
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is initiated and maintained by a relatively rare leukemia stem cells (LSCs) capable of self-renewal and proliferation. Recent data showed that LSCs (Lagadinou et al. Cell Stem Cell 2013) and residual cytarabine (Ara-C)-resistant AML cells (representing minimal residual disease, MRD) (Farge et al. Cancer Discovery 2017) are highly dependent on mitochondrial function for survival. This unique metabolic biology makes chemoresistant LSCs and AML cells vulnerable to pharmacological blockade of the oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). We have reported that a novel OXPHOS inhibitor IACS-010759 potently inhibits mitochondrial complex I, suppresses OXPHOS and selectively inhibits the growth of AML cells in vitro and in vivo (Molina et al. Nat Med 2018). In this study, we aimed to determine the effects of OXPHOS inhibition with IACS-010759 on residual AML cells surviving standard chemotherapy (Doxorubicin/Ara-C, DA) in cell line and patient-derived xenograft (PDX) AML models.
Consistent with our hypothesis, OCI-AML3 cells treated with DA in vitro induced elevated levels of reactive oxygen species, higher mitochondrial mass and membrane potential (Fig. 1A), indicating reliance on the mitochondrial metabolism. Further, Ara-C treatment resulted in significantly increased basal and maximal oxygen consumption rates (OCR) (36%±8%, p=0.03; 36%±3%, p=0.003, respectively) compared to control. In turn, targeting OXPHOS with IACS-010759 at 30 nM fully inhibited basal and Ara-C-induced OCR. These findings indicate that chemotherapy fosters mitochondrial respiration in AML, which could be abrogated by OXPHOS inhibitor.
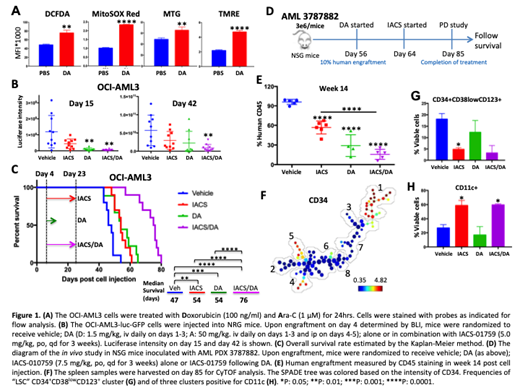
To test the efficacy of combining IACS-010759 (5 mg/kg) and standard chemotherapy (Doxorubicin: 1.5 mg/kg; Ara-C: 50 mg/kg) in vivo, we injected NRG mice with genetically engineered OCI-AML3/Luc/GFP cells. Bioluminescent imaging demonstrated significantly reduced leukemia burden in DA/IACS-010759 combination group compared to vehicle on days 15 and 42 (p<0.01) (Fig. 1B). DA/IACS-010759 combination significantly extended survival, compared to the vehicle or single-agent treatment arms (Fig. 1C). Mouse body weight monitoring indicated that therapy was well tolerated
We next examined the efficacy of IACS-010759 on leukemia cells surviving chemotherapy in a chemosensitive PDX AML model of minimal residual disease (Fig. 1D). Treatment of mice inoculated with a human AML PDX harboring FLT3-ITD mutation with DA reduced circulating leukemia burden (0.8 ± 0.6% vs 45.8 ± 8.2% blasts in vehicle-treated mice, p=0.001). The residual AML cells in DA-treated mice expanded and caused rapidly progressive leukemia (78.2 ± 6.2% vs 95.3 ± 1.0% in vehicle-treated mice, p=0.047) on week 6 post DA. Daily oral treatment of mice with IACS-010759 (7.5 mg/kg) as a single agent reduced leukemia burden, and delayed leukemia recurrence when administered post completion of DA (Fig. 1E). A SPADE tree was built based on 13 surface markers and colored by expression intensity of CD34 using CyTOF mass cytometry data (Fig. 1F). The data demonstrated reduced frequency of CD34+CD38lowCD123+ AML LSCs and increase in CD11c+ differentiated cells in both IACS and IACS/DA groups (Fig. 1G&H). In contrast, chemotherapy alone failed to significantly reduce fractions of LSCs or induce differentiation. Proliferation measured by Ki67 was greatly reduced by IACS/DA combination in all populations including LSCs (1.4 ± 0.3% vs 5.5 ± 0.4% in vehicle group, p<0.01). The expression of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α (HIF-1α) was downregulated, consistent with the decreased oxygen consumption induced by IACS-010759 (not shown).
In conclusion, minimal residual AML cells surviving chemotherapy depend on OXPHOS for survival. OXPHOS inhibition with complex I inhibitor IACS-010759 is effective in reducing LSCs and MRD, alone and in combination with chemotherapy in vivo. Our data advocate for combining IACS-010759 with chemotherapy for improved control of MRD upon identification of a recommended Phase II dose in a clinical trial of IACS-010759 in AML (NCT02882321).
Zhang:The University of Texas M.D.Anderson Cancer Center: Employment. Kuruvilla:The University of Texas M.D.Anderson Cancer Center: Employment. Kantarjian:Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Cyclacel: Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding; Immunogen: Research Funding; Actinium: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Honoraria; Ariad: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Agios: Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Astex: Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Jazz Pharma: Research Funding. Daver:Jazz: Consultancy; Hanmi Pharm Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; Agios: Consultancy; Immunogen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sunesis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Forty-Seven: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy, Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Astellas: Consultancy; Servier: Research Funding; NOHLA: Research Funding; Glycomimetics: Research Funding; Otsuka: Consultancy. Andreeff:BiolineRx: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; CLL Foundation: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Leukemia Lymphoma Society: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; NCI-RDCRN (Rare Disease Cliln Network): Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; German Research Council: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; NCI-CTEP: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Cancer UK: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Center for Drug Research & Development: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; NIH/NCI: Research Funding; CPRIT: Research Funding; Breast Cancer Research Foundation: Research Funding; Oncolyze: Equity Ownership; Oncoceutics: Equity Ownership; Senti Bio: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Eutropics: Equity Ownership; Aptose: Equity Ownership; Reata: Equity Ownership; 6 Dimensions Capital: Consultancy; AstaZeneca: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo, Inc.: Consultancy, Patents & Royalties: Patents licensed, royalty bearing, Research Funding; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy. Konopleva:Calithera: Research Funding; Stemline Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Forty-Seven: Consultancy, Honoraria; Eli Lilly: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Cellectis: Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; F. Hoffman La-Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech: Honoraria, Research Funding; Ascentage: Research Funding; Kisoji: Consultancy, Honoraria; Reata Pharmaceuticals: Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties; Ablynx: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; Agios: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal