Abstract
Background: FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3-internal tandem duplication (FLT3-ITD) mutation in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is associated with early relapse and poor survival. Quizartinib inhibits FLT3 kinase activity potently and selectively. In phase I and II studies, the composite response rate (CRR) was approximately 50% among patients with FLT3-ITD. There is in-vitro synergy between quizartinib and 5-AZA or LDAC. We hypothesize that adding quizartinib to a hypomethylating agent- such as 5-azacitidine (AZA) -or to cytarabine may improve the response rate expected from the use of either agent alone.
Objectives: The primary objective of phase I is to determine dose limiting toxicity (DLT) and maximally tolerated dose (MTD) of combination of quizartinib with either AZA or low-dose cytarabine (LDAC); for phase II is to determine the clinical activity of both combinations. This planned interim analysis reports on the recommended phase II dose (RP2D) and first futility analysis.
Methods: For phase I, pts with relapsed/refractory high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) or AML were eligible irrespective of FLT3 mutation and salvage status. For phase II: presence of FLT3-ITD is a requisite, pts must be >60 years with untreated MDS/CMML/AML or any age receiving first salvage treatment. Other requisites: performance status ECOG ≤2, adequate organ function and normal electrolytes (potassium, calcium and magnesium). Important exclusions include: QTcF> 450 msec, administration of drugs that prolong QT/QTc interval or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors or inducers; with the exception of antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals that are used as standard of care.
Treatment cycle is 28 days and comprises of AZA 75 mg/m2 subcutaneously (SQ) or intravenously (IV) for 7 days of every cycle, or cytarabine 20 mg SQ twice daily for 10 days of every cycle along with quizartinib at two planned dose levels: 60 mg (dose level 1) or 90 mg orally daily (dose level 2), uninterrupted. Patients are assigned to AZA or LDAC arm by physician choice or slot availability. Planned accrual for each arm in phase II is 26 pts each and an ORR of ≥50% will be considered favorable. Accrual of 26 pts will give a 95% credible interval for ORR of (0.32, 0.68). The study will be stopped for toxicity (>30%) and/or futility (ORR <50%) at interim analysis for each arm.
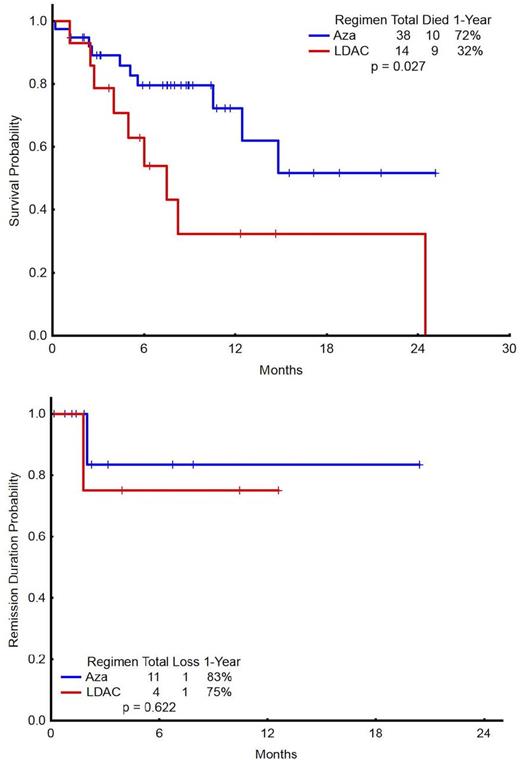
Results: Fifty-two (Phase I=12, phase II=40) pts have been enrolled: 38 to AZA arm and 14 to LDAC arm. Median age is 67 years (range, 23-83 years), 24 (46%) are female. Cytogenetics are diploid=24, +8=5, monosomy 7=3, miscellaneous=17, 11q=2 and t(8;21)= 1. Median number of prior therapies is 1 (range, 0-7); 7 patients had received prior FLT3 inhibitor: sorafenib (5), crenolanib (1), quizartinib (1). For both combinations quizartinib 60 mg daily was identified as the recommended phase II dose (RP2D).
Thirty-five Pts [8 in LDAC arm (23%) and 27 in AZA arm (77%)] of total 52 have responded with ORR 67 % (CR=8, CRp=7, CRi=18, PR=2); all with FLT3-ITD mutation without D835 mutation. ORR is 73% among pts with FLT3-ITD (N=48). Three of eight pts (38%) with prior FLT3 inhibitor exposure responded. Median time to response is 35 days (range, 14-187days). Among responders, two pts died (in CRi=1, PR=1): one with GI bleed and one with progressive pneumonia. Twelve responders discontinued therapy: 11 to receive a SCT and 1 due to loss of response with emergence of D835 mutation. Fifteen responders (CR=2, CRi=8, CRp=3, PR=2) had >50% reduction of FLT3-ITD allelic burden and eight additional pts (CR=5, CRi=1, CRp=2) had no detectable FLT3-ITD at response. The median survival was: 14.8 mo for the total study group: 7.5 mo for LDAC arm and not reached for AZA arm; median EFS has not been reached for either arm (Figure). Treatment emergent grade 3/4 toxicities irrespective of attribution include hypokalemia (15), hypotension (7), hypophosphatemia (7), hyponatremia (7), hypocalcemia (7), hyperbilirubinemia (1), elevated ALT (5), hypernatremia (2) hyperglycemia (1), QTcF prolongation (1, grade 3).
Conclusion: Combination of quizartinib and AZA or LDAC is highly active among patients with AML/MDS/CMML with FLT3-ITD mutation in absence of D835 mutation. Response rates appear higher than expected with either agent alone. Clinically significant QTcF prolongation is infrequent. Accrual to the study continues.
Jabbour:ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy. Konopleva:Calithera: Research Funding; Cellectis: Research Funding. Cortes:ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Teva: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal