Background: Polycythemia vera (PV) is a myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) characterized by clonal stem cell proliferation of the erythroid, myeloid, and megakaryocytic lines. The predominant clinical characteristic is an increase in red cell mass, resulting in hyperviscosity of the blood, which is responsible for most symptoms during early stages of disease. Disease progression typically results in symptomatic splenomegaly and severe constitutional symptoms, causing significant morbidity and a shortened life expectancy. Patients with PV may develop cardiovascular complications, myelofibrosis (MF), myelodysplasia, or acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Long-term (20-year) survival for PV is 18%, highlighting the poor long-term prognosis and need for additional therapies. Phlebotomy and low-dose aspirin are the standard of care for initial treatment; hydroxyurea (HU) remains the myelosuppressive agent of choice, despite the increased potential for leukemic transformation, estimated at 10% after 13 years of exposure. The Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor ruxolitinib is approved in the US and Europe for the treatment of patients who have had an inadequate response to or are intolerant of HU. In clinical trials, ruxolitinib produced responses in 23% of patients, compared with <1% in patients receiving best available therapy (Verstovsek, et al. Haematologica. 2016). Despite this significant improvement, there remains a substantial unmet need for patients with PV who are resistant to or intolerant of HU.
The tumor suppressor protein p53 is the master regulator of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in response to cellular stress or DNA damage. Murine double minute 2 (MDM2) is a key regulator of p53, inhibiting its activity via ubiquitination, nuclear export, and direct inhibition of transcriptional activity. MDM2 is upregulated in PV CD43+ stem/progenitor cells, making the p53-MDM2 axis an attractive target in PV. In PV, TP53 is observed to be wild-type in 94% of patients, suggesting MDM2 inhibition as a potentially successful strategy (Raza, et al. Am. J. Hematol. 2012). KRT-232 is a potent and selective oral small-molecule drug that targets MDM2 and prevents MDM2-mediated p53 inhibition, allowing p53 to mediate tumor cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. In a phase 1 dose-finding study, clinical responses were observed in 7/12 (58%) of PV patients treated with an alternative MDM2 inhibitor (Mascarenhas, et al. Blood, 2019). KRT-232 has been investigated as monotherapy and in combination with trametinib or dabrafenib in phase I studies of AML and melanoma; the most common treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) observed in these studies were nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, decreased appetite, anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and fatigue. The majority of TRAEs were grade 1 or 2.
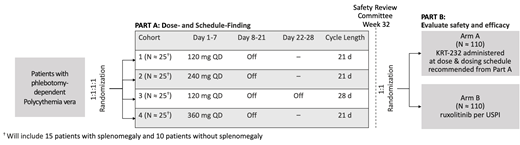
Methods: This randomized, open-label study aims to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of KRT-232 compared with ruxolitinib in up to 320 patients with phlebotomy-dependent PV (Figure). The study will be conducted in 2 parts. Part A will identify the recommended dose and schedule by testing 4 treatment cohorts. In Part B, patients will be randomized 1:1 to either KRT-232 or ruxolitinib in order to evaluate safety and efficacy using the recommended dose/schedule for KRT-232 from part A. This study will enroll patients ≥ 18 years of age with PV and an ECOG performance status ≤ 2. In Part A, patients who are phlebotomy dependent with and without splenomegaly are eligible and patients must be resistant to or intolerant of HU or have undergone treatment with interferon. In Part B, only phlebotomy-dependent patients with splenomegaly are eligible, and patients must be resistant or intolerant to HU. The primary endpoint is proportion of patients with splenomegaly achieving a response at Week 32, defined as having achieved both of the following: 1) the absence of phlebotomy eligibility from Week 8 through Week 32, with no more than one phlebotomy eligibility occurring after randomization and before the Week 8 visit and 2) a reduction in spleen volume as assessed by MRI (or CT) ≥ 35% from baseline at Week 32. Secondary endpoints include response rate, duration of response and improvement in patient-reported outcomes. Exploratory endpoints include molecular and biomarker analysis including TP53 mutational status. This trial is enrolling at multiple sites in the United States and Europe (NCT03669965, EduraCT: 2018-001672-38).
Gotlib:Deceiphera: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Blueprint Medicines: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Allakos: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. O'Connell:Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astex: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Shionogi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Research Funding. Garcia-Delgado:Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Hospital Virgen De La Victoria Malaga: Employment. Sbardellati:Kartos Therapeutics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Rothbaum:Kartos Therapeutics: Employment, Patents & Royalties: Pending; Quogue Bioventures LLC: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. McGreivy:Kartos Therapeutics: Employment, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Harrison:Janssen: Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Speakers Bureau; CTI: Speakers Bureau; Roche: Honoraria; Sierra Oncology: Honoraria; AOP: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Promedior: Honoraria; Shire: Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Speakers Bureau. Kiladjian:AOP Orphan: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy.
Yes, KRT-232 is an investigational small molecule MDM2 inhibitor. This trial-in-progress abstract describes a registered clinical trial that will evaluate the safety and efficacy of KRT-232 for patients with polycythemia vera.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal