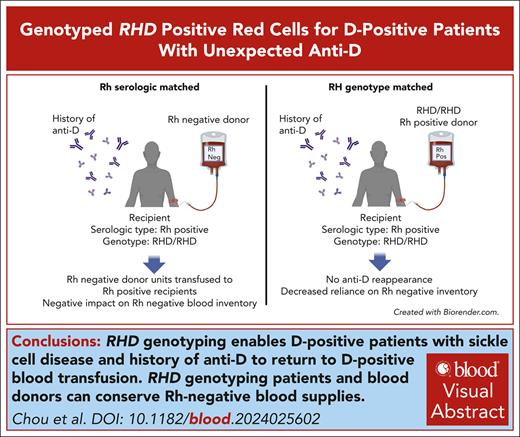
Key Points
RHD genotyping enables D-positive patients with sickle cell disease and history of anti-D to return to D-positive blood transfusion.
RHD genotyping patients and blood donors can conserve Rh-negative blood supplies.
Visual Abstract
Anti-D can occur in D-positive patients who inherit RHD genetic variants encoding partial D antigen expression, but unexpected anti-D is also found in the plasma of patients with sickle cell disease who have conventional RHD gene(s) and are transfused with units from Black donors. These anti-D are likely stimulated by variant Rh expressed on donor cells; however, patients with anti-D, regardless of cause, are transfused for a lifetime with D-negative (Rh-negative) blood. This results in significant increased use of Rh-negative units, especially for those requiring chronic transfusion, which can strain Rh-negative blood inventories. We tested whether D-positive patients who made anti-D and had conventional RhD by RHD genotyping could safely be returned to D-positive transfusions without anti-D reappearance or compromised red blood cell survival using RHD genotype-matched units from Black donors. Five patients receiving chronic red cell exchange received an increasing number of D-positive units per procedure with a total of 72 D-positive RHD genotyped units transfused, with no anti-D restimulation. Unexpected anti-C and anti-E were identified during the study associated with donors with variant RHCE alleles. RH genotyping of D-positive units for transfusion may improve use and allocation of valuable Black donor units and reduce demand for Rh-negative blood. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as NCT04156906.
Introduction
RH diversity among patients and donors contributes to Rh immunization in the population with sickle cell disease (SCD).1-4 Rh antibodies remained the most common specificities identified despite antigen matching for RhD, C, E, and K, in patients transfused with units from donors self-identifying as Black.1 Approximately 25% of anti-D were due to inheritance of RHD variants that encode partial D antigens, but the remaining anti-D were identified in the plasma of D-positive patients found to have conventional RhD by RHD genotyping.1,5 Black donors have similar RH variant gene frequencies as patients with SCD,6 suggesting that variant Rh protein(s) expressed on donor red blood cells (RBCs) likely stimulated the unexpected anti-D, and these are mimicking or cross-reactive antibodies.2,6-8 These unexpected anti-D may represent a broad immune response to a D-like structural epitope or conformation on the donor RBCs, resulting from an altered Rh protein in the Rh-membrane complex. The antibody is typically detectable in the plasma for only a few months.5 However, once anti-D is identified, patients are transfused with D-negative (Rh-negative) units for a lifetime. When RHD genotyping reveals the patient has conventional RHD, patients theoretically should be able to be returned to a D-positive transfusion protocol. The concern is that D-positive transfusions might reexpose the patient to the Rh variant that elicited the initial antibody production, with potential for a secondary response with uncertain immune consequences. Given the impact on national and our local Rh-negative blood inventories, we tested whether D-positive units could again be transfused to these patients in lieu of Rh-negative RBCs without anti-D reappearance or compromised cell survival using RHD genotyped units that encode conventional RhD to avoid variant RHD.
Study design
We performed an institutional review board–approved study to transfuse D-positive RHD genotyped units from donors self-identifying as Black to 5 D-positive patients who had conventional RHD alleles and had previously demonstrated anti-D (clinicaltrials.govNCT04156906). Eligible patients were those on a chronic red cell exchange (RCE) program from October 2021 to March 2024, had been RHD genotyped, and had conventional RHD alleles, and no longer demonstrated anti-D in their plasma for at least 6 months. Each subject received 1 D-positive RHD genotyped unit for 2 consecutive RCEs (remaining units were Rh negative) increasing by 1 D-positive unit at each subsequent visit until all units required for RCE were D positive (Figure 1A). A complete blood cell count, hemoglobin (Hb) quantification, and antibody test were performed within 3 days before each RCE visit and 5 to 12 days post-RCE with the addition of a comprehensive metabolic panel (supplemental Methods [available on the Blood website]).
Reexposure to D-positive RHD genotyped units in D-positive chronically transfused patients with conventional RHD and unexpected anti-D. (A) All participants received 1 D-positive RHD genotyped unit for their first 2 study visits, and the remainder of units required for the RCE were Rh negative. For each subsequent visit, we added 1 D-positive RHD genotyped unit until all units for the RCE were D positive. Study subjects returned 5 to 12 days post-RCE for a complete blood cell count, hemoglobin quantification, antibody test, and comprehensive metabolic panel. (B) For each study subject (RH genotype indicated under their study unique patient identification [UPID]), the number of units with only conventional RHD alleles, heterozygous RHD/RHD∗DAU0, homozygous RHD∗DAU0, or Rh negative is indicated. At visit 5 for UPID 145, 1 of 4 D-positive genotyped units demonstrated incompatibility; 1 Rh-negative unit was substituted for transfusion. Genotyping of the incompatible D-positive unit revealed the donor was Lu14+, which UPID 35 was immunized against.
Reexposure to D-positive RHD genotyped units in D-positive chronically transfused patients with conventional RHD and unexpected anti-D. (A) All participants received 1 D-positive RHD genotyped unit for their first 2 study visits, and the remainder of units required for the RCE were Rh negative. For each subsequent visit, we added 1 D-positive RHD genotyped unit until all units for the RCE were D positive. Study subjects returned 5 to 12 days post-RCE for a complete blood cell count, hemoglobin quantification, antibody test, and comprehensive metabolic panel. (B) For each study subject (RH genotype indicated under their study unique patient identification [UPID]), the number of units with only conventional RHD alleles, heterozygous RHD/RHD∗DAU0, homozygous RHD∗DAU0, or Rh negative is indicated. At visit 5 for UPID 145, 1 of 4 D-positive genotyped units demonstrated incompatibility; 1 Rh-negative unit was substituted for transfusion. Genotyping of the incompatible D-positive unit revealed the donor was Lu14+, which UPID 35 was immunized against.
Units from D-positive donors self-identifying as Black or Hispanic were genotyped by HEA Beadchip (Werfen, Warren, NJ) and laboratory-developed RH assays (supplemental Figure 1; supplemental Methods), including RHD and RHCE BeadChip arrays, as previously described.1,5 Although most RHD variants found in Black patients result in partial antigen expression, RHD∗DAU0 (RHD∗10.00) encoding 1 amino acid change (p.Thr379Met) does not result in loss or alteration of clinically relevant epitopes and has a frequency of 16% in African-American Black patients.6,9 In the absence of any reported clinical relevance, we considered RHD (RHD∗01) and RHD∗DAU0 as equivalent. Patients and donors associated with a new Rh antibody detected during the study, as well as Rh-negative donors, were retrospectively RH gene sequenced with targeted next-generation sequencing (Illumina), according to Stef et al, and analyzed with custom-developed software.10
The study was performed with approval from the institutional review board at the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
Results and discussion
Five adult patients with SCD with conventional RHD and a history of anti-D receiving chronic RCE participated in the study (Table 1). Anti-D was identified after patients had received between 42 and 341 D-positive units and was detectable in the patient’s plasma for 1 to 5 months. Following anti-D identification, 3579 Rh-negative units had been transfused to these 5 individuals before study entry. All participants received 1 D-positive RHD genotyped unit for their first 2 visits. For each subsequent visit, we added 1 RHD genotyped unit until all units required for RCE were D positive, with a maximum of 6 units at visit 7 for unique patient identification (UPID) 326. A total of 11 to 22 D-positive units were transfused to each subject during the study period (Figure 1B).
Study participant demographics, RH genotype, and alloimmunization history
| ID . | Age, y . | Sex . | Race . | ABO . | RHD alleles . | RHCE alleles . | Anti-D detection (months detected) . | Other antibodies . | No. of D+ units transfused before anti-D . | No. of D- units transfused following anti-D . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | 23 | M | Black | B | ∗RHD/∗RHD | ∗ce/∗cE | 2003 (5 mo) | 67 | 569 | |
| 35 | 36 | F | Black | A | ∗RHD/∗RHD | ∗ce/∗ceVS.02 | 2001 (1 mo) | -C∗ | 219 | 1431 |
| 145 | 26 | F | Black | O | ∗RHD/∗RHD | ∗Ce/∗ceVS.01 | 2011 (1 mo) | -Jsa -Lu14 | 42 | 818 |
| 326 | 20 | M | Hispanic | O | ∗RHD/∗Deleted D | ∗Ce/∗ce | 2013 (2 mo) | -Goa -Kpa -He -Lsa | 98 | 693 |
| 183 | 18 | M | Black | B | ∗RHD/∗DAU0 | ∗Ce/∗ce.01 | 2023 (1 mo) | 341 | 68 |
| ID . | Age, y . | Sex . | Race . | ABO . | RHD alleles . | RHCE alleles . | Anti-D detection (months detected) . | Other antibodies . | No. of D+ units transfused before anti-D . | No. of D- units transfused following anti-D . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | 23 | M | Black | B | ∗RHD/∗RHD | ∗ce/∗cE | 2003 (5 mo) | 67 | 569 | |
| 35 | 36 | F | Black | A | ∗RHD/∗RHD | ∗ce/∗ceVS.02 | 2001 (1 mo) | -C∗ | 219 | 1431 |
| 145 | 26 | F | Black | O | ∗RHD/∗RHD | ∗Ce/∗ceVS.01 | 2011 (1 mo) | -Jsa -Lu14 | 42 | 818 |
| 326 | 20 | M | Hispanic | O | ∗RHD/∗Deleted D | ∗Ce/∗ce | 2013 (2 mo) | -Goa -Kpa -He -Lsa | 98 | 693 |
| 183 | 18 | M | Black | B | ∗RHD/∗DAU0 | ∗Ce/∗ce.01 | 2023 (1 mo) | 341 | 68 |
RHCE∗ce.01 = ∗ce48C.
RHCE∗ceVS.01 = ∗ce733G.
RHCE∗ceVS.02 = ∗ce48C, 733G.
F, female; ID, identifier; M, male.
Apparent anti-C.
Seventy-two D-positive RHD genotyped Black and Hispanic donor units were transfused; 62 donors had conventional RHD, 5 were heterozygous RHD/RHD∗DAU0, and 5 were homozygous RHD∗DAU0 (Figure 1B). Overall, use of RHD genotyped units did not result in patients receiving older units (Figure 2A). Compared with units transfused in the preceding 6 RCEs before study entry, there was no difference by analysis of variance in the age of the Rh-negative units transfused before or on study, or D-positive RHD genotyped units (18 vs 16 vs 17 days; Figure 2A). On an individual basis, there was a significant difference for units transfused to UPID 326: on average, D-positive RHD genotyped units were 4 days older than Rh-negative units on study, and prestudy Rh-negative units were 3 days older than D- units on study.
No difference in age of units transfused and pretransfusion Hb or HbS level. (A) There was no difference by analysis of variance in the age of the units transfused that were prestudy Rh negative, on-study Rh negative, or D-positive RHD genotyped on study (18 vs 16 vs 17 days). (B) There was no significant difference between average pretransfusion levels of Hb or (C) HbS level before and on study. Dots represent individual unit or laboratory values, and the dots connected by lines represent the average for each study subject in A-C.
No difference in age of units transfused and pretransfusion Hb or HbS level. (A) There was no difference by analysis of variance in the age of the units transfused that were prestudy Rh negative, on-study Rh negative, or D-positive RHD genotyped on study (18 vs 16 vs 17 days). (B) There was no significant difference between average pretransfusion levels of Hb or (C) HbS level before and on study. Dots represent individual unit or laboratory values, and the dots connected by lines represent the average for each study subject in A-C.
Transfusion of D-positive RHD genotyped RBCs did not result in reappearance of anti-D. Unexpectedly, anti-E and anti-C were identified in UPIDs 18 and 183, who are E positive and C positive, respectively, and did not have variant RHCE alleles. On visit 5, UPID 18 had a mildly elevated HbS of 55% from expected <50%, and a decreased Hb of 9.2 g/dL from expected 11 g/dL; the antibody screen and direct antiglobulin test (DAT) were negative, and crossmatching with segments from units transfused at prior visit 4 with both pretransfusion plasma from visits 4 and 5 was compatible (supplemental Table 1). RCE was performed with 4 compatible D-positive RHD genotyped units from 2 homozygous DcE donors (double red, ie, 2-unit donation); the HbS was 29.7% immediately post-RCE. Seven days later, the HbS had increased to 49.7% (Hb, 9.7 g/dL), suggesting accelerated hemolysis of transfused red cells. Reference laboratory evaluation revealed anti-E only detectable by IgG gel using enzyme-treated cells and possible anti-Jkb with 5 of the 8 units from visits 4 and 5 being Jkb positive in this Jkb negative patient. To investigate a cause for anti-E reactivity, RH sequencing was performed on the patient and all units transfused on study, with the exception of 1 not available (supplemental Table 1). One D-positive donor from visit 1 has a novel change in RHCE∗cE, c.197C>G (p.Thr66Ser), suggesting this new RhcE variant was potentially the stimulus for anti-E reactivity.
On visit 4 for UPID 183, his DAT was positive, and the plasma demonstrated anti-C and was incompatible with a C-positive RHD genotyped unit scheduled for transfusion; 1 Rh-negative unit lacking C was substituted (Figure 1B; supplemental Table 2). His Hb and HbS levels were consistent with his typical pretransfusion levels. Reference laboratory evaluation confirmed weak reactivity with all C-positive reagent cells tested and his autologous RBCs after hypotonic saline wash. RH sequencing of samples from all on-study units and the patient found no RHCE∗Ce variants. Two units with variant RHCE∗ceAG (∗ce.06.01) were transfused at visit 1, suggesting this RHCE variant may have been the stimulus for the apparent anti-C.
To assess transfusion red cell outcome, the average pretransfusion Hb and HbS for the 6 RCEs before study enrollment were compared with the values measured on study for each patient (Figure 2B-C). Overall, there was no significant difference between average levels of Hb or HbS before and on study (estimated difference on and before study for Hb: −0.03 [95% confidence interval, −0.27 to 0.20], and HbS: −0.1 [95% confidence interval, −1.8 to 1.6]). The mean pretransfusion Hb for the 5 patients ranged from 9.4 to 11.5 g/dL before study and from 9.2 to 11.5 g/dL on study (Figure 2B). The mean pretransfusion HbS ranged from 29.6% to 47.9% before study and from 31.5% to 51.8% on study (Figure 2C). Individual comparisons of before and on-study levels of total Hb and HbS showed no differences except for UPID 326; UPID 326 had an on-study mean pretransfusion HbS 5% lower than the prestudy mean level.
Anti-D occurs in D-positive patients with SCD who have normal/conventional RHD alleles despite providing prophylactic serologic Rh (D, C, and E) and K-matched RBCs when transfused with primarily Black donors.1,5,6 Providing Rh-negative units for subsequent transfusion can negatively impact the Rh-negative blood inventory. We show here that transfusion of D-positive RHD genotyped units from American Black and Hispanic donors to D-positive patients with conventional RHD and a history of unexpected anti-D was safe and efficacious and did not stimulate anti-D reappearance using RHD genotyped donors to avoid exposure to variant RHD. Unexpected anti-C and anti-E were encountered in 2 patients with conventional RHCE∗Ce and conventional RHCE∗cE, respectively. Look-back investigation implicated transfusion from donors with variant RHCE alleles, supporting the hypothesis that variant RH in donors is responsible for unexpected Rh antibodies that complicate transfusion in patients with SCD,7 and underscoring the need for a transfusion strategy that includes both RHD and RHCE genotype matching. Limitations of this study include the small sample size, the short follow-up period, a relatively low number of D-positive unit exposures per individual, and the focus on American Black and Hispanic donors and patients. Future studies should address strategies for cost-effective and comprehensive RH genotyping for both patients and donors to determine if all Rh alloimmunization can be avoided.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patients who enrolled in the study, blood donors, and members of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Blood Bank and Apheresis Service and the New York Blood Center Immunohematology Laboratory who contributed to the study.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute HL147879 (S.T.C., C.M.W., and D.F.F.), HL134696 (S.T.C. and C.M.W.), and HL169401 (S.T.C., C.M.W., and D.F.F.), and a Distinguished Chair in Pediatrics (S.T.C.).
Authorship
Contribution: J.M., S.V., D.F.F., S.M., G.O., and C.M.W. performed the research, analyzed the data, and edited the manuscript; V.L. performed all statistical analysis; and S.T.C. designed the research study, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Stella T. Chou, 3615 Civic Center Boulevard, Abramson Research Building Room 316D, Philadelphia, PA 19104; email: chous@chop.edu.
References
Author notes
Data are available on request from the corresponding author, Stella T. Chou (chous@chop.edu).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

![Reexposure to D-positive RHD genotyped units in D-positive chronically transfused patients with conventional RHD and unexpected anti-D. (A) All participants received 1 D-positive RHD genotyped unit for their first 2 study visits, and the remainder of units required for the RCE were Rh negative. For each subsequent visit, we added 1 D-positive RHD genotyped unit until all units for the RCE were D positive. Study subjects returned 5 to 12 days post-RCE for a complete blood cell count, hemoglobin quantification, antibody test, and comprehensive metabolic panel. (B) For each study subject (RH genotype indicated under their study unique patient identification [UPID]), the number of units with only conventional RHD alleles, heterozygous RHD/RHD∗DAU0, homozygous RHD∗DAU0, or Rh negative is indicated. At visit 5 for UPID 145, 1 of 4 D-positive genotyped units demonstrated incompatibility; 1 Rh-negative unit was substituted for transfusion. Genotyping of the incompatible D-positive unit revealed the donor was Lu14+, which UPID 35 was immunized against.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/144/19/10.1182_blood.2024025602/2/m_blood_bld-2024-025602-gr1.jpeg?Expires=1767703335&Signature=npE6ypReDOrkgqpHUUW6jBFVYO4QYurR7jtiseP-7xc0sE0OtZKJc-DfMaxWnGlbeEBp5uuewi2GfdHYGZQ1xmHtCYgwoPrRYzIhxQzNnuaxv0k0WcPoPvknL2pj0hVGIP1ifkIzYGAnSQaBzbbymXHqJwHpCAH2mSJPvnViHE0cyuCSBPgJdXv0E49xK4gWF0pw6neI72Y-umKyr77ArAv7VzpOnazZcEZDTVhHlZtv4r2v8~eWuT4edjJ-61TgStG0KEJg6kStXn-8I3o~uRi6A6c1fMD9No1axP6L9JorWQFrFML3j5l7fNMosd7D3JV~r3o6lO-q037xJwPipQ__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal