Key Points
Less-deformable sickle red cells marginate toward blood vessel walls, leading to altered local wall shear stress and endothelial dysfunction.
Pathological biophysical alterations in sickle RBCs cause endothelial dysfunction independently from vaso-occlusion and adhesion.
Visual Abstract
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is canonically characterized by reduced red blood cell (RBC) deformability, leading to microvascular obstruction and inflammation. Although the biophysical properties of sickle RBCs are known to influence SCD vasculopathy, the contribution of poor RBC deformability to endothelial dysfunction has yet to be fully explored. Leveraging interrelated in vitro and in silico approaches, we introduce a new paradigm of SCD vasculopathy in which poorly deformable sickle RBCs directly cause endothelial dysfunction via mechanotransduction, during which endothelial cells sense and pathophysiologically respond to aberrant physical forces independently of microvascular obstruction, adhesion, or hemolysis. We demonstrate that perfusion of sickle RBCs or pharmacologically-dehydrated healthy RBCs into small venule-sized “endothelialized” microfluidics leads to pathologic physical interactions with endothelial cells that directly induce inflammatory pathways. Using a combination of computational simulations and large venule-sized endothelialized microfluidics, we observed that perfusion of heterogeneous sickle RBC subpopulations with varying deformability, as well as suspensions of dehydrated normal RBCs admixed with normal RBCs, leads to aberrant margination of the less-deformable RBC subpopulations toward the vessel walls, causing localized, increased shear stress. Increased wall stress is dependent on the degree of subpopulation heterogeneity and oxygen tension and leads to inflammatory endothelial gene expression via mechanotransductive pathways. Our multifaceted approach demonstrates that the presence of sickle RBCs with reduced deformability leads directly to pathological physical (ie, direct collisions and/or compressive forces) and shear-mediated interactions with endothelial cells and induces an inflammatory response, thereby elucidating the ubiquity of vascular dysfunction in SCD.
Introduction
The unique pathology in sickle cell disease (SCD) is caused by a single-point mutation in the beta globin gene, creating abnormal, sickle hemoglobin, which, upon deoxygenation, polymerizes within the red blood cell (RBC), decreasing its deformability and producing the characteristic “sickled” appearance.1 The classical paradigm of poorly deformable cells blocking the microcirculation, leading to vaso-occlusion and end-organ damage, has been expanded to incorporate the proadhesive, procoagulant, and inflammatory vasculopathy associated with endothelial cell (EC) activation driven by intravascular hemolysis, platelet activation, and inflammatory cytokines.2-7 This expanded view of SCD pathophysiology may still be incomplete because it overlooks a common yet consequential complication of SCD: chronic sickle vasculopathy, including its association with stroke. Because SCD vasculopathy, in which ECs are dysfunctional and proinflammatory,8-10 occurs even in the highly oxygenated arterial circulation, a new pathophysiologic understanding of SCD is needed. Current theories do not directly link the decreased deformability of sickle RBCs (sRBCs) to endothelial dysfunction, and sRBC-EC biophysical interactions have not been explored.
Cardiovascular bioengineering research has demonstrated that ECs mechanotransduce biophysical cues, such as the shear forces of the hemodynamic microenvironment, into cellular biological signals.11-13 Shear forces can be transduced by ion channels in the EC membrane and various kinases, resulting in the activation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase and the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS).14 ROS can further alter EC function via altered vascular tone by altering nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability or signaling.15 Moreover, pathological alterations of those forces lead to the activation of proinflammatory signals within ECs, including the upregulation of VCAM-1 and E-selectin, and the subsequent development of atherosclerotic plaques in situ, leading to increased risk of myocardial infarction and stroke.11 In addition, under normal homeostatic conditions, arterial wall shear stress is dependent only on the plasma fraction of blood, because RBCs do not come into contact with the endothelium due to the cell-free layer (CFL) created by the Fåhræus-Lindqvist effect.16,17 Recently, studies have demonstrated that decreasing RBC deformability diminishes or eliminates the CFL, potentially allowing RBCs to come into close proximity and perhaps even transiently have direct contact with the vessel wall.11 This is particularly pertinent in SCD due to the presence of a small population of irreversibly sickled cells (ISCs; 1%-10% of sRBCs), which are permanently rigid and dehydrated. These ISCs have substantially lower deformability from increased cellular viscosity secondary to cellular dehydration and increased membrane rigidity due to oxidative damage.18-20
Here, we present in vitro and in silico models that demonstrate biophysical alterations of sRBCs may directly induce endothelial dysfunction. Our models show that even small populations of less-deformable RBCs cause significant endothelial dysfunction, with the effects modulated by vessel geometry and the percentage of less-deformable cells. To this end, we leverage a multidisciplinary approach involving microfluidic systems, cell immunostaining, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), and computational simulations with sRBCs and pharmacologically-dehydrated RBCs (pdRBCs) to address this new biophysical paradigm.
Methods
Endothelialized microfluidic experiments
Blood from healthy donors or individuals with SCD was collected in accordance with institutional review board (IRB) protocols and RBCs isolated (supplemental Methods, available on the Blood website). Consent for all patient blood samples was obtained in accordance with Emory University IRB (protocol 105125). Consent for all healthy human blood samples was obtained in accordance with Emory University and Georgia Institute of Technology IRB (protocol H15258). To mimic the decreased deformability of sRBCs, healthy RBCs (hRBCs) were pharmacologically dehydrated with nystatin and high sucrose washes according to established practices to create RBCs with an increased mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration of 40 to 42 g/dL.21
Microfluidic devices (a branching microfluidic device mimicking a small-medium venule in which the smallest microchannels have a 30 μm diameter and a straight 4-channel microfluidic device mimicking a large venule measuring 50 μm high and 100 μm wide) were made from polydimethylsiloxane using standard soft lithography techniques (supplemental Methods).22
A uniform suspension of hRBCs and a binary suspension of 95% hRBCs/5% pdRBCs were perfused through the 50 μm microfluidic device at a volumetric flow rate of 1.25 mL per minute for 10 minutes. To determine margination, 5% of RBCs in each suspension (5% hRBCs in the uniform suspension and 5% pdRBCs in the binary suspension) were stained with octadecyl rhodamine B chloride (R18), and a MATLAB-derived program was used to visualize R18-stained RBCs (Figure 3B).
After creating the microfluidic devices, the system was “endothelialized” with human umbilical vein ECs as previously reported (supplemental Methods). When the device was endothelialized to confluence, hRBCs and sRBCs were isolated, resuspended in media to a 25% hematocrit, and perfused into the channels of the microdevice for 4 hours. pdRBCs were created, and parallel experiments were performed. Hematocrit and plasma-free hemoglobin were measured before and after the experiment in all conditions with the 50 μm microfluidic device to determine the degree of hemolysis occurring during experimentation. Post-experiment hematocrits ranged from 23.9% to 24.6% across all conditions. Plasma-free hemoglobin differences before and after experiments ranged from 1.5% to 5% across all conditions, except within the 100% pdRBCs, which saw increased hemolysis with a change of 23.6%. After 4 hours, the device was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and immunostained with antibodies against VCAM-1 (ABCAM) and E-selectin (Thermo Fisher). The device was then imaged using an inverted optical microscope (10×, Nikon Eclipse TE2000-U), and using ImageJ, mean fluorescence intensity was measured (endothelium exposed to hRBCs normalized to 1). For all endothelialized experiments, significance testing was performed using a Mann-Whitney U test (P < .05).
Computational models of sRBCs
Flowing suspensions of RBCs, modeled as deformable, fluid-filled elastic capsules with discoid radii of 4 μm, were created in straight cylindrical tubes with a 40 μm diameter. RBC membranes incorporated shear elasticity, volume conservation, bending resistance, and area dilatation. The membrane mechanics model and validation against experimental observations were previously modeled by our group.23
To mimic a sRBC suspension, binary mixtures of hRBCs with sRBCs were created. In the binary suspensions, the hRBC percentage was 95% or 90%, with sRBCs 5% or 10%, respectively. These binary suspension simulations were compared with uniform control suspensions comprising 100% hRBCs or 100% sRBCs. The overall volume fraction, representing hematocrit, was 20% across suspensions. The suspensions were subjected to unidirectional, pressure-driven flow, and RBC deformability was measured (supplemental Methods).
An immersed boundary method was used to measure fluid-structure interactions. Two types of immersed boundaries were considered, including deformable moving cellular membranes and rigid nonmoving cylindrical walls. We used “continuous forcing” and “direct forcing” immersed boundary methods for the RBC membranes and tube wall, respectively, with previously described approaches for numerical methodology followed.24,25
Microfluidic blood rheology deoxygenation experiments
Blood from healthy donors or individuals with SCD was collected in accordance with IRB protocols, and RBCs were isolated (supplemental Methods). Consent for all blood samples was obtained in accordance with Massachusetts General Hospital IRB (protocol 2006P000066) and Children's Hospital of Minnesota IRB (protocol STUDY00003). Plasma was removed after centrifugation at 400g for 5 minutes and replaced with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) to a hematocrit of 25%.
Microfluidic systems designed to investigate blood rheology were used as previously described.26 The microfluidic rheology platform (Figure 4A) allows for the perfusion of blood at a fixed-pressure, isolated control of reduced oxygen tension to the experimental channel, and simultaneous measurement of RBC velocity profiles using a Kanade-Lucas-Tomasi algorithm and MATLAB scripts (supplemental Methods).
Exchange transfusions of SCD blood samples were prepared ex vivo, with the final percentages of sRBCs totaling 10%, 30%, 70%, and 100% of the sample. A 100% hRBCs control was also used. Using the flow profiles generated for each condition, the wall velocity was measured, and the frictional resistance was calculated using the known pressure drop across the length of the experimental channel (supplemental Methods).
scRNA-seq
scRNA-seq was performed on ECs collected from our 50 μm microfluidic device after exposure to hRBCs or binary suspensions of 95% hRBCs/5% pdRBCs. Using the previously described protocol, after endothelialization of our microfluidic channels, RBC suspensions of 100% hRBCs or 95% hRBCs/5% pdRBCs were perfused; but after the experiment, ECs were trypsinized, resuspended in media, and prepared for scRNA-seq (supplemental Methods).
scRNA-seq was performed using a droplet-based ultra-high throughput scRNA-seq system enabling large-scale parallel single-cell gene expression studies. Sequencing was performed using massively parallel sequencing on the Illumina NovaSeq S4 platform, with scRNA-seq analysis performed via established methods (supplemental Methods). Differentially expressed genes were calculated using the Wilcoxon rank test with Bonferroni multiple test correction (P < .05), and enriched pathways were determined using Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted P values (adjusted P < .05).
Results
sRBCs and pdRBCs demonstrate increased endothelial inflammation at bifurcations in endothelialized microfluidic devices mimicking small venules
ECs were exposed to hRBCs and sRBCs in 30 μm microfluidic devices mimicking small-medium venules (Figure 1A-B), with parallel experiments completed using hRBCs and pdRBCs. Endothelium exposed to sRBCs and pdRBCs demonstrated increased VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression relative to hRBC-exposed endothelium (Figure 1C-D), and the expression increased as the amount of sRBCs or pdRBCs increased at bifurcations and within the smallest channels, with the highest amount of VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression seen in the 100% sRBC- or pdRBC-exposed endothelium.
ECs exposed to pdRBCs and sRBCs demonstrate increased endothelial inflammation within the smallest channels and at bifurcations in microfluidic devices mimicking small venules. (A) Macroscopic view of a microfluidic device designed to mimic a small-medium venule, in which the smallest channels are ∼30 μm in diameter. (B) Brightfield microscopy image at 10× original magnification of the initial branchpoint of our small-medium venule-mimicking microfluidic device endothelialized to confluence with human umbilical vein ECs. (C) Endothelial VCAM-1 (green) and E-selectin (red) expression in the first branchpoint of the microfluidic device after 4-hour perfusion of healthy control RBCs vs RBC suspensions containing varying amounts (5%, 10%, and 100%) of sRBCs (left) and nystatin-treated, less-deformable RBCs (right). All RBC suspensions were diluted in media to a hematocrit of 25% and perfused at a constant venular shear rate. (D) Graphical representation of mean normalized fluorescent intensity for VCAM-1 and E-selectin, both markers of inflammation, in ECs exposed to hRBCs (red) and RBC suspensions with varying amounts of sRBCs (left) and nystatin-treated, less-deformable RBCs (right) at the initial branchpoint shown. A total of 5 separate experiments were analyzed. VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression increased as the number of sickled RBCs increased. In the experiments using nystatin-treated RBCs, VCAM-1 and E-selectin had a statistically significant increase in expression as the number of less-deformable cells increased (VCAM-1 2.29 ± 0.46 standard error of the mean [SEM; P < .05]; E-selectin 1.7 ± 0.16 SEM [P < .05]) normalized fluorescent intensity in ECs exposed to 100% nystatin-treated RBCs), indicating that increased RBC-EC interactions occur at vessel branchpoints in the presence of less-deformable RBCs, which also exert increased compressive mechanical forces against the endothelium in the smallest vessels. Statistical analyses using a Mann-Whitney U test; ∗P ≤ .05. Error bars represent SEM.
ECs exposed to pdRBCs and sRBCs demonstrate increased endothelial inflammation within the smallest channels and at bifurcations in microfluidic devices mimicking small venules. (A) Macroscopic view of a microfluidic device designed to mimic a small-medium venule, in which the smallest channels are ∼30 μm in diameter. (B) Brightfield microscopy image at 10× original magnification of the initial branchpoint of our small-medium venule-mimicking microfluidic device endothelialized to confluence with human umbilical vein ECs. (C) Endothelial VCAM-1 (green) and E-selectin (red) expression in the first branchpoint of the microfluidic device after 4-hour perfusion of healthy control RBCs vs RBC suspensions containing varying amounts (5%, 10%, and 100%) of sRBCs (left) and nystatin-treated, less-deformable RBCs (right). All RBC suspensions were diluted in media to a hematocrit of 25% and perfused at a constant venular shear rate. (D) Graphical representation of mean normalized fluorescent intensity for VCAM-1 and E-selectin, both markers of inflammation, in ECs exposed to hRBCs (red) and RBC suspensions with varying amounts of sRBCs (left) and nystatin-treated, less-deformable RBCs (right) at the initial branchpoint shown. A total of 5 separate experiments were analyzed. VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression increased as the number of sickled RBCs increased. In the experiments using nystatin-treated RBCs, VCAM-1 and E-selectin had a statistically significant increase in expression as the number of less-deformable cells increased (VCAM-1 2.29 ± 0.46 standard error of the mean [SEM; P < .05]; E-selectin 1.7 ± 0.16 SEM [P < .05]) normalized fluorescent intensity in ECs exposed to 100% nystatin-treated RBCs), indicating that increased RBC-EC interactions occur at vessel branchpoints in the presence of less-deformable RBCs, which also exert increased compressive mechanical forces against the endothelium in the smallest vessels. Statistical analyses using a Mann-Whitney U test; ∗P ≤ .05. Error bars represent SEM.
sRBCs demonstrate increased margination and local wall shear stress fluctuations in computational simulations
Computational simulations were created for 4 RBC suspensions: 1 uniform suspension containing only hRBCs, 1 uniform suspension of only sRBCs, and 2 binary suspensions of hRBCs with small fractions of sRBCs (5% and 10%, respectively; Figure 2A). Because sRBCs are smaller than hRBCs, the number of RBCs in the 100% sRBC suspension is higher than that in other suspensions to achieve a 20% hematocrit across all suspensions.
sRBC subpopulations demonstrate increased margination and induce local wall shear stress fluctuations in computational simulations. (A) Angled views of snapshots taken from computational simulations of RBC suspensions composed entirely of hRBCs (left), binary suspensions with a majority of hRBCs and a minority population of sickle RBCs comprising 5% (second) and 10% (third) of the overall suspension, and a suspension composed entirely of sRBCs (right). Each simulation was conducted with a hematocrit of 20%. Because sRBCs have a smaller size than hRBCs, there is a larger number of total RBCs in the 100% sRBC suspension. Binary suspensions were designed to mimic ISCs in individuals with SCD. A CFL can be observed in homogeneous suspensions composed of 100% hRBCs or 100% sRBCs, whereas in binary suspensions, marginated sickle cells are concentrated within the CFL close to channel walls. (B) Steady-state radial hematocrit profiles (Ht) for hRBCs (red) and sRBCs (blue) in RBC suspensions containing 0%, 5%, 10%, and 100% sRBCs, respectively. The x-axis depicts distance from the center of the channel scaled with the radius of a hRBC (scaled radius, r/a), with 0 being the center of the channel and 5 representing the channel walls. In all cases, the hematocrit of the hRBCs as well as sRBCs in the 100% sRBC suspension, drops precipitously close to the wall, corresponding to the CFL. In binary suspensions, sRBCs tend to marginate and travel in higher percentages within the CFL close to channel walls, whereas hRBCs concentrate around the center of the channel. Sickle RBCs in the 100% sRBC suspension did not exhibit the same margination, maintaining the CFL; this can be attributed to the presence of deformable, hRBCs in the binary suspensions, which drive the sRBCs toward the walls. (C) Snapshot of the spatial distribution of additional wall shear stress () induced by hRBCs (left), binary sRBC suspensions comprising 5% (second) and 10% (third) sRBCs and 100% sRBCs (right), respectively. Blue regions indicate large fluctuations and are more numerous in the presence of sRBCs. (D) Probability density profile of excess wall shear stress induced by varying fractions of sRBCs (left). The binary suspensions created large fluctuations in wall shear stress in comparison with the hRBC suspension. The ratio between probability densities (right) shows large positive fluctuations in wall shear stress in binary suspensions of 5% and 10% sRBCs.
sRBC subpopulations demonstrate increased margination and induce local wall shear stress fluctuations in computational simulations. (A) Angled views of snapshots taken from computational simulations of RBC suspensions composed entirely of hRBCs (left), binary suspensions with a majority of hRBCs and a minority population of sickle RBCs comprising 5% (second) and 10% (third) of the overall suspension, and a suspension composed entirely of sRBCs (right). Each simulation was conducted with a hematocrit of 20%. Because sRBCs have a smaller size than hRBCs, there is a larger number of total RBCs in the 100% sRBC suspension. Binary suspensions were designed to mimic ISCs in individuals with SCD. A CFL can be observed in homogeneous suspensions composed of 100% hRBCs or 100% sRBCs, whereas in binary suspensions, marginated sickle cells are concentrated within the CFL close to channel walls. (B) Steady-state radial hematocrit profiles (Ht) for hRBCs (red) and sRBCs (blue) in RBC suspensions containing 0%, 5%, 10%, and 100% sRBCs, respectively. The x-axis depicts distance from the center of the channel scaled with the radius of a hRBC (scaled radius, r/a), with 0 being the center of the channel and 5 representing the channel walls. In all cases, the hematocrit of the hRBCs as well as sRBCs in the 100% sRBC suspension, drops precipitously close to the wall, corresponding to the CFL. In binary suspensions, sRBCs tend to marginate and travel in higher percentages within the CFL close to channel walls, whereas hRBCs concentrate around the center of the channel. Sickle RBCs in the 100% sRBC suspension did not exhibit the same margination, maintaining the CFL; this can be attributed to the presence of deformable, hRBCs in the binary suspensions, which drive the sRBCs toward the walls. (C) Snapshot of the spatial distribution of additional wall shear stress () induced by hRBCs (left), binary sRBC suspensions comprising 5% (second) and 10% (third) sRBCs and 100% sRBCs (right), respectively. Blue regions indicate large fluctuations and are more numerous in the presence of sRBCs. (D) Probability density profile of excess wall shear stress induced by varying fractions of sRBCs (left). The binary suspensions created large fluctuations in wall shear stress in comparison with the hRBC suspension. The ratio between probability densities (right) shows large positive fluctuations in wall shear stress in binary suspensions of 5% and 10% sRBCs.
The steady-state radial hematocrit profiles for hRBCs, binary sRBC suspensions, and 100% sRBCs illustrate segregation behavior (Figure 2B). SRBCs were found to strongly marginate and travel in higher percentages close to the channel walls in binary suspensions, whereas hRBCs tended to travel in the center of the channel. Interestingly, the 100% sRBC suspension did not exhibit the same margination behavior, traveling in a distribution similar to that of the hRBCs. This occurs because margination is a phenomenon unique to heterogeneous mixtures, because collisions between hRBCs and sRBCs drive the latter toward the wall.27,28
The wall shear stress for the RBC suspensions above was computed to characterize the hydrodynamic effects of RBC distribution on the blood vessel wall. Images of the spatial distribution of additional wall shear stress () induced by the suspensions are shown (Figure 2C). Blue regions indicate fluctuations of wall shear stress, which increase in the presence of sRBCs and arise at positions corresponding to a near-wall sRBC interaction. These differences are further quantified by the probability density profiles of excess wall shear stress (Figure 2D), because the binary suspensions created large positive fluctuations in wall shear stress compared with the hRBC suspension. This is attributable to sRBC margination. The ratio between these probability densities further highlights large positive fluctuations in wall shear stress that are pronounced in the sRBC binary suspensions. Thus, even when the relative number of sRBCs is small, the relative probability of large stress fluctuations is high.
Aberrant margination of sRBCs and pdRBCs in microfluidic devices mimicking large venules confirms the pathologic local wall shear stresses observed in computational simulations
Before performing additional endothelialized microfluidic experiments, a uniform suspension of hRBCs as well as a binary suspension of 95% hRBCs/5% pdRBCs were perfused through a large venule-mimicking 50 μm microfluidic device (Figure 3A-B). Similar to the results of our computational simulations, pdRBCs traveled in a higher percentage at vessel walls than hRBCs in a uniform suspension (25.8% of stained pdRBCs compared with 4.9% of stained hRBCs traveling within 10 μm of channel walls; Figure 3C).
Heterogeneous suspensions containing pdRBCs and sRBCs exhibit margination toward vessel walls leading to increased endothelial dysfunction in large venule-mimicking microfluidic systems. (A) Macroscopic view of a 50 × 100 μm straight-channel microfluidic device designed to mimic a large venule. (B) Cartoon depiction of our microfluidic experimental setup and corresponding video snapshot of a superposition of brightfield and fluorescence microscopy images of an RBC suspension comprising 5% pharmacologically dehydrated, less-deformable RBCs (stained with octadecyl rhodamine B chloride [R18] stain) and 95% hRBCs flowing through a straight microfluidic channel with a diameter of 100 μm at a constant flow rate. R18-stained RBCs traveling close to the channel wall as well as more centrally in the channel are circled by a dashed yellow line and solid line, respectively. (C) Graphical representation of the experiment shown in panel B, comparing an RBC suspension composed of 100% hRBCs (5% RBCs stained) with an RBC suspension with a majority hRBC population (95%) with a minority less-deformable and stained RBCs (5%). Software analysis tracking of the stained RBCs was performed and showed that, compared with hRBCs, less-deformable RBCs were more likely to marginate and travel in close proximity to vessel walls. (D) Endothelial VCAM-1 (green) and E-selectin (red) expression after 4-hour perfusion of healthy control RBCs vs RBC suspensions containing varying amounts (5%, 10%, and 100%) of sRBCs. All RBC suspensions were diluted in media to a hematocrit of 25% and perfused at a constant venular shear rate. Graphical representation of mean normalized fluorescent intensity for VCAM-1 (left) and E-selectin (right), both markers of inflammation, in ECs exposed to hRBCs (red) and RBC suspensions with varying amounts of sRBCs in the straight-channel microfluidic is also shown. A total of 5 separate experiments were analyzed. VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression increased as the amount of sRBCs increased (VCAM-1, 1.35 ± 0.12 SEM [P < .05]; E-selectin, 1.29 ± 0.10 SEM [P < .05]) normalized fluorescent intensity in the 100% sRBC-exposed ECs. Because sRBCs do not represent only ISCs (ie, the least-deformable RBCs), the 5% and 10% sickle suspensions likely did not contain enough of the least-deformable RBCs to lead to increased margination compared with the 100% sRBC suspension. (E) Endothelial VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression after 4-hour perfusion of healthy control RBCs vs RBC suspensions containing varying amounts (5%, 10%, and 100%) of nystatin-treated RBCs, with mean normalized fluorescent intensity for VCAM-1 (left) and E-selectin (right) in ECs exposed to hRBCs (red) and RBC suspensions with varying amounts of nystatin-treated RBCs in the straight-channel microfluidic. A total of 5 separate experiments were analyzed. VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression in heterogeneous suspensions with a minority of less-deformable cells at 5% or 10% of the total suspension showed greater expression than the 100% low-deformability suspension (VCAM-1, 1.7 ± 0.17 SEM [P < .05]; E-selectin, 2.91 ± 1.56 SEM [P < .05] normalized fluorescent intensity highest in 10% nystatin-treated RBC-exposed ECs), supporting our hypothesis that when the less-deformable cells are a minority subpopulation, there is increased margination and RBC-EC interactions and subsequent dysfunction. Statistical analyses using a Mann-Whitney U test; ∗P ≤ .05. Error bars represent SEM.
Heterogeneous suspensions containing pdRBCs and sRBCs exhibit margination toward vessel walls leading to increased endothelial dysfunction in large venule-mimicking microfluidic systems. (A) Macroscopic view of a 50 × 100 μm straight-channel microfluidic device designed to mimic a large venule. (B) Cartoon depiction of our microfluidic experimental setup and corresponding video snapshot of a superposition of brightfield and fluorescence microscopy images of an RBC suspension comprising 5% pharmacologically dehydrated, less-deformable RBCs (stained with octadecyl rhodamine B chloride [R18] stain) and 95% hRBCs flowing through a straight microfluidic channel with a diameter of 100 μm at a constant flow rate. R18-stained RBCs traveling close to the channel wall as well as more centrally in the channel are circled by a dashed yellow line and solid line, respectively. (C) Graphical representation of the experiment shown in panel B, comparing an RBC suspension composed of 100% hRBCs (5% RBCs stained) with an RBC suspension with a majority hRBC population (95%) with a minority less-deformable and stained RBCs (5%). Software analysis tracking of the stained RBCs was performed and showed that, compared with hRBCs, less-deformable RBCs were more likely to marginate and travel in close proximity to vessel walls. (D) Endothelial VCAM-1 (green) and E-selectin (red) expression after 4-hour perfusion of healthy control RBCs vs RBC suspensions containing varying amounts (5%, 10%, and 100%) of sRBCs. All RBC suspensions were diluted in media to a hematocrit of 25% and perfused at a constant venular shear rate. Graphical representation of mean normalized fluorescent intensity for VCAM-1 (left) and E-selectin (right), both markers of inflammation, in ECs exposed to hRBCs (red) and RBC suspensions with varying amounts of sRBCs in the straight-channel microfluidic is also shown. A total of 5 separate experiments were analyzed. VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression increased as the amount of sRBCs increased (VCAM-1, 1.35 ± 0.12 SEM [P < .05]; E-selectin, 1.29 ± 0.10 SEM [P < .05]) normalized fluorescent intensity in the 100% sRBC-exposed ECs. Because sRBCs do not represent only ISCs (ie, the least-deformable RBCs), the 5% and 10% sickle suspensions likely did not contain enough of the least-deformable RBCs to lead to increased margination compared with the 100% sRBC suspension. (E) Endothelial VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression after 4-hour perfusion of healthy control RBCs vs RBC suspensions containing varying amounts (5%, 10%, and 100%) of nystatin-treated RBCs, with mean normalized fluorescent intensity for VCAM-1 (left) and E-selectin (right) in ECs exposed to hRBCs (red) and RBC suspensions with varying amounts of nystatin-treated RBCs in the straight-channel microfluidic. A total of 5 separate experiments were analyzed. VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression in heterogeneous suspensions with a minority of less-deformable cells at 5% or 10% of the total suspension showed greater expression than the 100% low-deformability suspension (VCAM-1, 1.7 ± 0.17 SEM [P < .05]; E-selectin, 2.91 ± 1.56 SEM [P < .05] normalized fluorescent intensity highest in 10% nystatin-treated RBC-exposed ECs), supporting our hypothesis that when the less-deformable cells are a minority subpopulation, there is increased margination and RBC-EC interactions and subsequent dysfunction. Statistical analyses using a Mann-Whitney U test; ∗P ≤ .05. Error bars represent SEM.
Next, ECs were exposed to hRBCs and sRBCs perfused into the same 50 μm microfluidic device, with parallel experiments completed using hRBCs and pdRBCs. (Figure 3D-E). Endothelium VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression increased as the amount of sRBCs increased, similar to what was observed in our branching microfluidic experiments. Because sRBCs were not representative of just ISCs, the binary sickle suspensions likely did not contain enough of the least-deformable RBCs to lead to increased margination compared with the 100% sRBC suspension. Alternatively, in endothelium exposed to pdRBCs in experiments designed to closely mimic the number of ISCs in SCD blood, binary suspensions with a minority of low-deformability cells showed greater VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression than both 100% hRBC and pdRBC suspensions, supporting our hypothesis and aligning with computational simulations in which there is increased margination and RBC-EC interactions when the less-deformable cells are a minority subpopulation. Although transient adhesion cannot be completely ruled out in this system, it is generally not believed to play a significant role in EC inflammation in SCD, and all RBCs were removed from the microfluidics before EC immunostaining.
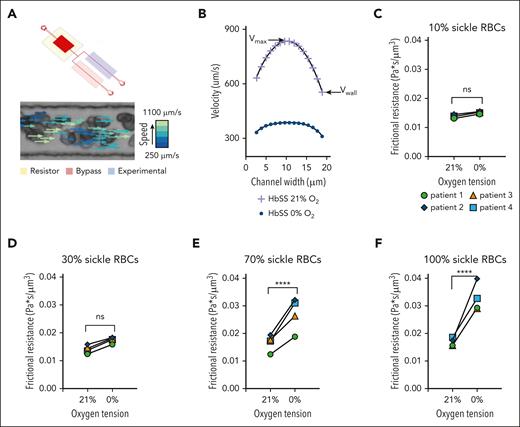
sRBCs exposed to different oxygen concentrations exhibit altered rheological properties, with changes in polymerized RBC number in specialized rheological microfluidics
RBC velocity profiles show a decrease in average velocity due to decreases in both wall velocity (Vwall) and maximum velocity (Vmax) in sRBC suspensions exposed to 21% and 0% oxygen, respectively (Figure 4B). To study the direct effect of polymerized sRBCs on bulk rheology, an exchange transfusion technique was used to compare rheological properties at 0% and 21% oxygen. Exchange transfusions of SCD blood samples were prepared to final sRBCs percentages totaling 10%, 30%, 70%, and 100%. A 100% hRBCs control showed no difference in frictional resistance at 0% oxygen (supplemental Figure 2). Using the flow profiles generated for each condition, Vwall was measured, and the frictional resistance was calculated using the known pressure drop across the length of the experimental channel (supplemental Methods). Rheological analysis for each transfusion ratio showed an increase in frictional resistance at 0% oxygen compared with 21% oxygen, indicating that the presence of sRBCs perturbs the rheology near the channel walls (Figure 4C-F). Additionally, the magnitude of the frictional resistance at 0% oxygen increased as the number of sRBCs increased, as indicated by the high transfusion ratio samples. These results couple nicely with our computational and endothelialized microfluidic data to elicit the alterations in blood flow, RBC-EC interactions, and subsequent endothelial dysfunction.
Microfluidic analysis of SCD RBC properties indicate changes in rheological properties in blood flow as the quantity of polymerized RBCs changes for both native and transfused blood. (A) The microfluidic rheology platform consists of a multilayer microfluidic device with a bifurcating blood channel designed to mimic the cross-sectional area of a small arteriole or venule as shown. The device allows for perfusion of blood at a fixed-pressure, isolated control of reduced oxygen tension to the experimental channel, as well as simultaneous measurement of RBC velocity profiles using the Kanade-Lucas-Tomasi algorithm and custom MATLAB scripts. All blood samples were prepared to a hematocrit of 25% in phosphate buffered saline. (B) RBC velocity profiles for 1 blood sample of a patient with SCD subjected to 21% oxygen and 0% oxygen showed a decrease in average velocity while demonstrating decreases in both the wall velocity (Vwall) and the max velocity (Vmax). (C-F) The direct effect of polymerized sRBCs on bulk rheology is determined using an exchange transfusion technique and measuring rheological properties at 0% oxygen and comparing with the 21% oxygen condition immediately before cycling oxygen off. Exchange transfusions of SCD blood samples are prepared ex vivo at ratios of 10%, 30%, 70%, and 100% SCD blood. Rheological analysis shows an increase in the frictional resistance for each condition indicating that the presence of sickled RBCs impedes flow near the channel walls. Statistical analyses used Welch t test; ∗P ≤ .05; ∗∗P ≤ .01; ∗∗∗P ≤ .001; ∗∗∗∗P ≤ .0001. ns, not significant.
Microfluidic analysis of SCD RBC properties indicate changes in rheological properties in blood flow as the quantity of polymerized RBCs changes for both native and transfused blood. (A) The microfluidic rheology platform consists of a multilayer microfluidic device with a bifurcating blood channel designed to mimic the cross-sectional area of a small arteriole or venule as shown. The device allows for perfusion of blood at a fixed-pressure, isolated control of reduced oxygen tension to the experimental channel, as well as simultaneous measurement of RBC velocity profiles using the Kanade-Lucas-Tomasi algorithm and custom MATLAB scripts. All blood samples were prepared to a hematocrit of 25% in phosphate buffered saline. (B) RBC velocity profiles for 1 blood sample of a patient with SCD subjected to 21% oxygen and 0% oxygen showed a decrease in average velocity while demonstrating decreases in both the wall velocity (Vwall) and the max velocity (Vmax). (C-F) The direct effect of polymerized sRBCs on bulk rheology is determined using an exchange transfusion technique and measuring rheological properties at 0% oxygen and comparing with the 21% oxygen condition immediately before cycling oxygen off. Exchange transfusions of SCD blood samples are prepared ex vivo at ratios of 10%, 30%, 70%, and 100% SCD blood. Rheological analysis shows an increase in the frictional resistance for each condition indicating that the presence of sickled RBCs impedes flow near the channel walls. Statistical analyses used Welch t test; ∗P ≤ .05; ∗∗P ≤ .01; ∗∗∗P ≤ .001; ∗∗∗∗P ≤ .0001. ns, not significant.
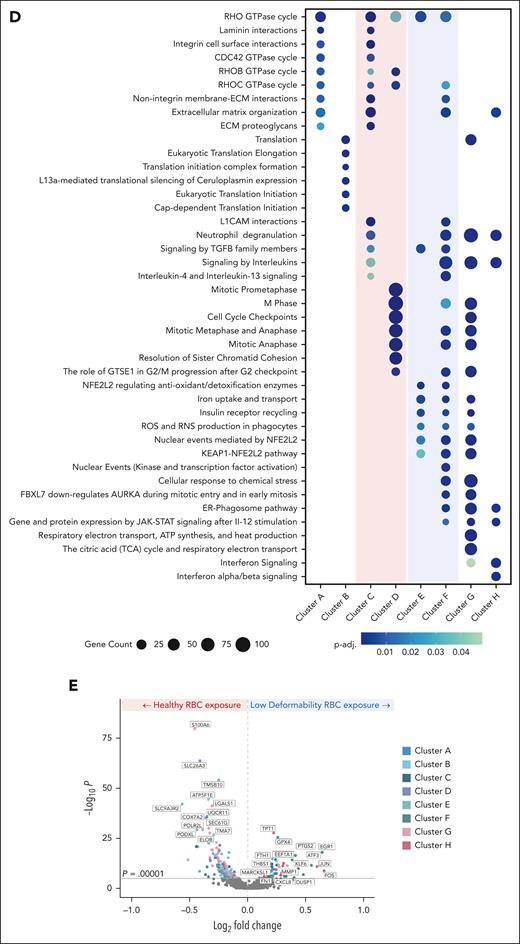
scRNA-seq reveals changes in the transcriptome of ECs exposed to heterogeneous RBC suspensions with a subpopulation of pdRBCs
To determine the effect of less-deformable RBCs on gene expression, scRNA-seq data were generated from ECs after exposure to hRBCs or binary suspensions of hRBCs with a small subpopulation of pdRBCs. Clustering of the hRBCs and pdRBC-exposed ECs based on transcriptomic profiles resulted in 8 distinct clusters visualized by uniform manifold approximation and projection (Figure 5A). ECs exposed to binary suspensions showed reduced proportions of clusters C and D and increased proportions of clusters E and F compared with hRBC-exposed ECs (Figure 5B). Top markers associated with each cluster (Figure 5C) showed hRBC-enriched clusters display upregulation of genes associated with cellular proliferation and migration. In contrast, pdRBC-exposed ECs demonstrate an upregulation of stress response genes and key regulatory factors of endothelial activation (supplemental Results). Pathway enrichment analysis further supported these findings (Figure 5D), because hRBC-associated clusters exhibit significant enrichment (p-adj. < .05) of cellular motility and cell cycle pathways. Conversely, pdRBC-associated clusters showed significant upregulation of oxidative stress pathways, including iron uptake and ROS/reactive nitrogen species (RNS) production, as well as increased cellular activation via kinase and transcription factor activity. Lastly, to investigate which genes were driving the transcriptomic differences between hRBC- and pdRBC-exposed ECs, a volcano plot was generated (Figure 5E). Several notable genes were observed to be significantly upregulated (P < .00001) after pdRBC exposure, including known markers of endothelial activation after injury and a key regulator of endothelial remodeling in response to disturbed flow.29 Interestingly, markers of ferroptosis were also upregulated, suggesting ferroptosis may play a role in endothelial dysfunction (supplemental Results).30 These results reinforce our earlier findings that RBC deformability influences blood flow, inducing shear stress and subsequent endothelial activation via the upregulation of oxidative stress pathways and key factors involved in endothelial injury response.
scRNA-seq reveals differential EC gene expression in endothelialized microfluidic devices exposed to a heterogeneous RBC suspension with a subpopulation of less-deformable RBCs compared with a homogeneous RBC suspension of hRBCs. Using the same 50 × 100 μm microfluidic device endothelialized to confluence with human umbilical vein ECs and RBC preparations as previously described (5% nystatin-treated with 95% hRBCs compared with 100% hRBCs), RBC suspensions were again perfused for 4 hours, but after the experiment, ECs were collected and prepared for scRNA-seq. (A) Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) embedding of scRNA-seq samples consisting of high-quality ECs portioned into 8 clusters with unique transcriptomic profiles. (B) Distribution of EC clusters after healthy vs nystatin-treated, low deformability RBC exposure. After exposure to nystatin-treated RBCs, a reduction in clusters C and D with a concomitant increase in clusters E and F was observed. (C) A heat map displaying the top markers expressed within each cluster. Columns represent individual cells, grouped by clusters, and rows display individual genes with the highest differential expression within each subcluster. Color bar shows gene expression levels, with red being high and blue being low gene expression. hRBC-enriched clusters C and D display an upregulation of genes associated with cellular proliferation and migration, including FP671120 (miR-3648), COL4A1 (collagen type IV), MKI67 (Ki-67), and CKS1B (CDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 1B). In contrast, clusters E and F, associated with nystatin-treated RBC exposure, demonstrate an upregulation of stress response genes, such as SRXN1 (sulfiredoxin 1) and ERG1 (early growth response protein 1), as well as several key regulatory factors involved in endothelial activation, including ANKRD1 (cardiac ankyrin repeat protein), KLF4 (Krüppel-like factor 4), FOS, and JUN. (D) Pathways enriched in each EC cluster. Clusters C and D, which were reduced in ECs exposed to nystatin-treated RBCs, are notably enriched in cellular proliferation and motility pathways, namely those involving RHO GTPase, laminin, integrin, and ECM proteoglycans, in addition to cell cycle pathways. Clusters E and F, enriched following nystatin-treated RBC exposure, exhibited significant enrichment of cellular response and oxidative stress pathways, including iron uptake, NFE2L2 signaling, and ROS and RNS production, as well as enriched cellular response and regulatory activity via kinase and transcription factor activation pathways. (E) A volcano plot illustrating differential gene expression in ECs exposed to nystatin-treated, low-deformability RBCs vs hRBCs, in which genes upregulated after nystatin-treated RBC exposure show a positive fold change, whereas those upregulated after hRBC exposure show a negative fold change (P < .00001). Several notable genes were observed to be significantly upregulated after nystatin-treated RBC exposure such as known markers of endothelial activation after injury, including THBS1, MMP1, CXCL8, EEF1A1, KLF6, and FN1. MARCKSL1, a key regulator of endothelial remodeling in response to disturbed flows, was also found to be upregulated. Markers of ferroptosis, GPX4, ATF3, PTGS2, and FTH1 were also upregulated. ECM, extracellular matrix; GTPase, guanosine triphosphate
scRNA-seq reveals differential EC gene expression in endothelialized microfluidic devices exposed to a heterogeneous RBC suspension with a subpopulation of less-deformable RBCs compared with a homogeneous RBC suspension of hRBCs. Using the same 50 × 100 μm microfluidic device endothelialized to confluence with human umbilical vein ECs and RBC preparations as previously described (5% nystatin-treated with 95% hRBCs compared with 100% hRBCs), RBC suspensions were again perfused for 4 hours, but after the experiment, ECs were collected and prepared for scRNA-seq. (A) Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) embedding of scRNA-seq samples consisting of high-quality ECs portioned into 8 clusters with unique transcriptomic profiles. (B) Distribution of EC clusters after healthy vs nystatin-treated, low deformability RBC exposure. After exposure to nystatin-treated RBCs, a reduction in clusters C and D with a concomitant increase in clusters E and F was observed. (C) A heat map displaying the top markers expressed within each cluster. Columns represent individual cells, grouped by clusters, and rows display individual genes with the highest differential expression within each subcluster. Color bar shows gene expression levels, with red being high and blue being low gene expression. hRBC-enriched clusters C and D display an upregulation of genes associated with cellular proliferation and migration, including FP671120 (miR-3648), COL4A1 (collagen type IV), MKI67 (Ki-67), and CKS1B (CDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 1B). In contrast, clusters E and F, associated with nystatin-treated RBC exposure, demonstrate an upregulation of stress response genes, such as SRXN1 (sulfiredoxin 1) and ERG1 (early growth response protein 1), as well as several key regulatory factors involved in endothelial activation, including ANKRD1 (cardiac ankyrin repeat protein), KLF4 (Krüppel-like factor 4), FOS, and JUN. (D) Pathways enriched in each EC cluster. Clusters C and D, which were reduced in ECs exposed to nystatin-treated RBCs, are notably enriched in cellular proliferation and motility pathways, namely those involving RHO GTPase, laminin, integrin, and ECM proteoglycans, in addition to cell cycle pathways. Clusters E and F, enriched following nystatin-treated RBC exposure, exhibited significant enrichment of cellular response and oxidative stress pathways, including iron uptake, NFE2L2 signaling, and ROS and RNS production, as well as enriched cellular response and regulatory activity via kinase and transcription factor activation pathways. (E) A volcano plot illustrating differential gene expression in ECs exposed to nystatin-treated, low-deformability RBCs vs hRBCs, in which genes upregulated after nystatin-treated RBC exposure show a positive fold change, whereas those upregulated after hRBC exposure show a negative fold change (P < .00001). Several notable genes were observed to be significantly upregulated after nystatin-treated RBC exposure such as known markers of endothelial activation after injury, including THBS1, MMP1, CXCL8, EEF1A1, KLF6, and FN1. MARCKSL1, a key regulator of endothelial remodeling in response to disturbed flows, was also found to be upregulated. Markers of ferroptosis, GPX4, ATF3, PTGS2, and FTH1 were also upregulated. ECM, extracellular matrix; GTPase, guanosine triphosphate
Discussion
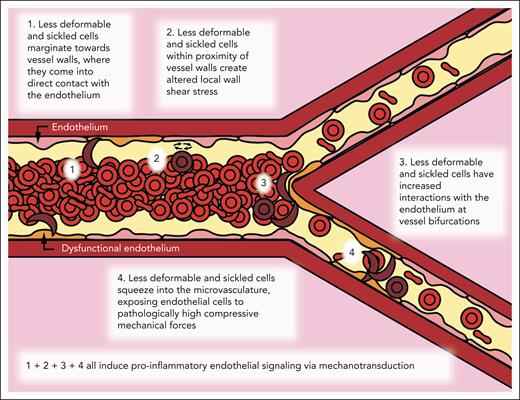
Overall, this work describes and uncovers a “missing biophysical link” in our understanding of SCD pathophysiology that explains how the decreased deformability of the sRBCs, in and of itself, can cause diffuse vascular dysfunction throughout the entire circulation via mechanobiological pathways that are completely independent of cell adhesion, hemolysis, and vaso-occlusion. Moreover, our data provide insight into how this newfound process contributes to alterations in flow within larger vessels down to the microvasculature. To the best of our knowledge, no previous studies have directly correlated the following: (1) these aforementioned processes; (2) how less-deformable RBCs can cause aberrant compressive forces in the microvasculature; (3) increased RBC margination and subsequent altered wall shear stress fluctuations in larger vessels; and (4) how all of these cause endothelial dysfunction in SCD.
Here, we leveraged a multidisciplinary approach of microfluidics, computational simulations, and scRNA-seq with sRBCs as well as pdRBCs to explore this new pathophysiologic paradigm that purely biophysical alterations of RBCs in SCD are sufficient to cause endothelial dysfunction (Figure 6). First, we leveraged small venule-mimicking microfluidic devices to explore whether less-deformable RBCs have increased interactions with the endothelium at bifurcations, leading to increased endothelial dysfunction as measured by surface expression of VCAM-1 and E-selectin.
Biophysical alterations of less-deformable and sRBCs directly induce endothelial inflammation via margination and increased RBC-endothelial interactions. Cartoon representation of our new paradigm of SCD vasculopathy, showing that when RBC suspensions are not uniform, such as in SCD, a subpopulation of the smallest and least-deformable sRBCs will tend to enter the CFL and marginate closer to vessel walls. These marginating RBCs not only come into direct contact (ie, RBC-EC collisions) with the endothelium but also create altered local wall shear stress, simply from coming into close proximity to the vessel wall, inducing endothelial inflammation via mechanobiological mechanisms. Furthermore, as these less-deformable and sRBCs flow into smaller areas of more complex geometries, such as at bifurcations, additional brief, collision-like events will occur secondary to their altered flow patterns, causing further exposure to increased mechanical forces. Finally, as sRBCs squeeze into the capillaries, ECs are exposed to pathologically increased compressive mechanical forces, which again induce a proinflammatory phenotype via mechanotransduction.
Biophysical alterations of less-deformable and sRBCs directly induce endothelial inflammation via margination and increased RBC-endothelial interactions. Cartoon representation of our new paradigm of SCD vasculopathy, showing that when RBC suspensions are not uniform, such as in SCD, a subpopulation of the smallest and least-deformable sRBCs will tend to enter the CFL and marginate closer to vessel walls. These marginating RBCs not only come into direct contact (ie, RBC-EC collisions) with the endothelium but also create altered local wall shear stress, simply from coming into close proximity to the vessel wall, inducing endothelial inflammation via mechanobiological mechanisms. Furthermore, as these less-deformable and sRBCs flow into smaller areas of more complex geometries, such as at bifurcations, additional brief, collision-like events will occur secondary to their altered flow patterns, causing further exposure to increased mechanical forces. Finally, as sRBCs squeeze into the capillaries, ECs are exposed to pathologically increased compressive mechanical forces, which again induce a proinflammatory phenotype via mechanotransduction.
Moreover, our computational simulations demonstrated that less-deformable sRBC subpopulations exhibit increased margination toward channel walls, altering the CFL and causing increased fluctuations in localized shear stress not observed in the homogeneous hRBC suspension. Additional microfluidic experiments confirmed these results using a large venule-mimicking microfluidic device. Importantly, binary suspensions with a subpopulation of pdRBCs yielded the highest VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression.
Our work was designed to isolate physical interactions by eliminating the role of biochemical ones, and a CFL remained even in the absence of aggregation, both experimentally and within our simulations. Although RBC aggregation, a complex process involving biochemical interactions mediated by plasma proteins such as fibrinogen, will influence the CFL, we demonstrate that the CFL occurs even in its absence, because the CFL and margination phenomena can arise purely from mechanical interactions between cells. The biophysical effects of RBC aggregates on endothelial dysfunction in SCD are currently being studied by our group but are beyond the scope of this paper.
Given the limited methods to measure microcirculation blood rheological parameters, we also developed a method coupling microfluidics and object-tracking technologies with mathematical modeling to separate RBC flow profiles into bulk and wall components,31 allowing for the evaluation of bulk viscosity and wall friction contributions to the overall resistance in SCD blood under a range of oxygen tensions. To explore the effect of deoxygenation, we quantified local rheological changes in sRBC suspensions such as frictional resistance, the resistance to RBC flow near channel walls. Quantifying frictional resistance is important because shear stress is highest near vessel walls, particularly in small vessels with a high surface area: volume ratio. Although the CFL lowers frictional resistance, margination of cells disrupting this layer will increase frictional resistance, resulting in an increase in overall viscosity. Additionally, artificial transfusions of sRBCs with hRBCs allowed for us to test the direct effect of polymerized sRBCs on local rheology by subjecting the sample to 0% oxygen. An increase in frictional resistance at 0% oxygen compared with 21% oxygen was observed even at modest transfusion ratios, showing the presence of small amounts of less-deformable cells disrupts flow near the wall. Furthermore, increasing the sRBC: hRBC ratio resulted in increasing frictional resistance in the deoxygenated case. Our results offer biophysical insight into the pathological role less-deformable red cells in sickle cell disease might have on endothelial dysfunction under physiological conditions and are consistent with the dose-dependent effect these cells had on endothelial activation in prior experiments.
Finally, scRNA-seq was performed on ECs exposed to hRBCs and a binary suspension with hRBCs and pdRBCs to determine whether less-deformable RBCs can induce differential gene expression. Differentially expressed genes involved in ROS, RNS, transforming growth factor beta (TGFB), and interleukin signaling were observed in ECs exposed to pdRBCs compared with hRBCs. Another interesting finding was the increase in differential gene expression of Krüppel-like factor 4 (Klf4) and Klf6 in pdRBC-exposed ECs, because the KLF family of transcription factors have both developmental and pathologic implications within the vasculature.32 Klf4 has been shown to be a regulator of endothelial activation in response to proinflammatory stimuli and shear stress,33 whereas Klf6 plays a role in vascular development, remodeling, and injury response.34 Additionally, we saw an upregulation in MARCKSL1 in pdRBC-exposed ECs, which produces an actin-binding protein responsible for modulating mechanical properties of the EC cortex to regulate cell shape and vessel structure during angiogenesis. Increased expression leads to an increase in both EC size and microvessel diameter,29 potentially explaining a mechanism of pathologic alterations of the cerebrovasculature in SCD.
Our scRNA-seq results confirm that transcription-level alterations occur in ECs when exposed to biophysically altered RBCs. Although previous studies have shown that these aforementioned pathways are involved in mechanotransduction in the context of how alterations in flow affect EC gene expression,35,36 to our knowledge, this is the first study to demonstrate that perfusion of biophysically altered RBCs also affects these pathways in ECs. These transcriptional changes explore early EC responses to biophysical RBC alterations. Further longitudinal experiments and subsequent data have the potential to yield even more meaningful results, particularly in determining which EC responses are mechanotransductive processes in direct response to aberrant physical forces.
Overall, this work helps elucidate the ubiquity of vascular dysfunction in SCD and has the potential to lead to a new paradigm of biophysical therapeutic strategies directed toward mitigating aberrant RBC margination in SCD (eg, erythrocytapheresis to intravenously remove the stiffest RBC populations). In addition to evaluating this paradigm across different flow regimes, such as in the disturbed flow of the intricate cerebral vasculature, ongoing efforts involve the development of a mouse model to study this new paradigm of how the biophysical properties of sRBCs lead to pathologic fluidic and mechanical forces that, in turn, drive SCD vasculopathy in vivo.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by an American Society of Hematology Research Training Award for Fellows, the National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI; grant T32HL139443), the Pediatric Loan Repayment Program (award L40HL149069), and the Atlanta Pediatric Scholars Program sponsored by the NIH, National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Child Health Research Career Development Award Program (grant K12HD072245 [C.C.]), NIH/NHLBI (grants R01HL140589 and R35HL145000 [W.A.L.]), and the National Science Foundation (grant CBET-2042221 [X.C. and M.D.G.]).
This work was performed in part at the Georgia Tech Institute for Matter and Systems, a member of the National Nanotechnology Coordinated Infrastructure (NNCI), which is supported by the National Science Foundation (ECCS-2025462).
Authorship
Contribution: C.C. and W.A.L. designed the study; X.C. and M.D.G. designed and created computational simulations; H.M.S. and D.K.W. designed and performed rheological microfluidic experiments; B.E.T., M.E.M., and M.B. performed single-cell RNA sequencing and its associated statistical analysis; C.C. performed microfluidic experiments; X.Z., M.E.F., R.G.M., Y.S., and D.R.M. designed and performed preliminary experiments; W.L. and C.H.J. developed and helped perform nystatin treatment of red blood cells; C.C., X.C., H.M.S., M.E.M., and B.E.T. performed data analysis; C.C. wrote the manuscript; all authors reviewed and edited the manuscript; and M.B., M.D.G., and W.A.L. oversaw the project.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Wilbur A. Lam, Emory University School of Medicine, Department of Pediatrics, 2015 Uppergate Dr, Atlanta, GA 30322; email: wilbur.lam@emory.edu; Michael D. Graham, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Engineering Hall Room 3010, 1415 Engineering Dr, Madison, WI 53706; email: mdgraham@wisc.edu; and Manoj Bhasin, Emory University School of Medicine, Department of Pediatrics, 1760 Haygood Dr, Atlanta, GA 30322; email: manoj.bhasin@emory.edu.
References
Author notes
Data are now available on the Gene Expression Omnibus (accession number GSE274340; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE274340).
Original data are available on request from the corresponding author, Wilbur A. Lam (wilbur.lam@emory.edu).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

![ECs exposed to pdRBCs and sRBCs demonstrate increased endothelial inflammation within the smallest channels and at bifurcations in microfluidic devices mimicking small venules. (A) Macroscopic view of a microfluidic device designed to mimic a small-medium venule, in which the smallest channels are ∼30 μm in diameter. (B) Brightfield microscopy image at 10× original magnification of the initial branchpoint of our small-medium venule-mimicking microfluidic device endothelialized to confluence with human umbilical vein ECs. (C) Endothelial VCAM-1 (green) and E-selectin (red) expression in the first branchpoint of the microfluidic device after 4-hour perfusion of healthy control RBCs vs RBC suspensions containing varying amounts (5%, 10%, and 100%) of sRBCs (left) and nystatin-treated, less-deformable RBCs (right). All RBC suspensions were diluted in media to a hematocrit of 25% and perfused at a constant venular shear rate. (D) Graphical representation of mean normalized fluorescent intensity for VCAM-1 and E-selectin, both markers of inflammation, in ECs exposed to hRBCs (red) and RBC suspensions with varying amounts of sRBCs (left) and nystatin-treated, less-deformable RBCs (right) at the initial branchpoint shown. A total of 5 separate experiments were analyzed. VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression increased as the number of sickled RBCs increased. In the experiments using nystatin-treated RBCs, VCAM-1 and E-selectin had a statistically significant increase in expression as the number of less-deformable cells increased (VCAM-1 2.29 ± 0.46 standard error of the mean [SEM; P < .05]; E-selectin 1.7 ± 0.16 SEM [P < .05]) normalized fluorescent intensity in ECs exposed to 100% nystatin-treated RBCs), indicating that increased RBC-EC interactions occur at vessel branchpoints in the presence of less-deformable RBCs, which also exert increased compressive mechanical forces against the endothelium in the smallest vessels. Statistical analyses using a Mann-Whitney U test; ∗P ≤ .05. Error bars represent SEM.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/144/19/10.1182_blood.2024024608/2/m_blood_bld-2024-024608-gr1.jpeg?Expires=1769084411&Signature=uqIr3qKJjUYfmMmsU14dWnlD9Tc6v6k0OmsZpygxKj-SOZOtLD2h5t4TUN-U9bW~TNo7fRrunnv0vjm6srrHh8BBJBpzGJ847jwJDPtdVMTj5BCK-S~A9ZYpallNLLQ5Ov~~ujjdzoVLDCGInAmGrfuHDzUgysLHh3R7APdhopWIb4Je0-DBqpSBlLWwhbv5B1L7HbJZqFvK2pjCc3PkCCO4NdFREt6HAGZ-m5PrELB2U1mD6ddpiMzTYvhqZCnhpdFGfx-fOPT3~ZZcSkI-Ath3WxbaAbmojxTyDhNAoaACyja59K6IZWLLeQptXm340P3JnNV3wgWjcsyYd0oDjA__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)

![Heterogeneous suspensions containing pdRBCs and sRBCs exhibit margination toward vessel walls leading to increased endothelial dysfunction in large venule-mimicking microfluidic systems. (A) Macroscopic view of a 50 × 100 μm straight-channel microfluidic device designed to mimic a large venule. (B) Cartoon depiction of our microfluidic experimental setup and corresponding video snapshot of a superposition of brightfield and fluorescence microscopy images of an RBC suspension comprising 5% pharmacologically dehydrated, less-deformable RBCs (stained with octadecyl rhodamine B chloride [R18] stain) and 95% hRBCs flowing through a straight microfluidic channel with a diameter of 100 μm at a constant flow rate. R18-stained RBCs traveling close to the channel wall as well as more centrally in the channel are circled by a dashed yellow line and solid line, respectively. (C) Graphical representation of the experiment shown in panel B, comparing an RBC suspension composed of 100% hRBCs (5% RBCs stained) with an RBC suspension with a majority hRBC population (95%) with a minority less-deformable and stained RBCs (5%). Software analysis tracking of the stained RBCs was performed and showed that, compared with hRBCs, less-deformable RBCs were more likely to marginate and travel in close proximity to vessel walls. (D) Endothelial VCAM-1 (green) and E-selectin (red) expression after 4-hour perfusion of healthy control RBCs vs RBC suspensions containing varying amounts (5%, 10%, and 100%) of sRBCs. All RBC suspensions were diluted in media to a hematocrit of 25% and perfused at a constant venular shear rate. Graphical representation of mean normalized fluorescent intensity for VCAM-1 (left) and E-selectin (right), both markers of inflammation, in ECs exposed to hRBCs (red) and RBC suspensions with varying amounts of sRBCs in the straight-channel microfluidic is also shown. A total of 5 separate experiments were analyzed. VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression increased as the amount of sRBCs increased (VCAM-1, 1.35 ± 0.12 SEM [P < .05]; E-selectin, 1.29 ± 0.10 SEM [P < .05]) normalized fluorescent intensity in the 100% sRBC-exposed ECs. Because sRBCs do not represent only ISCs (ie, the least-deformable RBCs), the 5% and 10% sickle suspensions likely did not contain enough of the least-deformable RBCs to lead to increased margination compared with the 100% sRBC suspension. (E) Endothelial VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression after 4-hour perfusion of healthy control RBCs vs RBC suspensions containing varying amounts (5%, 10%, and 100%) of nystatin-treated RBCs, with mean normalized fluorescent intensity for VCAM-1 (left) and E-selectin (right) in ECs exposed to hRBCs (red) and RBC suspensions with varying amounts of nystatin-treated RBCs in the straight-channel microfluidic. A total of 5 separate experiments were analyzed. VCAM-1 and E-selectin expression in heterogeneous suspensions with a minority of less-deformable cells at 5% or 10% of the total suspension showed greater expression than the 100% low-deformability suspension (VCAM-1, 1.7 ± 0.17 SEM [P < .05]; E-selectin, 2.91 ± 1.56 SEM [P < .05] normalized fluorescent intensity highest in 10% nystatin-treated RBC-exposed ECs), supporting our hypothesis that when the less-deformable cells are a minority subpopulation, there is increased margination and RBC-EC interactions and subsequent dysfunction. Statistical analyses using a Mann-Whitney U test; ∗P ≤ .05. Error bars represent SEM.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/144/19/10.1182_blood.2024024608/2/m_blood_bld-2024-024608-gr3.jpeg?Expires=1769084411&Signature=NSfZyI~R4PBMVuLX90uEsZIUefWw9PIkoUJf2lZ2hNSAJs~vXRSvPQ4VvnYSUiVajwsFgP0vMIVjUWn0sPfUsL-U8FoCa8lf6F3wgl7OAI8E~D39YBVMDYn89JcPdjNnIarbUnt5yoD0AO3M9XaHMr8nepXLnIez7SZbBvyPKSxKnw2OheTH1CzAmD8O~nqJxBy6utdnRL-lsjqNN7jjCI--uWRponqiOFbv8XsBgw7tZmFOlsXZqeo~7lMKELgvOPVtvzZVFE3aDBfhx5TnVH1NoXP8cTEE3BQkPzd8pIQfxIT4UvDz-~xnFtv3sWLNbNG2-x47jCZpeTpGwnfQ3A__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal