Abstract
Systemic administration of desmopressin (DDAVP) induces increased plasma levels of tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA), coagulation factor VIII, and von Willebrand factor (vWF). However, the mechanisms behind these responses are not known. We tested the hypothesis that DDAVP acts as a local stimulator of acute endothelial release of t-PA and vWF independently of central pathways. Healthy, young, nonsmoking male volunteers were studied. In a first study (n = 7), DDAVP and placebo were administered as randomized single-blind stepwise intrabrachial artery infusions (0.7, 7.0, and 70 ng/min). In a another subset of subjects (n = 4), a constant-rate DDAVP infusion of 70 ng/min was administered for 20 minutes in the brachial artery of the nondominant arm with the dominant arm as control. To rule out that the observed t-PA release was flow-dependent, 4 additional subjects received stepwise intra-arterial infusions of both DDAVP (7.0, 21, and 70 ng/min) and sodium nitroprusside (SNP; 0.5, 2.5, and 10 μg/min). Brachial venoarterial plasma concentration gradients and forearm plasma flow were used to determine net release/uptake rates of t-PA and vWF. At baseline, the average net release rate of t-PA was 6.7 ng/min across the whole forearm vascular bed, whereas there was no detectable basal release of vWF. Stepwise infusion of DDAVP induced a massive regulated release of t-PA with a peak after 15 minutes on the highest dose-step (ANOVA; P < .0001). The average maximum net release rate was 178 ng/min, and the total amount of t-PA released was, on the average, 3,000 ng. The majority was released in its active form. Constant-rate DDAVP infusion again markedly increased t-PA release in the infusion arm but had no effect whatsoever in the control arm. In contrast, DDAVP did not stimulate a local release of vWF in either study. Central hemodynamics were unchanged during infusions despite a local vasodilatory response with DDAVP. Endothelium-independent flow stimulation by SNP did not elicit any local t-PA release. We conclude that DDAVP induces a massive acute flow-independent release of t-PA, without the simultaneous release of vWF, in the human forearm vascular bed. The lack of a t-PA response in the control arm, as well as the unaltered central hemodynamics with DDAVP, confirms that the observed regulated t-PA release is local and independent of central mechanisms.
DESMOPRESSIN (1-desamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin [DDAVP]) is a synthetic analogue of the human neurohypophyseal hormone vasopressin and a potent V2-receptor agonist.1 It was originally developed as an antidiuretic drug, but was also shown to increase plasma levels of tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA), von Willebrand factor (vWF), and coagulation factor VIII (VIII:C).2-6 Since then, DDAVP has been used to enhance plasma levels of vWF/VIII in disorders such as mild hemophilia A, von Willebrand's disease, and congenital or acquired platelet dysfunction (see Lethagen6) as well as to evaluate “fibrinolytic capacity” in various patient groups.7-9 Despite the fact that DDAVP is widely used, both clinically and for experimental purposes, the mechanisms by which it enhances plasma levels of t-PA and vWF/VIII:C are not known.
Because both t-PA and vWF are synthesized, stored, and secreted by endothelial cells,10-14 it has commonly been assumed that DDAVP induces regulated endothelial release of both proteins by a common mechanism. However, there may be differences behind the rapid DDAVP-induced increases of the plasma concentrations of t-PA and vWF. The large difference in the half-lives of t-PA and vWF in the human circulation (3 to 5 minutes and 6 hours, respectively) renders the two proteins very different kinetic behavior in plasma. For t-PA, there must be a high continuous secretion of t-PA into the blood to maintain its steady-state plasma level, whereas systemic vWF levels may be sustained by a low-rate secretion mechanism. Also, in contrast to vWF, rapid changes in the plasma level of t-PA can be induced by changes in hepatic blood flow.15 Even though recent data indicate that DDAVP induces a true increase in the endothelial secretion of t-PA, because, if anything, DDAVP increases hepatic clearance,16there is clearly a need for simultaneous measurements of the endothelial secretion rates of t-PA and vWF in response to DDAVP in an in vivo setting.
It is of note that DDAVP does not enhance constitutive t-PA secretion in endothelial cells in culture.17 In addition, already in 1978 Cash et al18 observed that infusion of DDAVP into the brachial artery did not result in a measurable change in euglobulin clot lysis time in the outflowing venous blood, whereas infusion of epinephrine did. Therefore, it was suggested that DDAVP does not act directly on the vascular endothelium, but may exert its effect via a central receptor.18,19 Some investigators have proposed the existence of a pituitary-derived plasminogen activator releasing hormone (PARH), stimulated by DDAVP, as responsible for this effect (eg, Cash20). However, it has not been possible to identify a substance with t-PA releasing activity, different from vasopressin itself, in pituitary extracts.21 Furthermore, in patients with defective pituitary function, a normal release of t-PA with DDAVP has been demonstrated.22 23
To clarify the mechanisms behind the DDAVP-induced increases in plasma t-PA and vWF, the aim of the present study was to investigate endothelial release rates in a well-defined regional vascular district. We have recently developed in vivo models in humans for determination of net release rates of t-PA across different vascular beds, such as the forearm, or the coronary or cerebral circulations.24,25Because the forearm at rest only receives about 0.5% of cardiac output, the model is particularly well suited for studies of endothelial cell receptor agonists such as DDAVP, because the substance may be infused via the brachial artery in doses that induce profound local effects without activation of central reflexogenic mechanisms.26 In the present study, we used this perfused-forearm model to test the hypothesis that DDAVP induces an acute local release of t-PA and vWF, without involvement of central pathways.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Subjects
The study was conducted in 11 apparently healthy, nonsmoking, nonobese, normotensive males (22 to 29 years of age) recruited among university students. None of the subjects was on any medication, and none had a history of cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, or hypercholesterolemia.
The nature, purpose, and potential risks of the study were carefully explained to each subject before informed consent was obtained. The protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Göteborg, and the study was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki. All procedures were performed in accordance with the Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) guidelines and Standard Operating Procedures of our laboratory.
Experimental Protocol
Studies were performed after an overnight fast (10 hours) and commenced at 8.30 am. After catheterization and application of recording devices, the subjects rested for 45 minutes in the supine position in the dimly lit and soundproof room.
In a first study, 7 subjects received single-blind intra-arterial stepwise infusions of DDAVP or placebo. The infusions were administered 60 minutes apart in randomized order.
In another subset of subjects (n = 4), the highest dose of DDAVP used in the first study was chosen and administered as a single constant intra-brachial artery infusion in the nondominant arm, with the dominant arm as control.
Experimental Set-Up
An arterial polyethylene catheter (Viggo Products, British Viggo, Swindon, UK) was introduced percutaneously by the Seldinger technique into the brachial artery of the nondominant arm and advanced 10 cm in the proximal direction. Intra-arterial blood pressure was recorded continuously by an electrical transducer (EMT 35; Siemens-Elema, Stockholm, Sweden) and a Mingograph 82 (Siemens-Elema). Mean arterial pressure was obtained by electrical damping of the pressure signal. An indwelling cannula (Venflon; Viggo, Helsingborg, Sweden) was introduced retrogradely into a deep antecubital vein of the same arm for venous blood sampling from the muscle vascular bed. In the constant-rate infusion study, deep antecubital veins of both infusion and contralateral arms were cannulated. Electrocardiogram was continuously monitored on the Mingograph 82. Catheters were flushed with heparinized (5 IU/mL) saline after blood sampling. Venous occlusion plethysmography with a mercury-in-rubber strain-gauge was used to assess forearm blood flow.27 Forearm blood flow (FBF) in milliliters per minute and liters of tissue was calculated from 3 to 5 separate recordings on each point of measurement, using the computer software MAPPC (Elektromedicin AB, Kullavik, Sweden). Forearm volume was measured by water displacement. The coefficient of variation for two FBF measurements by the same observer was 5.6%.
Drugs
Isotonic saline (Kabi Pharmacia, Uppsala, Sweden) was used as placebo and for dilution of DDAVP (Minirin; Ferring, Malmö, Sweden). In the first protocol, the infusion was administered in three sequential dose steps: 0.7 ng/min for 5 minutes, 7.0 ng/mL for 5 minutes, and finally 70 ng/min for 15 minutes. Because of technical problems, the DDAVP infusion at the highest dose was interrupted after 5 minutes in 1 subject. In the second study, DDAVP was infused at a dose of 70 ng/min for 20 minutes. All infusions were administered at a constant rate of 1 mL/min by means of a syringe infusion pump (Injectomat; MTS, Schweinfurt, Germany).
Blood Sampling and Biochemical Assays
Stepwise DDAVP infusion.
All blood samples were obtained from the infusion arm according to the schedule depicted in Fig 1, which can be summarized as follows: preinfusion baseline, simultaneous arterial and venous samples at 8 and 3 minutes before infusion; dose-steps 1 and 2, venous samples after 2 and 4 minutes, arterial sample after 4 minutes; dose-step 3, venous samples after 2, 4, and 15 minutes, arterial samples after 4 and 15 minutes; and postinfusion period, simultaneous arterial and venous samples at 2 and 10 minutes after infusion.
Study design of placebo-controlled stepwise infusion of DDAVP in 7 healthy males. R, randomization. (○) Time points for arterial sampling. Open horizontal bars show where arterial values were interpolated for net release calculations. (•) Time points for venous sampling.
Study design of placebo-controlled stepwise infusion of DDAVP in 7 healthy males. R, randomization. (○) Time points for arterial sampling. Open horizontal bars show where arterial values were interpolated for net release calculations. (•) Time points for venous sampling.
Constant-rate DDAVP infusion.
Arterial sampling was from infusion arm. Venous sampling was from both infusion and contralateral arms: preinfusion baseline, simultaneous arterial and venous samples 5 minutes before infusion; during infusion, simultaneous arterial and venous samples after 10 and 20 minutes; postinfusion period, simultaneous arterial and venous samples 10 minutes after infusion.
The infusion line was always closed during arterial sampling. The number of arterial samples in the first study was therefore restricted to avoid unnecessary interruption of the infusion. Before each sample was obtained, the content of the catheters plus an additional 1 mL of blood were discarded. Thereafter, blood was collected in tubes containing 1/10 vol of 0.13 mol/L sodium citrate and 1/10 vol 0.45 mol/L sodium citrate buffer, pH 4.3 (Stabilyte; Biopool AB, Umeå, Sweden) for determination of vWF and t-PA, respectively. The tubes were kept on ice and plasma was isolated within 40 minutes by centrifugation at 4°C and 2,000g for 20 minutes. Plasma aliquots were immediately frozen and stored at −86°C. Blood handling procedures confided with the recommendations of the Leiden Fibrinolysis Workshop 6.28
For determination of total t-PA (t-PA antigen) the reagent kit TintElize t-PA (catalogue no. 1105; Biopool AB) was used, which detects free and complexed t-PA with equal efficiency.29 The free, active fraction of t-PA (t-PA activity) was determined by a biofunctional immunosorbant assay (BIA; Chromolize catalogue no. 1103; Biopool AB) calibrated against the international standard for t-PA (lot no. 86/670). Active t-PA was expressed in nanograms per milliliter using the specific activity of 0.60 IU/ng (data on file; Biopool AB). vWF antigen was assessed by means of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay principally according to Ingerslev.30 Polyclonal rabbit antihuman vWF antibodies were used for catching, and peroxidase-conjugated rabbit antihuman vWF was used for detecting (Dako, Copenhagen, Denmark). Our inhouse standard, pooled plasma from 10 men and 10 women (20 to 50 years of age), was calibrated against the 3rd International Standard for vWF (code 91/666; National Institute for Biological Standards and Controls, Hertfordshire, UK). All samples from one infusion were assayed on the same microtest plate, and all samples from 1 subject were analyzed in the same assay-run. All samples were determined in duplicate and intra-assay coefficients of variation were on the average 2.9%, 2.7%, and 4.3% for total t-PA, active t-PA, and vWF, respectively. The hematocrit level was determined in duplicate on arterial blood using a microhematocrit centrifuge (Hettich Haematokrit; Hettich Zentrifugen, Tuttlingen, Germany), with a coefficient of variation of 0.4%.
Calculated Net Release of t-PA
Arteriovenous concentration gradients (AV-gradients) of each individual were computed by subtraction of the plasma t-PA level measured in simultaneously collected venous and arterial blood. In the constant-rate infusion study, arterial values from infusion arm were used for computation of AV-gradients in both arms. At time points at which only venous samples were collected, AV-gradients were calculated using an interpolated arterial value (individual mean of measured arterial t-PA at the preceding and following time point). A positive difference (venous minus arterial) indicated a net release and a negative net uptake. Forearm plasma flow (FPF) was calculated from FBF and arterial hematocrit levels corrected for 1% trapped plasma. Individual net release or uptake rates at each time point were calculated from the AV-gradient times plasma flow per time across the forearm.26 The following formulas were used: FPF = FBF × (101 − Hematocrit) /100); Net Release = (CV− CA) × FPF, where CV denotes venous plasma concentration and CA arterial plasma concentration.
Pharmacokinetic Calculations
The local plasma concentration (CL) of DDAVP in the forearm at a given moment was estimated from the given dose (in nanograms) and the plasma volume (in milliliters) flowing through the limb during 1 minute on the actual dose (CL = Infusion Rate/[FPF × Forearm Volume]). The systemic plasma level (CP) of DDAVP at this dose was calculated according to the following formula: CP = (k0/[VD× kel]) × (1 − e−kel×t), where VD is the volume of distribution (200 mL × kg−1), k0 is the dose (in nanograms × kilograms bodyweight−1 × minute−1), kel is 0.01155 min−1 (based on a half-life of 55 minutes), and t is the infusion time.31
Statistical Analysis
Data are, unless otherwise stated, presented as the mean and standard error of the mean (SEM). The probability that the arteriovenous concentration gradients or the calculated net release/uptake indices were different from 0 was evaluated using the Student'st-test. Responses to intraarterial infusions were evaluated by one-way analyses of variance (ANOVA) for repeated measures with subject as random factor. Two-way ANOVA was used to test the hypothesis that responses to active and placebo infusions were different, as well as for comparison of the infusion arm with the contralateral arm. ANOVA of arterial levels of t-PA and hematocrit level were performed using time points at which the arterial levels actually were measured. ANOVA of net release was performed using all time points, thus including calculations based on interpolated arterial values as outlined above. Significance tests were considered significant at P < .05 (two-tailed test).
RESULTS
Stepwise DDAVP Infusion
Hemodynamics are summarized in Fig 2. At the highest dose-step of DDAVP (70 ng/min), a threefold increase in FBF was observed in the experimental arm. On the 7 ng/min DDAVP dose-step, there was only a small and insignificant increase in FBF, and no effect was observed during low-dose infusion. After discontinuation of the DDAVP infusion, FBF decreased slowly and had still not returned to baseline levels 10 minutes after the infusion was terminated. In the subjects who received DDAVP as the first stimulus (n = 3), FBF had returned to baseline levels before start of the placebo infusion (ie, 60 minutes after the end of the DDAVP infusion). No alterations in FBF in the experimental arm were observed during placebo infusion. There were no significant alterations in mean arterial pressure (MAP), heart rate (HR), FBF in the control arm, or hematocrit level (data not shown) in response to either infusion. There were also no adverse reactions.
FBF of both arms, MAP, and HR over time in response to stepwise intrabrachial artery infusions of DDAVP (0.7 to 7 to 70 ng/min for 5 to 5 to 15 minutes; ▪) and placebo (saline; ○) in 7 healthy male subjects. Means and SEM error bars. FBF in the infusion arm increased significantly in response to DDAVP (ANOVA, time × treatment interaction: P < .0001), but there were no effects on FBF in the control arm, MAP, or HR.
FBF of both arms, MAP, and HR over time in response to stepwise intrabrachial artery infusions of DDAVP (0.7 to 7 to 70 ng/min for 5 to 5 to 15 minutes; ▪) and placebo (saline; ○) in 7 healthy male subjects. Means and SEM error bars. FBF in the infusion arm increased significantly in response to DDAVP (ANOVA, time × treatment interaction: P < .0001), but there were no effects on FBF in the control arm, MAP, or HR.
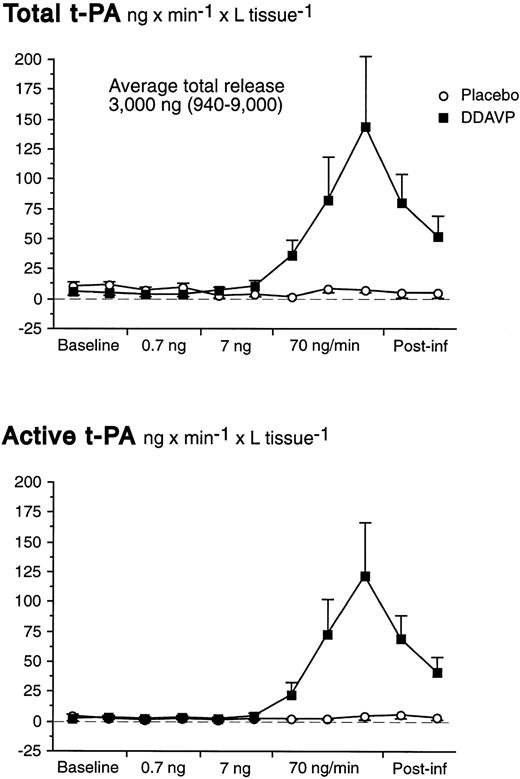
There was a significant basal net release of total t-PA of 6.7 ng/min from the whole forearm vasculature (t-test; P = .007). There were no significant changes of the t-PA release rate during the first two dose-steps of DDAVP. However, in response to the 70 ng/min DDAVP infusion release rates of both total and active t-PA increased dramatically (Table 1 and Fig 3). In fact, despite the marked increase in FBF at the highest dose-step, AV gradients of t-PA increased significantly (Table 1). The t-PA release response on the highest dose-step was rapid; net release rates had increased significantly already after 2 minutes and peaked at the end of the infusion.
Total t-PA Before, During, and After Placebo or 70 ng/min DDAVP Infusion
| n = 7 . | Baseline* . | Infusion . | Postinfusion . | ANOVA . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| After 2 Min . | After 4 Min . | After 15 Min† . | 2 Min Rest . | 10 Min Rest . | One-Way . | Two-Way Placebo v DDAVP . | ||
| Total t-PA | ||||||||
| Arterial plasma concentration (ng/mL) | ||||||||
| Placebo | 5.58 (0.99) | 6.04 (1.21) | 5.87 (1.23) | 6.12 (1.40) | 5.86 (1.07) | 6.26 (1.18) | NS | P = .053 |
| DDAVP | 5.27 (0.95) | 5.42 (0.92) | 5.57 (0.92) | 6.26 (1.04) | 5.93 (0.96) | 6.18 (1.07) | P < .0001 | |
| Venous plasma concentration (ng/mL) | ||||||||
| Placebo | 6.24 (1.06) | 6.18 (1.17) | 6.39 (1.34) | 6.56 (1.49) | 6.17 (1.17) | 6.53 (1.35) | NS | P < .0001 |
| DDAVP | 5.54 (0.94) | 6.31 (0.94) | 7.46 (1.02) | 9.10 (1.23) | 8.40 (1.00) | 8.16 (1.16) | P < .0001 | |
| A-V concentration gradient (ng/mL) | ||||||||
| Placebo | 0.66 (0.13) | 0.14 (0.06) | 0.52 (0.18) | 0.44 (0.21) | 0.32 (0.26) | 0.27 (0.27) | NS | P < .0001 |
| DDAVP | 0.28 (0.08) | 0.89 (0.17) | 1.89 (0.68) | 2.84 (0.84) | 2.47 (0.51) | 1.98 (0.57) | P < .0001 | |
| Net release (ng × L−1 × min−1) | ||||||||
| Placebo | 11.1 (1.97) | 2.41 (0.92) | 8.54 (2.92) | 8.00 (3.24) | 4.91 (3.89) | 5.11 (4.09) | NS | P < .0001 |
| DDAVP | 5.83 (2.63) | 37.1 (11.4) | 82.6 (36.1) | 144 (58.0) | 79.9 (23.8) | 52.6 (16.1) | P < .0001 | |
| Active t-PA | ||||||||
| Arterial plasma concentration (ng/mL) | ||||||||
| Placebo | 1.02 (0.15) | 1.09 (0.15) | 1.14 (0.15) | 0.89 (0.22) | 0.94 (0.20) | 1.00 (0.22) | NS | P < .0001 |
| DDAVP | 0.98 (0.12) | 1.08 (0.12) | 1.14 (0.13) | 1.35 (0.17) | 1.34 (0.17) | 1.25 (0.15) | P < .0001 | |
| Venous plasma concentration (ng/mL) | ||||||||
| Placebo | 1.23 (0.24) | 1.30 (0.20) | 1.29 (0.19) | 1.22 (0.20) | 1.27 (0.18) | 1.28 (0.20) | NS | P < .0001 |
| DDAVP | 1.16 (0.16) | 1.71 (0.24) | 2.79 (0.58) | 3.77 (0.71) | 3.50 (0.46) | 2.76 (0.45) | P < .0001 | |
| A-V concentration gradient (ng/mL) | ||||||||
| Placebo | 0.21 (0.09) | 0.21 (0.06) | 0.15 (0.05) | 0.32 (0.18) | 0.33 (0.16) | 0.28 (0.15) | NS | P < .0001 |
| DDAVP | 0.19 (0.05) | 0.64 (0.18) | 1.65 (0.53) | 2.42 (0.63) | 2.15 (0.38) | 1.50 (0.38) | P < .0001 | |
| Net release (ng × L−1 × min−1) | ||||||||
| Placebo | 3.92 (1.70) | 3.34 (1.06) | 2.60 (0.86) | 4.69 (2.71) | 5.98 (2.46) | 4.33 (2.14) | NS | P < .0001 |
| DDAVP | 3.38 (1.18) | 23.6 (9.44) | 73.7 (28.9) | 123 (44.3) | 70.4 (18.3) | 41.6 (12.4) | P < .0001 | |
| n = 7 . | Baseline* . | Infusion . | Postinfusion . | ANOVA . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| After 2 Min . | After 4 Min . | After 15 Min† . | 2 Min Rest . | 10 Min Rest . | One-Way . | Two-Way Placebo v DDAVP . | ||
| Total t-PA | ||||||||
| Arterial plasma concentration (ng/mL) | ||||||||
| Placebo | 5.58 (0.99) | 6.04 (1.21) | 5.87 (1.23) | 6.12 (1.40) | 5.86 (1.07) | 6.26 (1.18) | NS | P = .053 |
| DDAVP | 5.27 (0.95) | 5.42 (0.92) | 5.57 (0.92) | 6.26 (1.04) | 5.93 (0.96) | 6.18 (1.07) | P < .0001 | |
| Venous plasma concentration (ng/mL) | ||||||||
| Placebo | 6.24 (1.06) | 6.18 (1.17) | 6.39 (1.34) | 6.56 (1.49) | 6.17 (1.17) | 6.53 (1.35) | NS | P < .0001 |
| DDAVP | 5.54 (0.94) | 6.31 (0.94) | 7.46 (1.02) | 9.10 (1.23) | 8.40 (1.00) | 8.16 (1.16) | P < .0001 | |
| A-V concentration gradient (ng/mL) | ||||||||
| Placebo | 0.66 (0.13) | 0.14 (0.06) | 0.52 (0.18) | 0.44 (0.21) | 0.32 (0.26) | 0.27 (0.27) | NS | P < .0001 |
| DDAVP | 0.28 (0.08) | 0.89 (0.17) | 1.89 (0.68) | 2.84 (0.84) | 2.47 (0.51) | 1.98 (0.57) | P < .0001 | |
| Net release (ng × L−1 × min−1) | ||||||||
| Placebo | 11.1 (1.97) | 2.41 (0.92) | 8.54 (2.92) | 8.00 (3.24) | 4.91 (3.89) | 5.11 (4.09) | NS | P < .0001 |
| DDAVP | 5.83 (2.63) | 37.1 (11.4) | 82.6 (36.1) | 144 (58.0) | 79.9 (23.8) | 52.6 (16.1) | P < .0001 | |
| Active t-PA | ||||||||
| Arterial plasma concentration (ng/mL) | ||||||||
| Placebo | 1.02 (0.15) | 1.09 (0.15) | 1.14 (0.15) | 0.89 (0.22) | 0.94 (0.20) | 1.00 (0.22) | NS | P < .0001 |
| DDAVP | 0.98 (0.12) | 1.08 (0.12) | 1.14 (0.13) | 1.35 (0.17) | 1.34 (0.17) | 1.25 (0.15) | P < .0001 | |
| Venous plasma concentration (ng/mL) | ||||||||
| Placebo | 1.23 (0.24) | 1.30 (0.20) | 1.29 (0.19) | 1.22 (0.20) | 1.27 (0.18) | 1.28 (0.20) | NS | P < .0001 |
| DDAVP | 1.16 (0.16) | 1.71 (0.24) | 2.79 (0.58) | 3.77 (0.71) | 3.50 (0.46) | 2.76 (0.45) | P < .0001 | |
| A-V concentration gradient (ng/mL) | ||||||||
| Placebo | 0.21 (0.09) | 0.21 (0.06) | 0.15 (0.05) | 0.32 (0.18) | 0.33 (0.16) | 0.28 (0.15) | NS | P < .0001 |
| DDAVP | 0.19 (0.05) | 0.64 (0.18) | 1.65 (0.53) | 2.42 (0.63) | 2.15 (0.38) | 1.50 (0.38) | P < .0001 | |
| Net release (ng × L−1 × min−1) | ||||||||
| Placebo | 3.92 (1.70) | 3.34 (1.06) | 2.60 (0.86) | 4.69 (2.71) | 5.98 (2.46) | 4.33 (2.14) | NS | P < .0001 |
| DDAVP | 3.38 (1.18) | 23.6 (9.44) | 73.7 (28.9) | 123 (44.3) | 70.4 (18.3) | 41.6 (12.4) | P < .0001 | |
Values are the means, with the SEM in parentheses.
Abbreviation: NS, not significant.
Mean of two samples.
n = 6.
Net release rates of total and active t-PA during stepwise intrabrachial artery infusions of DDAVP (0.7 to 7 to 70 ng/min for 5 to 5 to 15 minutes; ▪) and placebo (saline; ○) in 7 healthy male subjects. Means and SEM error bars. Both total and active t-PA increased significantly in response to DDAVP (ANOVA, time × treatment interaction: P < .0001).
Net release rates of total and active t-PA during stepwise intrabrachial artery infusions of DDAVP (0.7 to 7 to 70 ng/min for 5 to 5 to 15 minutes; ▪) and placebo (saline; ○) in 7 healthy male subjects. Means and SEM error bars. Both total and active t-PA increased significantly in response to DDAVP (ANOVA, time × treatment interaction: P < .0001).
The maximum net release of total and active t-PA across the whole forearm vasculature were, on the average, 178 ng/min (range, 35 to 562 ng/min) and 150 ng/min (range, 65 to 449 ng/min), respectively. Release rates slowly declined after discontinuation of the active infusion and had not reached baseline levels 10 minutes after the end of the infusion. As shown in Table 1, the average release of total t-PA was somewhat higher before placebo than before DDAVP. However, it is unlikely that this was caused by a sustained action of DDAVP, because FBF had returned to baseline levels in those subjects who received DDAVP as the first stimulus. We have previously observed that there is a small oscillation in release rates under basal conditions that is not immediately reflected by measurable changes in active t-PA. There were no significant alterations in plasma concentrations of t-PA during the placebo infusion.
At baseline, the average proportion of t-PA present in its active form was 26% (SEM 6.0%) in the brachial vein and 24% (SEM 5.4%) in the brachial artery. In response to DDAVP, the amount of t-PA present in its active form increased to 45% (SEM 8.8%) in the brachial vein, whereas the active fraction was unchanged during the placebo infusion (ANOVA time × treatment interaction; P < .001). Arterial t-PA increased slightly at the very end of the infusion (Table1), but the ratio of active to total t-PA in the brachial artery remained constant throughout the experiment. Area-under-curve calculations showed that, on the average, a total of 3,000 ng of t-PA (range, 940 to 9,000 ng) was released by DDAVP during the highest dose-step and 10 minutes thereafter.
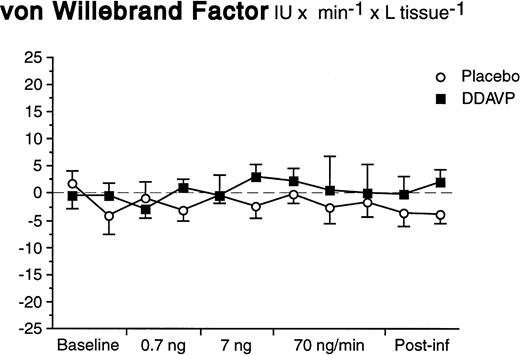
In contrast to what was observed for t-PA, there was neither a basal nor a significant stimulated release of vWF in response to DDAVP (Fig 4). The arterial and venous concentrations, AV-gradients, and net release rates remained constant during both DDAVP and placebo infusions (ANOVA time × treatment interaction; P = .92 for net release).
Net release rates of vWF during stepwise intrabrachial artery infusions of DDAVP (▪) and placebo (○). Means and SEM error bars. There were no significant differences between the responses to DDAVP and placebo (ANOVA, time × treatment interaction: P = .92).
Net release rates of vWF during stepwise intrabrachial artery infusions of DDAVP (▪) and placebo (○). Means and SEM error bars. There were no significant differences between the responses to DDAVP and placebo (ANOVA, time × treatment interaction: P = .92).
Constant-Rate DDAVP Infusion
Compared with the highest dose-step in the first study, FBF showed an identical response pattern. There was no increase in FBF in the control arm during or after the infusion (Fig 5). t-PA release rates in the infusion arm were comparable to the results from the stepwise infusion with a maximum of 110 ng/min (range, 25 to 200 ng/min) across the whole forearm vasculature. DDAVP induced no changes whatsoever in control forearm release rates of t-PA (Fig 5). Again, there was no release of vWF in either the infusion or control arm (data not shown).
Comparison of FBF and t-PA net release between infusion arm (▪) and control arm (○) during constant-rate infusion of DDAVP (70 ng/min for 20 minutes) in 4 healthy male subjects. Means and SEM error bars. Both FBF and t-PA net release increased significantly in the infusion arm as compared with the control arm (ANOVA, time × treatment interaction: P < .01 for both).
Comparison of FBF and t-PA net release between infusion arm (▪) and control arm (○) during constant-rate infusion of DDAVP (70 ng/min for 20 minutes) in 4 healthy male subjects. Means and SEM error bars. Both FBF and t-PA net release increased significantly in the infusion arm as compared with the control arm (ANOVA, time × treatment interaction: P < .01 for both).
Endothelium-Independent Flow Stimulation
To rule out the possibility that increased blood flow was the stimulus for endothelial t-PA release, an additional experiment was performed in 4 healthy male subjects. They received stepwise intra-arterial infusions of both DDAVP (7.0, 21, and 70 ng/min) and sodium nitroprusside (SNP; 0.5, 2.5, and 10 μg/min). Despite a greater FBF enhancement with SNP, there was no increase in t-PA release, whereas DDAVP again showed its potency as a local stimulator of acute release (ANOVA, time × treatment, P = .0003; Fig 6). As in the first study, there was no significant release on the 7.0 ng/min dose-step, but the intermediate dose (21 ng/min) elicited an average release of 38.9 ng/min and liters of tissue that was significantly different from the basal release (t-test; P = .03).
FBF and t-PA net release during stepwise intrabrachial artery infusions of DDAVP (7 to 21 to 70 ng/min for 5 to 5 to 15 minutes; ▪) and sodium nitroprusside (0.5 to 2.5 to 10 μg/min for 5 to 5 to 15 minutes; ○) in 4 healthy male subjects. Means and SEM error bars. Net release of t-PA increased significantly in response to DDAVP as compared with SNP (ANOVA, time × treatment interaction:P = .0003), but there was no significant difference in FBF between the two drugs.
FBF and t-PA net release during stepwise intrabrachial artery infusions of DDAVP (7 to 21 to 70 ng/min for 5 to 5 to 15 minutes; ▪) and sodium nitroprusside (0.5 to 2.5 to 10 μg/min for 5 to 5 to 15 minutes; ○) in 4 healthy male subjects. Means and SEM error bars. Net release of t-PA increased significantly in response to DDAVP as compared with SNP (ANOVA, time × treatment interaction:P = .0003), but there was no significant difference in FBF between the two drugs.
DISCUSSION
The results of the present study provide evidence that DDAVP acts as a local stimulator of acute, regulated release of t-PA in the human forearm vascular bed. The total lack of a t-PA response in the control arm precludes the possibility that the effect of DDAVP was mediated by central mechanisms. The use of the perfused-forearm model to determine instantaneous release rates of t-PA across an anatomically defined vascular bed in vivo ascertains that alterations in hepatic clearance could not have confounded the results we obtained. Furthermore, our findings show that the local t-PA release was due to a specific stimulatory effect of DDAVP rather than secondary to its vasodilator action, because endothelium-independent vasodilation by the nitric oxide donor SNP failed to induce any t-PA release.
The present findings challenge the common assumption that DDAVP does not act directly to induce a local release of t-PA. Already in 1978, Cash et al18 reported that infusion of DDAVP into the brachial artery of two subjects did not alter euglobulin clot lysis time of the venous effluent from the forearm, whereas epinephrine did. These observations have generally been taken to indicate that DDAVP does not by itself cause a local t-PA release but rather stimulates some central mechanism that, in turn, activates the secretory response. However, in the study by Cash et al, the estimations of clot lysis time were not corrected for changes in plasma flow, which is of critical importance when changes in local protein release rates are to be assessed. The amount of t-PA that is secreted locally will increase the arteriovenous concentration gradient only in proportion to the prevailing plasma flow, in which the released t-PA is diluted.24 26 Hence, a stimulated local t-PA release induced by an agent such as DDAVP, which is also a potent vasodilator, may easily go unrecognized if blood flow and t-PA release increase in parallel. In the present study, we simultaneously measured t-PA concentrations in inflow (arterial) and outflow (venous) plasma to calculate arteriovenous concentration gradients and plasma flow across the same vascular bed. By this procedure, a direct measurement of net t-PA release rates per minute is obtained. Our data clearly show that local t-PA release is markedly stimulated by DDAVP.
The t-PA response to DDAVP occurred in close conjunction with an enhanced forearm blood flow. Thus, an important issue is whether the local t-PA release may be induced by the increased blood flow per se rather than be due to receptor-mediated mechanisms. To investigate this possibility, we gave forearm infusions of sodium nitroprusside, which causes endothelium-independent vasodilation by direct actions on smooth muscle cell guanylate cyclase, to reach forearm blood flow levels well above those induced by DDAVP. However, despite marked vasodilator responses, nitroprusside did not induce any local t-PA release in any of the 4 subjects investigated. This finding confirms previous observations from our group that vasodilation by SNP has no effect on forearm t-PA release.26 Hence, the moderate enhancement of forearm blood flow in response to DDAVP that we observed in the present study is not a likely explanation of the massive acute release of t-PA. Rather, it is likely that the mechanisms of endothelium-dependent vasodilation and regulated t-PA release share some common agonist-mediated cellular signal transduction pathways. In fact, most substances shown to induce acute t-PA release also induce release of prostacyclin I2 (PGI2) and nitric oxide (NO). The vasodilator action of DDAVP has been ascribed to stimulation of extrarenal V2 receptors,32because anephric patients respond normally to DDAVP,2,9whereas patients with a V2 receptor defect (congenital diabetes insipidus) do not.33 The vasodilator action of vasopressin in the human forearm is mediated by V2-receptors and subsequent release of NO, because the response could be blocked either by the V2-receptor antagonist OTC-31260 or L-NMMA.33-35 However, the vasodilating mechanisms involved in V2-receptor activation by DDAVP are not clarified.33,36 37
Could the local t-PA secretory response of DDAVP shown in the present study explain the enhanced plasma levels of t-PA observed during systemic administration? In the DDAVP stimulation test protocol as generally applied, the drug is infused intravenously (IV) at a dosage of 0.3 to 0.4 μg/kg body weight over 10 to 30 minutes. The maximum systemic plasma concentration of DDAVP thus obtained is approximately 0.7 to 1.3 ng/mL, which results in a threefold increase in plasma t-PA levels.38 In our study, the calculated systemic plasma concentrations were maximum one tenth (70 pg/mL) of DDAVP concentrations achieved by common IV dosages. In contrast, the calculated local forearm plasma DDAVP concentration during the 70 ng/min dose-step was 2 ng/mL, and the corresponding increase in the net release of t-PA was 20-fold. The respective value in response to the 21 ng/min infusion was 0.8 ng/mL of DDAVP, which was associated with a nearly threefold increase in t-PA secretion. Thus, it is reasonable to assume that the dosage used during routine IV administration of DDAVP yields concentrations well within the range shown to induce t-PA release by the currently demonstrated local mechanism.
In view of the fact that the local concentration of DDAVP apparently was sufficient to stimulate endothelial cells to release t-PA, the absence of any stimulation of vWF release across the forearm was unexpected. It has generally been assumed that DDAVP stimulates secretion of t-PA and vWF through similar mechanisms, because, at least on the systemic level, plasma concentrations of both proteins increase in parallel in response to intravenous DDAVP administration. However, two recent studies show that regulated endothelial releases of t-PA and vWF do not always occur in concert. In the perfused rat hindlimb preparation, Smalley et al39 showed that adenosine diphosphate (ADP) caused an acute release of t-PA that was not associated with a simultaneous release of vWF. Also, our group recently showed that, whereas both mental stress and intrabrachial artery infusion of the endothelial receptor agonist methacholine induced a distinct acute release of t-PA across the human forearm, neither of the two stimuli induced an acute local release of vWF.40 Thus, at least in skeletal muscle vascular beds, release of t-PA and vWF is not necessarily obligatory linked. In this context, it is of note that Emeis' group recently reported evidence that t-PA is stored in separate particles different from the Weibel-Palade bodies, in which vWF is contained, and that different regulatory mechanisms are involved in the release of t-PA and vWF from their respective endothelial storage pools.41 However, it is not likely that such a tentative differential mechanism is specifically related to the V2-receptor as such, because both the vWF and t-PA responses to DDAVP are absent in patients with congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.42,43 In addition, Kinter et al44 recently showed that pretreatment with a V2-receptor antagonist (SK&F 105494) totally abolished the DDAVP-induced vWF response in anesthetized rhesus monkeys.
An interesting possibility to explain the different responses of t-PA and vWF to local DDAVP administration is that the regulated vWF release, unlike that of t-PA, might require a local or systemic intermediate mechanism. Hashemi et al45,46 have suggested that DDAVP-induced vWF secretion is mediated via release of platelet-aggregating factor (PAF) from monocytes, but proposed that the t-PA response might be linked to a different pathway. However, it takes 2 hours before the monocyte-induced increase in vWF is fully developed,46 which suggests that the mechanism behind is enhanced synthesis rather than acute release. Very recently, it was also shown in dogs that a PAF-receptor blocking agent (SR 27417) had no effect on DDAVP-induced increase in plasma levels of vWF, FVIII, or t-PA.47 In the present study, an enhanced net release of t-PA was observed already after 2 minutes of infusion, which is very similar to the time frame of the acute release of t-PA induced in perfused blood-free vascular beds after the addition of a variety of endothelial receptor agonists.10 Consequently, the present findings speak in favor of the hypothesis that at least the acute release of t-PA was mediated through a direct stimulatory effect of DDAVP on endothelial cell receptors. However, it could not be ruled out that a hitherto unidentified fast-acting local intermediary mechanism is involved.
In conclusion, the present results show that local administration of DDAVP induces a massive acute release of t-PA, without the simultaneous release of vWF, in the human forearm vascular bed. The lack of a t-PA response in the control arm as well as the unaltered central hemodynamics with DDAVP confirms that the observed t-PA release was independent of central mechanisms. Furthermore, the t-PA response is not due to the increased blood flow as such. The absence of a regulated release of vWF is in accordance with earlier data from our group showing that the processes of acute release of t-PA and vWF in the human forearm vascular bed are not obligatory linked.
Supported by grants from the Swedish Medical Research Council (09046), the Bank of Sweden Tercentenary Foundation, the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation, the Swedish Hypertension Society, the Åke Wiberg Foundation, the Magnus Bergvall Foundation, the Rune and Ulla Almlöv Foundation, the John and Brit Wennerström Foundation, the Swedish 1987 year Foundation for Stroke Research, and a post-doc fellowship to C.J. from the Berth von Kantzow Foundation.
Address reprint requests to Ulrika Wall, MD, Clinical Experimental Research Laboratory, Department of Medicine, Sahlgrenska University Hospital/Östra, S-416 85 Göteborg, Sweden.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. This article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.





This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal