Key Points
SCI is common in iTTP in clinical remission.
SCI is associated with mild and major cognitive impairment independent of stroke history and depression.
Abstract
Immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (iTTP) survivors have increased risk of cardiovascular disease, including strokes, and report persistent cognitive difficulties during remission. We conducted this prospective study involving iTTP survivors during clinical remission to determine the prevalence of silent cerebral infarction (SCI), defined as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) evidence of brain infarction without corresponding overt neurodeficits. We also tested the hypothesis that SCI is associated with cognitive impairment, assessed using the National Institutes of Health ToolBox Cognition Battery. For cognitive assessments, we used fully corrected T scores adjusted for age, sex, race, and education. Based on the diagnostic and statistical manual 5 criteria, we defined mild and major cognitive impairment as T scores with a 1 or 2 standard deviation (SD) and >2 SD below the mean on at least 1 test, respectively. Forty-two patients were enrolled, with 36 completing MRIs. SCI was present in 50% of the patients (18), of which 8 (44.4%) had prior overt stroke including during acute iTTP. Patients with SCI had higher rates of cognitive impairment (66.7% vs 27.7%; P = .026), including major cognitive impairment (50% vs 5.6%; P = .010). In separate logistic regression models, SCI was associated with any (mild or major) cognitive impairment (odds ratio [OR] 10.5 [95% confidence interval (95% CI), 1.45-76.63]; P = .020) and major cognitive impairment (OR 7.98 [95% CI, 1.11-57.27]; P = .039) after adjusting for history of stroke and Beck depression inventory scores. MRI evidence of brain infarction is common in iTTP survivors; the strong association of SCI with impaired cognition suggests that these silent infarcts are neither silent nor innocuous.
Introduction
Immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (iTTP) is a life-threatening disorder characterized by episodes of consumptive thrombocytopenia, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia and ischemic organ injury caused by an antibody-mediated deficiency of the von Willebrand factor (VWF)–cleaving protease, ADAMTS13.1 With prompt diagnosis and treatment, survival of patients with acute iTTP episodes has improved from <10% to >95%.2,3 In addition to the risk of relapse,3,4 patients who survive iTTP are at risk for multiple long-term health consequences,5 including higher rates of chronic morbidities, such as hypertension,6 obesity,6 depression,7-9 and autoimmune disease,10 and higher than expected rates of all-cause mortality that is driven by increased cardiovascular disease.11,12 In particular, individuals with iTTP have a nearly fivefold increased risk of stroke, which is associated with inadequate recovery of ADAMTS13 activity (not achieving complete ADAMTS13 remission defined as ADAMTS13 activity at or above the lower limit of normal) during clinical remission.13 Individuals with iTTP also report high rates of cognitive impairment,8,9,14,15 which have been variably attributed to comorbid depression9 or postulated to be due to diffuse microvascular insults.14
Silent cerebral infarctions (SCIs) are lesions with an appearance typical of infarction upon magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain but occurring in the absence of neurologic deficits corresponding to the location of the lesion. SCI are reported in the general population, among whom their prevalence increases with age16 and presence of disorders, such as sickle cell disease.17,18 Although termed silent because they occur in the absence of clinically recognized stroke symptoms, silent brain infarcts are associated with cognitive decline, dementia, and increased risk of overt stroke.19-23 The association of SCI with advanced age, hypertension, and other stroke risk factors24-26 suggests that they are a precursor lesion in the spectrum of cerebrovascular disease that includes stroke. We have already shown that patients who survive iTTP are at increased risk of stroke and other major adverse cardiovascular events11,13; however, SCI has never been evaluated in this population. We conducted the prospective neurologic sequelae of iTTP (NeST) cohort study to determine the prevalence and clinical correlates of SCI in individuals with iTTP in clinical remission and to test the hypothesis that SCI is associated with cognitive impairment.
Methods
Study design
We prospectively enrolled adult patients (aged ≥18 years) with iTTP followed in the hematology clinics at Johns Hopkins University between September 2020 and December 2022. iTTP diagnosis was based on ADAMTS13 activity <10% with an anti-ADAMTS13 antibody or inhibitor during an acute episode characterized by thrombocytopenia (platelet count <100 × 109/L) and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (hemoglobin level <10 g/dL, with schistocytes documented via a blood smear). All study assessments were performed after patients had achieved a clinical remission defined as a platelet count >150 × 109/L and lactate dehydrogenase level <1.5 times the upper limit of normal for 30 days after cessation of plasma exchange or anti-VWF therapy.27 Patients in clinical remission were enrolled regardless of the ADAMTS13 remission status. The target enrollment was 40 patients, but enrollment was continued beyond 40 patients due to some patients being unable to complete MRI because of claustrophobia or anxiety. Participants undergo annual study visits that include (1) screening for stroke with the National Institutes of Health (NIH) stroke scale, (2) brain MRI, (3) NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery, and (4) Beck depression inventory II (BDI-II; see flowchart in Figure 1). The goal of conducting an MRI at the first (enrollment) visit was to determine prevalence of SCI, whereas subsequent annual MRIs are planned to evaluate whether SCIs are progressive during clinical remission. Similarly, serial assessments allow us to evaluate cognitive function changes over time. Demographic and clinical data were collected from the electronic medical record and verified through patient interviews at enrollment. All patients provided written informed consent, and the institutional review board at Johns Hopkins University approved this study.
Study procedures
Brain MRI
Brain MRI was performed at enrollment and annual follow-up using a dedicated Siemens 3T Prisma MRI scanner (Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany) at the Johns Hopkins Division of Magnetic Resonance Research. All brain MRIs included sagittal 3D T1 weighted magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition gradient echo (MPRAGE) and 3D fluid–attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequences, axial diffusion weighted images (b = 0, 1000 s/mm2), axial 3D susceptibility weighted images, and axial T2 weighted fast spin echo sequences. T1, T2, and FLAIR images were primarily used for the stratification of patients with or without SCI. Each study MRI was reviewed by a board certified neuroradiologist who was blinded to clinical, laboratory, and cognitive assessments. The study staff members who performed clinical neurologic evaluation and cognitive testing and administered patient tools or questionnaires were blinded to MRI results. An SCI was defined as an ischemic (infarct-like) lesion manifesting as a focus of T2 and FLAIR hyperintensity, visible on 2 planes, measuring any length in greatest dimension, and with no corresponding neurologic deficit (upon clinical neurologic examination and with the NIH stroke scale) according to previously published liberal definitions of SCI.28,29 Additional, unscheduled MRIs could be performed in the course of routine clinical care if patients presented with neurologic deficits. Any lesions on these “nonresearch” MRIs done for clinical neurologic deficits would not be classified as an SCI, particularly if the lesion corresponded to the presenting symptom or deficit. If additional lesions (not corresponding to a deficit) were noted and confirmed upon subsequent research MRIs, they could be classified as SCI. If clinical MRIs were performed before the research scan, the neuroradiologist reviewed both scans to identify new lesions since the previous imaging.
Cognitive assessment using the NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery
The NIH Toolbox Cognition Battery is a comprehensive, validated set of neurobehavioral measurements administered via an iPad.30 This battery tests multiple cognitive domains, including executive function (dimensional change card sort test and flanker inhibitory control and attention test), processing speed (pattern comparison test), episodic memory (picture sequence memory test), working memory (list sort working memory test), language (oral reading recognition and picture vocabulary test) (Table 1). Tests were administered in a standardized fashion by one of 3 observers (J.Y., J.B., or A.W.) in a single session lasting from 45 to 60 minutes. An advantage of the NIH Toolbox Cognition Battery is that normative data from large populations are available to provide age, sex, and education-matched control scores to reduce the potential effect of these confounders on small changes in cognitive performance. Fully corrected T scores (normative mean 50 with a standard deviation [SD] of 10) adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, and educational attainment as well as composite scores for fluid cognition, crystallized cognition, and total cognition that have excellent reliability and validity were computed for individual tests.31 Per the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fifth edition (DSM-5), criteria, mild and major cognitive impairments were defined as T scores that are 1 or 2 SDs below the mean (between the third and 16th percentiles) and >2 SDs below the mean (below the third percentile) on at least 1 test, respectively.32 Although the NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery has been extensively validated in healthy populations and various disease states, to our knowledge, it has not previously been used in iTTP. To evaluate whether cognitive deficits in the NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery correlated with patient-reported cognitive function, we additionally asked participants to complete Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) cognitive function form 8a (mean T score 50 with SD 10).
Summary of cognitive subdomains and abilities tested using the NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery
| Subdomain . | Ability tested . | Toolbox measure . |
|---|---|---|
| Executive function | Capacity to plan, organize, and monitor the execution of strategically directed behaviors | Dimensional change card sort test |
| Flanker inhibitory control and attention test | ||
| Attention | Ability to focus attention on a task | Flanker inhibitory control and attention test |
| Episodic memory | Cognitive processes involving the acquisition, storage, and retrieval of new information | Picture sequence memory test |
| Processing speed | Amount of time it takes to process a set amount of information | Pattern comparison processing speed test |
| Working memory | Ability to store, process, and manipulate information across a series of tasks and modalities over a limited period of time (similar to shirt-term memory) | List-sorting working memory test |
| Language | Mental processes that translate thought into symbols (ie, words and gestures) that can be shared as a means of communication | Picture vocabulary test |
| Oral reading recognition test |
| Subdomain . | Ability tested . | Toolbox measure . |
|---|---|---|
| Executive function | Capacity to plan, organize, and monitor the execution of strategically directed behaviors | Dimensional change card sort test |
| Flanker inhibitory control and attention test | ||
| Attention | Ability to focus attention on a task | Flanker inhibitory control and attention test |
| Episodic memory | Cognitive processes involving the acquisition, storage, and retrieval of new information | Picture sequence memory test |
| Processing speed | Amount of time it takes to process a set amount of information | Pattern comparison processing speed test |
| Working memory | Ability to store, process, and manipulate information across a series of tasks and modalities over a limited period of time (similar to shirt-term memory) | List-sorting working memory test |
| Language | Mental processes that translate thought into symbols (ie, words and gestures) that can be shared as a means of communication | Picture vocabulary test |
| Oral reading recognition test |
BDI-II
The BDI-II is an extensively validated, self-administered depression screening tool. It includes 21 items, each scored on a 4-point Likert scale ranging from 0 to 3, with higher scores indicating worse symptoms. The total BDI-II score was interpreted as follows: absent/minimal depression, 0 to 13; mild depression, 14 to 19; moderate depression, 20 to 28; and severe depression, 29 to 63. At a cutoff of ≥14, the BDI-II detects depression with a sensitivity between 87.7% and 92% and specificity between 74% and 83%.33
Data management
We extracted data from the electronic medical record, including patient demographics, details of iTTP presentation, diagnosis and treatment, and the presence of comorbidities, including hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity (defined as body mass index >30 kg/m2), hyperlipidemia, atrial fibrillation, congestive heart failure, smoking, chronic kidney disease (defined as a glomerular filtration rate <60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 persisting over at least 3 months), systemic lupus erythematosus, and other autoimmune diseases. These data were verified through patient interviews at enrollment. All data were managed using RedCap.
Data analysis
Data were summarized as counts and percentages and medians and interquartile range (IQR, representing the 25th-75th percentiles [Q25%-75%]) for categorical and continuous variables, respectively. Logistic regression was used to identify clinical factors associated with SCI. Mean NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery scores were compared with population-normed scores using a single sided T test. Scores on individual cognition tests and composite cognition scores between patients with and without SCI were compared using the Wilcoxon rank sum test. The association of mild and major cognitive impairment with SCI was first evaluated using the χ2 test and then in multivariable logistic regression models adjusted for age, lifetime history of overt stroke, and BDI-II scores for depression. Finally, we compared BDI-II scores of patients with and without SCI using the Wilcoxon rank sum test. P < .05 was considered significant for all analyses. Analyses were performed using Stata version 17.
Results
Patients
Forty-two patients were enrolled and completed the first study visit between September 2020 and August 2022. Of these, 36 patients completed the study MRI (2 patients were excluded because of having metal shrapnel or implants, 2 were declined because of anxiety and claustrophobia, and another 2 started the scan but could not complete the MRI because of discomfort or claustrophobia). The median age of participants was 48 years (IQR, 35-56), 64.3% were female, and 66.7% self-identified as Black. The median time from iTTP diagnosis was 66.5 months (IQR, 20.3-109.8), and 23.8% had history of previous stroke (including 14.3% who had stroke during acute iTTP episodes). Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with and without SCI were similar and are summarized in Table 2.
Demographics and clinical characteristics of patients with and without SCI
| Variable . | Total cohort (N = 42) . | No SCI∗ (N = 18) . | SCI∗ (N = 18) . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y), median (IQR) | 48 (34-56) | 46.0 (27.3-49.5) | 49 (37.8-61.0) | .091 |
| Female sex, N (%) | 27 (64.3) | 14 (77.8) | 13 (72.2) | .700 |
| Race, all N (%) | .198 | |||
| White | 6 (14.3) | 5 (27.8) | 1 (5.6) | |
| Black | 28 (66.7) | 12 (66.7) | 16 (88.9) | |
| Other | 2 (4.8) | 1 (5.6) | 1 (5.6) | |
| Stroke during acute iTTP, N (%) | 6 (14.3) | 3 (16.7) | 3 (16.7) | 1.000 |
| Total number of iTTP episodes, median (IQR) | 2 (1-3) | 2 (1-3) | 2 (1-5) | .462 |
| Time from iTTP diagnosis (mo), median (IQR) | 66 (18-111) | 18 (5-89) | 73.0 (44-130) | .027 |
| Average ADAMTS13 activity over past 12 mo (%), mean (SD) | 64.18 (26.18) (N = 37) | 77.61 (24.64) N = 15 | 51.28 (25.51) (N = 15) | .007 |
| Current aspirin therapy, N (%) | 14 (34.15) | 4 (22.2) | 8 (44.4) | .157 |
| Hypertension, N (%) | 14 (33.3) | 6 (33.3) | 8 (44.4) | .494 |
| Diabetes mellitus, N (%) | 7 (16.7) | 3 (16.7) | 4 (22.2) | .674 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 8 (19.0) | 3 (16.7) | 4 (22.2) | .674 |
| Smoking (ever), N (%) | 4 (9.5) | 2 (11.1) | 2 (11.1) | 1.000 |
| CKD, N (%) | 5 (11.9) | 3 (16.7) | 2 (11.1) | .630 |
| HIV, N (%) | 1 (2.4) | 1 (5.6) | 0 (0.0) | .310 |
| Stroke (lifetime), N (%) | 10 (23.8) | 2 (11.1) | 8 (44.4) | .026∗ |
| Variable . | Total cohort (N = 42) . | No SCI∗ (N = 18) . | SCI∗ (N = 18) . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y), median (IQR) | 48 (34-56) | 46.0 (27.3-49.5) | 49 (37.8-61.0) | .091 |
| Female sex, N (%) | 27 (64.3) | 14 (77.8) | 13 (72.2) | .700 |
| Race, all N (%) | .198 | |||
| White | 6 (14.3) | 5 (27.8) | 1 (5.6) | |
| Black | 28 (66.7) | 12 (66.7) | 16 (88.9) | |
| Other | 2 (4.8) | 1 (5.6) | 1 (5.6) | |
| Stroke during acute iTTP, N (%) | 6 (14.3) | 3 (16.7) | 3 (16.7) | 1.000 |
| Total number of iTTP episodes, median (IQR) | 2 (1-3) | 2 (1-3) | 2 (1-5) | .462 |
| Time from iTTP diagnosis (mo), median (IQR) | 66 (18-111) | 18 (5-89) | 73.0 (44-130) | .027 |
| Average ADAMTS13 activity over past 12 mo (%), mean (SD) | 64.18 (26.18) (N = 37) | 77.61 (24.64) N = 15 | 51.28 (25.51) (N = 15) | .007 |
| Current aspirin therapy, N (%) | 14 (34.15) | 4 (22.2) | 8 (44.4) | .157 |
| Hypertension, N (%) | 14 (33.3) | 6 (33.3) | 8 (44.4) | .494 |
| Diabetes mellitus, N (%) | 7 (16.7) | 3 (16.7) | 4 (22.2) | .674 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 8 (19.0) | 3 (16.7) | 4 (22.2) | .674 |
| Smoking (ever), N (%) | 4 (9.5) | 2 (11.1) | 2 (11.1) | 1.000 |
| CKD, N (%) | 5 (11.9) | 3 (16.7) | 2 (11.1) | .630 |
| HIV, N (%) | 1 (2.4) | 1 (5.6) | 0 (0.0) | .310 |
| Stroke (lifetime), N (%) | 10 (23.8) | 2 (11.1) | 8 (44.4) | .026∗ |
CKD, chronic kidney disease.
SCI determination was based on brain MRI, which was completed by 36 of 42 patients.
Brain MRI findings and the prevalence and predictors of SCI in iTTP remission
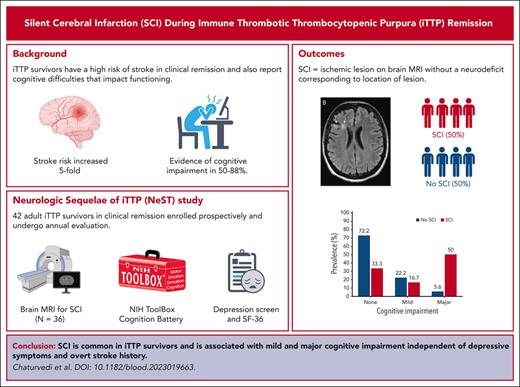
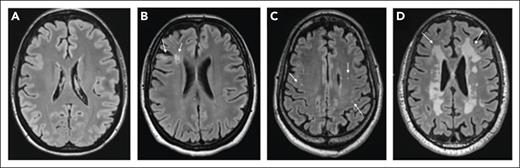
SCI were observed in 18 of 36 (50%) participants who completed the study MRI. None of the participants had a nonsilent infarct at the time of evaluation. Figure 2 shows examples of varied brain MRI findings in patients with iTTP, including normal imaging (Figure 2A), SCI manifesting as small FLAIR hyperintense lesions (>3 or 5 mm in length) involving the cortical or subcortical region and deep white matter (Figure 2B), smaller scattered punctate FLAIR hyperintense lesions in the subcortical and deep white matter attributed to nonspecific chronic small vessel ischemic changes (Figure 2D), and extensive and confluent FLAIR hyperintensity in the periventricular and deep white matter (Figure 2C). Among patients with SCI, 8 of 18 (44.4%) had a history of overt stroke, including 3 patients who had stroke during an acute iTTP episode, whereas 10 of 18 (55.6%) did not have a history of clinically overt stroke. Thus, even among some patients with a clinical history of stroke, new SCIs were detected with study MRIs. Figure 3 shows such an example of a 46-year-old woman (patient 1) who had an initial clinical MRI performed for dizziness that started during the iTTP episode but persisted for 3 months after achieving clinical remission; this MRI showed evidence of small chronic infarcts in bilateral cerebellar hemispheres. A research MRI performed 3 years later demonstrated multiple, small, chronic cortical infarcts that were new, without corresponding focal neurological deficits. She did not have any intercurrent iTTP episodes between the 2 MRIs. Her ADAMTS13 activity had been monitored every 3 months in remission and ranged from 38% to 100% (average, 72%; reference range, 70%-150%). Although she did not receive preemptive rituximab, she did receive immunosuppression for systemic lupus that might have led to improvement in ADAMTS13 activity.
Brain MRI findings in patients with iTTP (representative images). Normal MRI without ischemic findings (A), small FLAIR hyperintense foci (>3-5 mm in length, arrows) in the cortical/subcortical region and deep white matter (B), punctate FLAIR hyperintense lesions (arrows) in the white matter (C), and confluent FLAIR hyperintensity (arrows) in the periventricular and deep white matter (in a patient without overt neurologic findings) (D).
Brain MRI findings in patients with iTTP (representative images). Normal MRI without ischemic findings (A), small FLAIR hyperintense foci (>3-5 mm in length, arrows) in the cortical/subcortical region and deep white matter (B), punctate FLAIR hyperintense lesions (arrows) in the white matter (C), and confluent FLAIR hyperintensity (arrows) in the periventricular and deep white matter (in a patient without overt neurologic findings) (D).
Brain MRI findings of incident SCI since prior stroke. At baseline (top), small chronic infarcts in the cerebellar hemispheres are well depicted on T2 weighted sequences (arrows) of a MRI done in routine clinical care for dizziness persisting 3 weeks after achieving clinical remission after a first iTTP episode, which were unchanged on the follow-up research scan. At 3-year follow-up, upon the research MRI (bottom), there are multifocal new small chronic infarcts in the left parietal cortical regions seen on axial FLAIR images (arrowheads).
Brain MRI findings of incident SCI since prior stroke. At baseline (top), small chronic infarcts in the cerebellar hemispheres are well depicted on T2 weighted sequences (arrows) of a MRI done in routine clinical care for dizziness persisting 3 weeks after achieving clinical remission after a first iTTP episode, which were unchanged on the follow-up research scan. At 3-year follow-up, upon the research MRI (bottom), there are multifocal new small chronic infarcts in the left parietal cortical regions seen on axial FLAIR images (arrowheads).
Increasing age (odds ratio [OR], 1.06; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 1.01-1.13; P = .045) and history of stroke (OR, 8.32; 95% CI, 1.20-57.50; P = .032) were associated with SCI in a logistic regression model adjusted for number of iTTP episodes (OR, 1.20; 95% CI, 0.75-1.94; P = .442), and hypertension (OR, 1.13; 95% CI, 0.23-5.56; P = .876).
We did not have complete (every 3 months) remission ADAMTS13 data spanning the entire period from iTTP diagnosis to the time of research evaluations (including MRI) for all patients. However, remission ADAMTS13 data for the 12 months preceding research evaluation were available for 37 patients (including 30 who had completed MRI). As seen in Table 2, average remission ADAMTS13 activity preceding research MRI was lower in patients with SCI than in those without SCI (mean ± SD, 77.6 ± 24.64 vs 51.28 ± 25.51; P = .007). Although this does not cover the entire period of exposure, these preliminary results indicate a possible association of lower ADAMTS13 in remission with SCI.
SCI is associated with cognitive impairment in iTTP survivors
A total of 22 of 42 (52.3%) participants had cognitive impairment in at least 1 domain, among whom 10 (23.1%) had mild cognitive impairment (fully corrected T scores >1 SD and <2 SD below the normative mean) and 12 (28.57%) had major cognitive impairment (fully corrected T score >2 SD below the normative mean). Deficits were detected on tests of multiple cognitive domains; participants most commonly showed deficits on tests of executive function (38.1% on Flanker inhibitory control and attention test, 26.2% on dimensional change card sort test) and processing speed (23.8% on pattern comparison test) (Table 3). To assess whether the NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery picked up patient-reported cognitive impairment, we compared NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery scores with the scores on the (patient reported) PROMIS cognitive function 8a instrument. Overall, patients with any (mild or major) cognitive impairment on the NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery had significantly lower PROMIS cognitive function 8a scores than those with no cognitive impairment (median, 40.3 [IQR, 36.4-42.7] vs 46.2 [40.8-49.3]; P = .048), and there was a trend toward lower scores on the PROMIS cognitive function 8a instruments with increasing severity of cognitive impairment as assessed using the NIH Toolbox Cognition Battery (supplemental Figure 1, available on the Blood website); patients with no cognitive impairment on the NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery had the highest median PROMIS cognitive function 8a scores (46.2 [IQR, 44.4-51.1]), followed by patients with mild cognitive impairment (44.9 [IQR, 36.4-47.2]), and those with major cognitive impairment had the lowest scores (41.1 [IQR, 36.7-43.6]) (P for trend = .089).
Patterns of cognitive impairment in iTTP
| Test . | No cognitive impairment, % . | Mild cognitive impairment, % . | Major cognitive impairment, % . | Mean . | SD . | P∗ . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flanker inhibitory control and attention | 61.9 | 21.4 | 16.7 | 41.95 | 10.63 | <.001∗ |
| Pattern recognition | 76.2 | 16.7 | 7.1 | 53.74 | 16.11 | .140 |
| List-sorting working memory | 83.3 | 14.3 | 2.4 | 48.98 | 9.27 | .478 |
| Dimensional change card sort test | 73.8 | 21.4 | 4.8 | 50.64 | 14.74 | .779 |
| Oral reading recognition | 85.7 | 9.5 | 4.8 | 52.74 | 11.56 | .133 |
| Picture sequence memory | 85.7 | 14.3 | 0 | 51.05 | 9.79 | .492 |
| Picture vocabulary | 83.3 | 14.3 | 2.4 | 50.55 | 10.80 | .372 |
| Fluid cognition composite | 69.0 | 14.3 | 16.7 | 48.33 | 15.42 | .488 |
| Crystalized cognition composite | 85.7 | 11.9 | 2.4 | 52.19 | 10.00 | .163 |
| Total cognition composite | 76.2 | 11.9 | 11.9 | 50.05 | 13.42 | .982 |
| Test . | No cognitive impairment, % . | Mild cognitive impairment, % . | Major cognitive impairment, % . | Mean . | SD . | P∗ . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flanker inhibitory control and attention | 61.9 | 21.4 | 16.7 | 41.95 | 10.63 | <.001∗ |
| Pattern recognition | 76.2 | 16.7 | 7.1 | 53.74 | 16.11 | .140 |
| List-sorting working memory | 83.3 | 14.3 | 2.4 | 48.98 | 9.27 | .478 |
| Dimensional change card sort test | 73.8 | 21.4 | 4.8 | 50.64 | 14.74 | .779 |
| Oral reading recognition | 85.7 | 9.5 | 4.8 | 52.74 | 11.56 | .133 |
| Picture sequence memory | 85.7 | 14.3 | 0 | 51.05 | 9.79 | .492 |
| Picture vocabulary | 83.3 | 14.3 | 2.4 | 50.55 | 10.80 | .372 |
| Fluid cognition composite | 69.0 | 14.3 | 16.7 | 48.33 | 15.42 | .488 |
| Crystalized cognition composite | 85.7 | 11.9 | 2.4 | 52.19 | 10.00 | .163 |
| Total cognition composite | 76.2 | 11.9 | 11.9 | 50.05 | 13.42 | .982 |
P values are from a single sample T test comparing the distribution of the fully corrected T score (corrected for age, sex, race/ethnicity and educational attainment) to the normative population mean.
NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery scores for patients with and without SCI
| Test . | No SCI . | SCI . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|
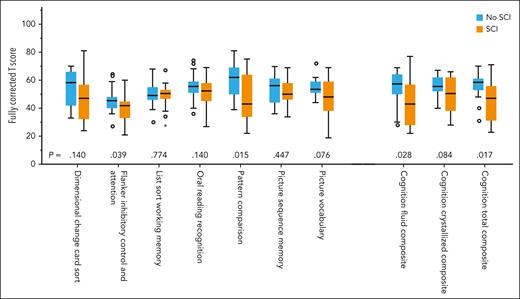
| Picture vocabulary | 53.5 (51-59) | 48 (38-59) | .076 |
| Oral reading recognition | 55.5 (51-59) | 52.5 (45-58) | .140 |
| List-sorting working memory | 49 (46-55) | 50.5 (47-53) | .774 |
| Picture sequence memory | 56 (44-61) | 50 (46-58) | .447 |
| Flanker inhibitory control and attention | 45.5 (40-48) | 42 (33-45) | .039 |
| Dimensional change cart sort test | 58.5 (42-66) | 47 (32-57) | .140 |
| Pattern recognition | 62 (50-69) | 43 (34-64) | .015 |
| Fluid cognition composite | 57.5 (50-64) | 43 (28-57) | .028 |
| Crystalized cognition composite | 55.5 (52-62) | 50.5 (38-62) | .084 |
| Total cognition composite | 58.5 (53-61) | 47 (31-56) | .017 |
| Test . | No SCI . | SCI . | P . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Picture vocabulary | 53.5 (51-59) | 48 (38-59) | .076 |
| Oral reading recognition | 55.5 (51-59) | 52.5 (45-58) | .140 |
| List-sorting working memory | 49 (46-55) | 50.5 (47-53) | .774 |
| Picture sequence memory | 56 (44-61) | 50 (46-58) | .447 |
| Flanker inhibitory control and attention | 45.5 (40-48) | 42 (33-45) | .039 |
| Dimensional change cart sort test | 58.5 (42-66) | 47 (32-57) | .140 |
| Pattern recognition | 62 (50-69) | 43 (34-64) | .015 |
| Fluid cognition composite | 57.5 (50-64) | 43 (28-57) | .028 |
| Crystalized cognition composite | 55.5 (52-62) | 50.5 (38-62) | .084 |
| Total cognition composite | 58.5 (53-61) | 47 (31-56) | .017 |
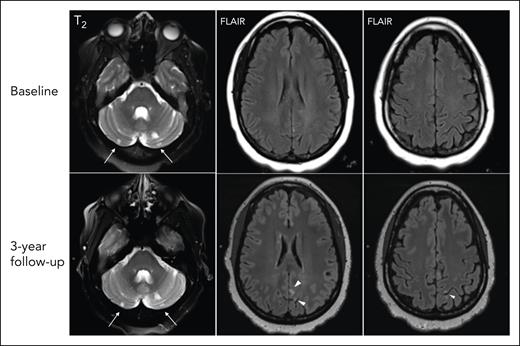
Participants with SCI had higher rates of cognitive impairment), including major impairment (50% vs 5.6%; P = .010), than participants without SCI (66.7% vs 27.7%; P = .026; Figure 4). Compared with participants without SCI, those with SCI also had lower scores for the cognition fluid composite (median, 57.5; IQR, 50-64 vs median, 43; IQR, 28-57; P = .028], cognition crystallized composite (median, 55.5; IQR, 52-62 vs median, 50.5; IQR, 38-62; P = .084] and cognition total composite (median, 58.5; IQR, 53-61 vs median, 47; IQR, 31-56; P = .017) as well as lower scores on the flanker inhibitory control and attention test (executive function) and pattern comparison test (processing speed) (Figure 5; Table 4).
Rate of minor and major cognitive impairment (CI) in patients with and without SCI. Most patients without SCI had no CI (72.22%), whereas most patients with SCI had major cognitive impairment on at least 1 test/construct (50%).
Rate of minor and major cognitive impairment (CI) in patients with and without SCI. Most patients without SCI had no CI (72.22%), whereas most patients with SCI had major cognitive impairment on at least 1 test/construct (50%).
NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery scores in iTTP patients without SCI and with SCI. Survivors of iTTP with SCI had lower scores on multiple tests of the NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery with significantly low scores on the flanker inhibitory control and attention test and pattern comparison test, which assess executive function and processing speed, respectively, compared with iTTP survivors who did not have SCI. Individuals with SCI also had lower cognition fluid composite and cognition total composite scores.
NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery scores in iTTP patients without SCI and with SCI. Survivors of iTTP with SCI had lower scores on multiple tests of the NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery with significantly low scores on the flanker inhibitory control and attention test and pattern comparison test, which assess executive function and processing speed, respectively, compared with iTTP survivors who did not have SCI. Individuals with SCI also had lower cognition fluid composite and cognition total composite scores.
Association of SCI with mild and major cognitive impairment
| Variable . | Any cognitive impairment . | Major cognitive impairment . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) . | P . | OR (95% CI) . | P . | |
| SCI | 10.5 (1.45-76.63) | .020 | 7.98 (1.11-57.27) | .039∗ |
| History of stroke | 0.49 (0.06-4.19) | .523 | 0.33 (0.04-2.93) | .325 |
| BDI-II score | 1.12 (1.01-1.25) | .034 | 1.03 (0.95-1.12) | .425 |
| Variable . | Any cognitive impairment . | Major cognitive impairment . | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) . | P . | OR (95% CI) . | P . | |
| SCI | 10.5 (1.45-76.63) | .020 | 7.98 (1.11-57.27) | .039∗ |
| History of stroke | 0.49 (0.06-4.19) | .523 | 0.33 (0.04-2.93) | .325 |
| BDI-II score | 1.12 (1.01-1.25) | .034 | 1.03 (0.95-1.12) | .425 |
SCI was associated with any (mild or major) cognitive impairment (OR, 10.5; 95% CI, 1.45-76.63; P = .020) in a logistic regression model adjusted for history of stroke (OR, 0.49; 95% CI, 0.06-4.19; P = .523), and BDI-II score (OR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.01-1.25; P = .034). SCI was also associated with major cognitive impairment (OR, 7.98; 95% CI, 1.11-57.27; P = .039) in a logistic regression model adjusted for history of stroke (OR, 0.33; 95% CI, 0.04-2.93; P = .325), and BDI-II score (OR, 1.03; 95% CI, 0.95-1.12; P = .425; Table 5).
Because 44.1% of participants had experienced overt strokes, which may also contribute to worse cognitive outcomes, we separately examined outcomes in patients with no history of stroke and no SCI (n =16), only SCI with no history of stroke (n = 10), documented stroke without SCI (n = 2), and both stroke history and SCI (n = 8). In the latter category, all patients had new SCI compared with imaging performed at the time of acute stroke. The presence of any (mild or major) cognitive impairment was lowest at 5 of 16 (31.3%) patients without SCI or stroke, followed by 4 of 10 (40.0%) patients with SCI without stroke history, and 6 of 8 (75%) in patients with both stroke history and SCI (P = .097). Although there was a trend toward more cognitive impairment in patients with SCI and stroke, the numbers of patients in each group were too small to conduct meaningful comparison (supplemental Table 1). BDI-II scores were not significantly different in any of the subgroups.
Depressive symptoms in participants with and without SCI
Median (IQR) BDI-II scores were not significantly different in patients without SCI and patients with SCI (median, 7.5; IQR, 4-17 vs median, 10.5; IQR, 7-18.5; P = .473). The proportion of patients with no or minimal depressive symptoms (BDI-II score, 0-13; 10 of 18 or 55.5% in each group) and mild, moderate, or severe symptoms did not differ in patients with or without SCI (Figure 4). Although patients with any (mild or major) cognitive impairment had numerically higher BDI-II scores than patients with no cognitive impairment (median, 14; IQR, 3-35 vs median, 9; IQR, 6-13; P = .357), the difference was not statistically significant, and the trend was not consistent throughout the spectrum of severity of cognitive impairment, with the median (IQR) BDI-II scores being highest for individuals categorized as having mild cognitive impairment (median, 19; IQR, 8-25) followed by those with no cognitive impairment (median, 9; IQR, 6-13) and major cognitive impairment (median, 6.5; IQR, 3-150). As shown in Table 5, BDI-II scores were significantly associated with the presence of any (mild or major) cognitive impairment but not major cognitive impairment alone in logistic regression models adjusted for stroke history and SCI.
Discussion
Cognitive difficulties are a leading cause of morbidity and a primary concern among patients who survive iTTP.9,14,34-36 In this prospective study, we show, for the first time to our knowledge, that SCIs are present in half of patients who survived iTTP in clinical remission and are strongly associated with both mild and major cognitive impairment. Patients who survive iTTP report persistent cognitive difficulties, especially problems with memory and concentration, which limit their activities and quality of life.9,14,34-36 The etiology of cognitive impairment in iTTP has not been definitively identified. Comorbid depression has been suggested as a cause based on an association of depression severity with worse cognitive performance in a European study that used self-reported cognitive performance as an outcome measure9; however, Han et al did not find an association of depressive symptoms among patients who survived iTTP in the Oklahoma registry.8 The pattern of cognitive impairments observed in iTTP is similar to that in hypertension,37 sickle cell disease,38,39 and other vascular disorders,40 suggesting that the cognitive impairment in iTTP could be due to acquired diffuse, subcortical microvascular lesions, although this had not been demonstrated until now. Our study demonstrates a clear link between cognitive impairment and ischemic brain lesions (SCIs), independent of depression. In light of these data, the term “silent” infarct is a misnomer, and these lesions are perhaps better characterized as “microinfarcts” or “subclinical” infarcts.
SCI, which refers to the often-incidental finding of brain infarction in the absence of overt neurologic deficits, is an increasingly recognized phenomenon, with the widespread use of brain imaging in the past several decades.41 In representative community-based samples, the prevalence of SCI is estimated to be from 10% to 20% and increases with age.20,41-46 For example, SCI prevalence was 12% in the Framingham heart study, with a mean age of 62 years45 and 20% in the Rotterdam cohort, with a mean age of 72 years.42 The 50% prevalence in our cohort (with a median age <50 years) was much higher than in these general population-based cohorts in which the average participant was much older. A 2010 study from Ohio State University and University College London reported that 9 of 23 patients with iTTP had ischemic findings upon brain MRI.36 These rates were comparable with rates observed in sickle cell disease, in which SCI are recognized as a risk factor for cognitive impairment and future stroke.47 Even in general population-based cohorts, SCI are associated with neurocognitive dysfunction,20,21 a twofold or threefold higher risk of future stroke,48,49 and early mortality,50 suggesting that these lesions are not silent at all. Our results confirm that SCIs are a risk factor for cognitive impairment in iTTP, and prospective follow-up of our cohort will establish whether these are a risk factor for future stroke. We also identified increasing age and a history of stroke as associations of SCI, which has also been observed in studies of community-dwelling adults and suggests shared pathophysiology and risk factors of stroke and SCI that are both part of the spectrum of cerebrovascular disease. Although we did not find an association between SCI and other traditional cerebrovascular risk factors, such as hypertension,51 this may be due to the small sample size and needs to be evaluated in larger cohorts.
Following are critical, unanswered questions: is SCI a risk factor for future stroke? Do SCIs progress or increase during iTTP remission, or are they merely sequelae of acute iTTP? How can we prevent these SCI and their devastating sequelae?
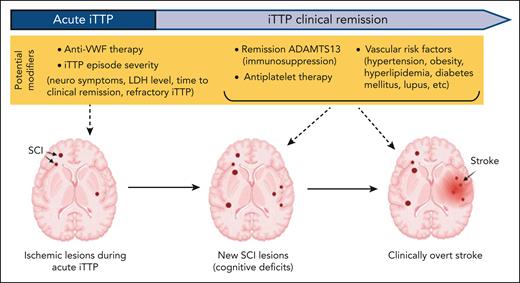
Identifying the phase of iTTP in which most SCI occur may help identify the timing and type of interventions to improve outcomes (Figure 6). For example, anti-VWF therapy (caplacizumab) during acute iTTP may reduce SCIs due to ischemic injury during acute episodes. This is supported by data from the UK iTTP registry, in which MRI abnormalities during acute iTTP (in patients with neurologic manifestations at presentation) were associated with cognitive impairments during clinical remission.52 In contrast, if SCIs are progressive during remission, aggressive management of cardiovascular risk factors and immunosuppression to maintain higher remission ADAMTS13 levels may reduce SCI progression in remission. The fact that some patients in this study had SCIs upon imaging that were not detected in previous clinical imaging supports the hypothesis that SCIs do progress in the absence of recurrent iTTP. To definitively answer these questions, we are continuing to enroll patients, and even including patients who received anti-VWF with their initial iTTP diagnosis, and will follow-up with the participants with annual brain MRI and cognitive assessments to evaluate for incidental SCIs, clinically overt stroke, and changes in neurocognitive performance. We have shown that remission ADAMTS13 activity is a risk factor for stroke.13 Our preliminary results examining remission ADAMTS13 activity results from the 12 months leading up to the research MRIs suggests an association between lower remission ADAMTS13 and SCI; however, this does not reflect the entire period of exposure from iTTP diagnosis to the current evaluation of SCI and will need to be confirmed in more complete data sets with a larger sample size.
Proposed model of progressive cerebrovascular disease in iTTP and opportunities for intervention. Ischemia occurs during acute iTTP, but additional lesions (in the same or other sites) may occur during remission and contribute to cognitive deficits. Based on shared pathophysiology, SCI is a likely precursor lesions for stroke. Potential factors contributing to ischemic injury are highlighted in yellow. Targeting microvascular thrombi in acute iTTP could reduce SCI from the acute event and targeting remission ADAMTS13 and other cardiovascular risk factors could mitigate ongoing injury during remission.
Proposed model of progressive cerebrovascular disease in iTTP and opportunities for intervention. Ischemia occurs during acute iTTP, but additional lesions (in the same or other sites) may occur during remission and contribute to cognitive deficits. Based on shared pathophysiology, SCI is a likely precursor lesions for stroke. Potential factors contributing to ischemic injury are highlighted in yellow. Targeting microvascular thrombi in acute iTTP could reduce SCI from the acute event and targeting remission ADAMTS13 and other cardiovascular risk factors could mitigate ongoing injury during remission.
To summarize, there are several potential approaches that may reduce neurologic morbidity in iTTP. These include microthrombi-targeted treatments to reduce acute ischemic injury, immunosuppression to target higher remission ADAMTS13 activity, antiplatelet or anticoagulant therapy, or a combination of these approaches. Until more data on effectiveness of these approaches are available, it is reasonable to screen for and address any other cardiovascular risk factors. Our current clinical approach is to aggressively manage cardiovascular risk factors by (1) screening for and optimizing management of hypertension and hyperlipidemia including referral to the appropriate specialists as needed, (2) starting aspirin in patients with low bleeding risk who have a history of stroke (including stroke during acute iTTP), known coronary artery disease, diabetes mellitus, active smoking, lupus, or a >10% estimated risk of cardiovascular disease at 10 years53 (with the understanding that traditional risk calculators likely underestimate risk in iTTP), and (3) preemptive rituximab when remission ADAMTS13 is <20% to 30% to prevent iTTP relapse (until additional data are available to support targeting a higher ADAMTS13 activity).
Strengths of this study include prospective enrollment and that brain MRI was performed during clinical remission in the absence of overt neurologic symptoms using a standardized protocol with blinded adjudication and rigorous, prespecified criteria for SCI. Additionally, to our knowledge, this is the first study to evaluate the effect of cerebral ischemic lesions and depression on cognitive performance in the same study. We also used the validated NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery and were able to show that NIH ToolBox Cognition Battery scores correlated with patient-reported cognitive function on the PROMIS cognitive function short form 8a.
Limitations of the study include the fact that this is a single center study, and the majority of subjects are Black, reflecting the demographic makeup of our city and of patients at our institution. Although this approximates the demographic distribution of iTTP in the United States,3 the single center nature of study may still limit generalizability. Moreover, the small number of patients makes it challenging to comprehensively evaluate multiple risk factors for SCI. A major limitation is the fact that we did not have complete ADAMTS13 data for the entire period from iTTP diagnosis to the current research evaluation, which limited our analyses of ADAMTS13 activity and risk of SCI. We are collecting ADAMTS13 prospectively and plan to evaluate the association of remission ADAMTS13 with new incident SCI on follow-up MRI, which will address this critical gap. Finally, the patients in this study had their initial iTTP episodes before caplacizumab was available at our institution, so we were unable to evaluate whether the rate of SCI and cognitive impairment was lower in patients who received early treatment with caplacizumab because this could have conceivably protected against ischemic brain injury during acute iTTP. To overcome these issues, we plan to expand to a multicenter study leveraging the US Thrombotic Microangiopathy Consortium network.
In conclusion, MRI evidence of brain infarction is common in patients who survived iTTP with or without a history of stroke during acute iTTP episodes or during clinical remission. The strong association of SCI with cognitive impairment suggests that these lesions are neither silent nor innocuous. Prospective follow-up with serial MRI and clinical evaluation continues and will inform whether SCI are progressive and a risk factor for stroke in which case SCI may also serve as an additional clinically significant end point for trials of novel therapeutic strategies. Until specific strategies to improve neurologic outcomes of iTTP are developed, aggressive screening and management of cardiovascular risk factors may reduce adverse neurovascular sequelae in patients who survived iTTP.
Acknowledgments
S.C. thanks Michael R. DeBaun for critical input regarding study design, interpretation, and preparation of the manuscript, and for his invaluable mentorship.
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute grant K99HL150594 (S.C.) and an American Society of Hematology Scholar Award (S.C.). R.F.G. is supported by the NIH National Institute for Neurological Disorders and Stroke intramural research program.
Authorship
Contribution: S.C. designed the research, performed, and interpreted the analyses, and wrote the initial draft of the manuscript; J.Y., J.B., and A.W. served as study coordinators and conducted study assessment; S.S. collected and analyzed parts of the data and critically reviewed the manuscript; G.F.G., P.K., C.M.L., J.C.Y., R.P.N., H.L., S.M.L., E.M.B., and R.A.B. assisted with patient recruitment and critically reviewed the manuscript; R.F.G. was involved with study design and provided critical mentoring and critically reviewed the manuscript; D.D.L. led the neuroradiology team, designed MRI sequences, established MRI protocols, interpreted all study MRIs, and critically reviewed the manuscript; and all authors read and approved the final draft of the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: S.C. is on advisory boards and provides consultancy for Alexion, Sanofi, UCB, Sobi, and Takeda; and reports honoraria/royalties from UpToDate and Dynamed. S.M.L. provides consultancy for Bluebird bio, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Novartis, and Magenta; reports honoraria from Novartis; reports research funding from Imara, Novartis, GBT, Takeda, CSL Behring, HRSA, PCORI, and MD CHRC; and reports stocks in Pfizer and Teva. R.P.N. provides consultancy for Elsevier. A.R.M. is on the advisory board of PharmEssentia. M.B.S. provides consultancy for CSL Behring, Johnson & Johnson, and Pfizer; is a member of data safety monitoring board of CSL Behring; receives funding from AHRQ, NovoNordisk, PCORI, Sanofi, and Tremeau; and receives honoraria from Pfizer. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Shruti Chaturvedi, Ross Research Building, Room 1025, 720 Rutland Ave, Baltimore, MD 21205; e-mail: schatur3@jhmi.edu.
References
Author notes
Data are available on request from the corresponding author, Shruti Chaturvedi (schatur3@jhmi.edu).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal