Key Points
A preclinical cell-based model identifies SNPs associated with cytarabine sensitivity that also associate with outcome in leukemia patients.
SNPs within the MCC gene were associated with cytarabine sensitivity in lymphoblastoid cell lines and leukemic blasts from patients.
Abstract
A whole-genome approach was used to investigate the genetic determinants of cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity. We performed a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies involving 523 lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) from individuals of European, African, Asian, and African American ancestry. Several of the highest-ranked single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were within the mutated in colorectal cancers (MCC) gene. MCC expression was induced by cytarabine treatment from 1.7- to 26.6-fold in LCLs. A total of 33 SNPs ranked at the top of the meta-analysis (P < 10−5) were successfully tested in a clinical trial of patients randomized to receive low-dose or high-dose cytarabine plus daunorubicin and etoposide; of these, 18 showed association (P < .05) with either cytarabine 50% inhibitory concentration in leukemia cells or clinical response parameters (minimal residual disease, overall survival (OS), and treatment-related mortality). This count (n = 18) was significantly greater than expected by chance (P = .016). For rs1203633, LCLs with AA genotype were more sensitive to cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity (P = 1.31 × 10−6) and AA (vs GA or GG) genotype was associated with poorer OS (P = .015), likely as a result of greater treatment-related mortality (P = .0037) in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). This multicenter AML02 study trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT00136084.
Introduction
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most common form of acute leukemia in adults and also occurs in children. Despite the genetic heterogeneity of the disease, patients have been treated for decades with similar combinations of cytarabine and anthracyclines with little improvement in overall survival (OS).1 Although the majority of patients (50%-60%) under 60 years achieve complete remission with traditional anthracycline- and cytarabine-based induction regimens, the long-term survival rates continue to be around 30% to 40% for adults and 60% for children.2-6 Outcomes are worse for patients ≥60 years, with complete response rates in the range of 40% to 55% and poor long-term survival rates.7 The main reason for treatment failure among patients with AML is resistance to therapy.8-10 In addition, treatment with cytarabine is associated with a number of adverse side effects including myelosuppression, infections, mucositis, neurotoxicity, and acute pulmonary syndrome.11
Cytarabine requires activation through intracellular phosphorylation to araC-triphosphate (ara-CTP). The mechanism of action of cytarabine involves the incorporation of ara-CTP in place of deoxycytidine triphosphate, resulting in chain termination, blocking DNA and RNA synthesis and causing leukemic cell death.12,13 One of the greatest predictors of response to cytarabine is the intracellular concentration of ara-CTP ex vivo and in circulating blasts of patients.14,15 Resistance is likely due to inefficient uptake of ara-CTP, reduced levels of deoxycytidine kinase (DCK), increased levels of the deactivating enzymes 5′-nucleotidase (NT5C2) or cytidine deaminase (CDA), or increased cellular deoxycytidine triphosphate pools that compete with ara-CTP for incorporation in DNA.
Candidate approaches and genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have been used to identify genetic variables that are important in interindividual variability in sensitivity to cytarabine. Candidate gene studies revealed that genes within the cytarabine pharmacokinetic pathway, including DCK, CDA, NT5C2, Cytosolic 5′-nucleotidase 3 (NT5C3), and human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1, contribute to sensitivity to cytarabine.16
In previous work,17,18 we found genetic variants associated with cytarabine sensitivity in 85 European (CEU [refers to the HapMap samples of Northern and Western European descents]) and 89 African (YRI [refers to the Yoruba HapMap samples from Ibadan, Nigeria]) lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) that were specific to each population (505 single-nucleotide polymorphisms [SNPs] for CEU and 397 SNPs for YRI at P < 1 × 10−4, with no overlap) as well as associated variants in the “African American from the Southwestern United States” (ASW) population. The results of these cell-based models can be used in conjunction with clinical trials for discovery of SNPs associated with chemotherapeutic sensitivity, given the challenge of accruing large patient cohorts receiving the same drug regimen for discovery and replication GWAS in oncology. In this study, our goal was to identify variants that associate with cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity in 523 LCLs from different world populations representing European, African, Asian, and African American ancestries, providing a robust set of SNPs for studies in clinical trials. We evaluated the significance of the most highly ranked SNPs (P < 10−5) with cytarabine-induced apoptosis and with treatment outcome in AML patients who received cytarabine-containing therapy.
Materials and methods
Meta-analysis of six GWA studies
Details on the cytotoxicity assays in LCLs and the GWAS in individual panels are found in the supplemental Materials section. To determine SNP associations with cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity across populations, we conducted a meta-analysis on the results of the individual GWAS from the 6 panels using METAL, which combines SNP P values across studies taking into account a study-specific weight (sample size) and direction of effect (positive or negative β).19 z scores, derived from the P values for each SNP, were combined across studies in a weighted sum, wherein the weights were defined to be proportional to the square root of the sample size for each study.19 The Q-Q plot of the corresponding P values was generated using the R statistical software. Local region plots of top associated SNPs were generated by LocusZoom.20
Association of top meta-analysis SNPs with apoptosis
Apoptosis may underlie cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity; thus, the top 37 SNPs (P < 1 × 10−5) selected from the meta-analysis of cytotoxicity in LCLs were tested for association with cytarabine-induced apoptosis. The apoptotic effects of cytarabine were determined in CEU1/2, YRI1/2, ASW, and Han Chinese in Beijing, China (CHB) samples. Apoptosis, as measured by caspase 3/7 activation induced by 40 µM cytarabine 24 hours after drug treatment, was measured as previously described.21 Association analyses with apoptosis were done within each panel; results were then combined into a single P value for each SNP using the meta-analysis method.
Clinical samples
Details of the multicenter AML02 study trial (NCT00136084) protocol and outcome are described elsewhere.2 Briefly, from October 13, 2002, to June 19, 2008, 232 children with de novo AML (n = 206), therapy-related or myelodysplastic syndromes–related AML (n = 12), or mixed-lineage leukemia (n = 14) were randomized to receive high-dose cytarabine (3 g/m2 intravenously over 3 hours, given every 12 hours on days 1, 3 and 5; n = 113) or low-dose cytarabine (100 mg/m2 intravenously over 30 minutes, given every 12 hours on days 1-10; n = 11) plus daunorubicin (50 mg/m2 intravenously over 6 hours on days 2, 4, and 6) and etoposide (100 mg/m2 intravenously over 4 hours on days 2-6). All patients were chemonaïve at the time of enrollment except for 4 subjects who had AML as a second malignancy. Patients were randomly assigned to receive high-dose or low-dose cytarabine. The patient population was 69.6% white, 18.7% African American, and 11.7% with other ethnic backgrounds. Primary bone marrow samples were obtained after informed consent was obtained from patients or from their parents/guardians, with assent from the patients, as appropriate, in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. This study and the use of these samples were approved by the institutional review board at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital.
The top 37 SNPs selected from the meta-analysis in LCLs were genotyped in genomic DNA from these AML patients using a Sequenom (iPLEX) mass spectrometry–based multiplex genotyping assay (Sequenom, San Diego, CA) at BioMedical Genomics Center, University of Minnesota. Of the 37 SNPs, 34 SNPs were successfully genotyped (3 failed genotyping, including 1 within MCC) and 1 SNP was not polymorphic in AML patients.
Minimal residual disease (MRD), relapse-free survival (RFS), event-free survival, OS, and treatment-related mortality (TRM) were determined as previously described.2 Ex vivo sensitivity to cytarabine (50% inhibition/inhibitory concentration [IC50]) of leukemic cells obtained at diagnosis was determined in patients enrolled on the AML02 protocol using the 4-day MTT (3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-dimethyltetrazolium bromide) cytotoxicity assay as described previously.22,23 The statistical analysis of clinical samples is described in the supplemental Materials section.
Evaluation of meta-analysis LCL SNPs in patients
We tested the 33 SNPs that had an association with cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity in LCLs (P < 1 × 10−5) for association (P < .05 and concordant direction) with either cytarabine IC50 in leukemia cells or with clinical response parameters (MRD on day 22, OS, or TRM). We refer to these SNPs as “clinically validated SNPs.”
For assessment of the statistical significance of the number of clinically validated SNPs, patient label was permuted (n = 5000) in the white patients while preserving the genotype correlation structure among the 33 SNPs and the correlation structure among the clinical traits tested. In each permuted data set, the association tests with the clinical phenotypes were performed; SNPs with P < .05 were selected. A permuted data set was considered a “success” if the number of (unique) selected SNPs from the association tests was equal to or greater than the number of clinically validated SNPs. Empirical significance of the excess of clinically validated SNPs was estimated as the proportion of such “successes.”
MCC gene expression after cytarabine treatment
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was performed to measure the level of expression of MCC over time following cytarabine treatment. Details can be found in our supplemental Materials section.
Results
Cellular sensitivity phenotypes
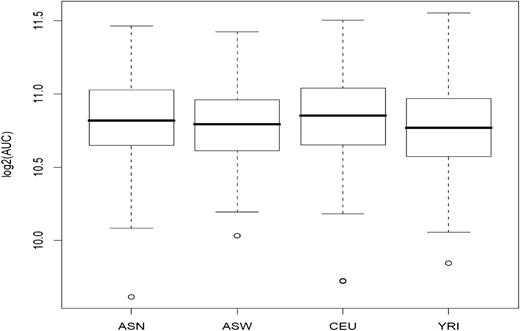
Previously, genetic variants associated with cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity were identified in 85 CEU, 89 YRI, and 83 ASW from the International HapMap LCL collection.17,18 In the present study, we extended these studies to increase power to detect associations and to identify cross-population SNPs. Prior to performing a meta-analysis, we evaluated an additional 89 CEU (174 total), 87 YRI (176 total), and 90 ASN (refers to Han Chinese in Beijing, China and Japanese in Tokyo, Japan, and consisting of 45 Japanese from Tokyo and 45 Han Chinese from Beijing) for cellular sensitivity to cytarabine using a short-term growth inhibition assay. We determined the percent survival at 5 different concentrations for each cell line, from which the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated. Figure 1 illustrates the box plot of the distribution of log2 AUC values in the 4 populations of cell lines. The log2 AUC values in each cell line panel showed no departure from normality, with the exception of the ASW panel, which was thus rank-transformed to normality (supplemental Figure 1).
Cellular sensitivity to cytarabine in 523 HapMap LCLs. LCLs from world populations (ASN, ASW, CEU, and YRI) were phenotyped for the growth inhibitory effects of cytarabine. The mean (standard deviation) log2 AUC was 10.81 (±0.30 μM) for ASN, 10.78 (±0.27 μM) for ASW, 10.83 (±0.30 μM) for CEU, and 10.78 (±0.29 μM) for YRI.
Cellular sensitivity to cytarabine in 523 HapMap LCLs. LCLs from world populations (ASN, ASW, CEU, and YRI) were phenotyped for the growth inhibitory effects of cytarabine. The mean (standard deviation) log2 AUC was 10.81 (±0.30 μM) for ASN, 10.78 (±0.27 μM) for ASW, 10.83 (±0.30 μM) for CEU, and 10.78 (±0.29 μM) for YRI.
Meta-analysis across population panels identifies SNPs associated with cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity
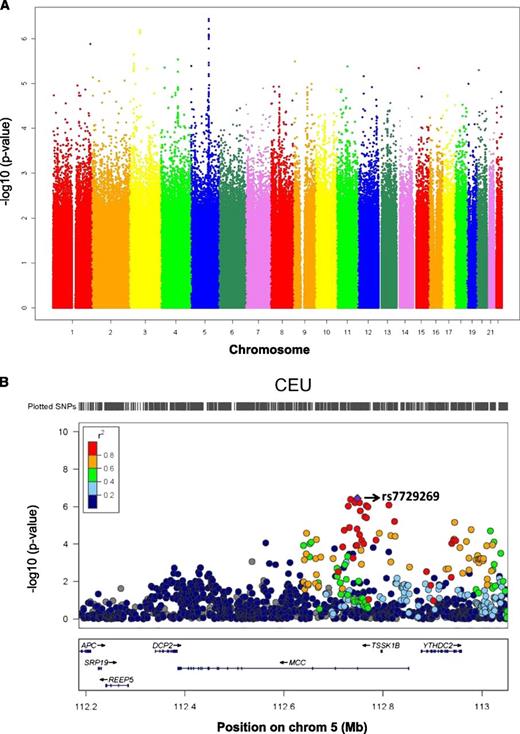
Using quantitative transmission disequilibrium tests, GWAS were performed in each panel of LCLs to identify SNP associations with cellular sensitivity to cytarabine. To increase the density of interrogated SNPs, ungenotyped markers in phase 3 of the CEU, YRI, and ASW samples were imputed using BEAGLE. To increase statistical power, we conducted a meta-analysis on the results of the individual GWAS of each of the 6 panels. The meta-analysis combined the results of individual GWAS from each panel to identify SNPs associated with cytarabine AUC across populations, accounting for sample size and direction of effect. Approximately 60% of the most highly ranked SNPs (P < 10−4; n = 370) had consistent allelic direction of effect in all 6 panels, as perhaps expected, since such SNPs would rise to the top of the meta-analysis results. Figure 2A illustrates a Manhattan plot summarizing the results of the meta-analysis. Table 1 lists the top 37 SNPs (P < 10−5), their location, P value, and the directionality in each panel evaluated (ASN, CEU1/2, CEU3, ASW, YRI1/2, and YRI3). While most of these SNPs were common (minor allele frequency [MAF] > 5%) in all the panels, several SNPs were specific to a population class (eg, monomorphic in the other populations) and therefore were not interrogated in as many individuals (Table 1 column heading “Weight”).
Meta-analysis of GWAS in CEU, YRI, ASW, and ASN populations. (A) The Manhattan plot shows the meta-analysis results on GWAS of cellular susceptibility to cytarabine in 4 world populations (n = 523 individual samples). The highest-ranked SNP was rs7729269 (P = 3.67 × 10−7) in the gene MCC. (B) The plot shows P values from the meta-analysis of GWAS in CEU, YRI, ASW, and ASN populations for the top SNP associations with cytarabine log2 AUC in a specific region on chromosome 5. The colors, as indicated in the legend, denote the extent of LD between the SNPs; for this purpose, we use only the CEU reference population. The bottom panel illustrates the chromosomal region and genes that these SNPs fall on. The figure was made in LocusZoom.
Meta-analysis of GWAS in CEU, YRI, ASW, and ASN populations. (A) The Manhattan plot shows the meta-analysis results on GWAS of cellular susceptibility to cytarabine in 4 world populations (n = 523 individual samples). The highest-ranked SNP was rs7729269 (P = 3.67 × 10−7) in the gene MCC. (B) The plot shows P values from the meta-analysis of GWAS in CEU, YRI, ASW, and ASN populations for the top SNP associations with cytarabine log2 AUC in a specific region on chromosome 5. The colors, as indicated in the legend, denote the extent of LD between the SNPs; for this purpose, we use only the CEU reference population. The bottom panel illustrates the chromosomal region and genes that these SNPs fall on. The figure was made in LocusZoom.
To ascertain the significance of SNPs within known candidate genes in the cytarabine pathway (CDA, NT5C2, NT5C3, SLC29A1, and DCK),24 we retrieved the meta-analysis P value for each of the SNPs located within the pathway and polymorphic at MAF > 5% in any of the populations examined here (supplemental Table 1). Several of the SNPs in 3 genes (CDA, NT5C2, and SLC29A1) showed nominal significance in our LCL model (P < .05).
Within the context of an unbiased genome-wide approach, we were also interested in identifying novel susceptibility loci outside the known cytarabine pathway. While no SNP reached genome-wide significance (Bonferroni) from the meta-analysis, we found that restricting the meta-analysis to SNPs that are expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs; P < 5 × 10−8 with a gene expression trait in the populations17 for which we have genome-wide gene expression data) allowed us to identify a highly significant SNP (after Bonferroni correction; n = 4686 tests), rs4073360 (P = 6.9 × 10−6), that is a common (MAF > 5%) variant in all HapMap populations. Furthermore, the distribution of association P values for the expression-associated SNPs (at a less stringent P < 10−4 with a gene expression trait)25,26 shows enrichment for low-cytarabine–association P values.
A genic region that contains the highest-ranked SNP associations from the meta-analysis was identified on chromosome 5. Figure 2B illustrates a plot of the meta-analysis P values for the genomic interval on chromosome 5 that contains the top signals; the plot also illustrates the degree of linkage disequilibrium (LD) between the highest-ranked SNP (rs7729269; P = 3.67 × 10−7; purple diamond) and surrounding SNPs in the region in CEU. The SNP rs7729269 is a common variant (MAF of 0.27 in CEU, 0.06 in ASN, 0.16 in ASW, and 0.075 in YRI) in all populations and is located in an intron of MCC. The MCC gene harbors several of the highest-ranked SNPs that are in strong LD (r2 > 0.80), most of which (ie, 10 of 12) show association with gene expression traits (P < 10−4) as potential eQTLs. In particular, rs7729269 is a potential eQTL (in CEU) for the ectodysplasin A2 receptor (EDA2R) gene. We found that higher gene expression of EDA2R was significantly associated with cellular resistance to cytarabine in CEU (P = .02) and in YRI (P = .004).
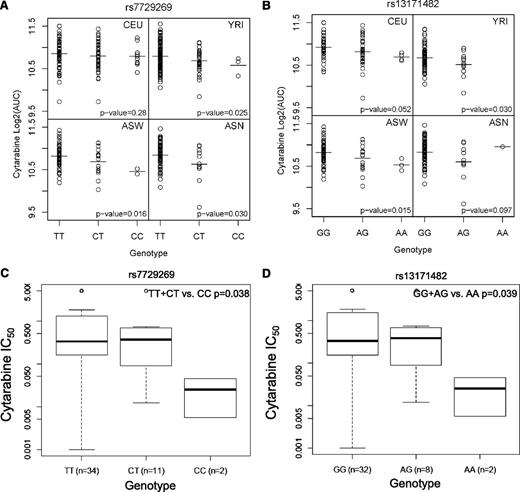
The most significant LCL cytotoxicity SNP, rs7729269, showed nominally significant associations (P < .05) with concordant direction of effect in YRI, ASW, and ASN populations (Figure 3A). Each additional C allele results in lower AUC in the cytotoxicity assay and therefore confers sensitivity to cytarabine. Another SNP within MCC, rs13171482, shows concordant direction in all 4 populations (Figure 3B).
Association of SNPs within MCC with cytarabine sensitivity in LCLs and in leukemic blasts.MCC SNPs plotted against log2 AUC in LCLs for (A) rs7729269 and (B) rs13171482, and MCC SNPs plotted against IC50 (dose required to inhibit growth of 50% of cells) in leukemic blasts for (C) rs7729269 and (D) rs13171482.
Association of SNPs within MCC with cytarabine sensitivity in LCLs and in leukemic blasts.MCC SNPs plotted against log2 AUC in LCLs for (A) rs7729269 and (B) rs13171482, and MCC SNPs plotted against IC50 (dose required to inhibit growth of 50% of cells) in leukemic blasts for (C) rs7729269 and (D) rs13171482.
Evaluation of cytarabine-induced apoptosis
Using the preclinical LCL model, we phenotyped 4 LCL panels (YRI1/2, ASW, CEU1/2, and CHB) for caspase 3/7 activation following treatment with 40 µM cytarabine. Upon evaluation of the top 37 cytotoxicity-associated SNPs (P < 1 × 10−5) for their association with cytarabine-induced caspase 3/7 activation, 14 SNPs showed nominal association with apoptosis at a P < .05 (Table 1 bolded SNPs). A total of 12 of the 14 SNPs were within the MCC gene. Thus, the MCC SNPs are associated with greater cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity through activation of caspase 3/7.
Evaluation of the relationship of GWAS findings with intrinsic growth
Previously, we demonstrated a strong association between the rate of cellular proliferation and sensitivity to cytarabine, as measured by AUC, within each population.17,27 Nevertheless, we found no association (P > .05) between any of the top 37 SNPs and intrinsic growth rate.28 Thus, it is unlikely that the observed associations of the 37 SNPs with cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity were mediated by the rate of basal proliferation. Furthermore, the expression of the MCC gene was not correlated with intrinsic growth rate (P = .11).
Validation of SNPs from the LCL model in clinical samples
To determine the degree to which our cell-based approach identified patients responsive to cytarabine, we evaluated SNPs (n = 37) identified in LCLs at the P < 1 × 10−5 threshold (Table 1) in AML patients from a previously reported clinical trial.2 A total of 33 SNPs were successfully genotyped and tested in the patient population. Among these SNPs, 12 SNPs (located in the gene MCC) were in high LD (rs7729269, rs13189050, rs6594713, rs13181534, rs10053341, rs6870401, rs13171482, rs6887482, rs10061462, rs7714760, rs6594714, and rs13174075). Located within the gene SNYPR, 5 SNPs (rs10510896, rs12638620, rs13068980, rs17068377, and rs17068392) were in LD. Of the remaining SNPs, 4 SNPs on chromosome 3 (rs1533140, rs1567582, rs6550825, and rs6550826) were in LD with each other with r2 > 0.85. The remaining 12 SNPs were not in LD with any other SNP and all were in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium criteria is enforced within each population.)
We evaluated whether SNPs identified in the LCL model were associated with in vitro chemosensitivity of leukemic blasts obtained at diagnosis (n = 69) or with treatment response in AML patients. Of the 33 SNPs tested that had an association with cytarabine cytotoxicity in LCLs, 10 SNPs within MCC (as well as the intergenic eQTL, rs4956103) were found to be nominally significant (P < .05) with in vitro cytarabine IC50 in leukemic blasts (Table 1 and supplemental Table 2). These 10 SNPs also showed the same directionality for cellular sensitivity to drug as measured by LCL cytotoxicity and LCL apoptosis and for chemosensitivity of leukemic blasts from AML patients, as illustrated for rs7729269 and rs13171482 (in Figure 3C-D, Table 1, and supplemental Table 2).
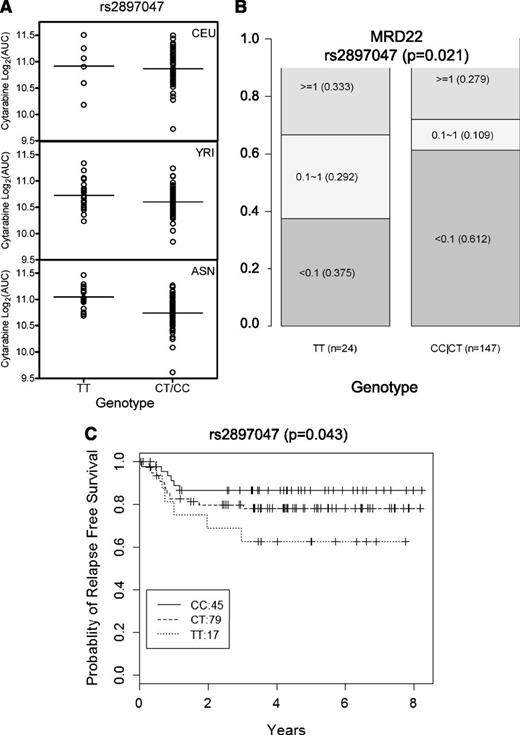
Association of SNPs was also evaluated with clinical end points, including MRD on day 22, RFS, event-free survival, OS, and TRM. Of the 33 SNPs evaluated in all patients, rs2897047, a SNP near Iroquois-class homeodomain protein (IRX2) and associated with cellular sensitivity to cytarabine in LCLs (P = 4.06 × 10−6), was also associated with day 22 MRD (P = .021) and RFS (P = .043) (Figure 4). LCLs carrying TT genotype were resistant to cytarabine, and patients with TT genotype did not respond as well to cytarabine as measured by MRD at day 22 (37.5% TT genotype patients had <0.1 MRD compared with 61.2% patients who had <0.1 MRD carrying CC and CT genotype). Consistent with cellular resistance to cytarabine in cells and higher MRD at day 22, those with a TT genotype had a poorer RFS (Figure 4C).
SNP rs2897047 association with log2 AUC in LCLs and association with MRD and RFS in all AML patients. Association of SNP rs2897047 with (A) log2 AUC for cellular sensitivity to cytarabine in a cell-based model (meta-analysis P = 4.06 × 10−6) illustrated in CEU, YRI, and ASN; (B) MRD at day 22 in all AML patients (P = .0218), where the numbers in each box represent MRD levels <0.1, 0.1 to 1, or ≥1 and the numbers in parentheses indicate fraction of patients within each MRD category; and (C) RFS (P = .043) in all AML patients.
SNP rs2897047 association with log2 AUC in LCLs and association with MRD and RFS in all AML patients. Association of SNP rs2897047 with (A) log2 AUC for cellular sensitivity to cytarabine in a cell-based model (meta-analysis P = 4.06 × 10−6) illustrated in CEU, YRI, and ASN; (B) MRD at day 22 in all AML patients (P = .0218), where the numbers in each box represent MRD levels <0.1, 0.1 to 1, or ≥1 and the numbers in parentheses indicate fraction of patients within each MRD category; and (C) RFS (P = .043) in all AML patients.
There were 5 SNPs (rs12036333, rs9883101, rs6550826, rs1533140, and rs17202778) associated with TRM. Rare alleles were associated with greater sensitivity to cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity and with greater probability of TRM. Most TRMs were due to infection secondary to chemotherapeutic immune suppression; one was due to veno-occlusive disease and another due to intracranial hemorrhage. The SNP rs12036333 was associated with LCL cytotoxicity (P = 1.31 × 10−6), with AA genotype associated with greater in vitro cytarabine sensitivity, and in AML patients AA genotype was associated with inferior OS (P = .015) as well as greater TRM (P = .0037) compared with those with GA/GG genotype (Figure 5).
SNP rs12036333 association with log2 AUC in LCLs and association with OS and TRM. Association of SNP rs12036333 (AA versus GA/GG) with (A) log2 AUC for cellular sensitivity to cytarabine in cell-based model in all populations (P = .007), (B) OS (P = .0146), and (C) TRM in white AML patients (P = .0037).
SNP rs12036333 association with log2 AUC in LCLs and association with OS and TRM. Association of SNP rs12036333 (AA versus GA/GG) with (A) log2 AUC for cellular sensitivity to cytarabine in cell-based model in all populations (P = .007), (B) OS (P = .0146), and (C) TRM in white AML patients (P = .0037).
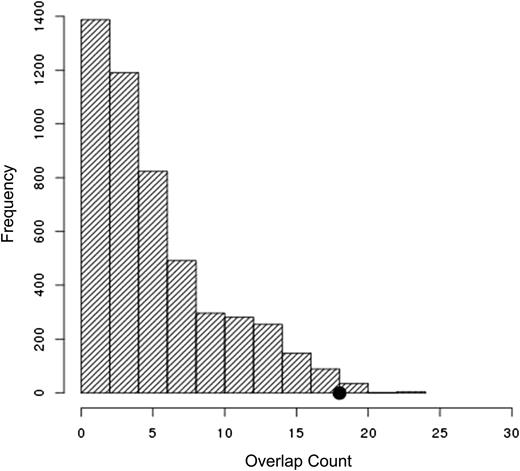
Of the 33 SNPs tested that had an association with cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity in LCLs (P < 1 × 10−5), 18 were associated (P < .05) with cytarabine IC50 in leukemia cells, day 22 MRD, RFS, OS, or TRM (supplemental Table 2). The number of such clinically validated SNPs was statistically significant (P = .016; Figure 6) from a permutation analysis (see the Materials and methods section).
Top SNPs identified in LCLs are enriched for top associations with clinical phenotypes. Of the 33 SNPs tested that had an association with cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity in LCLs (P < 1 × 10−5), 18 were associated (P < .05) with cytarabine IC50 in leukemia cells, day 22 MRD, RFS, OS, or TRM. The number of clinically validated SNPs is highly significant (P = .016) given the correlation structure of the genotypes evaluated and that of the phenotypes examined.
Top SNPs identified in LCLs are enriched for top associations with clinical phenotypes. Of the 33 SNPs tested that had an association with cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity in LCLs (P < 1 × 10−5), 18 were associated (P < .05) with cytarabine IC50 in leukemia cells, day 22 MRD, RFS, OS, or TRM. The number of clinically validated SNPs is highly significant (P = .016) given the correlation structure of the genotypes evaluated and that of the phenotypes examined.
Effect of cytarabine treatment on MCC gene expression
There was no significant relationship between baseline MCC gene expression and sensitivity to cytarabine as measured by cytotoxicity or apoptosis (data not shown). We surmised that a potential mechanism for sensitivity to cytarabine by SNPs within MCC might involve variation in modulation of gene expression following drug treatment. To test whether MCC modulation occurred after cytarabine treatment, we treated 5 CEU and 5 YRI LCLs with vehicle alone or 10 µM cytarabine for 2, 6, 18, and 24 hours. We found that all 10 cell lines demonstrated induction, with variability observed in the degree and the time course ranging from 1.3 to 26.6 times MCC expression relative to control (supplemental Figure 2). This induction was statistically significant at all time points tested (P = .03 at 6 hours, 7.1 × 10−10 at 18 hours, and 7.1 × 10−11 at 24 hours). Interestingly, the cell line (12044) with 26.6-fold induction was among the most sensitive and the cell line (12812) with 1.3-fold induction was among the most resistant to cytarabine. However, the relationship between fold change and cytarabine sensitivity failed to achieve significance in these 10 cell lines, perhaps due to small size. We also measured NFKB1expression at the same time points and saw a modest expression decrease at 24 hours (P = .059) (data not shown).
Using limma29 as implemented in the Bioconductor project, we reanalyzed 2 gene expression profiling data sets, one from a study of cytarabine-treated human diffuse large cell lymphoma cell lines versus untreated cells30 and another from a recently deposited data into Gene Expression Omnibus involving primary AML cells treated with cytarabine (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA174047).31 In the former, we found that MCC expression was significantly induced (P = .029) by cytarabine treatment (supplemental Figure 3). In the latter, AML samples treated with cytarabine showed higher exon-level MCC expression (1.5-fold change; transcript isoform NM_001085377, Affymetrix Human Exon 1.0 ST Array probe set ID 2871377) relative to untreated samples (P = .05), although probe sets also annotated to a second transcript isoform for the gene (NM_002387) and showing concordant direction of effect did not attain nominal significance. These findings from 2 additional independent microarray data sets (Gene Expression Omnibus database under accession number GSE5681 for human diffuse large cell lymphoma cell line and GSE40442 for AML samples) are consistent with the results of our experiments in LCLs showing induction of MCC.
Discussion
We performed a meta-analysis of the results of GWA studies for cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity in HapMap panels composed of 4 different populations (European, Asian, African American, African) that included a total of 523 LCLs. The top 37 SNPs (P < 10−5) were also evaluated for cytarabine-induced apoptosis in LCLs and in a clinical cohort of AML patients. A total of 14 of the 37 cytotoxicity SNPs were associated with apoptosis as measured by caspase 3/7 activation in the LCL model; of these, 12 are in LD within the introns of MCC. These same MCC variants were also significant in in vitro leukemic blasts (IC50) with consistent directionality such that the allele most sensitive to cytarabine in the LCL model was also the allele associated with the greater sensitivity in patient samples. Although the role of MCC in cytarabine sensitivity in AML is not understood, we found that MCC expression was variably induced following cytarabine treatment in LCLs of CEU and YRI ancestry, with fold increases ranging from 1.3 to 26.6. In addition, an intergenic SNP (rs2897047) near IRX2 and associated with cellular sensitivity to cytarabine in LCLs was associated with day 22 MRD and RFS in AML patients. The rare alleles of 5 SNPs were associated with cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity and a greater probability of TRM. Identifying patients upfront who are highly sensitive to cytarabine may have clinical utility and improve outcomes. In total, 18 SNPs were found to be associated with a clinical outcome in AML patients, which is significantly more than expected by chance.
Previously, we demonstrated that the cumulative incidence of relapse was significantly higher among those with high levels of MRD compared with patients with low levels of MRD (P < .0001).2 In this study, we have identified that carriers of the TT allele of rs2897047 (near IRX2) have a greater incidence of relapse and more disease burden at day 22 as determined by MRD positivity, consistent with our findings in LCLs that cells with TT genotype were more resistant to cytarabine. The SNP rs2897047 is in LD with rs6872448 (r2 = 0.87 in CEU) which is in a DNase-hypersensitive site and likely to be a regulatory SNP for IRX2 based on ENCODE data in GM12891 and HeLaS3 cells.32 Notably, 3 genes highly predictive of outcome in a recent Children’s Oncology Group study33 included IRX2. IRX2 expression was correlated with worse outcome in acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients.33
Furthermore, of the 5 SNPs associated with cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity in LCLs and with TRM in AML patients, 3 SNPs in high LD (r2 > 0.80)—namely, rs9883101, rs6550826, and rs1533140—flank the nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group D, member 2 (NR1D2) gene, which, in AML, shows significant (nominal P = .018) evidence of nonsilent mutations being elevated, on the basis of The Cancer Genome Atlas data.34 Our preliminary analyses of data involving cytarabine treatment of AML cells show that cytarabine reduces the exon-level (P = .015; transcript isoform NM_005126, Affymetrix Human Exon 1.0 ST Array probe set ID 2614151) expression of NR1D2 in AML cells relative to untreated ones.31 Furthermore, this region has been found to harbor a cis-eQTL, rs1567581, for NR1D2 in human monocytes (JK Pritchard’s eQTL resource)35 that is in complete LD (D′ = 1; r2 = 0.132) with rs6550826 and has nominal association with cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity in LCLs (P = .002) and concordant direction of effect in all population panels examined here. The impact of this locus on response to cytarabine thus merits further investigation.
Our data related to the MCC SNPs demonstrate that (1) Genetic variants within MCC are associated with cytarabine-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in LCLs. (2) MCC variants are also associated with in vitro cytarabine sensitivity of leukemic blasts from AML patients. (3) Several SNPs within MCC (rs7729269, rs6594713, rs13181534, rs6870401, rs6887482, rs10061462, rs6594714, and rs13174075) are potential eQTLs for EDA2R, a gene shown to be a direct p53 target36 and involved in p53-mediated apoptosis.37 EDA2R (also known as XEDAR) is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily that interacts with tumor necrosis factor receptor–associated factors and activates the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling, and consequently promotes cell proliferation. (4) Upon treatment of LCLs with cytarabine, there is an increase in MCC that is variable within the CEU and YRI cell lines.
Because of the clinical importance of this drug, there have been numerous studies to uncover the biological mechanisms of resistance. Evidence suggests that cytarabine activates NF-κB, a nuclear transcription factor, in myeloid cells.38 Activation of NF-κB may be accompanied by the acquisition of cytarabine resistance; the activation is assumed to induce transcription of genes that function in a feedback and block apoptosis.39 Constitutive activation of NF-κB is found in human leukemia stem cells but not in normal hematopoietic stem cells.40 Interestingly, the tumor suppressor gene MCC has been shown to be a transcriptional regulator of the NF-κB pathway in colorectal cells41 and HEK293 cells.42 Knockdown of MCC results in the accumulation of the inhibitor of κBα (IκBα) protein, encoded by NFKBIA, a first-response gene specifically and rapidly regulated by NF-κB pathway activation. Indeed, MCC has been shown to modulate NF-κB pathway signaling indirectly in colorectal cells.41 One feasible explanation for the role of MCC is that greater induction of this gene by cytarabine associates with suppression of NF-κB and ultimately greater sensitivity to cytarabine.
GeneCard queries for the relative expression levels of MCC in a variety of tissues identified MCC in malignant cells of the bone marrow, spleen, and whole blood.43 Of note, we also found that increased cytosine modification at the cytosine guanine dinucleotide cg01272202 was correlated with both lower expression of MCC and reduced cytarabine sensitivity in the CEU (P = .005) and YRI (P = .076) cell lines (W.Z. and M.E.D., unpublished data). Further studies of the contribution of MCC genetic variation and expression to cytarabine sensitivity are warranted.
We evaluated a set of SNPs in known candidate genes24 and identified nominally significant (P < .05) SNPs in CDA, SLC29A1, and NT5C2. For example, SNPs in the 5′-untranslated region of NT5C2 were associated with NT5C2 expression and cytarabine sensitivity in the HapMap cell lines and with NT5C2 messenger RNA expression and cytarabine sensitivity in diagnostic leukemic blasts from pediatric patients with AML.23 The NT5C2 SNP rs4917384 has been shown to be significantly associated with induction 1 response (measured as day 22 MRD) in AML patients.23 In AML patients, higher CDA levels have been associated with disease recurrence and lower CDA levels with longer duration of remission.44 Identifying (nominally) significant SNPs within candidate genes provides some level of confidence in the GWAS results.
It is plausible that some pharmacogenetic effects may be dose specific. However, our study did not have an adequate number of subjects to provide statistically robust results for dose-specific pharmacogenetic effects. Previous trials use different doses of cytarabine and combine cytarabine with different agents. Thus, we chose to perform an arm-stratified statistical analysis to identify pharmacogenetic effects that are not strongly impacted by dose. We believe that these types of pharmacogenetic effects have greater potential to be confirmed in independent cohorts and thus be translated to improve clinical practice. Finally, as previously described by Rubnitz et al,2 the 2 arms differ very little in terms of any of the clinical outcome, including those considered in this study. For example, there were 4 TRMs in each arm (low-dose and high-dose araC).
Recent studies from a number of groups using preclinical cell-based models have taken top GWAS findings identified in LCLs and validated them in prospective clinical trials.23,45-47 The current study further demonstrates the utility of the model system and provides an overall measure of the significance of the findings from its use in predicting response in AML patients treated with cytarabine.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Pharmacogenomics of Anticancer Agents Research Group LCL core for maintaining and distributing LCLs as well as Dr Stephanie Huang for helpful discussions.
This work was supported by grants from: the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, Specialized Center of Research grant (M.E.D.); the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of General Medical Sciences grant U01 GM61393 (M.E.D., N.J.C.); the National Human Genome Research Institute R21HG006367 (W.Z., M.E.D.); Clinical Therapeutics, Training grant 5T32GM007019 (C.M.H.); the Department of Defense, Breast Cancer Research Program grant BC087674 (M.W.); the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute, Cancer Biology Training grants T32CA009594 (H.E.W.) and R01CA132946 (J.K.L.); and the Cancer Research Foundation of the University of Chicago Comprehensive Cancer Center (M.E.D.).
Authorship
Contribution: E.R.G., J.K.L., A.L.S., and M.E.D. designed the research; E.R.G., A.L.S., S.S.W., M.W., I.H., L.G., C.M.H., and W.Z. collected data and analyzed and interpreted preclinical data; E.R.G. and N.J.C. contributed analytical tools; S.P., J.E.R., R.C.R., S.R., D.C., and K.R.C. designed, directed, or collected data for the AML02 clinical trial; J.K.L. and A.K.M. genotyped the clinical samples; E.R.G., S.P., H.E.W., X.C., and H.K.I. performed the statistical analysis; and E.R.G., J.K.L., A.L.S., and M.E.D. wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: M. Eileen Dolan, 900 E 57th St, KCBD Room 7100, The University of Chicago, Chicago, IL 60637; e-mail: edolan@medicine.bsd.uchicago.edu.