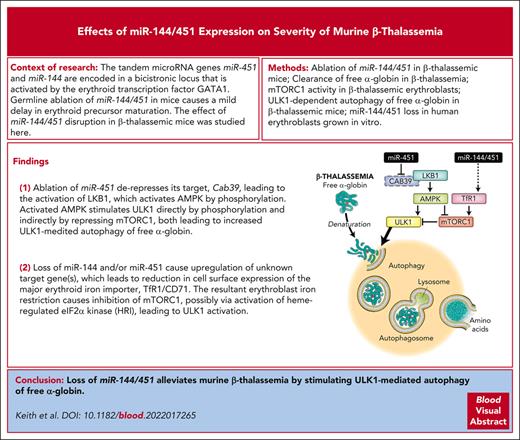
Key Points
Loss of miR-144/451 in erythroid cells of Hbbth3/+ mice alleviates β-thalassemia by stimulating ULK1-dependent autophagy of free α-globin.
Loss of miR-144/451 stimulates ULK1 by activating the LKB1/AMPK axis and inducing erythroblast iron restriction.
Abstract
Most cells can eliminate unstable or misfolded proteins through quality control mechanisms. In the inherited red blood cell disorder β-thalassemia, mutations in the β-globin gene (HBB) lead to a reduction in the corresponding protein and the accumulation of cytotoxic free α-globin, which causes maturation arrest and apoptosis of erythroid precursors and reductions in the lifespan of circulating red blood cells. We showed previously that excess α-globin is eliminated by Unc-51–like autophagy activating kinase 1 (ULK1)-dependent autophagy and that stimulating this pathway by systemic mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) inhibition alleviates β-thalassemia pathologies. We show here that disrupting the bicistronic microRNA gene miR-144/451 alleviates β-thalassemia by reducing mTORC1 activity and stimulating ULK1-mediated autophagy of free α-globin through 2 mechanisms. Loss of miR-451 upregulated its target messenger RNA, Cab39, which encodes a cofactor for LKB1, a serine-threonine kinase that phosphorylates and activates the central metabolic sensor adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase (AMPK). The resultant enhancement of LKB1 activity stimulated AMPK and its downstream effects, including repression of mTORC1 and direct activation of ULK1. In addition, loss of miR-144/451 inhibited the expression of erythroblast transferrin receptor 1, causing intracellular iron restriction, which has been shown to inhibit mTORC1, reduce free α-globin precipitates, and improve hematological indices in β-thalassemia. The beneficial effects of miR-144/451 loss in β-thalassemia were inhibited by the disruption of Cab39 or Ulk1 genes. Together, our findings link the severity of β-thalassemia to a highly expressed erythroid microRNA locus and a fundamental, metabolically regulated protein quality control pathway that is amenable to therapeutic manipulation.
Introduction
β-thalassemia is a common anemia caused by mutations in the HBB gene that reduce or eliminate the expression of the β-globin subunit of adult hemoglobin (HbA, α2β2). Consequently, excess free α-globin forms toxic precipitates that cause premature destruction of red blood cells (RBCs; hemolysis) and impaired maturation of their bone marrow precursors (ineffective erythropoiesis). Like most tissues, erythroid cells possess protein quality control mechanisms that eliminate unstable misfolded proteins, including free α-globin.1-8 We have shown previously that β-thalassemic erythroid precursors eliminate free α-globin by a noncanonical autophagy pathway that is dependent on Unc-51–like autophagy activating kinase 1 (ULK1).9 In general, ULK1 is inhibited by mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) when nutrients are available to fuel cell growth, and it is activated by adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase (AMPK) when nutrients are depleted.10,11 mTORC1 is activated in β-thalassemic erythroblasts, and treating β-thalassemic mice with the mTORC1 inhibitor rapamycin caused ULK1-dependent reductions in α-globin precipitates and reductions in pathological phenotypes.9,12 However, the overall regulation of free α-globin degradation in β-thalassemia is not fully understood.
MicroRNAs are small RNAs that bind specific messenger RNAs (mRNAs) through Watson-Crick base pairing to inhibit their expression by stimulating nucleolytic cleavage and/or inhibiting translation.13 The microRNAs miR-451 and miR-144 are encoded in tandem within a bicistronic locus that is activated by the erythroid transcription factor GATA1.14 Germ line disruption of the miR-144/451 gene in mice causes a mild delay in erythroid precursor maturation and makes RBCs more sensitive to oxidative stress.15-17 More than 50 miR-451 or miR-144 target mRNAs have been identified in erythroid cells through bioinformatic prediction with experimental validation15-17 and by immunoprecipitation of Argonaute proteins, components of the RNA-induced silencing complex that binds microRNAs complexed to their target mRNAs.18 Additional miR-144 and miR-451 targets have been identified in nonerythroid tissues.19
A few miR-144 or miR-451 target mRNA interactions have been examined functionally in erythroid cells. For example, miR-451 protects against oxidative stress by repressing Ywhaz mRNA, which encodes the cytoplasmic adapter protein 14-3-3ζ.17 Loss of miR-451 causes upregulation of 14-3-3ζ, which sequesters the transcription factor FOXO3A to inhibit the activation of its target genes, some of which encode antioxidant proteins. In addition, miR-451 facilitates erythroid precursor survival during recovery from acute anemia by targeting mRNA-encoding calcium-binding protein 39 (CAB39), a cofactor for liver kinase B1 (LKB1/STK11), which is a serine-threonine kinase that regulates cell growth, differentiation, and polarity by activating its substrate AMPK and other related kinases.20-23 Erythroid precursors in miR-144/451−/− mice with normal Hbb alleles exhibit increased Cab39 expression, increased activities of LKB1 and AMPK, and decreased activity of mTORC1.20 Considering that AMPK activates ULK1 directly via phosphorylation and indirectly by inhibiting mTORC1,10,11,24-26 we theorized that loss of miR-451 could accelerate ULK1-mediated autophagic clearance of free α-globin in β-thalassemia. In addition, we noted that loss of miR-144/451 was associated with signs of erythroid iron restriction, which has been shown to reduce the pathophysiology β-thalassemia.27,28
Based on these previous studies, we hypothesized that eliminating miR-144/451 can alleviate β-thalassemia through multiple mechanisms. Here, we show that homozygous disruption of the miR-144/451 locus in Hbbth3/+ β-thalassemic mice caused improvements in hematological indices that were associated with multiple effects in erythroid precursors including the upregulation of CAB39, reduced activity of mTORC1, reduced expression of the major erythroblast iron importer transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1), intracellular iron restriction, and enhanced ULK1-dependent autophagy of free α-globin.
Methods
Additional details about materials and methods used are provided in supplemental Methods, available on the Blood website.
Animals
Animal care and experimental protocols were approved by the institutional animal care and use committee at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. Breeding and analysis of Hbbth3/+, miR-144/451−/−, and Ulk1−/− mice were performed as previously described.1,17,29 The mice were backcrossed using a C57BL/6J background (The Jackson Laboratory) for at least 10 generations.
Mouse hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Embryonic day 14.5 fetal livers were dissociated and treated with ammonium-chloride-potassium RBC lysing buffer (Quality Biological, 118-156-101), enriched for hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) by using an EasySep Kit (STEMCELL, 19856), and stimulated for 16 or 18 hours in HSPC maintenance medium consisting of StemSpan Serum-Free Expansion Medium (SFEM) (STEMCELL, 09650) with murine colony-stimulating factor (2 μg/mL; PeproTech), human FLT3L (4 μg/mL; PeproTech), murine interleukin-3 (0.4 μg/mL; R&D Systems), and murine interleukin-11 (4 μg/mL; R&D Systems). After stimulation, 5 × 105 cells were injected into the tail veins of mice that had been lethally irradiated at 11.25 Gy.
Genome editing of fetal liver HSPCs
Fetal liver HSPCs were stimulated in maintenance medium for 16 or 18 hours, mixed with ribonucleoprotein consisting of caspase-9 (Cas9) (Berkeley Qb3 MacroLab) and single-guide RNA (sgRNA) targeting Cab39 (AGTCAGCTACCAGGGTGCCGNGG) (Synthego) at a 1:2 molar ratio with Cas9 at 40 μM, and electroporated using a Neon Transfection System (Thermo Fisher Scientific) at 1700 V, with 1 pulse of 20 milliseconds. Subsequently, cells were incubated overnight in HSPC maintenance medium then injected into the tail veins of recipient mice.
To determine indel frequencies, HSPCs were grown in maintenance medium for 72 hours, and the Cab39 gene was amplified via polymerase chain reaction (PCR), using oligonucleotide primers that contain adapters for Illumina sequencing: forward: 5′-TGCACATAGGTCTGAAGGTAAA-3′; reverse: 5′-GCCTGAGTCAACAGGGATCTT-3′. The PCR products were barcoded and pooled, then next-generation sequencing was performed using a MiSeq or MiniSeq instrument (Illumina), and the results were analyzed using CRIS.py84.30
Human cells
Granulocyte colony factor–mobilized peripheral blood mononuclear cells from an anonymous healthy donor (HD) were purchased from StemExpress (CP024). Bone marrow cells from an anonymous patient with transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia (IVS2-1 G>A) were provided by Robert A. Krance (Baylor College of Medicine). CD34+ cells were enriched via magnetic bead separation, using standard methods and then cryopreserved. The St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital institutional review board ruled that the related work was not human subject–based research.
Cas9 disruption of MIR-144/451 in human CD34+ cells
Cryopreserved CD34+ cells were thawed and grown for 24 hours in stem cell expansion medium composed of X-VIVO -10 medium (Lonza, BEBP02-055Q) with 100 ng/μL human stem cell factor (R&D Systems, 255-SC/CF), 100 ng/μL human thromopoietin (R&D Systems, 288-TP/CF), and 100 ng/μL human Flt-3 ligand (R&D Systems, 308-FK/CF). Cells were mixed with 2 ribonucleoproteins (55 μM each) consisting of Cas9 (Berkeley Qb3 MacroLab) complexed with sgRNA targeting either the coding region of MIR-144 (Integrated DNA Technologies, IDT; MIR144: TATAGATGATGTACTAGTCCNGG) or the coding region of MIR-451 (IDT, MIR451: ACTAAACTCAGTAATGGTAA-NGG) in 20 μL (final reaction volume) of P3 solution (Lonza Biosciences, V4XP-3032). They were electroporated using a Lonza 4D-Nucleofector (program DS-130), then transferred to stem cell expansion medium, and maintained from 0.5 × 106 cells per mL to 1 × 106 cells per mL for 72 hours. Indel frequencies were determined via PCR amplification of a segment of genomic DNA encompassing both microRNAs (forward: ACAGAATCAAGGAGACGCTGGCCTGC, reverse: TGGGATTGGGGGTAGGGGAGGGAAT), followed by next-generation sequencing.
Measurement of intracellular nonheme iron
Ter119+ cells were isolated using MicroBeads (Miltenyi Biotec; 130-049-901). One million cells were resuspended in 100 μL of 0.53 N hydrochloric acid and 5.3% trichloroacetic acid, incubated at 100°C for 1 hour, and analyzed with an Iron-SL Assay kit (Sekisui Diagnostics, 157-30), using the Ricca Iron AA Standard (AFE1KH-500) for calibration. Data were normalized to the total protein concentration, as determined with a Pierce BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 6.0 software and R (R-3.2.5). Data are shown as the mean ± standard deviation. A two-sample Student t test was used to compare continuous variables in 2 groups, depending on the normality of the data. The Benjamini-Hochberg method was used to control the false discovery rate at a level of 0.05 in the analyses of RBC survival at different time points. Otherwise, P values < .05 were considered to indicate statistical significance. All tests were two-tailed.
Results
Ablation of miR-144/451 reduces β-thalassemia pathologies
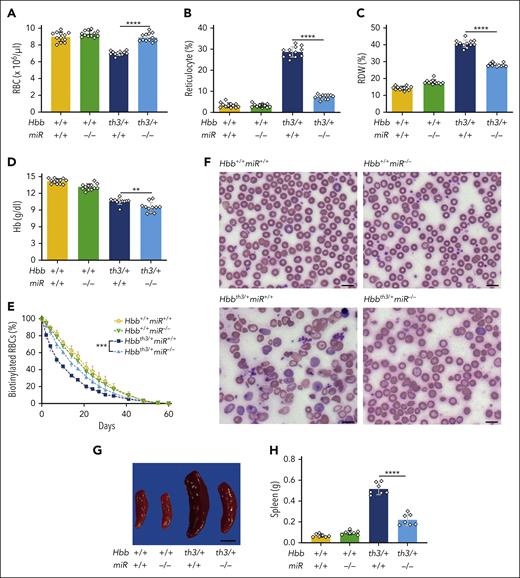
To determine the impact of miR-144/451 on mTORC1 activity and β-thalassemia phenotypes, we intercrossed miR-144/451−/− and Hbbth3/+ mice.17,31 The latter strain harbors a heterozygous deletion of the tandem adult β-globin genes Hbb-b1 and Hbb-b2 and exhibits moderately severe hemolytic anemia resembling nontransfusion-dependent human β-thalassemia (ie, thalassemia intermedia). Both Hbbth3/+miR-144/451+/+ and Hbbth3/+miR-144/451−/− mice were born at a normal Mendelian ratio. Loss of miR-144/451 in 8-week-old and 15- to 23-week-old Hbbth3/+ mice resulted in an increased RBC count, a decreased reticulocyte count, and a decreased RBC distribution width (RDW), which reflects the heterogeneity in size (Figure 1A-C; supplemental Figure 1; supplemental Tables 1 and 2). Hb levels were slightly decreased by the loss of miR-144/451 in younger β-thalassemic mice and slightly increased in older ones (Figure 1D; supplemental Figure 1D).
Ablation of miR-144/451 alleviates β-thalassemia in mice. β-thalassemic (Hbbth3/+) and miR-144/451−/− (miR−/−) mice were intercrossed and analyzed. (A-D) Erythroid indices (y-axis) of 8-week-old mice according to the genotype (x-axis). n = 12 mice for each genotype. (E) RBC survival. RBCs in 8-week-old mice were biotinylated at time 0. Loss of biotin-labeled RBCs over time was quantified via streptavidin labeling and flow cytometry. Differences between Hbbth3/+miR+/+ and Hbbth3/+miR−/− mice were significant at all time points at which measurements were made between days 2 and 34 (Benjamini-Hochberg false discovery rate–adjusted P value = .002-.02). (F) Representative images of blood smears (Giemsa stain) from mice with the indicated genotypes. Images were obtained using an Eclipse Ni microscope and a 40× objective lens; bars represent 5 μm. (G) Representative images of spleens from mice with the indicated genotypes. Bar represents 1 cm. (H) Summary of spleen weights. n = 7 mice for each genotype. All bar charts show data as mean values ± standard deviation (SD); ∗∗∗∗P <.0001; ∗∗∗P <.001; ∗∗P <.01.
Ablation of miR-144/451 alleviates β-thalassemia in mice. β-thalassemic (Hbbth3/+) and miR-144/451−/− (miR−/−) mice were intercrossed and analyzed. (A-D) Erythroid indices (y-axis) of 8-week-old mice according to the genotype (x-axis). n = 12 mice for each genotype. (E) RBC survival. RBCs in 8-week-old mice were biotinylated at time 0. Loss of biotin-labeled RBCs over time was quantified via streptavidin labeling and flow cytometry. Differences between Hbbth3/+miR+/+ and Hbbth3/+miR−/− mice were significant at all time points at which measurements were made between days 2 and 34 (Benjamini-Hochberg false discovery rate–adjusted P value = .002-.02). (F) Representative images of blood smears (Giemsa stain) from mice with the indicated genotypes. Images were obtained using an Eclipse Ni microscope and a 40× objective lens; bars represent 5 μm. (G) Representative images of spleens from mice with the indicated genotypes. Bar represents 1 cm. (H) Summary of spleen weights. n = 7 mice for each genotype. All bar charts show data as mean values ± standard deviation (SD); ∗∗∗∗P <.0001; ∗∗∗P <.001; ∗∗P <.01.
We measured the RBC lifespan by injecting mice with N-succinimidyl-6-[biotinamido] hexanoate and quantifying the loss of circulating biotinylated cells over time. Disrupting miR-144/451 increased the half-life of circulating β-thalassemic RBCs from 8.3 to 13.2 days, as compared with 17.8 days for RBCs of Hbb+/+miR-144/451−/− mice and 18.8 days for RBCs of wild-type (Hbb+/+miR-144/451+/+) mice (Figure 1E). Loss of miR-144/451 improved the morphology of β-thalassemic RBCs, as evidenced by reductions in abnormal shape occurrence (poikilocytosis), size heterogeneity (anisocytosis), and target cells (Figure 1F). In addition, 8-week-old and 15- to 23-week-old Hbbth3/+miR-144/451−/− mice exhibited less ineffective erythropoiesis when compared with age-matched Hbbth3/+miR-144/451+/+ mice, as evidenced by their smaller spleens with reduced erythroid hyperplasia and the enhanced maturation of splenic and bone marrow erythroid precursors (Figure 1G-H; supplemental Figures 2 and 3). Therefore, loss of miR-144/451 reduces hemolysis and ineffective erythropoiesis in β-thalassemia.
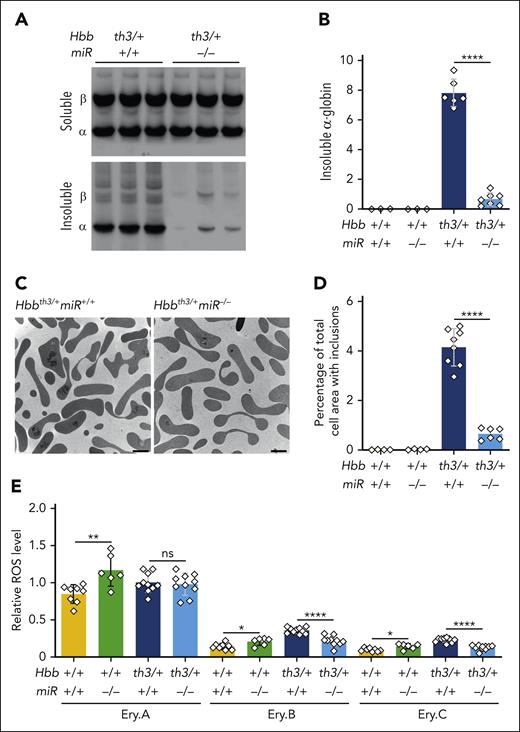
Ablating miR-144/451 caused a reduction in insoluble α-globin in β-thalassemic RBCs, as measured via biochemical fractionation followed by Triton–acetic acid–urea gel electrophoresis (Figure 2A-B), and in β-thalassemic reticulocytes, as measured via transmission electron microscopy (Figure 2C-D). In nonthalassemic (Hbb+/+) developmental stage–matched erythroid precursor populations Ery.A, Ery.B, and Ery.C, the levels of reactive oxygen species were increased by the loss of miR-144/451 (Figure 2E), consistent with our report that miR-451 protects against oxidant stress by enhancing the expression of FOXO3A-regulated antioxidant genes.17 In contrast, disruption of miR-144/451 in β-thalassemic mice caused reductions in the levels of reactive oxygen species in Ery.B and Ery.C erythroblasts, most likely by preventing the accumulation of free α-globin, a strong pro-oxidant (Figure 2E).32 Similarly, loss of miR-144/451 exacerbated hemolysis caused by administration of the oxidant drug phenylhydrazine in mice with WT Hbb alleles but not in β-thalassemic mice (supplemental Figure 4).
miR-144/451 disruption reduces the accumulation of insoluble α-globin and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in β-thalassemia. (A) Soluble and insoluble RBC globin proteins. Equal volumes of RBCs (normalized by hematocrit) were lysed, centrifuged to separate insoluble and soluble proteins, fractionated by Triton–acetic acid–urea (TAU) gel electrophoresis to resolve α- and β-globin proteins, and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. (B) Results of multiple experiments performed as described in panel A. The y-axis represents the relative levels of insoluble α-globin, as measured via automated image analysis of TAU gels, and expressed in arbitrary units. n = 3 to 6 mice for each genotype. (C) Thiazole orange–stained reticulocytes were isolated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting to a purity of ∼95%, then analyzed for electron-dense α-globin precipitates by transmission electron microscopy using an FEI Tecnai 200Kv FEG Transmission Electron Microscope with an ATM XR41 digital camera. Representative micrographs show reticulocytes from mice with the indicated genotypes. Bars represent 2 μm. (D) Areas of α-globin inclusions in reticulocytes (y-axis) determined by automated image analysis of electron micrographs prepared in the same manner as those in panel C. n = 4 to 8 mice for each genotype. Approximately 200 cells from each mouse were analyzed. (E) Flow cytometry quantification of ROS, determined by 2′, 7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate staining of bone marrow erythroblasts. Ery.A, Ery.B, and Ery.C represent distinct developmental stages defined by the expression of erythroid maturation markers and cell size (supplemental Figure 2). n = 6 to 10 mice for each genotype. Bar charts show data as mean values ± SD; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001; ∗∗P < .01; ∗P < .05; ns, not significant.
miR-144/451 disruption reduces the accumulation of insoluble α-globin and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in β-thalassemia. (A) Soluble and insoluble RBC globin proteins. Equal volumes of RBCs (normalized by hematocrit) were lysed, centrifuged to separate insoluble and soluble proteins, fractionated by Triton–acetic acid–urea (TAU) gel electrophoresis to resolve α- and β-globin proteins, and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. (B) Results of multiple experiments performed as described in panel A. The y-axis represents the relative levels of insoluble α-globin, as measured via automated image analysis of TAU gels, and expressed in arbitrary units. n = 3 to 6 mice for each genotype. (C) Thiazole orange–stained reticulocytes were isolated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting to a purity of ∼95%, then analyzed for electron-dense α-globin precipitates by transmission electron microscopy using an FEI Tecnai 200Kv FEG Transmission Electron Microscope with an ATM XR41 digital camera. Representative micrographs show reticulocytes from mice with the indicated genotypes. Bars represent 2 μm. (D) Areas of α-globin inclusions in reticulocytes (y-axis) determined by automated image analysis of electron micrographs prepared in the same manner as those in panel C. n = 4 to 8 mice for each genotype. Approximately 200 cells from each mouse were analyzed. (E) Flow cytometry quantification of ROS, determined by 2′, 7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate staining of bone marrow erythroblasts. Ery.A, Ery.B, and Ery.C represent distinct developmental stages defined by the expression of erythroid maturation markers and cell size (supplemental Figure 2). n = 6 to 10 mice for each genotype. Bar charts show data as mean values ± SD; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001; ∗∗P < .01; ∗P < .05; ns, not significant.
miR-144/451 disruption stimulates the clearance of free α-globin in β-thalassemia
We analyzed late-stage erythroid precursors (reticulocytes) by pulse labeling with 35S-labeled amino acids followed by a chase with unlabeled amino acids, separation of the nascent proteins into soluble and insoluble fractions, and Triton–acetic acid–urea gel electrophoresis to distinguish α- and β-globins. Previously, we used this assay to show that β-thalassemic reticulocytes eliminate free α-globin via ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis and autophagy.1,9 After a 30-minute pulse, most nascent α-globin and β-globin molecules were in the soluble fraction, and the levels were unaffected by miR-144/451 status (Figure 3A-B). In contrast, the level of insoluble α-globin after the pulse was reduced by 40% with miR-144/451 disruption. After a 6-hour chase with unlabeled amino acids, the levels of soluble radiolabeled α-globin and β-globin were unchanged, reflecting their incorporation into stable HbA tetramers. In contrast, labeled insoluble α-globin was partially cleared by autophagy and proteasomal degradation, as evidenced by the effects of their inhibition with chloroquine and MG132, respectively (Figure 3C-D). In β-thalassemic erythroblasts, the clearance of nascent insoluble α-globin over 6 hours was increased by 62% ± 16% after the loss of miR-144/451 (Figure 3E). This difference was reduced to 44% ± 21% in the presence of MG132 and to 12% ± 9% in the presence of chloroquine (Figure 3E; supplemental Figure 5). Therefore, the loss of miR-144/451 accelerates the clearance of free α-globin mainly by enhancing its autophagic flux (Figure 3F). Our previous studies indicated that mTORC1 is abnormally active in β-thalassemic erythroblasts, which is predicted to inhibit ULK1-mediated autophagy.9
miR-144/451 disruption enhances the autophagic flux and proteasomal degradation of insoluble free α-globin. Reticulocytes in whole blood from mice with the indicated genotypes were pulse-labeled with 35S-amino acids; chased with unlabeled amino acids ± a proteasome inhibitor (MG132 [MG]; 10 μM), a lysosome inhibitor (chloroquine [CQ]; 100 μM), or vehicle (Veh); separated via centrifugation into soluble and insoluble fractions; subjected to TAU gel electrophoresis to separate globin proteins; and analyzed by autoradiography. (A) Autoradiogram immediately after a 30-minute pulse with 35S-amino acids. Each lane represents a biological replicate experiment using equivalent input cell numbers from different mice. (B) Relative levels of soluble and insoluble globin determined by quantitative image analysis of TAU gel autoradiograms, as shown in panel A. (C) Representative TAU gel autoradiograms showing soluble and insoluble globin chains after 3-hour and 6-hour chases with unlabeled amino acids. (D) Results of multiple experiments performed as described for panel C and quantified using automated image analysis. n = 5 mice for each genotype. (E) Percentage increases in the clearance of insoluble α-globin in Hbbth3/+miR−/− vs Hbbth3/+miR+/+ reticulocytes after a 6-hour chase with MG, CQ, or Veh. (F) Summary of data from panel E indicating the relative contributions of autophagy (CQ-inhibited) or proteasomal (MG-inhibited) degradation to the enhanced clearance of free α-globin conferred by miR-144/451 disruption. Data are shown as mean values ± SD; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001; ∗∗P < .01; ∗P < .05.
miR-144/451 disruption enhances the autophagic flux and proteasomal degradation of insoluble free α-globin. Reticulocytes in whole blood from mice with the indicated genotypes were pulse-labeled with 35S-amino acids; chased with unlabeled amino acids ± a proteasome inhibitor (MG132 [MG]; 10 μM), a lysosome inhibitor (chloroquine [CQ]; 100 μM), or vehicle (Veh); separated via centrifugation into soluble and insoluble fractions; subjected to TAU gel electrophoresis to separate globin proteins; and analyzed by autoradiography. (A) Autoradiogram immediately after a 30-minute pulse with 35S-amino acids. Each lane represents a biological replicate experiment using equivalent input cell numbers from different mice. (B) Relative levels of soluble and insoluble globin determined by quantitative image analysis of TAU gel autoradiograms, as shown in panel A. (C) Representative TAU gel autoradiograms showing soluble and insoluble globin chains after 3-hour and 6-hour chases with unlabeled amino acids. (D) Results of multiple experiments performed as described for panel C and quantified using automated image analysis. n = 5 mice for each genotype. (E) Percentage increases in the clearance of insoluble α-globin in Hbbth3/+miR−/− vs Hbbth3/+miR+/+ reticulocytes after a 6-hour chase with MG, CQ, or Veh. (F) Summary of data from panel E indicating the relative contributions of autophagy (CQ-inhibited) or proteasomal (MG-inhibited) degradation to the enhanced clearance of free α-globin conferred by miR-144/451 disruption. Data are shown as mean values ± SD; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001; ∗∗P < .01; ∗P < .05.
Disruption of miR-144/451 inhibits mTORC1 in β-thalassemic erythroblasts
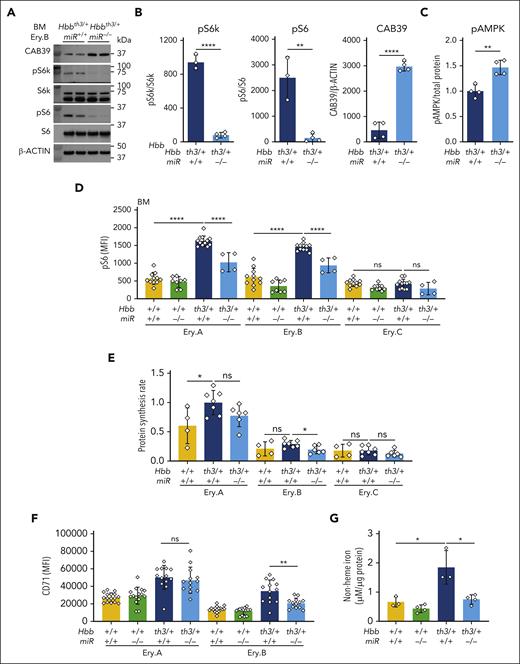
Western blot analysis of developmental stage–matched Ery.B erythroblasts from 8-week-old and 15- to 23-week-old β-thalassemic mice showed that disruption of miR-144/451 inhibited mTORC1 activity, as evidenced by decreases in the phosphorylation of p70-S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) at Thr389 and ribosomal protein S6 at Ser235 and Ser236 (Figure 4A-B; supplemental Figure 6A). miR-451 represses Cab39 mRNA, which encodes a cofactor for LKB1, an AMPK activator.18,20 Accordingly, disrupting miR-144/451 caused an increase in Cab39 protein (Figure 4A-B) and increased phosphorylation of AMPK at an LKB1-activating target site (Figure 4C; supplemental Figure 7A-C). Consistent with western blot studies, phospho-flow cytometry of developmental stage–matched erythroblasts showed that mTORC1 activity is abnormally elevated in β-thalassemia and suppressed by disruption of miR-144/451 (Figure 4D; supplemental Figure 6B-C). In vivo labeling of nascent ribosomal peptides with O-propargyl-puromycin revealed that loss of miR-144/451 caused a reduction in protein synthesis rates in Ery.B precursors, consistent with suppression of mTORC1 activity (Figure 4E). Loss of miR-144/451 caused mild reductions in blood Hb concentration, mean corpuscular volume, and mean corpuscular Hb (Figure 1D; supplemental Figure 1; supplemental Tables 1 and 2), suggesting functional iron deficiency.17 Erythroblasts from miR-144/451−/− mice with β-thalassemia showed reductions up to 45% in the levels of cell-surface TfR1 receptor (CD71), reduced intracellular levels of nonheme iron, and activation of heme-regulated inhibitor kinase (HRI), as evidenced by phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha (eIF2α) (Figure 4F-G; supplemental Figure 7D-F). Loss of miR-144/451 caused minimal changes in circulating iron or ferritin levels (supplemental Table 3). Notably, activation of HRI because of dietary iron deficiency suppresses erythroblast mTORC1 activity.33 Hence, the current findings indicate that miR-144/451 loss inhibits mTORC1, in part by reducing erythroblast TfR1 expression and iron uptake.
mTORC1 activity is enhanced in β-thalassemia and suppressed by miR-144/451 disruption in 8-week-old mice. (A) Western blot analysis of indicated proteins and phosphoproteins (p) in the erythroblast population Ery.B from the bone marrow of mice with the indicated genotypes. (B) Quantification of multiple western blot experiments depicted in panel A. n = 3 or 4 mice for each genotype. pS6 Ser235/236 and pS6k Thr389 levels were normalized to the levels of the respective total proteins. CAB39 was normalized to β-actin. (C) pThr172 AMPKα levels in embryonic day 14.5 (E14.5) fetal liver cells of the indicated genotype as measured using sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and normalized to total cellular protein determined using the bicinchoninic acid assay. (D) Flow cytometry quantification of pS6 Ser235/236 in Ery.A, Ery.B, and Ery.C bone marrow erythroblasts. n = between 4 and 13 mice for each genotype. (E) In vivo protein synthesis rates in individual maturation stage–matched bone marrow erythroblasts, as determined via flow cytometry for O-propargyl-puromycin incorporated into nascent proteins during translation. n = between 4 and 7 mice for each genotype. (F) CD71 MFI in Ery.A and Ery.B bone marrow erythroblasts. n = 13 or 15 mice for each genotype. (G) Nonheme iron levels in splenic Ter119+ erythroblasts, normalized to total cellular protein. n = 3 or 4 mice for each genotype. Bar charts show data as mean values ± SD; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001; ∗∗P < .01; ∗P < .05; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.
mTORC1 activity is enhanced in β-thalassemia and suppressed by miR-144/451 disruption in 8-week-old mice. (A) Western blot analysis of indicated proteins and phosphoproteins (p) in the erythroblast population Ery.B from the bone marrow of mice with the indicated genotypes. (B) Quantification of multiple western blot experiments depicted in panel A. n = 3 or 4 mice for each genotype. pS6 Ser235/236 and pS6k Thr389 levels were normalized to the levels of the respective total proteins. CAB39 was normalized to β-actin. (C) pThr172 AMPKα levels in embryonic day 14.5 (E14.5) fetal liver cells of the indicated genotype as measured using sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and normalized to total cellular protein determined using the bicinchoninic acid assay. (D) Flow cytometry quantification of pS6 Ser235/236 in Ery.A, Ery.B, and Ery.C bone marrow erythroblasts. n = between 4 and 13 mice for each genotype. (E) In vivo protein synthesis rates in individual maturation stage–matched bone marrow erythroblasts, as determined via flow cytometry for O-propargyl-puromycin incorporated into nascent proteins during translation. n = between 4 and 7 mice for each genotype. (F) CD71 MFI in Ery.A and Ery.B bone marrow erythroblasts. n = 13 or 15 mice for each genotype. (G) Nonheme iron levels in splenic Ter119+ erythroblasts, normalized to total cellular protein. n = 3 or 4 mice for each genotype. Bar charts show data as mean values ± SD; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001; ∗∗P < .01; ∗P < .05; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.
Disruption of Cab39 impairs erythropoiesis in Hbbth3/+miR-144/451−/− mice
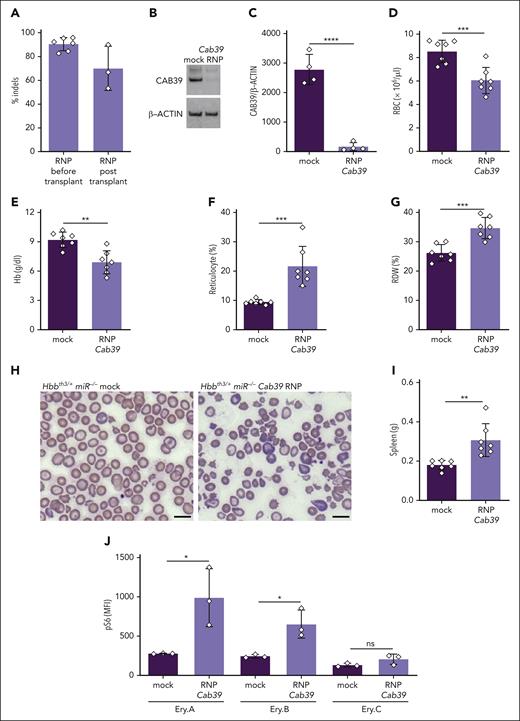
Our findings indicate that miR-144/451 disruption suppresses erythroblast mTORC1 activity via at least 2 mechanisms: (1) inducing intercellular iron deficiency via CD71 suppression and (2) upregulating CAB39, which stimulates LKB1 and AMPK. To investigate the latter, we disrupted the Cab39 locus in β-thalassemic HSPCs and studied the effects on erythroid progeny after transplantation. Lineage-negative Hbbth3/+miR-144/451−/− embryonic day 14.5 (E14.5) fetal liver HSPCs (expressing CD45.2) were transfected with Cas9-sgRNA ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex targeting Cab39, or with Cas9 alone (as a mock treatment), then transplanted into lethally irradiated C57BL/6 hosts (expressing CD45.1; supplemental Figure 8A). After 8 weeks, there was ∼80% engraftment of donor hematopoietic cells (expressing CD45.2; supplemental Figure 8B). The Cab39 indel frequency in donor HSPCs was >85% before transplantation, with a >90% reduction in CAB39 protein (Figure 5A-C; supplemental Figure 8C). At 4 to 6 weeks after transplantation, the Cab39 indel frequency was >65%. Disrupting Cab39 antagonized the beneficial effects of miR-144/451 loss in β-thalassemic mice, as evidenced by a reduced RBC count, reduced hemoglobin concentration, increased reticulocyte count and RDW, worsened RBC morphology, and increased spleen mass (Figure 5D-I; supplemental Table 4). In addition, Cab39 disruption in Hbbth3/+miR-144/451−/− hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) caused erythroid hyperplasia and impaired the maturation of erythroid precursors in the spleen and bone marrow (supplemental Figure 8D-H), indicating worsened ineffective erythropoiesis. Disrupting Cab39 also caused increased mTORC1 activity in β-thalassemic erythroblasts (Figure 5J). One limitation of this experiment is that Cas9 disruption of the Cab39 gene probably reduces its expression to a greater extent than occurs through physiological suppression of Cab39 mRNA by miR-451. Nevertheless, the current findings demonstrate that CAB39 reduces erythroblast mTORC1 activity and inhibits the pathophysiology of β-thalassemia, thereby supporting a model in which miR-451 loss alleviates β-thalassemia by derepressing Cab39 mRNA.
Depletion of CAB39 eliminates the beneficial effects of miR-144/451 disruption in β-thalassemia. Lineage-negative (Lin−) E14.5 Hbbth3/+miR−/− fetal liver HSPCs (expressing CD45.2) were electroporated with Cas9 + Cab39 sgRNA ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex (edited) or Cas9 only (mock), then transplanted into lethally irradiated C57BL/6 recipient mice (expressing CD45.1). (A) Cab39 editing efficiency, as measured via next-generation sequencing (NGS) of HSPCs maintained in vitro for 72 hours after electroporation (before transplantation) or of whole bone marrow cells collected from recipient mice 8 weeks after transplantation. n = between 3 and 6 mice for each condition. (B) Western blot analysis of CAB39 in Lin− HSPCs maintained in vitro for 72 hours after electroporation. (C) Results of multiple experiments performed as in panel B. The y-axis represents the relative protein staining intensity on western blots as measured by automated image analysis, normalized to β-actin, and shown in arbitrary units. (D-G) Erythroid indices (y-axis) according to genotype (x-axis) at 8 weeks after transplantation. n = 7 mice for each condition. (H) Representative images of blood smears (Giemsa stain) from mice with the indicated genotypes. Images were obtained using an Eclipse Ni microscope and a 40× objective lens. Bars represent 5 μm. (I) Summary of spleen weights. n = 7 mice for each condition. (J) Flow cytometry quantification of S6 phosphorylation in maturation stage–matched bone marrow erythroblasts. n = 3 mice for each genotype. Bar charts show data as mean values ± SD; ∗∗∗∗P <.0001; ∗∗∗P <.001; ∗∗P <.01; ∗P < .05. RNP, ribonucleoprotein.
Depletion of CAB39 eliminates the beneficial effects of miR-144/451 disruption in β-thalassemia. Lineage-negative (Lin−) E14.5 Hbbth3/+miR−/− fetal liver HSPCs (expressing CD45.2) were electroporated with Cas9 + Cab39 sgRNA ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex (edited) or Cas9 only (mock), then transplanted into lethally irradiated C57BL/6 recipient mice (expressing CD45.1). (A) Cab39 editing efficiency, as measured via next-generation sequencing (NGS) of HSPCs maintained in vitro for 72 hours after electroporation (before transplantation) or of whole bone marrow cells collected from recipient mice 8 weeks after transplantation. n = between 3 and 6 mice for each condition. (B) Western blot analysis of CAB39 in Lin− HSPCs maintained in vitro for 72 hours after electroporation. (C) Results of multiple experiments performed as in panel B. The y-axis represents the relative protein staining intensity on western blots as measured by automated image analysis, normalized to β-actin, and shown in arbitrary units. (D-G) Erythroid indices (y-axis) according to genotype (x-axis) at 8 weeks after transplantation. n = 7 mice for each condition. (H) Representative images of blood smears (Giemsa stain) from mice with the indicated genotypes. Images were obtained using an Eclipse Ni microscope and a 40× objective lens. Bars represent 5 μm. (I) Summary of spleen weights. n = 7 mice for each condition. (J) Flow cytometry quantification of S6 phosphorylation in maturation stage–matched bone marrow erythroblasts. n = 3 mice for each genotype. Bar charts show data as mean values ± SD; ∗∗∗∗P <.0001; ∗∗∗P <.001; ∗∗P <.01; ∗P < .05. RNP, ribonucleoprotein.
miR-144/451 loss stimulates ULK1-dependant autophagy of free α-globin in β-thalassemia
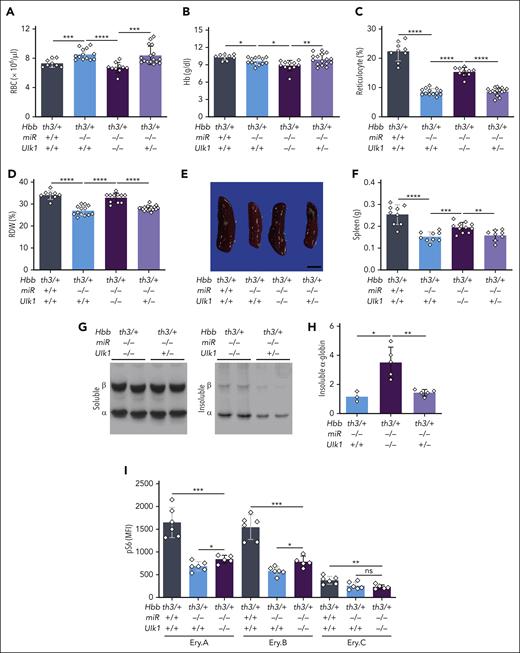
Free α-globin is degraded by an ULK1-dependent, ATG5-independent autophagy pathway.9 Considering that ULK1 is activated by AMPK and inhibited by mTORC1,10 we hypothesized that loss of miR-144/451 reduced the severity of β-thalassemia by activating ULK1. To test this, we interbred Hbbth3/+miR-144/451−/− mice with Ulk1−/− mice. As most Hbbth3/+Ulk1−/− mice do not survive postnatally,9 we generated E14.5 embryos (expressing CD45.2) with the genotypes Hbbth3/+miR-144/451+/+Ulk1+/+, Hbbth3/+miR-144/451−/−Ulk1+/+, Hbbth3/+miR-144/451−/−Ulk1−/−, and Hbbth3/+miR-144/451−/−Ulk1+/− and transplanted their fetal liver HSCs into lethally irradiated C57BL/6 recipients (expressing CD45.1; supplemental Figure 9A). After 8 weeks, the extent of donor hematopoietic cell engraftment exceeded 90% for all genotypes (supplemental Figure 9B). Analysis of recipient mice showed that the loss of Ulk1 in Hbbth3/+miR-144/451−/− HSCs caused decreases in the RBC count and hemoglobin concentration and increases in the reticulocyte count, RDW, and spleen mass, as compared with those indices in recipients of Hbbth3/+miR-144/451−/− HSCs with intact Ulk1 alleles (Figure 6A-F; supplemental Table 5). Disrupting Ulk1 also caused erythroid hyperplasia and impaired maturation of erythroid precursors in the spleen and bone marrow (supplemental Figure 10). Therefore, loss of Ulk1 causes worsening of β-thalassemia in Hbbth3/+miR-144/451−/− mice. The increased β-thalassemia pathologies caused by loss of Ulk1 in Hbbth3/+miR-144/451−/− hematopoietic cells were accompanied by a threefold increase in RBC α-globin precipitates (Figure 6G-H), corresponding to approximately half the levels detected in RBCs from Hbbth3/+ mice with intact miR-144/451 and Ulk1 alleles (compare Figure 6H with Figure 2B). Disrupting Ulk1 in Hbbth3/+miR-144/451−/− erythroblasts caused a relatively modest but significant increase in mTORC1 activity (Figure 6I).
Ablation of Ulk1 reduces the beneficial effects of miR-144/451 disruption in β-thalassemia. WT C57BL/6 mice (expressing CD45.1) received transplantation with Lin− E14.5 fetal liver HSPCs with the indicated genotypes and analyzed 8 weeks after transplantation. (A-D) Erythroid indices (y-axis) according to the genotype (x-axis). n = 10 to 12 mice for each genotype. (E) Representative spleens at 8 weeks after transplantation. Bars represent 0.5 cm. (F) Summary of spleen weights. n = between 8 and 11 mice for each genotype. (G) TAU gels stained with Coomassie brilliant blue showing soluble and insoluble α- and β-globin proteins in RBC lysates. (H) Relative insoluble α-globin levels in RBCs as determined by TAU gel analysis, performed as described in panel G, and quantified using automated image analysis. n = 3 to 5 mice for each genotype. (I) Flow cytometry quantification of S6 phosphorylation in maturation stage–matched bone marrow erythroblasts. n = 5 to 6 mice for each genotype. Bar charts show the data as mean values ± SD; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗P < .01; ∗P < .05.
Ablation of Ulk1 reduces the beneficial effects of miR-144/451 disruption in β-thalassemia. WT C57BL/6 mice (expressing CD45.1) received transplantation with Lin− E14.5 fetal liver HSPCs with the indicated genotypes and analyzed 8 weeks after transplantation. (A-D) Erythroid indices (y-axis) according to the genotype (x-axis). n = 10 to 12 mice for each genotype. (E) Representative spleens at 8 weeks after transplantation. Bars represent 0.5 cm. (F) Summary of spleen weights. n = between 8 and 11 mice for each genotype. (G) TAU gels stained with Coomassie brilliant blue showing soluble and insoluble α- and β-globin proteins in RBC lysates. (H) Relative insoluble α-globin levels in RBCs as determined by TAU gel analysis, performed as described in panel G, and quantified using automated image analysis. n = 3 to 5 mice for each genotype. (I) Flow cytometry quantification of S6 phosphorylation in maturation stage–matched bone marrow erythroblasts. n = 5 to 6 mice for each genotype. Bar charts show the data as mean values ± SD; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗P < .01; ∗P < .05.
In general, the beneficial effects of miR-144/451 disruption on abnormal β-thalassemic blood indices were reduced by ∼50% with the loss of Ulk1. Therefore, miR-144/451 loss alleviates β-thalassemia occurrence through both ULK1-dependent and -independent activities. The latter likely occurs through suppression of mTORC1 activity and may include reduced globin protein synthesis (Figure 4E) and enhanced degradation of free α-globin via the ubiquitin-proteasome system (Figure 3E-F).34
Effects of MIR-144/451 loss in human erythroblasts generated in vitro
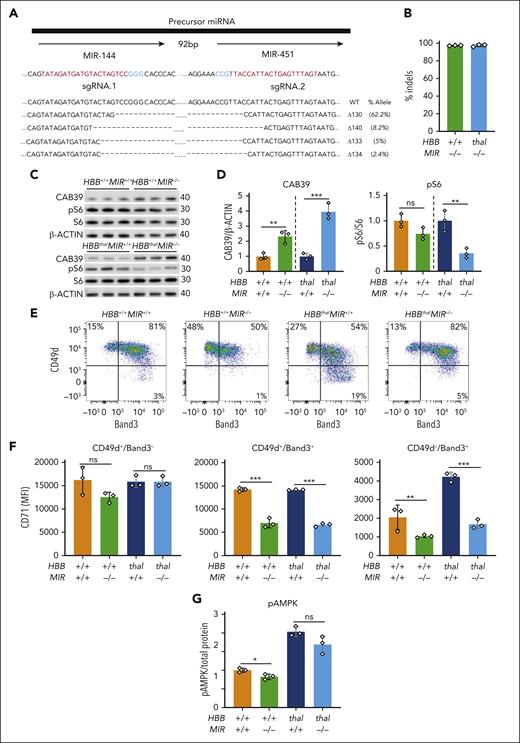
We transfected CD34+ HSPCs from healthy donors (HDs) or patients with β-thalassemia with two Cas9-sgRNA RNPs targeting the coding regions of MIR-144 and MIR-451, then analyzed the erythroid progeny generated by in vitro differentiation. The targeting strategy resulted in high-frequency (98%-100%) deletions that disrupted the coding regions for both microRNAs, with >90% reductions in their expression (Figure 7A-B; supplemental Figure 11A-B). Western blot analysis showed increased CAB39 protein levels in HD and β-thalassemia erythroblasts (Figure 7C-D) and reduced mTORC1 activity in β-thalassemic erythroblasts (Figure 7D). Flow cytometry analysis showed that MIR-144/451 disruption caused between 51% and 53% reductions in the levels of TfR1 receptor (CD71) on maturation stage–matched (CD49d+Band3−) erythroblasts (Figure 7E-F). These findings are similar to our observations in mice. In contrast to our mouse studies, however, we observed no increase in AMPK phosphorylation at Thr172 in MIR-144/451–disrupted human erythroblasts (Figure 7G; supplemental Figure 11C).
Effects of MIR-144/451 disruption on normal and β-thalassemic human erythropoiesis in vitro. CD34+ cells obtained from a healthy donor (HBB+/+) or from a patient with β-thalassemia (HBBthal) were electroporated with Cas9-sgRNA ribonucleoprotein complexes targeting the tandem MIR-144 and MIR-451 coding sequences then induced to undergo in vitro erythroid differentiation. (A) The tandem microRNA genes separated by 92 bp are shown on top. sgRNAs targeting MIR-144 and MIR-451 are shown below in red, and the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequences are in blue. Sequence alignments showing the 4 most common indels detected via NGS 72 hours after editing are shown (bottom). Dashes indicate deletions. The size and frequency of each deletion are shown (right). (B) MIR-144/451 editing efficiency as measured via NGS of HSPCs. n = 3 for each genotype. (C) Western blot analysis of the indicated proteins in MIR-144/451–disrupted and control cells on day 12 of erythroid differentiation. (D) Results of multiple experiments performed as in panel C. CAB39 was normalized to β-actin, and pS6 was normalized to S6. Data from HBB+/+ and HBBThal were normalized separately. (E) Representative flow cytometry plots showing the gating strategy for determining CD71 expression in developmental stage–matched erythroid precursors on day 12 of erythroid differentiation. (F) Summary of multiple experiments performed showing CD71 MFI in erythroblast populations defined by the gating strategy shown in panel E. (G) pThr172 AMPKα levels in erythroblasts on day 12 of differentiation as measured via sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and normalized to total protein determined by the bicinchoninic acid assay (BCA). Bar charts show mean values ± SD of 3 biological replicate experiments using cells from the same CD34+ cell donors; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗P < .01; ∗P < .05.
Effects of MIR-144/451 disruption on normal and β-thalassemic human erythropoiesis in vitro. CD34+ cells obtained from a healthy donor (HBB+/+) or from a patient with β-thalassemia (HBBthal) were electroporated with Cas9-sgRNA ribonucleoprotein complexes targeting the tandem MIR-144 and MIR-451 coding sequences then induced to undergo in vitro erythroid differentiation. (A) The tandem microRNA genes separated by 92 bp are shown on top. sgRNAs targeting MIR-144 and MIR-451 are shown below in red, and the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequences are in blue. Sequence alignments showing the 4 most common indels detected via NGS 72 hours after editing are shown (bottom). Dashes indicate deletions. The size and frequency of each deletion are shown (right). (B) MIR-144/451 editing efficiency as measured via NGS of HSPCs. n = 3 for each genotype. (C) Western blot analysis of the indicated proteins in MIR-144/451–disrupted and control cells on day 12 of erythroid differentiation. (D) Results of multiple experiments performed as in panel C. CAB39 was normalized to β-actin, and pS6 was normalized to S6. Data from HBB+/+ and HBBThal were normalized separately. (E) Representative flow cytometry plots showing the gating strategy for determining CD71 expression in developmental stage–matched erythroid precursors on day 12 of erythroid differentiation. (F) Summary of multiple experiments performed showing CD71 MFI in erythroblast populations defined by the gating strategy shown in panel E. (G) pThr172 AMPKα levels in erythroblasts on day 12 of differentiation as measured via sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and normalized to total protein determined by the bicinchoninic acid assay (BCA). Bar charts show mean values ± SD of 3 biological replicate experiments using cells from the same CD34+ cell donors; ∗∗∗P < .001; ∗∗P < .01; ∗P < .05.
Maturation of late-stage β-thalassemic erythroblasts was impaired when compared with that of HD erythroblasts, as illustrated by cell morphology, flow cytometry for CD49d and Band 3, and the fraction of anucleate reticulocytes on differentiation day 18 (supplemental Figure 11D-E). Similar to our observations in mice, loss of MIR-144/451 in HD erythroblasts caused impaired maturation (supplemental Figures 1 and 11). However, MIR-144/451 disruption also caused impaired maturation of human β-thalassemic erythroblasts, in contrast to the enhanced maturation observed after miR-144/451 disruption in β-thalassemic mice. With MIR-144/451 alleles intact, apoptosis was increased in human β-thalassemic erythroblasts as compared with those from HDs. Disrupting MIR-144/451 in HD human erythroblasts resulted in approximately threefold increased apoptosis as compared with that in unedited samples, whereas the same treatment in β-thalassemic erythroblasts caused no change in the levels of apoptosis (supplemental Figure 11I). Therefore, Cas9 disruption of MIR-144/451 in human erythroblasts caused some biochemical changes that overlapped with those observed in MIR-144/451−/− mouse erythroblasts. However, in contrast to our observations in mice, MIR-144/451 loss did not alleviate β-thalassemic defects in human erythroid maturation. The latter observation may be due to species-specific effects or physiological differences between in vitro and in vivo erythropoiesis.
Discussion
The accumulation of toxic free α-globin is a major determinant of β-thalassemia pathophysiology.2,32,35 Previously, we showed that free α-globin is eliminated via ULK1-dependent autophagy, which is enhanced by inhibition of the ULK1 antagonist mTORC1.9 Here, we have shown that disrupting the bicistronic microRNA locus miR-144/451 in β-thalassemic mouse erythroid precursors reduces hemolysis and ineffective erythropoiesis by stimulating ULK1-mediated autophagy of free α-globin via 2 mechanisms (supplemental Figure 12). First, the loss of miR-451 derepressed its target Cab39 mRNA, resulting in the activation of AMPK and the repression of mTORC1, both of which are known to stimulate ULK1 activity.10,11 Second, by reducing the expression of the major iron importer TfR1, loss of miR-144/451 caused erythroblast iron restriction, which has been shown to reduce α-globin precipitates and improve hematological indices in β-thalassemia.27,28 Derepression of additional miR-144 or miR-451 target genes might also have contributed to our findings. For example, miR-144 represses mRNA-encoding nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 (NRF2), a transcription factor that regulates the expression of antioxidant genes. In sickle cell disease and thalassemia, elevated levels of miR-144 are associated with low levels of NRF2, oxidative stress, and severe anemia.36,37 Therefore, induction of NRF2 by miR-144 loss may inhibit hemolysis and ineffective erythropoiesis in β-thalassemia by protecting against oxidant stress. It will be interesting to deconvolute further the effects of miR-144/451 in β-thalassemia by disrupting each microRNA gene individually in mice.
In general, mTORC1 and AMPK inhibit or activate ULK1-mediated autophagy, respectively, according to the metabolic state.10,25,26 This study and a previous one show that mTORC1 is pathologically activated in β-thalassemia.9 Potential causes of excessive mTORC1 activation in β-thalassemia include the accumulation of branched-chain amino acids generated by α-globin degradation,38 erythropoietin receptor signaling enhancement,39 and iron overload.33,40-44 Our data are consistent with previous findings that TfR1 haploinsufficiency causes erythroblast iron restriction and improves ineffective erythropoiesis in β-thalassemia.45,46 Although it is not fully understood how iron restriction alleviates β-thalassemia, suppressing mTORC1 activity is a likely mechanism. Dietary iron deficiency inhibits mTORC1 by activating HRI, consistent with our findings that miR-144/451 disruption in β-thalassemic erythroblasts causes increased eIF2α phosphorylation.33 Iron may also regulate erythroblast mTORC1 activity through other mechanisms.43,44,47,48
Further studies are required to identify how the loss of miR-144/451 inhibits TfR1 expression. After delivering transferrin-iron complex into cells via receptor-mediated endocytosis, TfR1 is returned to the cell surface through recycling endosomes.49 miR-144 and miR-451 target several mRNAs encoding endosomal membrane trafficking proteins that could regulate TfR1 recycling. One candidate is Rab14 mRNA, which is targeted by both miR-144 and miR-451. Manipulation of Rab14 in rat kidney cells altered the TfR1 distribution within endosomal compartments and upregulation of Rab14 expression in miR-144 and miR-451-depleted erythroblasts caused delayed maturation with reduced expression of TfR1.50,51
Loss of miR-144/451 in nonthalassemic mice causes several erythroid abnormalities. First, mild hemolytic anemia with RBC susceptibility to oxidant stress occurs via upregulation of the miR-451 target Ywhaz (14-3-3ζ), which inhibits nuclear localization of the antioxidant transcription factor, FOXO3A.15,17 Second, erythroid maturation is delayed, in part, by upregulation of the miR-451 targets Cox10 and Ywhaz.15-18 Third, activation of LKB1 and AMPK via increased expression of the miR-451 target Cab39 impairs recovery from anemia caused by hemolysis, blood loss, or 5-fluoruracil.20 In contrast to these deleterious effects, disrupting the miR-144/451 locus has beneficial effects in β-thalassemia, including reduced oxidant stress, increased RBC lifespan, and improved erythroid maturation. The opposing outcomes of miR-144/451 loss during normal vs β-thalassemic erythropoiesis illustrate how microRNAs can exert distinct effects in the context of specific physiological stresses and genetic interactions.13,52 During β-thalassemic erythropoiesis, the potentially adverse consequences of miR-144/451 loss are outweighed by the benefits resulting from the reduction of free α-globin.
In vitro erythroid differentiation of normal donor and CD34+ cells from patients with β-thalassemia recapitulated some findings that we observed in mice. For example, MIR-144/451 disruption caused increased CAB39 expression, reduced mTORC1 activity, and reduced TfR1 expression. However, in contrast to studies in mice, we observed no activation of AMPK via phosphorylation of Thr172 or improved maturation of human β-thalassemic erythroblasts. These differences may be due to species-specific properties of erythropoiesis or to the artificial conditions of in vitro erythroid culture used for human cells. Supporting the latter explanation, mTORC1 and AMPK activities are exquisitely sensitive to nutrient levels, cytokines, and other metabolic signals occurring in vivo that cannot be reproduced easily in vitro.26 It may be informative to investigate the effects of MIR-144/451 disruption on human β-thalassemic erythropoiesis after xenotransplantation of CD34+ cells into immunodeficient mice.
Considering that mTORC1 and AMPK are key metabolic sensors and effectors, it is interesting to note that miR-451 expression is also subject to metabolic regulation. In human glioma cells under metabolic stress, activated AMPK suppresses MIR-144/451 transcription, causing upregulation of CAB39, activation of LKB1, and further activation of AMPK.53,54 This feed-forward loop facilitates the survival of nutrient-depleted glioma cells by stimulating their migration and inhibiting anabolic pathways. Defining the metabolic alterations that dysregulate miR-144/451, mTORC1, and AMPK in β-thalassemia should further elucidate how protein quality control pathways can be manipulated therapeutically to detoxify free α-globin. Similarly, new drugs being developed to manipulate mTORC1, AMPK, and ULK1 therapeutically for numerous diseases might be repurposed for treating β-thalassemia.55-57
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to C. Savage, G. Charleton and staff (St. Jude Animal Resource Center), Joseph Emmons and staff (St. Jude Veterinary Pathology Core), Camenzind Robinson and staff (St. Jude Cellular Imaging Shared Research), Shondra Miller and staff (Center for Advanced Genome Engineering), David Cullins (St. Jude Hematology Flow Cytometry Core), and Richard Ashmun, Stacie Woolard, and staff (St. Jude Flow Cytometry Core). The authors thank Keith A. Laycock (St. Jude Department of Scientific Editing) for scientific editing of the manuscript. The authors thank Anita Impagliazzo (impag1@lumos.net) for graphic design. The authors thank Hongbo Chi and Nicole Chapman (St. Jude Department of Immunology) for helpful discussions.
This work was supported by grants R01 DK61692 and R01HL165798 from National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (M.J.W.) and the Cooley’s Anemia Foundation Research Junior faculty Fellowship (C.L.). The St. Jude Children's Research Hospital shared resource core facilities are supported by NIH National Cancer Institute grant P30CA21765 and St. Jude/ALSAC.
The content of this manuscript is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Authorship
Contribution: J.K., M.J.W., and C.L. conceived the project and designed and interpreted experiments; J.K. and G.E.C. performed most of the experiments; A.G.F. and R.B.A.S. helped with animal analysis and performed iron studies; Y.Y. helped with fetal liver genome editing and experiments during review; J.Z. genotyped animals; K.M., M.D., R.T., and C.W. assisted with animal breeding and experiments; H.S. performed histopathological analysis; and J.K., G.E.C., M.J.W., and C.L. wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: M.J.W. serves on advisory boards for Cellarity Inc, Novartis, Dyne Therapeutics, bluebird bio, and Vertex Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
The current affiliation for C.L. is Genomic Medicine Unit, Rare Blood Disorders, Sanofi, Waltham, MA.
Correspondence: Christophe Lechauve, Genomic Medicine Unit, Rare Blood Disorders, Sanofi, 225 2nd Ave, Waltham, MA 02451; e-mail: christophe.lechauve@sanofi.com; and Mitchell J. Weiss, Department of Hematology, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, 262 Danny Thomas Pl, MS 355, Memphis, TN 38105; e-mail: mitch.weiss@stjude.org.
References
Author notes
∗J.K. and G.E.C. contributed equally to this study.
Data are available on request from the corresponding authors, Christophe Lechauve (christophe.lechauve@sanofi.com) and Mitchell J. Weiss (mitch.weiss@stjude.org).
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.

![miR-144/451 disruption enhances the autophagic flux and proteasomal degradation of insoluble free α-globin. Reticulocytes in whole blood from mice with the indicated genotypes were pulse-labeled with 35S-amino acids; chased with unlabeled amino acids ± a proteasome inhibitor (MG132 [MG]; 10 μM), a lysosome inhibitor (chloroquine [CQ]; 100 μM), or vehicle (Veh); separated via centrifugation into soluble and insoluble fractions; subjected to TAU gel electrophoresis to separate globin proteins; and analyzed by autoradiography. (A) Autoradiogram immediately after a 30-minute pulse with 35S-amino acids. Each lane represents a biological replicate experiment using equivalent input cell numbers from different mice. (B) Relative levels of soluble and insoluble globin determined by quantitative image analysis of TAU gel autoradiograms, as shown in panel A. (C) Representative TAU gel autoradiograms showing soluble and insoluble globin chains after 3-hour and 6-hour chases with unlabeled amino acids. (D) Results of multiple experiments performed as described for panel C and quantified using automated image analysis. n = 5 mice for each genotype. (E) Percentage increases in the clearance of insoluble α-globin in Hbbth3/+miR−/− vs Hbbth3/+miR+/+ reticulocytes after a 6-hour chase with MG, CQ, or Veh. (F) Summary of data from panel E indicating the relative contributions of autophagy (CQ-inhibited) or proteasomal (MG-inhibited) degradation to the enhanced clearance of free α-globin conferred by miR-144/451 disruption. Data are shown as mean values ± SD; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001; ∗∗P < .01; ∗P < .05.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/142/10/10.1182_blood.2022017265/2/m_blood_bld-2022-017265-gr3.jpeg?Expires=1767767488&Signature=IZTcd6E34JqJ0bH9t3xU0T6YPbuLXx2UJMa-XWVMlZMfa2KbcLQ6Dy5NuvxY5b1zuHRZWnBb~VyVGfO6HOsga-m7RmUNu7D8oJ89PnYLCvE4Xh~ghSEU21XPyBfZpNM5ruK4VJpX0ZswHahFV9Xnhg-to41DBkDQmg4BNwjl5cJQcsn7Qo0c9T93moDEKAxmrGsVWg3q2itTmR7mC1EfHGbGTIXw7srI17BFe~saPu2KYLh~EZ~tYupb~RRIC9DyTOxmyGFtp6VdbLn07KJhbkXmypIGrz1gGgbZSe235gvMFyle3P4~wb9BsTnjl4QNnrk5Z6ixAYpNG1Djdv4Y6Q__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal