Abstract
INTRODUCTION: STAG2is a component of the cohesin complex involved in the cohesion of sister chromatids, transcriptional regulation and DNA repair. Recent sequencing studies have identified cohesion mutations in myeloid malignancies with data suggesting a potential adverse impact on survival.
METHODS: We conducted whole exome sequencing of 114 previously untreated patients with MDS or CMML. Exome capture hybrid was performed using Agilent SureSelect All Exon V4. Sequencing was performed with Illumina HiSeq 2000 and aligned to the hg19 human genome reference. Common virtual normal in house pool was used for somatic variant calling. Clinical and demographic data was obtained from clinical records. Generalized linear models were used to study the association of response (OR = overall and CR = complete) and potential risk factors. Response was defined following 2006 IWG criteria. The Kaplan-Meier produce limit methods were used to estimate the median overall survival (OS) and leukemia-free survival (LFS).
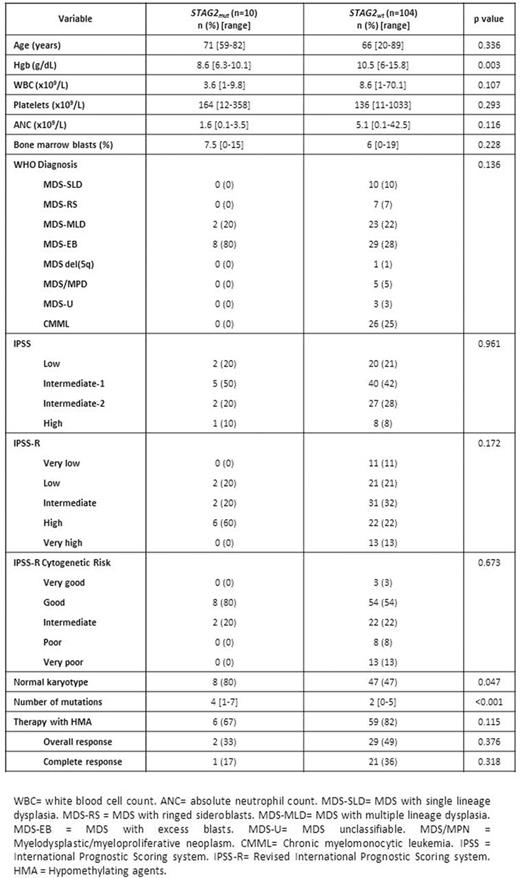
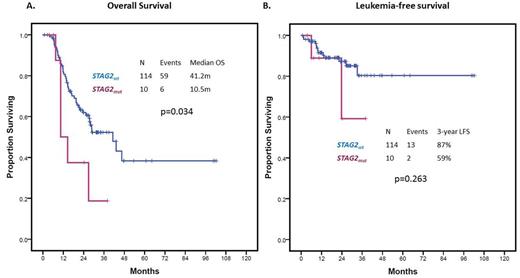
RESULTS: A total of 10 (9%) patients carried high-confidence STAG2 mutations. Patient characteristics are shown in Table 1. Patients with STAG2 mutations tended to have lower Hgb (8.6 vs 10.5 g/dL, p=0.003) and higher median number of driver mutations (4 vs 2, p<0.001). Two patients (20%) had MDS-MLD and the remaining 8 (80%) had MDS-EB, therefore, STAG2 mutation was associated with excess blasts (rho=0.314, p=0.001). There were no cases of CMML with STAG2 mutation. Seven (70%) patients had Low/Int-1 IPSS category and where therefore lower-risk by IPSS and 3 (30%) had Int-2/High IPSS and were therefore higher-risk by IPSS. A total of 65 (57%) patients in the study cohort, 6 (67%) of patients with STAG2 mutation, were treated with hypomethylating agents. STAG2 mutations correlated with normal karyotype (rho=0.190, p=0.04), RUNX1 (rho=0.232, p=0.013), SRSF2 (rho=0.192, p=0.04), ATR (rho=0.303, p=0.001) and NRAS (rho=0.279, p=0.003) mutations. The mean variant allele frequency of STAG2 mutations was 0.35 (range 0.11-072). Seven appeared as clonal driver mutations and 3 as subclonal based on clonal heterogeneity testing. Presence of STAG2 mutation did not significantly impact OR (OR=0.45, 95%CI: 0.08-2.65, p=0.376) or CR (OR=0.32, 95% CI: 0.04-2.97, p=0.318) to therapy with hypomethylating agents. Median follow up of the cohort was 21.6 months (range 1-102 months). Presence of STAG2 mutations was associated with decreased OS (HR=2.45, 95% CI: 1.04-5.80, p=0.041) (Figure 1A). Within the lower-risk IPSS group, STAG2 mutations were associated with an even greater impact on OS (HR = 3.32, 95%CI 1.12-9.82, p=0.030). By multivariate analysis including other prognostic variables such as cytogenetics, Hbg <8g/dL, platelets <50x109/L, ANC <0.8 x109/L or blast >10%, STAG2 mutation retained its independent adverse impact on OS (HR 2.69, 1.03-6.99, p=0.042). STAG2 mutations did not predict for shorter LFS (HR = 2.30, 95% CI 0.51-10.27, p=0.263) (Figure 1B).
CONCLUSION: STAG2 mutations can be found in close to 10% patients with MDS. As previously reported, they tend to appear in patients with MDS-EB and correlate with survival outcomes. In our study, presence of STAG2 mutation was independently associated with adverse overall survival in patients with MDS, particularly in those classified as lower-risk by IPSS, but did not predict for shorter LFS. Contrary to previous reported data, STAG2 mutations did not predict for higher responses to azacitidine or decitabine.
Jabbour:ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy. Ravandi:Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding. Cortes:ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Teva: Research Funding. DiNardo:Novartis: Other: advisory board, Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Agios: Other: advisory board, Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Other: advisory board, Research Funding. Daver:BMS: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Otsuka: Consultancy, Honoraria; Sunesis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Ariad: Research Funding; Kiromic: Research Funding. Konopleva:Reata Pharmaceuticals: Equity Ownership; Abbvie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Stemline: Consultancy, Research Funding; Eli Lilly: Research Funding; Cellectis: Research Funding; Calithera: Research Funding. Kantarjian:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; ARIAD: Research Funding; Pfizer Inc: Research Funding; Delta-Fly Pharma: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal