Erythroid Kruppel-like factor (EKLF) is a transcription factor of the C2H2 zinc-finger class that is essential for definitive erythropoiesis. We generated immortal erythroid cell lines from EKLF−/− fetal liver progenitor cells that harbor a single copy of the entire human β-globin locus and then reintroduced EKLF as a tamoxifen-inducible, EKLF–mutant estrogen receptor (EKLF-ER™) fusion protein. Addition of tamoxifen resulted in enhanced differentiation and hemoglobinization, coupled with reduced proliferation. Human β-globin gene expression increased significantly, whereas γ-globin transcripts remained elevated at levels close to endogenous mouse α-globin transcript levels. We conclude that EKLF plays a role in regulation of the cell cycle and hemoglobinization in addition to its role in β-globin gene expression. The cell lines we used will facilitate structural and functional analyses of EKLF in these processes and provide useful tools for the elucidation of nonglobin EKLF target genes.
Introduction
The human β-globin locus spans more than 70 kilobases (kb) on chromosome 11 and includes 5 genes that are developmentally expressed according to the order in which they are arranged (5′ ε, Aγ, Gγ, δ, and β 3′).1 The mouse β-globin cluster is similarly organized (5′ εγ, βh0, βh1, βmaj, and βmin 3′). However, mice, unlike humans, have no fetal-stage–specific genes. Instead, the murine genes (βh0 and βh1) that are most similar to the human γ-globin genes (Gγ and Aγ) in sequence and position relative to the locus control region (LCR) are expressed only in embryonic erythrocytes derived from the yolk sac. Although expression of each gene in the β-globin locus is directed by a unique proximal promoter, high-level expression of each gene in vivo depends on the LCR, which is located approximately 6 kb 5′ of the ε gene. The mechanisms of globin gene switching are incompletely understood but are likely to involve a complex interplay between stage-specific transcription factors bound to cis elements in the LCR and others bound to the individual globin gene promoters.
Erythroid Kruppel-like factor (EKLF) is a transcription factor that was identified by subtractive hybridization of DS-19 MEL and J774 monocyte-macrophage cell lines as part of a strategy to identify novel erythroid-specific genes.2 The carboxy (C) terminus of EKLF contains 3 C2H2-type zinc fingers similar to those in the Drosophila gap gene Kruppel, and the amino (N) terminus is rich in proline and acidic residues.2 Modeling studies based on conserved amino acids in the fingers of EKLF and Zif268 and the crystal structure of Zif268 bound to DNA suggest that EKLF binds to the consensus sequence 5′-NCNCNCCCN-3′.3 Sites of this nature are found in the promoters of several erythroid-specific genes, including the adult β-globin gene. Consistent with its binding specificity, EKLF activates β-globin gene reporter constructs containing an intact β-globin CACC box (CCACACCCT) but does not activate those containing a CACC box mutated to sequences present in the β-CACC box of certain patients with β-thalassemia.3 Furthermore, EKLF binds poorly to the γ-globin CACC box and does not activate the γ-globin promoter in transient assays.
Gene targeting of embryonic stem cells to generate EKLF null (EKLF−/−) mice demonstrated that EKLF has an essential role in the regulation of the β-globin gene in vivo.4,5These mice died before embryonic-day 16 (E16) of severe anemia and β-globin deficiency. The α-globin, βh1-globin, GATA-1, EpoR, and PBGD genes all contain critical CACC box elements that conform to the 5′-NCNCNCCCN-3′ consensus in their proximal promoters, but all are expressed normally in the absence of EKLF,5 suggesting that EKLF performs a selective role at the β-globin promoter. Also, EKLF−/− mice with a complete copy of the human β-globin locus had elevated levels of γ-globin messenger RNA (mRNA) in the fetal liver, indicating a role for EKLF in γ-globin silencing in vivo.6,7 Like all targeted gene-disruption experiments that result in a lethal phenotype, the EKLF null phenotype revealed only the first developmental stage at which EKLF has a critical function. There may be other, undetermined roles for EKLF in definitive erythropoiesis, an idea supported by antisense experiments that suggest a role for EKLF in heme synthesis8 and by the failure to rescue EKLF−/− embryos by correcting the globin chain imbalance.9
To enable more complete analysis of the function of EKLF, we used the J2 retrovirus that expresses 2 complimentary oncogenes, v-raf and v-myc,10 to immortalize erythroid cell lines from EKLF−/− murine fetal livers. These cell lines are also homozygous for a single copy of a 150-kb YAC transgene that contains the entire human β-globin locus.6,11 The J2 retrovirus was chosen as the immortalizing agent because previous studies showed that it preferentially transforms erythroid progenitors, which nevertheless retain some ability to differentiate in response to erythropoietin.12 Immortalized erythroid cell lines were then transduced with the murine stem cell virus (MSCV)–internal ribosome entry site (IRES)–green fluorescent protein (GFP) retroviral vector13 containing a fusion between EKLF and the ligand-binding domain (LBD) of the mutant murine estrogen receptor (EKLF-ER™).14
In stably transduced cells, EKLF-ER™ remains dormant in the cytoplasm until tamoxifen is added. Tamoxifen binds to the LBD of ERTM, resulting in translocation of the hybrid protein to the nucleus. Once in the nucleus, EKLF-ER™ can bind to its cognate CACC sites and activate transcription of target genes. Because the LBD of ERTM is specific to tamoxifen, estrogens present in culture medium cannot induce translocation of EKLF-ER™ to the nucleus.14 This situation provides a system in which the transcriptional activity of EKLF can be tightly regulated, thus allowing the role of EKLF in both β-globin gene regulation and other aspects of definitive erythropoiesis to be studied more precisely. Using this system, we found an unexpected role for EKLF in cellular proliferation and hemoglobinization. We also confirmed the existence of a role for EKLF in human β-globin gene expression. The cell lines we employed should prove to be useful tools for analyzing how EKLF performs these different functions.
Methods
Generation of EKLF−/− cell lines carrying the entire β-globin locus
EKLF+/− mice5 were bred with mice that contained a single copy of the human β-globin locus derived from a 150-kb YAC (βYAC).11 Male and female EKLF+/− mice that had 2 alleles of the βYAC transgene were subsequently derived by interbreeding.6 Homozygosity for the βYAC was confirmed by the demonstration that 20 progeny of the chosen breeding pair produced exclusively βYAC+ mice when mated to mice without the βYAC transgene.
EKLF+/−βYAC++ mice were interbred and pregnant females were killed to obtain litters at E14.5 of development. Fetal livers were surgically removed and placed into phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and single-cell suspensions were made by passage through a 23-gauge needle. The EKLF genotype was determined as described previously.5 All embryos from this cross necessarily had 2 alleles of the βYAC transgene.
Immortalization of cell lines by using the J2 retrovirus
Fetal liver cells were plated at a density of 1 × 105 cells/mL on irradiated (3 Gy) ψ2-J2 retroviral producer cells10 15 in the presence of 20% fetal-calf serum (FCS), high-glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium (DMEM), kit ligand (KL; 250 ng/mL), interleukin (IL) 3 (1000 U/mL), and IL-6 (2 ng/mL). Cells were harvested after 48 hours by trypsinization (0.25% trypsin and 1 mM EDTA) of the adherent layer, which contained both hematopoietic cells and irradiated ψ2 producer cells. Producer cells were depleted by adherence to fresh dishes and viable small (hematopoietic) cells were counted by trypan blue (0.4%) exclusion and plated at a density of 2 × 103 cells/mL and 2 × 104 cells/mL in 1% methylcellulose that contained Epo (2 U/mL) as the sole growth factor. Epo and KL were kindly supplied by Amgen (Thousand Oaks, CA); the other growth factors were obtained from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN).
Individual colonies were picked from the methylcellulose at 5 days and plated in 96-well plates in 100 μL 10% FCS/DMEM. Colonies that grew robustly were expanded (1:3) to progressively larger volumes. When 5-mL cultures reached a density of about 5 × 105 cells/mL, aliquots were frozen and cultures were maintained by serial splitting (1:3) every 2 to 3 days. Two EKLF−/−βYAC++cell lines (A2 and B1) were maintained in continuous tissue culture for more than 6 months in high-glucose DMEM (Gibco BRL, Gaithersburg, MD) supplemented with 10% FCS (batch US142490; Gibco BRL) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Gibco BRL). We found that different batches of serum varied in their capacity to maintain the cell lines and highly recommend testing of batches.
Construction of retroviral vectors
The primers AP68 5′-CGGGATCCGTGGACACCAGCCAGCCAT-3′ and AP58 5′-CGGGATCCGAGGTGACGCTTCATGTGCAGA-3′, which each contain a terminal BamHI restriction site (underlined), were used to generate a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) product from pSG5-EKLF.2 The PCR product that contained the entire open reading frame of murine EKLF was digested with BamHI and ligated into the BamHI site of pBabe Puro mycERTM from which c-myc had been excised.14 The presence of an in-frame EKLF-ER™ fusion complementary DNA was confirmed by sequencing across the cloning site. The primers SEEK3 5′-CGGAATTCGTGGACACCAGCCAGCCAT-3′ and SEEK4 5′-CGGAATTCTCAGATCGTGTTGGGGAAGC-3′, which each contain a terminal EcoRI restriction site (underlined), were subsequently used to amplify the entire EKLF-ER™ open reading frame from pBabePuroEKLF-ER™. This PCR product was digested withEcoRI and ligated into the EcoRI site of the retroviral vector MSCV-IRES-GFP13 to generate MSCV-EKLF-ER™-IRES-GFP.
Infection of EKLF−/−cell lines with MSCV-EKLF-ER™
Helper-free amphotropic retroviral stocks were produced essentially as described previously.13,16 Briefly, 10 μg of the plasmid MSCV-EKLF-ER™-IRES-GFP and 10 μg of the amphotropic helper plasmid ppam3, which encodes gap, pol, andenv retroviral genes, were cotransfected into 293T cells.16 After 72 hours, supernatants were snap frozen at −80°C. The transfected 293T cells were trypsinized and subjected to fluorescence-activated cell-sorter scanning (FACS) analysis. Nontransfected 293T cells were used to set the FACS gains and analysis gates. Approximately 60% of 293T cells were green, which correlates with a retroviral titer of about 1 × 106/mL according to our previous experience.13 A formal retroviral titer was not determined.
Hematopoietic cell lines were cocultured in retroviral supernatant (50%), DMEM, 10% FCS, and Polybrene (4 μg/mL) as described previously.16 After 24 hours, the cells were centrifuged (500g) and resuspended in a second aliquot of viral supernatant as described above. After an additional 72 hours, cells were harvested by centrifugation, washed 4 times in 5% FCS/PBS, and subjected to FACS. Nontransduced control A2 and B1 cell lines were used to set the FACS machine gains, compensations, and sorting gates. Cells were sorted according to side scatter, forward scatter, and GFP+ characteristics.
Sorted GFP+ cells were cloned immediately by culture in 35-mm Petri dishes containing 1% methylcellulose (Life Technologies, Rockville, MD) in Iscove modified Dulbecco medium (IMDM), 10% FCS, and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. After clones had been in semisolid culture for 5 to 8 days, a Nikon E800 microscope and GFP-BP filter block were used to check them for GFP expression by observing green fluorescence after exposure to UV light. Individual GFP+ clones were picked from the methylcellulose and expanded in DMEM as described above.
Southern blotting
Genomic DNA was extracted from 40-mL cultures of all cell lines by using a standard method. DNA (20 μg) was digested withBamHI and resolved on a 0.7% Tris-borate-EDTA agarose gel. DNA was transferred to Hybond N+ (Amersham, Little Chalfont, United Kingdom) by alkali blotting, and the membrane was probed with a 250-base-pair BamHI/SacI EKLF fragment from pSG5-EKLF2 by using a standard protocol.
RNAse protection analyses
Total RNA was prepared17 and RNAse protection analyses were performed as described previously.6 Total RNA (2 μg) was hybridized simultaneously with murine α-globin and either human β-globin or human γ-globin riboprobes, which were generated as described previously.18 RNAse-protected mRNAs were resolved on a 6% denaturing polyacrylamide gel, which was subjected to autoradiography.
Western blotting
Cultures of cell lines were harvested and lysed in 200 μL ice-cold lysis buffer (1% Triton X-100, 0.15 M sodium chloride, 0.01 M sodium phosphate (pH 7.2), 10% glycerol, 10 mM sodium pyrophosphate, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 1 μg/mL leupeptin, 20 μg/mL aprotinin, and 2 μg/mL pepstatin). For Western blots, 5 μg of extracts were resolved on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (Amersham). The membranes were probed with a rabbit anti-EKLF polyclonal antibody19 followed by a donkey antirabbit immunoglobulin (Ig)–horseradish peroxidase (HRP; NA934; Amersham). Hybridization was visualized by using the ECL Plus chemiluminescence system (Amersham). The Western blots were stripped by incubating in stripping buffer (100 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 2% SDS, and 6.25 mM Tris HCl, pH 6.7) at 50°C for 30 minutes. They were reprobed with rat anti-GATA-1 IgG (sc-265; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) followed by sheep antirat Ig HRP (Amersham).
Induction of nuclear transportation with 4-hydroxytamoxifen (tamoxifen)
For the induction experiments, 20-mL cell cultures were set up in duplicate for each mutant line and the parent cell lines at a density of 1 × 105 cells/mL. Immediately before an experiment, 100 μL tamoxifen stock (1 mM; Sigma, St Louis, MO) in ethanol or 100% ethanol alone was diluted in 10 mL of culture medium. Then, 200 μL of this was added to one of each of the pairs of cultures to yield a final tamoxifen concentration of 100 nM. During the next 3 days, the number of viable cells in each culture was determined by counting the cells in 0.4% trypan blue with a hemocytometer. Four independent experiments were performed for each cell line. The cell counts in tamoxifen compared with ethanol were considered dependent variables for each experiment. Therefore, to test the null hypothesis that there was no significant difference between the cell counts for cultures grown in ethanol and those grown in tamoxifen, a pairedt test was performed.
Immunofluorescence
Cells (1 × 105) were cytocentrifuged at 500g on glass slides and fixed in methanol and acetone (1:1). To detect γ-globin, slides were incubated with an FITC-conjugated antibody raised against hemoglobin F as described previously.6 To detect EKLF protein, slides were incubated in rabbit polyclonal anti-EKLF (1:500) followed by antirabbit-biotin (1:1000; Amersham) and streptavidin-Cy3 (1:1000; Amersham). Finally, specimens were stained with 0.01% 4′6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) HCl in PBS for 10 minutes to identify all cell nuclei in the field. Fluorescence was detected with a Nikon E-800 microscope. Photographs of the same field were made after passage of emitted light through blue (UV-2B) and red (B-1E) filter blocks. Images were scanned into Photoshop software (Adobe, San Jose, CA). Images from control and tamoxifen-treated samples were treated identically.
Results
Establishment of EKLF−/− erythroid cell lines
To design a biologic assay for EKLF function, we wanted to establish EKLF null erythroid cell lines that also contained the complete human β-globin locus. Nonimmortalized cells of this phenotype existed in the fetal livers of a cross between EKLF+/− and βYAC transgenic mice.6 Thus, we decided to use an immortalization strategy that was reported to preferentially transform erythroid fetal liver progenitors that nevertheless retain some ability to differentiate in response to erythropoietin.12
The J2 retrovirus has 2 complimentary oncogenes, a hybrid v-raf-mil serine threonine kinase, and v-myc.10 Fetal liver cells from EKLF−/−βYAC++ and EKLF+/−βYAC++ E14.5 embryos were cocultured for 3 days with the irradiated retroviral producer cell line ψ2-J2. Nonadherent cells were harvested and replated at a density of 1 × 105 cells/mL in methylcellulose cultures containing 10% FCS/IMDM and Epo (2 U/mL) as the only hematopoietic growth factor. After 4 to 5 days, 3 types of colonies were evident: small red colonies with the typical appearance of colony-forming units–erythroid (CFU-e) (Figure 1A) and 2 types of larger colonies. Most of the large colonies had a central area of redness consistent with some degree of hemoglobinization (Figure 1A). The others were white and had the appearance of macrophage colonies (data not shown). Although the erythroid colonies from EKLF−/−embryos were not as well hemoglobinized as colonies derived from EKLF+/− litter mates, their erythroid-colony morphologic characteristics were still evident. All the small red colonies disintegrated within a few days, whereas most of the larger hemoglobinized colonies continued to grow. These were assumed to represent the clonal progeny of a cell transformed by the J2 retrovirus.
Characterization of immortalized EKLF−/−cell lines.
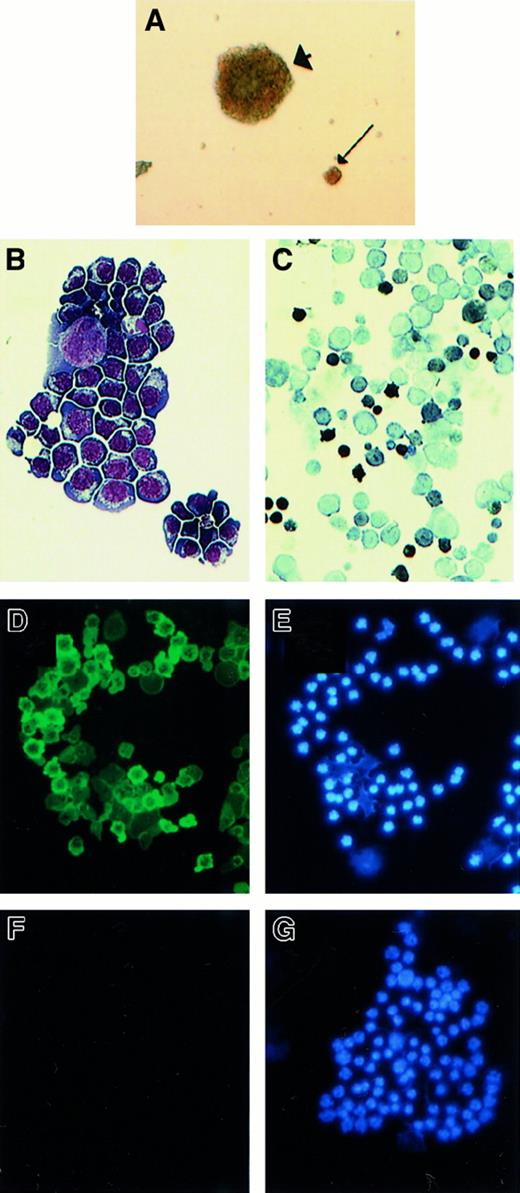
(A) Appearance of transduced EKLF−/− colonies in methylcellulose after 5 days of culture in Epo (2 U/mL). Typical colony-forming unit–erythroid and a large erythroid colony are indicated by arrow and arrowhead, respectively (magnification × 40). (B-E) Cytocentrifuge specimens of the EKLF−/− cell line B1. (B) May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain showing erythroblast morphologic features. (C) Stain for hemoglobin usingo-dianisidine and Harris hematoxylin as counterstain. (D) Expression of human γ-globin by direct immunofluorescence with an FITC-conjugated antibody raised against hemoglobin F. (E) The same field as in panel D but photographed after UV excitation to demonstrate blue nuclear fluorescence (DAPI). (F,G) Cytocentrifuge specimens of a negative control cell line, J2E, which contains no human DNA sequences and shows no detectable γ-globin. The slide was treated as described for panels C and 1D.
Characterization of immortalized EKLF−/−cell lines.
(A) Appearance of transduced EKLF−/− colonies in methylcellulose after 5 days of culture in Epo (2 U/mL). Typical colony-forming unit–erythroid and a large erythroid colony are indicated by arrow and arrowhead, respectively (magnification × 40). (B-E) Cytocentrifuge specimens of the EKLF−/− cell line B1. (B) May-Grünwald-Giemsa stain showing erythroblast morphologic features. (C) Stain for hemoglobin usingo-dianisidine and Harris hematoxylin as counterstain. (D) Expression of human γ-globin by direct immunofluorescence with an FITC-conjugated antibody raised against hemoglobin F. (E) The same field as in panel D but photographed after UV excitation to demonstrate blue nuclear fluorescence (DAPI). (F,G) Cytocentrifuge specimens of a negative control cell line, J2E, which contains no human DNA sequences and shows no detectable γ-globin. The slide was treated as described for panels C and 1D.
Ninety-six consecutive colonies of this phenotype were picked from cultures derived from both EKLF−/− and EKLF+/− embryos, and these were expanded in 100 μL medium in 96-well plates. All wells were examined daily and expanded (1:3) when the medium began to become acidic. Cells from each clone were expanded further (1:3) according to the same criteria. There was a striking difference between the frequency of EKLF−/− and of EKLF+/− clones that could be expanded (Table1). Many EKLF−/− clones continued to grow robustly and 15 of 96 reached 2.5 × 106 cells. These were all subsequently maintained for more than 2 months. Two selected clones from separate primary infections (named A2 and B1) were maintained in continuous culture for more than 6 months. On the other hand, only one EKLF+/−clone reached 2.5 × 106 cells, and it could not be maintained.
Expansion of clones from fetal-liver cells infected with the J2 retrovirus, according to genotype
| Culture . | Genotype . | |
|---|---|---|
| EKLF−/− . | EKLF+/− . | |
| 96-well | 35/96 | 14/96 |
| 24-well | 25/96 | 5/96 |
| 6-well | 17/96 | 1/96* |
| Frozen cell lines† | 15/96‡ | 1/96* |
| Culture . | Genotype . | |
|---|---|---|
| EKLF−/− . | EKLF+/− . | |
| 96-well | 35/96 | 14/96 |
| 24-well | 25/96 | 5/96 |
| 6-well | 17/96 | 1/96* |
| Frozen cell lines† | 15/96‡ | 1/96* |
Values are the numbers of clones that expanded in a total of 96.
This single clone from EKLF+/− fetal liver was maintained in continuous culture for 6 weeks, during which it was always composed of a mixture of adherent macrophages and nonadherent cells.
Cells were frozen after they reached a density of 5 × 105 cells/mL in 5 mL medium.
All these clones from EKLF−/− fetal liver had erythroid morphologic features.
Phenotype of EKLF−/− lines
All the EKLF−/− clones had erythroid morphologic features on May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining of cytocentrifuge preparations (Figure 1B). This finding was confirmed by positive staining for hemoglobin with o-dianisidine (Figure 1C). EKLF−/− erythroid cell lines expressed large amounts of human γ-globin as detected by direct immunofluorescence (Figure 1D), whereas a control cell line, J2E,12 did not (Figure 1F). The single EKLF+/− cell line displayed macrophage morphologic characteristics on May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining (not shown). This line became exclusively adherent after 6 weeks in culture and could not be expanded further or rescued from frozen stocks. Thus, we found that the absence of EKLF results in an enhanced ability of the transforming genes raf-mil and v-myc to immortalize erythroid progenitor cells. The J2 virus is capable of immortalizing wild-type fetal liver cells, but it is very inefficient unless additional mutations, such as loss of p53, are present.15 Our results suggest that the absence of EKLF, like the absence of p53, enhances erythroid cell immortalization by v-myc and v-raf-mil.
Western blot analysis confirmed that the EKLF null cell lines B1 and A2 did not express EKLF but did express the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1. Also, electromobility gel-shift experiments using nuclear extracts from these lines and the βmaj CACC box probe5 failed to detect EKLF bound to DNA (data not shown). In conclusion, the J2 retrovirus enabled the efficient generation of EKLF−/− erythroid cell lines.
Reintroduction of EKLF
To establish an in vivo assay for EKLF, we attempted to derive stable subclones of A2 and B1 by using an expression vector, pEF1α-EKLF. The EF1α expression vector was previously used successfully to express transcription factors in erythroid cell lines.20 However, with this expression vector, we were never able to derive stable sublines of A2 or B1 that expressed EKLF, and we think that transduced cells underwent terminal differentiation during selection for stable expression. Therefore, we employed an efficient inducible expression system. We expressed EKLF as a fusion protein with the LBD of the tamoxifen-inducible ERTM.14 Expression was driven by the retroviral promoter/enhancer in MSCV, which is efficient in hematopoietic cells.21 Lastly, we chose to express GFP from the same bicistronic mRNA as EKLF-ER™ by using the encephalomyocarditis virus IRES to enable positive selection of expressing cells.13
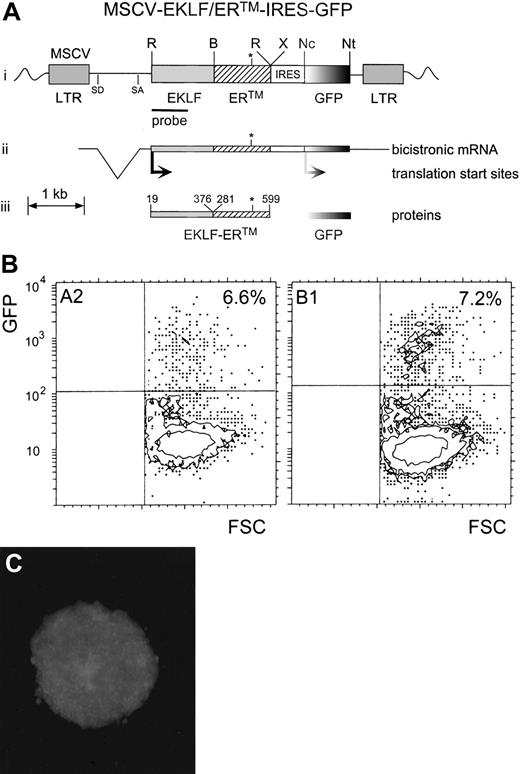
The retroviral vector, MSCV-EKLF-ER™-IRES-GFP, was derived as described above (Figure 2A). Amphotropic infectious retroviral stocks were prepared, and A2 and B1 parent cell lines were infected. After 72 hours in culture, GFP+retrovirally transduced cells were sorted by FACS. Retroviral transduction was moderately efficient, with about 7% of cells showing green fluorescence (Figure 2B). Sorted GFP+ cells were immediately cloned in methylcellulose. Colonies were checked for green fluorescence after exposure to UV light (Figure 2C) and picked for expansion and analysis. Five subclones from the parental A2 line and 7 subclones (from 2 independent experiments) from the parental B1 cell line were expanded for further analysis.
Reintroduction of a conditionally active EKLF protein into EKLF−/− cell lines.
(A) Map of the retroviral vector, MSCV-EKLF-ER™-IRES-GFP. The proviral version of the retroviral vector is indicated with relevant restriction sites (i), as well as splice donor (SD) and splice acceptor (SA) sites for generation of the subgenomic bicistronic RNA (ii). EKLF-ER™ and GFP are independently translated (iii) from a bicistronic mRNA by virtue of the IRES. R indicates EcoR1; B, BamH1; X, Xba1; Nc, Nco1; Nt, Not1; LTR, long-terminal repeat; and the bar, the position of the EKLF probe used for Southern blotting. The asterisk indicates the position of the G525R amino acid substitution in the LBD of ERTM that renders it refractory to estrogen but sensitive to tamoxifen. (B) Dot plots from flow cytometric analysis of GFP expression in B1 and A2 cells after infection with MSCV-EKLF-ERTM-IRES-GFP. Shown are dot plots of forward scatter (FSC) compared with the intensity of GFP. Nontransduced control cells were used to determine the GFP and FSC analysis quadrants shown. In each case, the percentage of cells expressing GFP is indicated in the top right corner. (C) Green fluorescence of a colony of transduced B1 cells after sorting and cloning of GFP+ cells.
Reintroduction of a conditionally active EKLF protein into EKLF−/− cell lines.
(A) Map of the retroviral vector, MSCV-EKLF-ER™-IRES-GFP. The proviral version of the retroviral vector is indicated with relevant restriction sites (i), as well as splice donor (SD) and splice acceptor (SA) sites for generation of the subgenomic bicistronic RNA (ii). EKLF-ER™ and GFP are independently translated (iii) from a bicistronic mRNA by virtue of the IRES. R indicates EcoR1; B, BamH1; X, Xba1; Nc, Nco1; Nt, Not1; LTR, long-terminal repeat; and the bar, the position of the EKLF probe used for Southern blotting. The asterisk indicates the position of the G525R amino acid substitution in the LBD of ERTM that renders it refractory to estrogen but sensitive to tamoxifen. (B) Dot plots from flow cytometric analysis of GFP expression in B1 and A2 cells after infection with MSCV-EKLF-ERTM-IRES-GFP. Shown are dot plots of forward scatter (FSC) compared with the intensity of GFP. Nontransduced control cells were used to determine the GFP and FSC analysis quadrants shown. In each case, the percentage of cells expressing GFP is indicated in the top right corner. (C) Green fluorescence of a colony of transduced B1 cells after sorting and cloning of GFP+ cells.
To check for clonal independence, Southern blotting was performed on genomic DNA (Figure 3A). An 8.8-kb band present in all lanes represents the endogenous targeted EKLF gene locus. All the transduced A2 subclones contained integrated EKLF-ERTM and all had independent sites of proviral integration, confirming their clonal independence. Western blot analysis demonstrated that all the subclones derived from the parent cell lines A2 and B1 (except A2.2) expressed EKLF, although the levels of expression varied in comparison with the levels of GATA-1 expression (Figure 3B and 3C). Clone A2.2 showed no expression of EKLF even though Southern blotting demonstrated the presence of the EKLF-ER™ transgene. This served as a useful negative control cell line.
Characterization of EKLF-ER™–transduced cell lines.
(A-C) Analysis of clonality and expression in GFP+cell lines. (A) Southern blot of genomic DNA from the parent EKLF−/− line A2 and GFP+ subclones (named A2.1 through 6). The probe used is described in the legend for Figure2A. The endogenous 8.8-kb EKLF BamHI fragment (situated 5′ of the region deleted in the targeting construct) is indicated. Each cell line has a least one band of alternative size corresponding to a unique site of proviral integration, indicating independent clonality in each case. (B,C) Western blots for EKLF in whole-cell lysates made from sublines derived from the parent lines B1 (B) and A2 (C). The blots were probed with an antibody specific for EKLF (top) or, after stripping, for GATA-1 (bottom). Mock and EKLF represent extracts from nontransfected 293T cells and 293T cells transfected with an expression vector designed to express a glutathione-S-transferase–EKLF fusion protein, respectively. Migration of molecular-weight makers is indicated on the left side. The position of EKLF-ER™ and GATA-1 are indicated. (D-G) Nuclear translocation of EKLF on stimulation with 4-hydroxytamoxifen. Immunofluorescence staining of B1.4 cells for EKLF (Cy3 [red]; E,G) and DAPI (blue; D, F) after 72 hours of treatment with 100 nM 4-hydroxytamoxifen (F,G) or ethanol as a vehicle control (D,E). The overlaid line in panel D shows the boundary of the nucleus of a single large cell. The outer circle in panel E shows the cytoplasmic boundary of the same cell after excitation of Cy3 (EKLF). Most detectable EKLF protein shifted from the cytoplasm (area between the 2 circles in panel E) to the nucleus (G) after 72 hours in tamoxifen.
Characterization of EKLF-ER™–transduced cell lines.
(A-C) Analysis of clonality and expression in GFP+cell lines. (A) Southern blot of genomic DNA from the parent EKLF−/− line A2 and GFP+ subclones (named A2.1 through 6). The probe used is described in the legend for Figure2A. The endogenous 8.8-kb EKLF BamHI fragment (situated 5′ of the region deleted in the targeting construct) is indicated. Each cell line has a least one band of alternative size corresponding to a unique site of proviral integration, indicating independent clonality in each case. (B,C) Western blots for EKLF in whole-cell lysates made from sublines derived from the parent lines B1 (B) and A2 (C). The blots were probed with an antibody specific for EKLF (top) or, after stripping, for GATA-1 (bottom). Mock and EKLF represent extracts from nontransfected 293T cells and 293T cells transfected with an expression vector designed to express a glutathione-S-transferase–EKLF fusion protein, respectively. Migration of molecular-weight makers is indicated on the left side. The position of EKLF-ER™ and GATA-1 are indicated. (D-G) Nuclear translocation of EKLF on stimulation with 4-hydroxytamoxifen. Immunofluorescence staining of B1.4 cells for EKLF (Cy3 [red]; E,G) and DAPI (blue; D, F) after 72 hours of treatment with 100 nM 4-hydroxytamoxifen (F,G) or ethanol as a vehicle control (D,E). The overlaid line in panel D shows the boundary of the nucleus of a single large cell. The outer circle in panel E shows the cytoplasmic boundary of the same cell after excitation of Cy3 (EKLF). Most detectable EKLF protein shifted from the cytoplasm (area between the 2 circles in panel E) to the nucleus (G) after 72 hours in tamoxifen.
Tamoxifen-inducible nuclear expression
Nuclear translocation of the hybrid EKLF-ER™ protein was achieved by adding 100 nM tamoxifen. To check that nuclear translocation was successful, about 1 × 105 cells were cytocentrifuged after 3 days of culture and fixed in methanol and acetate (1:1). The fixed cells were incubated with a rabbit anti-EKLF polyclonal antibody followed by antirabbit streptavidin-Cy3. The cells were costained with DAPI to identify all cell nuclei in the field. The blue (DAPI) and red (EKLF) images of the same cell field were photographed independently. Addition of tamoxifen resulted in efficient translocation of EKLF-ER™ protein to the nucleus of B1.4 cells (Figure 3F and 3G), whereas addition of ethanol vehicle did not (Figure 3D and 3E). Thus, until tamoxifen was added, EKLF was efficiently held as an inactive ERTM fusion protein in the cytoplasm of these cell lines grown in serum-containing medium.
Reduced proliferation and enhanced differentiation
Cell cultures of transduced A2 and B1 sublines were cultured for 3 days in either tamoxifen (100 nM) or ethanol (0.01%) as a vehicle control. Viable cells were counted daily for 3 days. The A2.2 subline and the A2 parent line did not show any significant change in growth between the ethanol-treated cultures and the tamoxifen-treated cultures, and they did not express EKLF. Conversely, the A2.1 and A2.3 cell lines showed a significant reduction in growth on addition of tamoxifen (P < .1 and P < .05, respectively), whereas the A2.4 and A2.6 cell lines demonstrated a small but nonsignificant reduction in cell growth on addition of tamoxifen (Figure 4B). Thus, there was a correlation between EKLF expression levels and a block in cell proliferation in these independent sublines.
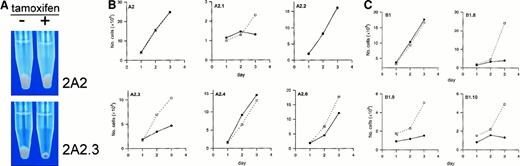
EKLF induces hemoglobinization and slowing of growth when activated by 4-hydroxytamoxifen.
(A) Photograph of cell pellets of A2 and A2.3 that were seeded at a density of 105 cells/mL and cultured for 72 hours in ethanol (minus sign) or 4-hydroxytamoxifen (plus sign). Cells were washed in PBS, transferred to Eppendorf tubes, repelleted, and photographed. (B,C) Growth curves for cells treated for 3 days in either vehicle (open boxes) or 100 nM 4-hydroxytamoxifen (solid circles). Counts of viable cells were done daily in a hemocytometer by using trypan blue exclusion and plotted as the mean cell numbers from 4 independent experiments. Tamoxifen induced a significant slowing of growth in the 2 subclones of A2 that expressed substantial amounts of EKLF (A2.3 and A2.1) but had no significant effect on the parent line A2 or the derived line A2.4 that expressed barely detectable amounts of EKLF-ER™ (B). There appeared to be some slowing of growth of the A2.6 cell line with tamoxifen, but results were not significant. All 3 subclones of B1 (B1.8, B1.9, and B1.10) showed a marked slowing of growth on activation of EKLF (C). ■ indicates EtOH; ●, tamoxifen.
EKLF induces hemoglobinization and slowing of growth when activated by 4-hydroxytamoxifen.
(A) Photograph of cell pellets of A2 and A2.3 that were seeded at a density of 105 cells/mL and cultured for 72 hours in ethanol (minus sign) or 4-hydroxytamoxifen (plus sign). Cells were washed in PBS, transferred to Eppendorf tubes, repelleted, and photographed. (B,C) Growth curves for cells treated for 3 days in either vehicle (open boxes) or 100 nM 4-hydroxytamoxifen (solid circles). Counts of viable cells were done daily in a hemocytometer by using trypan blue exclusion and plotted as the mean cell numbers from 4 independent experiments. Tamoxifen induced a significant slowing of growth in the 2 subclones of A2 that expressed substantial amounts of EKLF (A2.3 and A2.1) but had no significant effect on the parent line A2 or the derived line A2.4 that expressed barely detectable amounts of EKLF-ER™ (B). There appeared to be some slowing of growth of the A2.6 cell line with tamoxifen, but results were not significant. All 3 subclones of B1 (B1.8, B1.9, and B1.10) showed a marked slowing of growth on activation of EKLF (C). ■ indicates EtOH; ●, tamoxifen.
After 3 days in tamoxifen, the cell pellets of lines A2.1, A2.3, A2.4, and A2.6 all had a red appearance consistent with an increase in hemoglobin content (Figure 4A). The pellet sizes were also much smaller, particularly in the A2.1 and A2.3 sublines that expressed higher levels of EKLF. On the other hand, lines A2.2 and A2 were pale after tamoxifen treatment, like the ethanol-treated cultures. All the B1 sublines tested (B1.8, B1.9, and B1.10) had high levels of EKLF expression and behaved like the A2.3 line. They all displayed a significant slowing in cell growth (Figure 4C) on activation of EKLF and the cell pellets were markedly red compared with those in the ethanol-treated control cultures (data not shown).
Role of EKLF in globin gene expression
Previous studies suggested that EKLF may play a role in the γ-globin to β-globin gene switch.6,7 22 Therefore, we wanted to determine whether activation of EKLF in the null cell lines resulted in a change in human globin gene expression. The results of RNAse protection assays for human β, human γ, and murine α-globin stable mRNA transcripts are shown in Figure5A and 5B. As expected, no change in β-globin expression was observed in the parent EKLF null cell lines, A2 and B1, after tamoxifen treatment. However, a marked increase in human β-globin expression was detected in the A2.3, A2.4, and B1.2-B1.6 cell lines after tamoxifen was added. There was no significant increase in β-globin in 2 sublines of A2 (A2.1 and A2.6) that expressed low levels of EKLF. Again, there was a consistent correlation between EKLF expression and tamoxifen-induced β-globin gene expression in the independent sublines. The levels of γ-globin transcripts in all the sublines of A2 and B1 remained high after addition of tamoxifen and were similar to those of the endogenous mouse α-globin transcripts in each line. This most likely reflects the remarkable stability of γ-globin mRNA rather than indicating a lack of a link between human β-globin gene activation and γ-globin gene silencing in these cell lines. Thus, additional experiments examining transient γ-globin transcripts must be done to confirm whether these lines will be valuable tools for a structural and functional analysis of the role of EKLF in human hemoglobin switching.
EKLF-ER™ induced activation of the human β-globin gene.
RNAse protection assays of total RNA from A2 (A) and B1 (B) cell lines treated for 72 hours in ethanol (minus sign) or 4-hydroxytamoxifen (plus sign). The human β-globin gene was induced in most cell lines in response to 4-hydroxytamoxifen, whereas the level of human γ-globin expression remained elevated at levels similar to that of the endogenous mouse α-globin gene. The parent cell lines A2 and B1 did not express any β-globin in response to 4-hydroxytamoxifen treatment.
EKLF-ER™ induced activation of the human β-globin gene.
RNAse protection assays of total RNA from A2 (A) and B1 (B) cell lines treated for 72 hours in ethanol (minus sign) or 4-hydroxytamoxifen (plus sign). The human β-globin gene was induced in most cell lines in response to 4-hydroxytamoxifen, whereas the level of human γ-globin expression remained elevated at levels similar to that of the endogenous mouse α-globin gene. The parent cell lines A2 and B1 did not express any β-globin in response to 4-hydroxytamoxifen treatment.
Discussion
The principal aim of these experiments was to develop a cell-based assay for the role of EKLF in erythropoiesis and globin gene regulation. To achieve this, we used the J2 retrovirus, which encodes the complimentary oncogenes v-myc and v-mil-raf, to immortalize fetal liver progenitor cells from EKLF−/−embryos that also had 2 copies of a βYAC transgene.10 The derived clonal cell lines had typical erythroid morphologic features and were benzidine positive. EKLF was reintroduced into 2 independent EKLF−/− lines (B1 and A2) as a fusion gene linked to the LBD of ERTMby using the retroviral vector MSCV-IRES-GFP.13 The inclusion of the IRES allowed easy identification and sorting of GFP+ cells (using FACS analysis) that should also express EKLF-ER™.
Studies of several transcription factors and some protein kinases have been aided by linking them to the LBD of steroid hormone receptors. Most commonly, the LBD of the human estrogen receptor (hER) is used. The resultant fusion proteins are inactive in the absence of their specific ligand because they are excluded from the nucleus by a variety of cytoplasmic inhibitor proteins, including heat shock protein (Hsp) 70 and Hsp90. Addition of ligand to the culture medium results in dissociation of the fusion protein from inhibitory complexes and translocation to the nucleus. Although hER has been used successfully for this purpose, the system has had considerable technical complications. The most troublesome problem is activation of hER by estrogens in FCS. To overcome this problem, Littlewood et al14 used the LBD of ERTM, which is unable to bind estrogen but is able to bind the synthetic steroid, 4-hydroxytamoxifen. They fused the LBD of ERTM to the C-terminal end of c-Myc and showed thatMyc-induced proliferation and apoptosis in fibroblasts depended entirely on the presence of 4-hydroxytamoxifen and that addition of estrogen to the culture medium had no effect.14 Similarly, we successfully fused the LBD of ERTM to the C-terminal end of EKLF and demonstrated that addition of 4-hydroxytamoxifen to the culture medium resulted in translocation of the hybrid EKLF-ER™ protein to the nucleus. There was minimal, if any, activation of the sensitive EKLF target gene, human β-globin, in the presence of 10% FCS alone. Thus, use of ERTM, along with the MSCV-IRES-GFP vector, enabled us to create a system in which the activity of the transcription factor EKLF can be tightly regulated in an erythroid cellular environment.
EKLF is a negative regulator of cellular proliferation
Our ability to control the transcriptional activity of EKLF in this study revealed an unexpected role for it in cellular proliferation. The greatly enhanced frequency of derivation of immortal clones from EKLF−/− compared with EKLF+/−fetal liver cells using the J2 retrovirus suggested that EKLF discourages immortalization. In other words, the absence of EKLF resulted in a markedly increased rate of transformation by the cooperating oncogenes, v-mil-raf and v-myc. This result is similar to that of Metz et al,15 who showed that absence of p53 resulted in an increased frequency of immortalization of erythroid cells by v-mil-raf and v-myc. Thus, like p53, EKLF could be considered a suppressor of immortalization. Superficially, these results appear to contradict those of Spadaccini et al,8 who inactivated EKLF in themyc-raf–transformed erythroid cell line J2 by using an antisense oligonucleotide approach. Although these authors showed effects on globin gene expression and hemoglobinization, they found no effects on proliferation. In view of our results and those of Metz et al15 showing that wild-type fetal liver progenitors are difficult to immortalize with the J2 virus,15 we suggest that the J2E cell line probably underwent additional undetermined mutational events during its initial derivation. These may preclude it from slowing in growth rate in response to a reduction (albeit incomplete) in EKLF levels. Our results that begin from an EKLF null background offer a cleaner system in which to address the role of EKLF in proliferation.
The activation of EKLF-ER™ with tamoxifen resulted in a slowing of proliferation consistent with the role of EKLF-ER™ as an antiproliferation factor (Figure 4). Other C2H2zinc-finger proteins, such as the Wilms tumor 1 (WT-1) protein, have an antiproliferative effect. WT-1 has a proline-rich N-terminus and 4 C-terminus zinc fingers and it binds to GC-rich promoter sites similar to those bound by EKLF.23 WT-1 is lost in many cases of inherited Wilms tumor,24 and enforced reexpression of WT-1 in a cell line derived from a Wilms tumor (RM1) resulted in cessation of proliferation.25 If EKLF is also a tumor suppressor, then erythroleukemia might be expected to occur in mice lacking EKLF. Unfortunately, EKLF−/− embryos die of severe anemia before birth. Thus, EKLF−/− erythroid cells may not have the opportunity to acquire additional genetic mutations before the embryo dies. Interestingly, the short arm of chromosome 19 (the site of human EKLF) is frequently lost in cases of human erythroleukemia,26 whereas it is rarely lost in other subtypes of acute leukemia. This is consistent with the idea that EKLF has antiproliferative and tumor suppressor roles in human erythroblasts.
EKLF induces terminal differentiation and hemoglobinization
Reintroduction of EKLF into EKLF−/− erythroid cell lines resulted in marked hemoglobinization, as demonstrated by the finding of small red cell pellets (Figure 4A). Thus, EKLF may coordinate expression of other genes involved in terminal differentiation and hemoglobinization of erythroblasts. We previously showed that correction of the globin chain imbalance in EKLF−/− fetal liver erythroblasts fails to substantially improve their intrinsic defect,9 thereby suggesting that other EKLF target genes must be important. Also, Spadaccini et al8 introduced an antisense EKLF construct into the erythroid cell line J2E and reported that hemoglobinization was impaired. They showed that expression of 2 rate-limiting enzymes in the heme biosynthetic pathway, aminolevulinic acid synthetase (ALAS) and ferrochelatase, were expressed at reduced levels when EKLF was inhibited. Interestingly, the erythroid-specific promoter of ALAS has an EKLF binding site that is functionally critical.27Future studies with our cell lines could determine the nature of other potential EKLF target genes involved in terminal differentiation and hemoglobinization.
EKLF and globin gene regulation
Activation of EKLF resulted in a dramatic activation of the human β-globin gene in the cell lines we used, confirming the critical role of EKLF in β-globin gene expression. The cell lines also expressed high levels of γ-globin, but the levels of processed γ-globin RNA transcripts did not decrease after activation of EKLF. In view of the suggested role of EKLF as a mediator of competition between the β-globin promoter and γ-globin promoter for the LCR,6,7 these results were initially surprising. They may simply reflect the long half-life of processed γ-globin transcripts. Alternatively, EKLF may not play a direct role in γ-globin gene silencing. Future dynamic studies of the rate of generation of new γ-globin transcripts, using such techniques as “nuclear run-ons” or in situ hybridization with probes specific for prespliced nuclear RNA species28 will resolve this issue.
We appreciate the expert cell-culture advice from Peta Tillbrook and Peter Klinken and the comments from Stuart Orkin.
Supported by an Australian NH & MRC grant (981010), grant PO1 HL53749-03 from the National Institutes of Health, Cancer Center Support CORE Grant P30 CA 21765, the American Lebanese Syrian Associated Charities (ALSAC), and the Assisi Foundation of Memphis. E.C. was supported by an Australian Postgraduate Research Fellowship, and A.P. by a Wellcome Senior Research Fellowship.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Andrew Perkins, Department of Physiology, Monash University, Wellington Road, Vic 3186, Australia.

![Fig. 3. Characterization of EKLF-ER™–transduced cell lines. / (A-C) Analysis of clonality and expression in GFP+cell lines. (A) Southern blot of genomic DNA from the parent EKLF−/− line A2 and GFP+ subclones (named A2.1 through 6). The probe used is described in the legend for Figure2A. The endogenous 8.8-kb EKLF BamHI fragment (situated 5′ of the region deleted in the targeting construct) is indicated. Each cell line has a least one band of alternative size corresponding to a unique site of proviral integration, indicating independent clonality in each case. (B,C) Western blots for EKLF in whole-cell lysates made from sublines derived from the parent lines B1 (B) and A2 (C). The blots were probed with an antibody specific for EKLF (top) or, after stripping, for GATA-1 (bottom). Mock and EKLF represent extracts from nontransfected 293T cells and 293T cells transfected with an expression vector designed to express a glutathione-S-transferase–EKLF fusion protein, respectively. Migration of molecular-weight makers is indicated on the left side. The position of EKLF-ER™ and GATA-1 are indicated. (D-G) Nuclear translocation of EKLF on stimulation with 4-hydroxytamoxifen. Immunofluorescence staining of B1.4 cells for EKLF (Cy3 [red]; E,G) and DAPI (blue; D, F) after 72 hours of treatment with 100 nM 4-hydroxytamoxifen (F,G) or ethanol as a vehicle control (D,E). The overlaid line in panel D shows the boundary of the nucleus of a single large cell. The outer circle in panel E shows the cytoplasmic boundary of the same cell after excitation of Cy3 (EKLF). Most detectable EKLF protein shifted from the cytoplasm (area between the 2 circles in panel E) to the nucleus (G) after 72 hours in tamoxifen.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/97/6/10.1182_blood.v97.6.1861/6/m_h80610805003.jpeg?Expires=1763496843&Signature=rQhlXJXB2nR6nlf94X9KX~INTUEzoxMjeNUV4SdYpy-fYDFS5LNYHeGQNhWr6ZIKc-XPfhjuciIk2H4SkEwFgPh2BJD1s5lZR7Hf37YEfJnHIXPK5jZtZdNTgYbXL00GyGeaiT-SBIz2jlrBwlCZ~s8CJLXEo9~SITyfWu9EgTidhY7FQWwUbv56rIWxcFiLGjzq2Lg8Iov2xAWUekjaP3hyO80n29bSjSdVwRaGQ7OejdWOgNz5CksQXksfWvgKeMz5npBo7yQuaZxU6kVUMFkw9n~w23Gf3rQjt~KzN-uHPL081KLOiZauI-BykBF~GlPMpKihIknzzIax0rUJzg__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal