
Background: Therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia (t-AML) is associated with higher risk cytogenetics and disease biology, which partly account for poorer outcomes compared with de novo AML. Normal karyotype (NK) among patients (pts) with t-AML is rare, and the relative contribution of prior chemotherapy or radiotherapy exposure to outcomes of pts with AML with NK is uncertain.
Methods: We reviewed all pts with newly diagnosed AML treated at MD Anderson Cancer Center between 2007 and 2019. Patients were separated into two groups (t-AML and de novo AML) based on their prior administration of chemotherapy or radiotherapy for an antecedent neoplasm. We analyzed patients' characteristics and outcomes including remission rates, relapse rates and survival. Survival curves were estimated by Kaplan-Meier method. Gray's method was used for cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) analysis. Multivariate analyses for relapse-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) were conducted using Cox proportional hazards regression model including age, t-AML (vs. de novo AML), European LeukemiaNet (ELN) 2017 risk classification, and type of therapy (intensive chemotherapy vs. low intensity/hypomethylating agent-based therapy) as covariates.
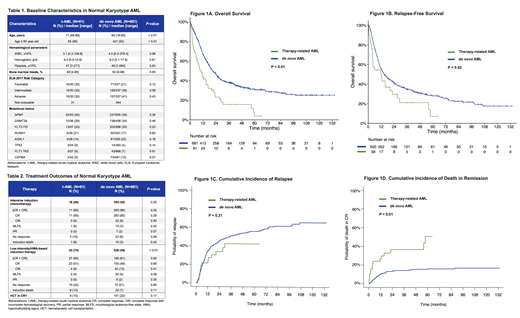
Results: A total of 1977 pts with AML who had complete cytogenetic information available were identified. Among 742 pts (38%) with NK, 61 pts (8%) had t-AML and 681 pts (92%) had de novo AML. NK was present in 18% of all t-AML (61/340 pts). Prior therapy in pts with NK t-AML was chemotherapy (24 pts, 39%), radiation (21 pts, 34%), or both (16 pts, 26%). Characteristics of pts with NK AML are summarized in Table 1. Median age was higher for t-AML vs. de novo AML (71 years [range, 48-89] vs. 64 years [range, 18-92], p < 0.01). No statistically significant difference was noted by mutational status or ELN 2017 risk category. Pts with t-AML were less likely to receive intensive induction chemotherapy (26% vs. 52%, p < 0.01). However, rates of allogeneic stem cell transplant were similar (15% and 22% in t-AML and de novo AML, respectively, p = 0.17). Response rates by type of treatment are shown in Table 2. In pts who received low-intensity therapy, no significant difference was seen in CR/CRi rates between t-AML and de novo AML (60% vs. 61%, p=0.92). However, in pts who received intensive chemotherapy, there was a trend for higher CR/CRi rates in pts with de novo AML compared with t-AML (86% vs. 69%, p=0.05).
With a median follow-up of 54 months, median OS was significantly shorter for pts with t-AML compared with de novo AML: 10.2 months vs. 20.6 months (hazard ratio [HR] 2.07, 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.54-2.78, p < 0.01, Figure 1A). Similarly, RFS was significantly worse for t-AML with a median of 12.0 months compared to 14.8 months for de novo AML (HR 1.55, 95% CI 1.06-2.26, p = 0.02, Figure 1B). Although pts with t-AML had worse OS and RFS, interestingly, this was not driven by higher relapse rates. The 5-year CIR rate was similar for pts with t-AML and de novo AML (42% vs. 56%, p = 0.21, Figure 1C). In contrast, the 5-year cumulative incidence of death in CR/CRi was significantly higher in patients with t-AML compared to patients with de novo AML (51% vs 16%, p < 0.01, Figure 1D), suggesting that non-relapse death is the main driver of worse outcomes for pts with t-AML.
In multivariate analysis, age ≥60 was independently associated with shorter OS (HR 1.79, 95% CI 1.06-3.01, p=0.03) whereas favorable ELN 2017 risk category was prognostic of longer OS (HR 0.62, 95% CI 0.40-0.96, p=0.03). Additionally, there was a trend toward poor OS for adverse ELN 2017 risk category (HR 1.35, 95% CI 0.99-1.86, p=0.06) and better OS with intensive chemotherapy (HR 0.64, 95% CI 0.40-1.01, p=0.06). However, t-AML was not independently associated with OS (HR 1.34, 95% CI 0.83-2.17, p = 0.24) or RFS (HR 1.02, 95% CI 0.53-1.98, p = 0.95).
Conclusions: t-AML with NK is rare entity that comprises <5% of all AML cases. In this large cohort, although the mutation frequency of these pts was similar to those with de novo disease, t-AML with NK was associated with worse survival, which was mostly driven by older age, decreased likelihood of receiving intensive chemotherapy, and a higher rate of death in remission compared to pts with de novo AML with NK. Together, these findings suggest that a clinical history of prior chemotherapy or radiation in patients with NK AML should not impact prognostication or therapeutic decisions.
Ravandi:Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Cyclacel LTD: Research Funding; Macrogenix: Consultancy, Research Funding; Selvita: Research Funding; Menarini Ricerche: Research Funding; Xencor: Consultancy, Research Funding. Kadia:Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Jazz: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Bioline RX: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Genentech: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding. Daver:Astellas: Consultancy; Sunesis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Servier: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Research Funding; Forty-Seven: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy, Research Funding; Agios: Consultancy; Hanmi Pharm Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; NOHLA: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Glycomimetics: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Otsuka: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Research Funding; Immunogen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Jazz: Consultancy. DiNardo:notable labs: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; agios: Consultancy, Honoraria; syros: Honoraria; daiichi sankyo: Honoraria; abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; jazz: Honoraria; medimmune: Honoraria. Bose:Incyte Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; Blueprint Medicine Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kartos: Consultancy, Research Funding; Constellation: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Astellas: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; Promedior: Research Funding; CTI BioPharma: Research Funding. Borthakur:Bayer Healthcare AG: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Eli Lilly and Co.: Research Funding; Argenx: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Oncoceutics: Research Funding; Xbiotech USA: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; FTC Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Eisai: Research Funding; Cantargia AB: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Arvinas: Research Funding; Agensys: Research Funding; Strategia Therapeutics: Research Funding; Polaris: Research Funding; BioLine Rx: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; GSK: Research Funding; Cyclacel: Research Funding; BioTheryX: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Tetralogic Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; PTC Therapeutics: Consultancy; NKarta: Consultancy; Oncoceutics, Inc.: Research Funding. Garcia-Manero:Amphivena: Consultancy, Research Funding; Helsinn: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Astex: Consultancy, Research Funding; Onconova: Research Funding; H3 Biomedicine: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding. Cortes:Forma Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Research Funding; Merus: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Immunogen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sun Pharma: Research Funding; Biopath Holdings: Consultancy, Honoraria; BiolineRx: Consultancy; Astellas Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Kantarjian:Cyclacel: Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria; Immunogen: Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Actinium: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Ariad: Research Funding; Jazz Pharma: Research Funding; Agios: Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Astex: Research Funding. Short:AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Takeda Oncology: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal