Abstract
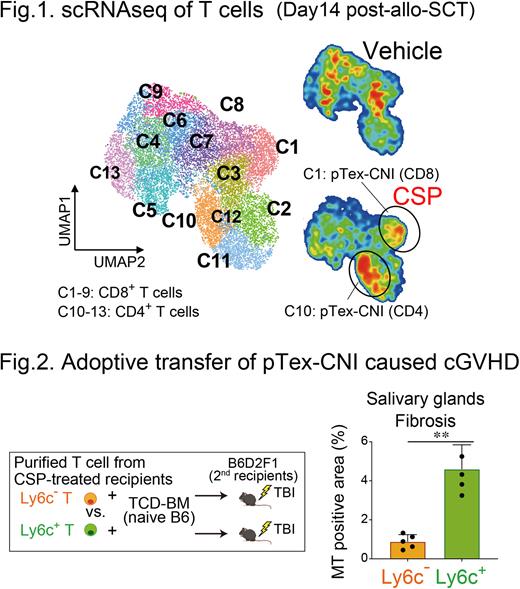
[Introduction] Calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs) reduce acute GVHD by inhibiting NFAT signaling in donor T cells but fail to prevent chronic GVHD (cGVHD). We have previously shown that donor alloreactive T cells differentiated into exhausted T cells with severely impaired alloreactivity after mouse allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT) (Asakura S: JCI 2010). Given the critical role of NFAT signaling in T-cell exhaustion, we explored the role of CNIs in donor T-cell exhaustion and tolerance induction after allo-SCT using mouse SCT models with host alloantigen (allo-Ag)-specific 2C TCR-transgenic (2C) T cells and single cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) of donor T cells. [Methods] B6D2F1 recipients (H-2b/d) were lethally irradiated and transplanted with 1 x 106 2C T cells (CD8.1+) plus 1 x 106 wild type T cells (WT, CD45.1+) of B6 background (H-2b) together with T-cell-depleted bone marrow cells (TCD-BM) from WT B6 (CD45.2+) on day 0. In some experiments, recipients were p.o. injected with 25 mg/kg cyclosporin (CSP) daily on days 0-14. [Results] Flowcytometric analysis (FCM) showed 2C CD8+ T cells differentiated into terminally exhausted T cells (Tex) expressing multiple co-inhibitory receptors such as PD-1 and TIGIT on day 14 after allo-SCT, that led to unresponsiveness of donor T cells to PD-1 blockade. Next, we performed scRNAseq of donor T cells harvested from CSP- or vehicle-treated recipients on day 14 after allo-SCT. UMAP analysis identified 4 clusters of CD4+ T cells (C10-C13) and 9 clusters of CD8+ T cells (C1-C9), and all of them expressed Tox and Pdcd1, indicating that all donor T cells entered differentiation pathway to exhaustion. CSP remarkably increased C10 (CD4+) and C1 (CD8+) characterized by lower expression of Tox and Pdcd1 and higher expression of Ly6c2 compared to other clusters (Fig 1). FCM confirmed CSP significantly expanded PD-1+TIGIT-, and TOXlow cells in 2C and WT CD8+ and WT CD4+ donor T cells on day 14, and these cells persisted at least 2 wks after cessation of CSP. After adoptively transferred into irradiated secondary B6D2F1 recipients, Ly6C+ T cells purified from CSP-treated recipients were differentiated into Ly6C- Tex, while Ly6C- T cells remained to be Ly6C-, indicating that CSP-induced Ly6C+ donor T cells are precursors of Tex (pTex) like cells. We named these cells as pTex-CNI, based on lower TCF-1 expression compared to TCF-1high canonical pTex. We found that, among various agents known to suppress GVHD or Tex differentiation, only CSP and ibrutinib induced ToxlowPD-1+TIGIT-Ly6C+ pTex-CNI, suggesting that NFAT inhibition is critical for pTex-CNI induction. Importantly, only Ly6C+ donor T cells, but not Ly6C- cells, induced cGVHD after adoptive transfer, suggesting that pTex-CNI play a critical role in pathophysiology of cGVHD (Fig 2). pTex-CNI demonstrated marked proliferative response and differentiation toward Tex upon PD-1 blockade as canonical pTex did in tumor and viral infection models in the previous reports (Sade-Feldman M: Cell 2018, Hudson WH: Immunity 2019). Administration of PD-L1 mAbs from day 14 enhanced OXPHOS of donor T cells and eradicated host-type leukemia cells only in CSP-treated recipients. Post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy) is widely used in clinical allo-SCT, and CNIs are started either before SCT or after PTCy typically on day 5. We found that pTex-CNI were induced only when CSP was added to PTCy from day -1, but not from day 5, suggesting that NFAT inhibition early after allo-SCT is critical for induction of pTex-CNI. Finally, we confirmed that T cells from the patients who underwent HLA-matched PBSCT with tacrolimus (TAC)-based GVHD prophylaxis started from day -1 expressed significantly lower levels of PD-1, TIGIT, and TOX on day 28 compared to those from patients underwent haploidentical PBSCT with PTCy-based GVHD prophylaxis combined with TAC started from day 5. [Conclusion] Our study for the first time demonstrated that CNI inhibits terminal differentiation of donor exhausted T cells after allo-SCT. In mouse models, pTex-CNI contributed to development of cGVHD and PD-1 blockade-induced anti-tumor response after allo-SCT. The timing of CNI initiation in PTCy-based allo-SCT could determine the persistence of donor T cell alloreactivity after allo-SCT, that could impact on the strategies of cessation of immunosuppressants and treatment of relapsed diseases. These should be tested in the future clinical studies.
Disclosures
Teshima:Chugai: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Astellas: Research Funding; TEIJIN PHARMA: Research Funding; Fuji Pharma: Research Funding; Janssen: Other: Manuscript preparation; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Manuscript preparation, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Merck Sharp & Dohme: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi: Research Funding; NIPPON SHINYAKU: Research Funding; Luca Science Inc.: Research Funding; Kyowa Kirin: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal