Abstract
Background:Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) is a hematopoietic malignancy of the elderly with a heterogenous molecular pathophysiology. Whereas mutations in components of the RAS pathways are among the most common somatic mutations in CMML the JAK2 V617F mutation which is a typical finding in polycythemia vera and around 50% of patients with essential thrombocythemia and primary myelofibrosis, respectively, is by far less frequently detected in CMML but can be consistently found in a subgroup of patients in larger series. Due to the fact that JAK2 V617F-positive CMML is a rare disease the clinical, hematological and in vitro growth characteristics of this entity are poorly investigated. In the "Austrian Biodatabase for Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia (ABCMML)" we retrospectively and prospectively collect clinical, biologic, and molecular information of patients with CMML from different centers in a real life setting.
Aims:Our aim was to characterize the clinical, hematological, molecular and biologic features of CMML patients harboring a JAK2 V617F mutation.
Methods:The diagnosis of CMML was established according to diagnostic criteria of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of 2008 (Vardiman et al, Blood 2009). Clinical and hematological data were obtained from patients records. For molecular characterization we used next-generation sequencing with amplicon-based target enrichment of 39 CMML associated genes. Only mutations with an allele burden of >10% were considered positive in this analysis. Autonomous colony-forming units granulocyte/macrophage (CFU-GM) growth in the absence of exogenous cytokines was assessed using semisolid cultures as previously described (Geissler et al, J Exp Med 1996).
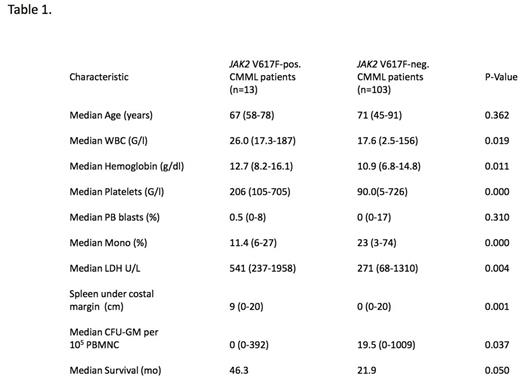
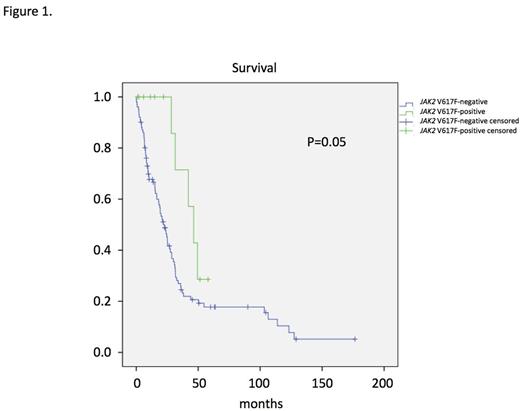
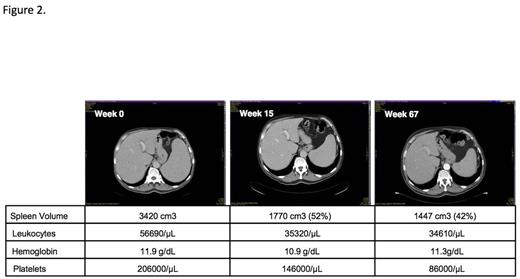
Results:Up to now targeted NGS data are available in 116 patients and in vitro culture data in 75 patients respectively. We identified 13 CMML patients who had a JAK2 V617F mutation with an allele frequency >10%. Clinical, hematological, and biologic characteristics in these patients were compared with 103 patients who had NGS sequencing and were negative for the JAK2 V617F mutation. As shown in Table 1 JAK2 V617F-positive CMML patients had significantly higher WBC counts, higher hemoglobin values, higher platelet counts and more pronounced splenomegaly as compared to JAK2 V617F-negative patients. On the other hand the percentage on monocytes in peripheral blood and the numbers of CFU-GM growing in vitro without addition of exogenous growth factors were lower in CMML patients with the JAK2 V617F mutation as compared to patients without this mutation. The majority of JAK2 V617F-positive patients had additional mutations that can be also found in JAK2 V617F-negative patients, in particular mutations in genes of epigenetic regulation and RNA-splicing, respectively. As shown in Figure 1 there was a trend towards a better survival of patients with the JAK2 V617F mutation as compared to JAK2 V617F-negative patients (p=0.05). In a JAK2 V617F-positive CMML patient with splenomegaly, who was treated with the JAK1/2 inhibitor ruxolitinib off label, we were able to demonstrate the disappearance of constitutional symptoms and a durable spleen response lasting for over 56 months (Fig. 2).
Conclusion:Out data show that CMML patients with the JAK2 V617F mutation have hematological, biologic and clinical characteristics different from JAK2 V617F-negative CMML patients. These findings suggest that JAK2 V617F-positive CMML patients should be regarded as a distinct subgroup which may benefit from specific targeted treatments.
Geissler:Novartis: Honoraria. Pfeilstöcker:Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Burgstaller:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Zach:Novartis: Other: Honoraria for Advisory Board. Hörmann:Novartis: Other: Honoraria for Advisory Board. Jäger:Roche: Other: Personal fees, Research Funding. Sperr:Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria. Kusec:Novartis: Other: Honoraria for lectures. Valent:Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria; Celegene: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal