Abstract
Background: AML is characterized by molecular heterogeneity and specific mutations are prognostically important (Papaemmanuil, Gerstung et al, NEJM,2016). Mutational analysis of NPM1, CEBPA, and FLT3 is included in the 2010 European LeukemiaNet recommendations for AML (Döhner et al, Blood, 2010). Additional recurrently mutated genes have since been identified with potential value for prognosis and prediction of treatment (Tx) response. The phase 3 AZA-AML-001 study showed AZA prolonged median overall survival (OS) vs CCR (10.4 vs 6.5 months [mos]; P=0.101) and improved 1-year survival (46.5% vs 34.2%) in older patients (pts) with AML (Dombret et al, Blood, 2015).
Aim: To investigate relationships between gene mutations and OS in the subpopulation of AZA-AML-001 pts with available baseline bone marrow (BM) for molecular analyses ("biomarker" cohort).
Methods: Eligible pts were age ≥65 years with newly diagnosed AML (>30% BM blasts), ECOG performance status (PS) score 0-2, WBC count ≤15x109/L, and NCCN-defined intermediate- or poor-risk cytogenetics. Pts received AZA (75 mg/m2/day [d] x 7d/28d cycle) or a preselected CCR: intensive chemotherapy (7 + 3 regimen), low-dose ara-C, or best supportive care only. DNA was isolated from BM mononuclear cells and targeted sequencing of 39 genes was performed with Haloplex target enrichment (Agilent) on Illumina HiSeq 2500 using 2x100bp read lengths. FLT3 tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) mutations were determined by next-generation sequencing (NGS) and internal tandem duplications (ITD) were determined by capillary electrophoresis sizing of PCR amplicons. Target regions varied by gene from all exons to hot-spots. Log-rank test, stratified by ECOG PS score (0-1 vs 2) and cytogenetic risk (intermediate vs poor) at baseline, was used to assess OS of pts with mutations (mut) in genes detected in ≥5 pts vs OS in pts with wild-type (wt) genes within the AZA and CCR arms. Median OS was estimated using Kaplan-Meier methods.
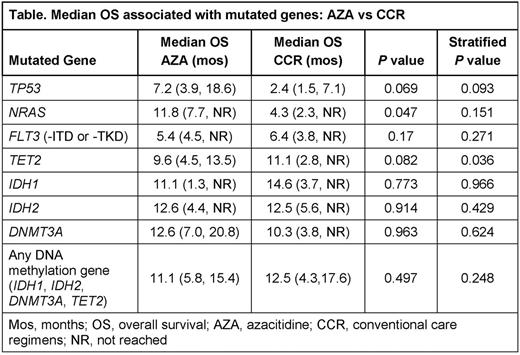
Results: The biomarker cohort comprised 156 of all 488 pts in AZA-AML-001 (32%; AZA n=83, CCR n=73). Baseline characteristics and hematologic response rates were well-matched between biomarker and non-biomarker pts. Mutations were detected in 33 of 39 sequenced genes. The most frequently mutated genes were DNMT3A (27%), TET2 (25%), IDH2 (23% [R140 15%, R172 8%]), TP53 (21%), RUNX1 (18%), NPM1 (16%), NRAS (12%), FLT3 (12% [-ITD 10%, -TKD 5%]), ASXL1 (11%), and STAG2 (10%). Stratified log-rank tests showed that median OS was significantly reduced for CCR pts with TP53mut (2.4 vs 12.5 mos with TP53wt; P=0.026) and with NRASmut (4.3 vs 10.3 mos with NRASwt; P=0.020). In the AZA arm, median OS was not significantly different between pts with TP53mutor TP53wt (7.2 vs 12 mos; P=0.40) or between pts with NRASmut or NRASwt (11.8 vs 8.9 mos; P=0.95), but was reduced in pts with FLT3mut (5.4 vs 12.0 mos with FLT3wt; P=0.017). Compared with similar pts treated with CCR, pts with TP53mut and/or NRASmut treated with AZA had nominally better median OS (7.2 vs 2.4 mos for TP53mut; 11.8 vs 4.3 mos for NRASmut), and pts with FLT3mut had nominally worse OS (5.4 vs 6.4 mos) (Table). Median OS was similar for pts with or without mutations in each of the genes known to influence DNA methylation (DNMT3A, IDH1, IDH2, and TET2); however, there was a statistical difference in OS within the AZA arm for pts with TET2mut (P=0.005) despite similar median OS for pts with TET2mut vs TET2wt (9.6 vs 9.5 mos) that was not observed within the CCR arm (P=0.45). Median OS for pts with a mutation in any 1 of the DNA methylation genes listed above was similar in the AZA and CCR arms (Table).
Conclusion: These exploratory analyses suggest older AML pts with TP53 or NRAS mutations have a better prognosis when treated with AZA than with CCR. Mutations in genes that regulate DNA methylation did not impact median OS with AZA Tx, although the potential negative effects of TET2mut and FLT3mut warrant further evaluation. Prognostic implications of isolated gene mutations can vary due to co-mutations; larger pt cohorts are needed to establish the influence of recurring co-mutational patterns in AZA-treated pts.
Tang:Celgene: Employment, Equity Ownership. MacBeth:Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Dombret:Agios: Honoraria; Sunesis: Honoraria; Ambit (Daiichi Sankyo): Honoraria; Karyopharm: Honoraria; Kite Pharma.: Honoraria, Research Funding; Menarini: Honoraria; Menarini: Honoraria; Astellas: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Servier: Honoraria; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria; Roche/Genentech: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria; Ariad: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Jazz Pharma: Honoraria, Research Funding. Seymour:Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel support, Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Stone:Pfizer: Consultancy; Sunesis Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; ONO: Consultancy; Jansen: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celator: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Juno Therapeutics: Consultancy; Merck: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Xenetic Biosciences: Consultancy. Beach:Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal