potentially render improved hemostatic responses in VWF-deficient and platelet-depleted conditions, as long as the concomitant collagen-binding (via CBP) and integrin αIIbβ3-binding (via FMP) properties of SP are able to enhance the recruitment of active platelets on collagen-exposing surface.
Ex-vivo addition of SP to VWD blood improves T-TAS perfusions’ parameters
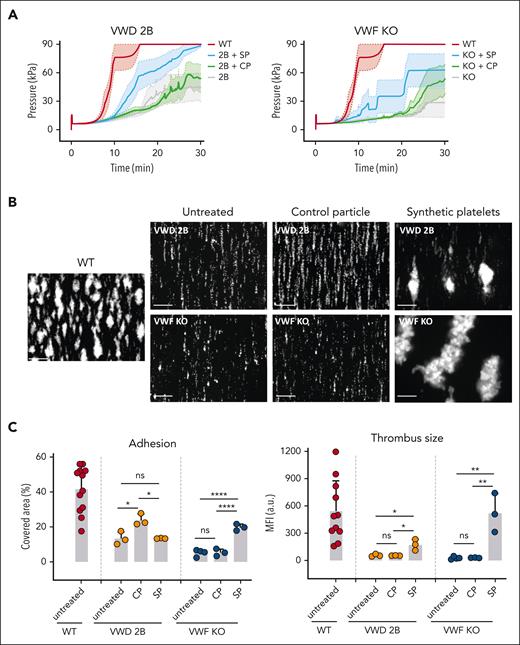
In the T-TAS perfusion system, the AUC is an integrated parameter, representative of the pressure generated by platelet adhesion and thrombus formation inside a collagen- and tissue factor-coated chip. By analyzing changes in pressure as a function of time, Figure 2A left panel clearly shows that SP addition to murine VWD-2B blood led to a significant increase in AUC (1308 with a 95% confidence interval [CI] 1278-1329) compared with untreated VWD-2B blood (710; 95% CI, 687-734; P < .0001) or with undecorated/CP-supplemented blood (733; 95% CI, 717-748; P < .0001). For murine VWF-KO blood, we also measured significantly increased AUC when blood was supplemented with SP (988; 95% CI, 954-1022) compared with untreated blood (422; 95% CI, 407-436; P < .0001) or with CP-treated blood (558; 95% CI, 541-575; P < .0001) (Figure 2A, right panel). For SP-treated VWD-2B or SP-treated VWF-KO blood, the AUC remained lower than for WT blood (1916, 95% CI 1900-1933), indicating that thrombus formation was not completely rescued.
In vitro effect of SP nanoparticles added to VWD murine blood in perfusion assays. (A) SPs or CP were added to VWD-2B blood (left panel) or to VWF-KO blood (right panel) at a ratio of 50 particles per platelet. Particle-supplemented blood or unsupplemented blood (untreated) was perfused over AR chips in the T-TAS Plus system. Graphs represent changes in pressure (a measure for thrombus formation) as a function of time. The colored area represents the standard error of the mean for each condition. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey's correction. (B-C) SPs or CP were added to VWD-2B murine blood or to VWF-KO murine blood at a ratio of 50 particles per platelet. Particle-supplemented blood or unsupplemented blood (untreated) was perfused over collagen in a parallel flow chamber at 1500 s−1. untreated representative images of thrombus formation are shown in B while percentage platelet coverage, representing adhesion or mean fluorescence intensity as a marker of thrombus size are represented in C. Results obtained with untreated WT murine blood is shown for comparison. Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 3. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey's correction. ∗P ≤ .05; ∗∗P ≤ .01; ∗∗∗∗P ≤ .0001. a.u., arbitrary units; ns, not significant.
In vitro effect of SP nanoparticles added to VWD murine blood in perfusion assays. (A) SPs or CP were added to VWD-2B blood (left panel) or to VWF-KO blood (right panel) at a ratio of 50 particles per platelet. Particle-supplemented blood or unsupplemented blood (untreated) was perfused over AR chips in the T-TAS Plus system. Graphs represent changes in pressure (a measure for thrombus formation) as a function of time. The colored area represents the standard error of the mean for each condition. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey's correction. (B-C) SPs or CP were added to VWD-2B murine blood or to VWF-KO murine blood at a ratio of 50 particles per platelet. Particle-supplemented blood or unsupplemented blood (untreated) was perfused over collagen in a parallel flow chamber at 1500 s−1. untreated representative images of thrombus formation are shown in B while percentage platelet coverage, representing adhesion or mean fluorescence intensity as a marker of thrombus size are represented in C. Results obtained with untreated WT murine blood is shown for comparison. Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 3. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey's correction. ∗P ≤ .05; ∗∗P ≤ .01; ∗∗∗∗P ≤ .0001. a.u., arbitrary units; ns, not significant.
Altogether, the T-TAS perfusion assays show a significant improvement of platelet adhesion when SP were added to VWD blood.
Ex-vivo addition of SP to VWD blood significantly improved thrombus formation in a parallel plate flow chamber
To build on the encouraging results obtained with the T-TAS system, additional blood perfusion studies were performed using a more “classical” collagen-coated parallel plate flow chamber. The addition of SP to VWD-2B blood significantly increased thrombus formation compared with both untreated blood or blood supplemented with CP (174 ± 59 vs 58 ± 9, P = .016 and 174 ± 34 vs 55 ± 2, P = .015, respectively) (Figure 2B, upper panels) as measured by the mean fluorescent intensity, a surrogate marker for thrombus size (Figure 2C, left panel).
The addition of SP to VWF-KO blood also led to a strong increase in thrombus formation compared with untreated blood (523 ± 213 vs 28 ± 14, P = .002) and blood supplemented with CP (523 ± 213 vs 31 ± 2, P = .003), (Figure 2B, bottom panels and Figure 2C, left panel). Interestingly, thrombi formed in VWF-KO blood supplemented with SP appeared bigger than those formed in VWD-2B supplemented with SP.
In terms of percentage platelet coverage, the addition of SP to VWF-KO blood led to an increase in platelet adhesion (Figure 2C, right panel) with 20% ± 2% covered area compared with 5.2% ± 1.9% with untreated blood and 5.3% ±2% with CP. The results are less clear with VWD-2B blood where in terms of percentage covered area, an increase was seen only in the presence of CP (24% ± 3.4%) compared with untreated blood (13.4% ± 3.7%) or with SP-supplemented blood (13.4% ± 0.2%). However, despite this increased surface coverage seen with control particles, no thrombus formation was observed.
Compared with WT conditions, only thrombus size obtained in SP-treated VWF-KO blood was normalized. All other parameters remained below WT read-outs.
Colocalization of platelets with SP can clearly been seen when both entities were labeled with distinct fluorochromes in thrombi formed using SP-treated VWF-KO blood (supplemental Figure 3).
SP significantly reduced bleeding in VWD mice
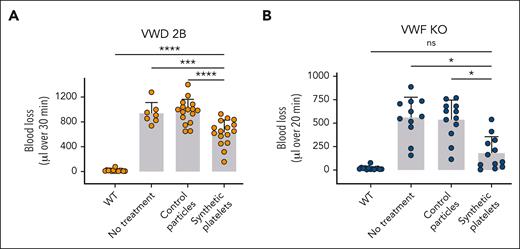
We next assessed the bleeding phenotype of VWD-2B and VWF-KO mice treated with SP. As expected, untreated VWD-2B mice lost large amounts of blood compared with WT mice (938 ± 161 vs 18 ± 17 μL, P < .0001; Figure 3A). Treatment with CP did not improve hemostasis in these mice (966 ± 192 vs 938 ± 161 μL, P = .98). In contrast, addition of SP significantly reduced blood loss by an average of 35% (631 ± 199 vs 966 ± 192 μL with control particles, P < .001 and 631 ± 199 vs 938 ± 161 μL without treatment, P = .001). Nevertheless, complete correction was not obtained (631 ± 199 vs 18 ± 17 μL in WT mice; P < .0001) (Figure 3A). Of note, SP did not affect the multimeric profile of VWD-2B mice (supplemental Figure 4).
In vivo effect of SP nanoparticles in VWD-2B and VWF-KO murine models. Mice were injected with CP or SP nanoparticles (2 mg/kg) or not injected. Bleeding was measured for 30 minutes (VWD-2B) (A) or 20 minutes (VWF-KO) (B) after amputation of 3 mm of the tail tip. Blood was collected in warm saline and quantified using a hemoglobin calibration curve. Each dot represents an individual mouse. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's correction.∗P ≤ .05; ∗∗∗P ≤ .001; ∗∗∗∗P ≤ .0001. ns, not significant.
In vivo effect of SP nanoparticles in VWD-2B and VWF-KO murine models. Mice were injected with CP or SP nanoparticles (2 mg/kg) or not injected. Bleeding was measured for 30 minutes (VWD-2B) (A) or 20 minutes (VWF-KO) (B) after amputation of 3 mm of the tail tip. Blood was collected in warm saline and quantified using a hemoglobin calibration curve. Each dot represents an individual mouse. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's correction.∗P ≤ .05; ∗∗∗P ≤ .001; ∗∗∗∗P ≤ .0001. ns, not significant.
For VWF-KO mice, untreated mice as well as CP treated-mice bled profusely compared with WT mice (561 ± 207 μL and 539 ± 194 μL vs 19 ± 17 μL) (Figure 3B). SP treatment of VWF-KO mice demonstrated an important efficacy in reducing bleeding (183 ± 167 μL vs 561 ± 207 μL in untreated mice, P = .01). Strikingly, blood loss after SP treatment was no longer statistically different than blood loss in WT mice (183 ± 167 μL vs 19 ± 17 μL, P = .15). SP thus appeared more efficient in VWF-KO mice compared with VWD-2B mice, probably because of the platelet function defect described in the latter model.
Mechanisms underlying hemostatic efficacy of SP in VWD
To investigate whether the 3 different peptides were equally important in the hemostatic efficiency of SP in VWD murine models, we tested different combinations of particles harboring only 1 peptide or combinations of 2 peptides (Figure 4).
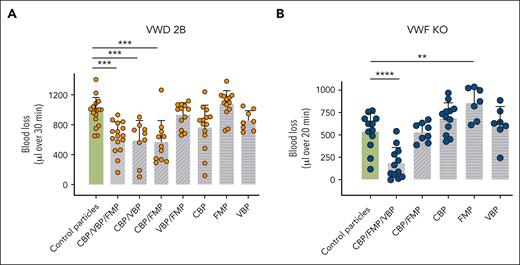
In vivo effect of various peptide-decorated particles in VWD-2B and VWF-KO murine models. Mice were injected with control particles, SP nanoparticles or particles decorated with various combinations of peptides (2 mg/kg). Bleeding was measured for 30 minutes (VWD-2B) (A) or 20 minutes (VWF-KO) (B) after amputation of 3 mm of the tail tip. Blood was collected in warm saline and quantified using a hemoglobin calibration curve. Each dot represents an individual mouse. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's correction. ∗∗P ≤ .01; ∗∗∗P ≤ .001; ∗∗∗∗P ≤ .0001. SP nanoparticles (3 peptides) are represented with the plain gray bar whereas particles decorated with dual peptides appear in diagonally striped bars and single-decorated particles appear in horizontally striped bars.
In vivo effect of various peptide-decorated particles in VWD-2B and VWF-KO murine models. Mice were injected with control particles, SP nanoparticles or particles decorated with various combinations of peptides (2 mg/kg). Bleeding was measured for 30 minutes (VWD-2B) (A) or 20 minutes (VWF-KO) (B) after amputation of 3 mm of the tail tip. Blood was collected in warm saline and quantified using a hemoglobin calibration curve. Each dot represents an individual mouse. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's correction. ∗∗P ≤ .01; ∗∗∗P ≤ .001; ∗∗∗∗P ≤ .0001. SP nanoparticles (3 peptides) are represented with the plain gray bar whereas particles decorated with dual peptides appear in diagonally striped bars and single-decorated particles appear in horizontally striped bars.
In VWD-2B, particles decorated with any of the single peptides were not efficient in reducing blood loss (CBP: 761 ± 287 μL, FMP: 1072 ± 174 μL, and VBP: 856 ± 125 μL vs 966 ± 192 μL with CP, P = .08, .71, and .81 respectively). Second, when using particles decorated with combinations of 2 peptides, only “CBP + VBP” and “CBP + FMP” combinations were as efficient as SP in correcting blood loss (CBP + VBP: 587 ± 255 μL and CBP + FMP: 568 ± 173 μL vs 631 ± 199 μL with SP; P = .99 and .97 respectively). In contrast, particles decorated with the “VBP + FMP” combination did not show any efficacy (929 ± 156 μL vs 966 ± 192 μL with CP; P = .99) (Figure 4A).
In VWF-KO mice, similar to VWD-2B mice, particles decorated with single peptides were not efficient in reducing blood loss with even a slight increase with FMP (CBP: 636 ± 239 μL; FMP: 859 ± 161 μL; VBP: 618 ± 200 μL vs 539 ± 194 μL with CP; P = .16, .0016, and .82 respectively). Surprisingly, the combination of CBP + FMP was less efficient in reducing blood loss than SP (530 ± 100 μL vs 183 ± 167 μL; P = .0001), pointing to an unexpected effect of the VBP (Figure 4B), likely because of the phospholipid binding capacity of this factor-VIII derived peptide. However, particles decorated with VBP only did not show any hemostatic efficacy. Complete statistical analysis is provided in supplemental Table 1.
In conclusion, CBP appears to be the most important peptide in the SP but is not sufficient by itself to support hemostasis in VWD-2B mice whereas all 3 peptides are necessary in VWF-KO mice.
SP colocalizes with platelets and fibrin in the clot observed after tail-clip
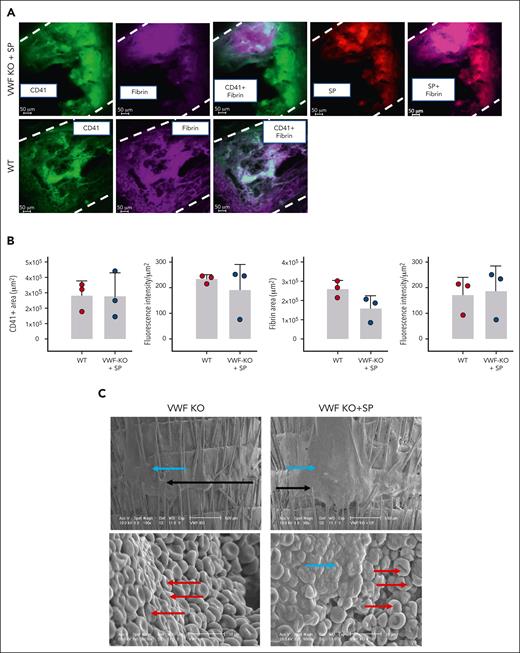
Next, we sought to image the clots observed after SP treatment in the tail-clip experiment. Here, we only imaged clots from the treated VWF-KO mice. SP, labeled with Rhodamine B could be seen as colocalizing with platelets and fibrin in the clots formed in VWF-KO mice after SP treatment (Figure 5A). A large clot, occluding the vessel from side to side could clearly be seen in SP-treated VWF-KO mice. Although this experiment is mostly of a qualitative nature, our attempt to quantify these data suggested that both the area and fluorescence intensity of the platelets and fibrin signals were similar to those obtained after imaging of a clot formed in WT mice (Figure 5B).
Imaging of the clots obtained after SP treatment of VWF-KO mice. (A) Representative images of the fluorescent staining of clots recovered after amputation of the tail tip of mice with VWF WT and VWF-KO injected with SP (2 mg/kg). Dashes represent the vessel’s edges. Rhodamine-labeled SP are visible in red, fibrin/fibrinogen is visible in magenta and CD41-labeled platelets appear in green. (B) Quantification of the platelets (CD41+) and fibrin area and fluorescence intensity in WT (n = 3) and VWF-KO mice injected with SP (n = 3). Data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using a Mann-Whitney test. (C) Scanning electron microscopy of the clot recovered after tail vein transection in mouse with VWF-KO left untreated and treated with SP. In the upper images, black arrows indicate the transection area recognizable by the hair that appear sectioned and the blue arrows point to the clot. In the bottom left image, red arrows show individualized red blood cells. In the bottom right image, blue arrow shows the clot characterized by aggregated red blood cells and red arrows show individualized red blood cells. Two mice per group were imaged and representative images are shown.
Imaging of the clots obtained after SP treatment of VWF-KO mice. (A) Representative images of the fluorescent staining of clots recovered after amputation of the tail tip of mice with VWF WT and VWF-KO injected with SP (2 mg/kg). Dashes represent the vessel’s edges. Rhodamine-labeled SP are visible in red, fibrin/fibrinogen is visible in magenta and CD41-labeled platelets appear in green. (B) Quantification of the platelets (CD41+) and fibrin area and fluorescence intensity in WT (n = 3) and VWF-KO mice injected with SP (n = 3). Data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using a Mann-Whitney test. (C) Scanning electron microscopy of the clot recovered after tail vein transection in mouse with VWF-KO left untreated and treated with SP. In the upper images, black arrows indicate the transection area recognizable by the hair that appear sectioned and the blue arrows point to the clot. In the bottom left image, red arrows show individualized red blood cells. In the bottom right image, blue arrow shows the clot characterized by aggregated red blood cells and red arrows show individualized red blood cells. Two mice per group were imaged and representative images are shown.
SP leads to substantial hemostatic clot as visible by scanning electron microscopy
To extend our observation of the SP-induced clot formation in VWF-KO mice, we collected the clot obtained after lateral tail vein transection in untreated and SP-treated mice. On the upper panels of Figure 5C, the sectioned hair indicates the area where the cut was performed (shown by the black arrows). In the untreated VWF-KO mouse, a thin thrombus could be spotted as covering the scar, thrombus formed of individualized red blood as visible at higher magnification. Upon SP treatment (Figure 5C, right panels), a larger thrombus was visible, covering the entire scar section with red blood cells aggregated together in the clot.
Discussion
Platelet-mimicking nanoparticles are currently under preclinical development to mitigate bleeding in various hemostatic dysfunction settings spanning thrombocytopenia, coagulopathy, and trauma.11-15 However, they have not yet been tested in congenital bleeding disorders linked to platelet and VWF defects. Considering our team’s interest in developing tailored therapeutic options for different VWD types/subtypes, we hypothesized that, by circumventing the VWF-GPIbα axis, SP could represent an attractive option for VWD type 2B. In vitro, using a BioFlux microfluidic system, we first showed the capacity of SP to rescue human platelet recruitment in thrombocytopenic conditions and in VWF-deficient conditions, serving as a basis for testing their efficacy in our VWD-2B and VWF-KO mouse models. Next, using VWD-2B or VWF-KO murine blood, we confirmed that SP indeed significantly improved thrombus formation in perfusion assays both in a regular parallel plate perfusion chamber (Maastricht flow chamber),26 and in the T-TAS assay.
Building on these in vitro results, and when injected in vivo, SP were able to reduce bleeding in VWD-2B mice and to achieve near-complete correction of hemostasis in VWF-KO mice. These results raise a number of questions: firstly, regarding why SP are functional in VWF-KO mice because platelets are fully functional in these mice, and second, why SP are more efficient in the VWF-KO than VWD-2B mice? SP have been shown to collaborate with platelets10-13 and in the absence of platelet-VWF interaction in VWF-KO mice, we can rationalize that the adhesion of SP to vascular collagen creates a new landing platform for native platelets to adhere to. Platelets would therefore be recruited to sites of vascular injury via SP, a hypothesis supported by the colocalization of SP with platelets and fibrin following tail-clip injury. As to why SP display higher efficiency in VWF-KO mice compared to VWD-2B animals, it should be emphasized that the latter model is characterized by thrombocytopenia/thrombocytopathy. Platelet counts in VWD-2B mice are reduced by 50% than VWF-KO.16 Although this decrease is not very profound, the inability of these VWD-2B platelets to fully activate27 may also explain why less coagulation will take place on their surface, limiting fibrin formation and ultimately, hampering bleeding correction.
To investigate mechanisms by which SP contributed to hemostasis in VWD mice, we tested several types of particles decorated with different peptide combinations. In VWD-2B mice, only particles decorated with combination of “CBP + VBP” and “CBP + FMP” proved as efficient as SP to reduce bleeding, highlighting the pivotal role of collagen in injury site-specific particle anchoring and hemostatic action. However, the CBP alone was not efficient, suggesting that at least, another platelet-mimicking characteristic was necessary for particle efficiency. Nevertheless, restoring full hemostasis in VWD-2B remains difficult because both defects in VWF and in platelets need to be overcome.28 New generations of platelet-inspired nanoparticles are currently under development: platelet-mimicking procoagulants nanoparticles, with a plasmin-triggered exposure of phosphatidylserine at the site of injury,12 or the release of thrombin at the site of injury.29 Increasing site-specific coagulation outputs with such particles might be key to improve their potential use in VWD-2B. It should also be emphasized that our VWD-2B mouse model carries the p.V1316M variant, one of the most severe VWD-2B causing mutation. Milder forms of VWD-2B may potentially be more responsive to SP treatment.
In VWF-KO mice, the result that the combination of ‘CBP + FMP’ was less efficient than SP to correct the hemostatic defect can appear very surprising at first glance. Indeed, VBP, the missing peptide in these dual-decorated particles, should be of no use in the absence of VWF. However, this VBP is derived from the FVIII C2 domain and binds not only to the VWF D’-D3 region but also to phospholipids.8 It seems conceivable therefore that even in the absence of VWF, this peptide contributes to the hemostatic response by reenforcing the interactions between SP and activated platelets. However, particles decorated with the VBP peptide alone have no hemostatic efficiency by themselves. Although theoretically, this peptide could compete with FVIII for VWF binding in the VWD-2B mice, this is unlikely to occur given that its concentration (≤500 nM) is lower than the IC50 (6 μM).30
Imaging of the clots in the presence of SP was carried out only in VWF-KO mice for technical reasons. Indeed, imaging clots of bleeding mice, such as was the case for VWD-2B mice, proved unsuccessful. The clots obtained in VWF-KO mice treated with SP appeared very similar to those obtained in WT mice as visible by fluorescent analysis. The overlap between platelets and fibrin in SP-treated mice suggests that by recruiting platelets, SP contribute not only directly to the formation of the platelet-enriched thrombus but also indirectly to the availability of platelet-exposed procoagulant phospholipids on which coagulation can occur. Scanning electron microscopy confirmed that SP led to a more compact and solid thrombus than those obtained in untreated VWF-KO mice.
So where does such an approach fit as a potential treatment for VWD? Originally, the study was intended to test a new therapeutic for VWD-2B but, although promising, the SP particle design does not appear to be optimally efficient in this VWD subtype. However, this technology has the advantage that it can be further tailored for augmenting coagulation by incorporating additional prohemostatic molecules on the particle surface or in the particle core, mimicking platelet’s procoagulant and secretory functions. Therefore, the present study should be seen as a first proof-of-concept that platelet-mimicking particles can be used for patients with VWD-2B. For severe VWD (type 3), SP particles have proven very efficient. Because of their unique characteristics, they can thus be considered as a potential new therapeutic approach for severe VWD. Indeed, their manufacturing process and stability, that is, lyophilizability, no requirement for cold storage and >6 months shelf-life, may render them very attractive compared with VWF concentrates. Furthermore, from a pharmacokinetic point of view, SP have a clear advantage over VWF concentrates. In mice, 2 hours after injection, only about 10% of VWF can still be detected.31 In contrast, 2 hours after injection in mice, only 15% of SPs have been cleared from the circulation,13 and recent studies with procoagulant platelet-mimicking particles have reported a half-life of 12 hours.12 SP thus display a much longer circulatory half-life than VWF. The use of SP could also be considered in patients with severe VWD who have developed alloantibodies, precluding the use of VWF concentrates.
In summary, there is clearly room for such a technology in a VWD setting and our results warrant further investigation of platelet-inspired nanoparticles as a novel strategy for the hemostatic management of VWD.
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by INSERM and by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-21-CE14-0076-01 to C.V.D.). J.R. holds a British Heart Foundation Intermediate Fellowship (FS/IBSRF/20/25039). A.S.G. is supported by NIH R01 HL121212.
Authorship
Contribution: S.R., N.L., J.R., J.S., D.D., T.S., F.A., C.C., O.D.C., P.J.L., and C.V.D. performed experiments and analyzed the data; A.D., E.G., C.P., M.B., and A.S.G. provided essential reagents; J.R., P.J.L., A.S.G., and C.V.D. designed the study; S.R., C.V.D., and A.S.G. wrote the manuscript; and all authors contributed to the final editing of the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: A.D., E.G., C.P., and M.B. are employees of Haima Therapeutics LLC. A.S.G. is cofounder and chief scientific adviser for Haima Therapeutics. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Cécile V. Denis, Laboratory for Hemostasis, Inflammation & Thrombosis, INSERM U1176, 80 rue du General Leclerc, 94276 Le Kremlin-Bicêtre Cedex, France; e-mail: cecile.denis@inserm.fr; and Anirban Sen Gupta, Case Western Reserve University, Department of Biomedical Engineering, 10900 Euclid Ave, Cleveland, OH 44106; e-mail: axs262@case.edu.
References
Author notes
Data are available upon request from corresponding author Cécile V. Denis (cecile.denis@inserm.fr).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal