Key Points
TNFRSF14 gene aberrations, common in FL, increase the ability of lymphoma cells to stimulate allogeneic T-cell responses.
TNFRSF14 lesions were associated with increased acute GVHD supporting stratified transplantation approaches in the allogeneic setting.
Abstract
Donor T-cell immune responses can eradicate lymphomas after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (AHSCT), but can also damage healthy tissues resulting in harmful graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Next-generation sequencing has recently identified many new genetic lesions in follicular lymphoma (FL). One such gene, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily 14 (TNFRSF14), abnormal in 40% of FL patients, encodes the herpes virus entry mediator (HVEM) which limits T-cell activation via ligation of the B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator. As lymphoma B cells can act as antigen-presenting cells, we hypothesized that TNFRSF14 aberrations that reduce HVEM expression could alter the capacity of FL B cells to stimulate allogeneic T-cell responses and impact the outcome of AHSCT. In an in vitro model of alloreactivity, human lymphoma B cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations had reduced HVEM expression and greater alloantigen-presenting capacity than wild-type lymphoma B cells. The increased immune-stimulatory capacity of lymphoma B cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations had clinical relevance, associating with higher incidence of acute GVHD in patients undergoing AHSCT. FL patients with TNFRSF14 aberrations may benefit from more aggressive immunosuppression to reduce harmful GVHD after transplantation. Importantly, this study is the first to demonstrate the impact of an acquired genetic lesion on the capacity of tumor cells to stimulate allogeneic T-cell immune responses which may have wider consequences for adoptive immunotherapy strategies.
Introduction
Follicular lymphoma (FL) is a common germinal center B-cell malignancy characterized by slow progression but inevitable relapse after conventional chemoimmunotherapy.1,2 However, some patients can be cured by the graft-versus-lymphoma (GVL) effect provided by donor T cells in the setting of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (AHSCT).3
FL B cells carry the hallmark t(14;18) translocation which results in cytoplasmic overexpression of the Bcl-2 protein. Two recent studies have reported that additional tumor-specific genetic aberrations of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily 14 (TNFRSF14) gene, which encodes the herpes virus entry mediator (HVEM), occur at high frequencies (18%-46%) in FL patients. However, these studies reported conflicting impact of TNFRSF14 aberrations on clinical outcome, suggesting that their functional effects might be influenced by factors such as differing treatment approaches.4,5
HVEM is a type I transmembrane molecule which acts as a molecular switch through interactions with several different ligands including B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA), LIGHT, CD160, lymphotoxin A, and glycoprotein D to regulate a range of immune responses.6 Interaction between HVEM expressed on antigen-presenting cells and the coinhibitory receptor BTLA on T cells limits T-cell activation and proliferation.7 BTLA has intracellular immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs consistent with immune-inhibitory function, and BTLA-deficient animal models display exaggerated immune responses.6 Importantly, BTLA is expressed by naive CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, the T-cell compartments known to be enriched for alloreactive specificity, and agonistic antibody-mediated BTLA stimulation reduces donor T-cell–mediated acute GVHD in murine transplant models, consistent with a functional role for BTLA in controlling donor T-cell alloresponses in this setting.8-10
Activated FL B cells can act as potent alloantigen-presenting cells in vitro11 and patients with FL often undergo AHSCT with significant residual lymphoma. We hypothesized that TNFRSF14 aberrations would reduce expression of HVEM and increase the ability of FL B cells to stimulate allogeneic T-cell responses. We therefore determined the functional effect of TNFRSF14 aberrations on the alloantigen-presenting capacity of human FL B cells in vitro. We also determined the impact of TNFRSF14 aberrations on clinical alloreactivity in FL patients after HLA-matched reduced-intensity conditioning AHSCT.
Materials and methods
Patient samples
Lymph node biopsies were obtained from FL patients after written consent. The study was approved by the Local Research Ethical Committee (05/Q0605/140) and was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
TNFRSF14 mutation and deletion analysis of FL B cells
Tumor DNA from pre-AHSCT lymph node biopsies from FL patients was screened for TNFRSF14 mutations by polymerase chain reaction amplification/Sanger sequencing and for deletions by multiplex ligation-probe amplification as previously described.12 Primers used for Sanger sequencing are summarized in supplemental Table 1 (available on the Blood Web site).
FL B-cell sorting, activation, and phenotyping
FL B cells were stained with CD10–fluorescein isothiocyanate (clone 97C5) and CD20–peridinin chlorophyll (PerCP; clone LT20) antibodies (both from Miltenyi Biotec) and purified by fluorescence-activated cell sorting of dual-positive events on a FACSAria device (Becton Dickinson). Dead cells were excluded using 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Purity of sorted FL B cells was routinely >90% and sorted FL B cells were routinely >95% light chain–restricted assessed with anti-immunoglobulin light chain κ–Alexa Fluor 700 (clone MHK-49) and anti-immunoglobulin light chain λ–allophycocyanin (APC; clone MHL-38) antibodies (supplemental Figure 1). Following sorting, FL B cells were activated for 48 hours with 1 µg/mL soluble CD40L (InVivoGen), 5 µg/mL AffiniPure F(ab′)2 fragment goat anti-human immunoglobulin A (IgA) + IgG + IgM (H+L; Jackson ImmunoResearch), 5 µg/mL CpG (R&D Systems), and 50 ng/mL interleukin-4 (IL-4; R&D Systems) to optimally upregulate expression of molecules involved in antigen presentation as previously described.13,14 Immunophenotyping of CD10+CD20+ FL B cells was performed by flow cytometry using the following antibodies: HVEM-phycoerythrin (PE; clone 122), CD58-PE (clone TS2/9), major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I–Pacific Blue (clone W6/32) HLA-DR–APC (clone L243), CD80-PE-cyanine 7 (Cy7; 2D10), CD86-APC (clone IT2.2), and their corresponding isotype controls (all from Biolegend).
Measurement of FL-B-cell–stimulated T-cell alloresponses
Untouched CD3+ T cells were purified by negative selection from healthy allogeneic donor peripheral blood mononuclear cells using the Pan T-cell isolation kit (Miltenyi Biotec). Postsort purity assessed by flow cytometry was routinely >95%. T cells were stimulated with activated irradiated (30 Gy) FL B cells at a ratio of 3:1 (T:B cell) for primary allogeneic cocultures. For secondary allogeneic cocultures, T cells received a second round of stimulation on day 3 with irradiated FL B cells. Flow cytometry was used to measure expression of CD4–Alexa Fluor 700 (clone RPA-T4), CD8-PerCP (clone SK1), CD25-APC (clone 4E3), CD127-PE (clone MB15-18C9), and FOXP3-PE-Cy7 (clone) on allogeneic T cells. Proliferation of allogeneic T cells was measured by thymidine incorporation as previously described, and T-cell subset-specific proliferation measured by carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester (CFSE) dye dilution assay.15 Cytokine secretion in allogeneic cocultures was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) on culture supernatant harvested at day 5 of primary and secondary cocultures using Ready-Set-Go ELISA kits (eBioscience). Intracellular cytokine staining (interferon γ [IFN-γ]–fluorescein isothiocyanate [clone 4S.B3], tumor necrosis factor α [TNF-α]-PerCP Cy5.5 [clone MAb11], IL-2–PE [clone MQ1-17H12]) and CD107a-PE-Cy5 (clone eBioH4A3) assays were performed on T cells in allogeneic cocultures as previously described.16 Dead cell exclusion was performed with DAPI, V450-50, or R780/60 fixable viability (from eBioscience). For allospecific proliferation and cytokine secretion, values for T cells stimulated with autologous B cells were subtracted from the values for T cells in allogeneic cultures. For some allogeneic coculture experiments, BTLA agonistic (clone MIH26; Biolegend) or antagonistic antibodies (clone 3B1; Genentech) or their respective isotype controls were added at 50 µg/mL.
Clinical outcome of FL patients undergoing AHSCT
Patients underwent T-replete AHSCT from fully HLA-matched related or unrelated donors using reduced-intensity conditioning with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide. Seventeen of the 23 patients in this cohort were included in our previous series.17 Patient and donor demographics and details of conditioning are in Table 1. GVHD prophylaxis was methotrexate (5 mg/m2 on days +3, +6, and +11), and cyclosporine (3 mg/kg per day) until day +90 to 120. Remission status prior to AHSCT was assessed using Cheson criteria, modified for computed tomography positron emission tomography status where appropriate.18,19 Acute and chronic GVHD was defined using updated National Institutes of Health (NIH) criteria and graded by consensus criteria confirmed when possible by tissue biopsy.20,21 All patients with grades 2-4 acute GVHD were treated initially with 1 to 2 mg/kg methylprednisolone. Acute GVHD was defined as steroid-refractory if progression occurred after 3 days of steroid therapy or there was no response after 7 days.22
Patient and donor demographics and transplant outcome
| Patient . | Age, y . | Prior therapies . | Prior autograft . | Prior rituximab . | Donor . | Disease status . | TNFRSF14 mutation . | TNFRSF14 deletion . | Acute GVHD* . | Chronic GVHD . | Outcome . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 48 | 8 | Yes | Yes | Sibling | Not CR | Yes | Yes | NE | NE | Died PD |
| D+12 | |||||||||||
| 2 | 43 | 5 | No | No | Sibling | Not CR | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Died GVHD |
| D+217 | |||||||||||
| 3 | 66 | 5 | No | Yes | Unrelated | Not CR | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Died GVHD |
| D+378 | |||||||||||
| 4 | 61 | 4 | No | Yes | Unrelated | Not CR | Yes | No | Yes | NE | Died GVHD |
| D+87 | |||||||||||
| 5 | 57 | 3 | Yes | Yes | Unrelated | Not CR | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Died GVHD |
| D+159 | |||||||||||
| 6 | 54 | 3 | No | Yes | Unrelated | Not CR | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Died GVHD |
| D+232 | |||||||||||
| 7 | 49 | 6 | Yes | Yes | Sibling | CR | No | Yes | Yes | No | Died PD |
| D+138 | |||||||||||
| 8 | 49 | 8 | No | Yes | Unrelated | CR | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Alive CR |
| D+2726 | |||||||||||
| 9 | 64 | 3 | No | Yes | Unrelated | CR | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Died GVHD |
| D+1714 | |||||||||||
| 10 | 52 | 3 | Yes | No | Sibling | CR | Yes | No | No | Yes | Alive CR |
| D+2230 | |||||||||||
| 11 | 60 | 7 | No | Yes | Unrelated | CR | Yes | Yes | No | No | Alive CR |
| D+2292 | |||||||||||
| 12 | 49 | 4 | Yes | Yes | Unrelated | CR | No | Yes | No | No | Alive CR |
| D+1359 | |||||||||||
| 13 | 61 | 5 | No | Yes | Sibling | Not CR | No | No | Yes | No | Alive CR |
| D+3206 | |||||||||||
| 14 | 54 | 6 | Yes | No | Sibling | Not CR | No | No | Yes | No | Died PD |
| D+160 | |||||||||||
| 15 | 51 | 4 | No | Yes | Sibling | CR | No | No | No | Yes | Alive CR |
| D+2313 | |||||||||||
| 16 | 53 | 5 | Yes | Yes | Sibling | CR | No | No | No | Yes | Alive CR |
| D+2988 | |||||||||||
| 17 | 34 | 8 | Yes | Yes | Sibling | Not CR | No | No | No | No | Alive CR† |
| D+4810 | |||||||||||
| 18 | 49 | 3 | No | Yes | Sibling | Not CR | No | No | No | No | Alive CR‡ |
| D+3207 | |||||||||||
| 19 | 50 | 5 | No | Yes | Sibling | Not CR | No | No | No | No | Died CR§ |
| D+582 | |||||||||||
| 20 | 34 | 3 | No | Yes | Sibling | CR | No | No | No | No | Alive CR |
| D+1728 | |||||||||||
| 21 | 46 | 7 | Yes | Yes | Unrelated | Not CR | No | No | No | No | Alive CR |
| D+1205 | |||||||||||
| 22 | 30 | 3 | No | No | Sibling | CR | No | No | No | Yes | Alive CR |
| D+3611 | |||||||||||
| 23 | 46 | 4 | Yes | No | Sibling | CR | No | No | No | No | Alive CR |
| D+4312 |
| Patient . | Age, y . | Prior therapies . | Prior autograft . | Prior rituximab . | Donor . | Disease status . | TNFRSF14 mutation . | TNFRSF14 deletion . | Acute GVHD* . | Chronic GVHD . | Outcome . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 48 | 8 | Yes | Yes | Sibling | Not CR | Yes | Yes | NE | NE | Died PD |
| D+12 | |||||||||||
| 2 | 43 | 5 | No | No | Sibling | Not CR | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Died GVHD |
| D+217 | |||||||||||
| 3 | 66 | 5 | No | Yes | Unrelated | Not CR | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Died GVHD |
| D+378 | |||||||||||
| 4 | 61 | 4 | No | Yes | Unrelated | Not CR | Yes | No | Yes | NE | Died GVHD |
| D+87 | |||||||||||
| 5 | 57 | 3 | Yes | Yes | Unrelated | Not CR | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Died GVHD |
| D+159 | |||||||||||
| 6 | 54 | 3 | No | Yes | Unrelated | Not CR | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Died GVHD |
| D+232 | |||||||||||
| 7 | 49 | 6 | Yes | Yes | Sibling | CR | No | Yes | Yes | No | Died PD |
| D+138 | |||||||||||
| 8 | 49 | 8 | No | Yes | Unrelated | CR | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Alive CR |
| D+2726 | |||||||||||
| 9 | 64 | 3 | No | Yes | Unrelated | CR | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Died GVHD |
| D+1714 | |||||||||||
| 10 | 52 | 3 | Yes | No | Sibling | CR | Yes | No | No | Yes | Alive CR |
| D+2230 | |||||||||||
| 11 | 60 | 7 | No | Yes | Unrelated | CR | Yes | Yes | No | No | Alive CR |
| D+2292 | |||||||||||
| 12 | 49 | 4 | Yes | Yes | Unrelated | CR | No | Yes | No | No | Alive CR |
| D+1359 | |||||||||||
| 13 | 61 | 5 | No | Yes | Sibling | Not CR | No | No | Yes | No | Alive CR |
| D+3206 | |||||||||||
| 14 | 54 | 6 | Yes | No | Sibling | Not CR | No | No | Yes | No | Died PD |
| D+160 | |||||||||||
| 15 | 51 | 4 | No | Yes | Sibling | CR | No | No | No | Yes | Alive CR |
| D+2313 | |||||||||||
| 16 | 53 | 5 | Yes | Yes | Sibling | CR | No | No | No | Yes | Alive CR |
| D+2988 | |||||||||||
| 17 | 34 | 8 | Yes | Yes | Sibling | Not CR | No | No | No | No | Alive CR† |
| D+4810 | |||||||||||
| 18 | 49 | 3 | No | Yes | Sibling | Not CR | No | No | No | No | Alive CR‡ |
| D+3207 | |||||||||||
| 19 | 50 | 5 | No | Yes | Sibling | Not CR | No | No | No | No | Died CR§ |
| D+582 | |||||||||||
| 20 | 34 | 3 | No | Yes | Sibling | CR | No | No | No | No | Alive CR |
| D+1728 | |||||||||||
| 21 | 46 | 7 | Yes | Yes | Unrelated | Not CR | No | No | No | No | Alive CR |
| D+1205 | |||||||||||
| 22 | 30 | 3 | No | No | Sibling | CR | No | No | No | Yes | Alive CR |
| D+3611 | |||||||||||
| 23 | 46 | 4 | Yes | No | Sibling | CR | No | No | No | No | Alive CR |
| D+4312 |
CR, complete remission; D, day; DLI, donor lymphocyte infusion; MI, myocardial infarction; NE, not evaluable; PD, progressive disease.
Spontaneous acute excluding DLI-induced.
Progressed D+72 given DLI.
Progressed D+85 given DLI.
Died of MI in CR.
Statistical considerations
Data for in vitro experiments were analyzed using Prism version 5.0. (GraphPad Software, Inc). Two-tailed tests are used throughout. Equal variance was not assumed for unpaired Student t tests and Welch correction was used where appropriate. Clinical outcome data were analyzed using SPSS Statistics 22 (IBM) and STATA 12 (Statacorp). The statistical significance of differences in frequencies of categorical variables was assessed using the Fisher exact test. Cumulative incidence of death from acute GVHD was calculated using the method of Fine and Gray with competing risks.23 Patients transplanted in partial remission were deemed to have persistent disease if detectable at day +100 (or earlier if indicated) and were censored at this date. Overall survival curves were constructed using the method of Kaplan and Meier24 and differences between groups were assessed using the log-rank statistic.25
Results
FL B cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations have reduced HVEM expression but retain expression of other molecules important in alloantigen presentation
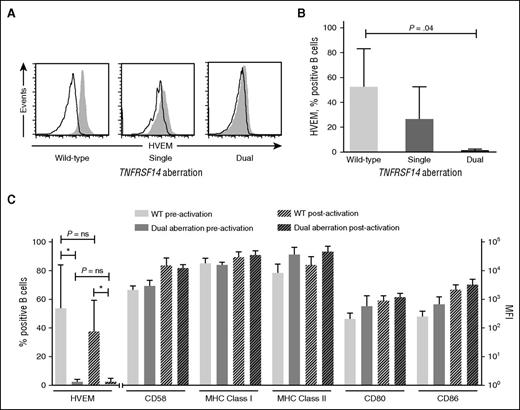
We initially sought to determine the impact of TNFRSF14 aberrations in human FL B cells on the expression of HVEM and other molecules important to stimulation of T-cell alloresponses. We used flow cytometry to compare surface HVEM expression on TNFRSF14 wild-type (WT) FL B cells and FL B cells with single or dual TNFRSF14 aberrations. The individual genetic lesions in FL B cells used for in vitro experiments are detailed in supplemental Table 2. Samples with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations were selected whose genetic lesions were predicted to result in loss of expression of HVEM (eg, homozygous deletions, nonsense mutations plus deletions).
In WT cases, ∼50% of FL B cells expressed HVEM at levels above isotype control, whereas HVEM expression was virtually undetectable in FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations. As expected, FL B cells from patients with single TNFRSF14 aberrations had HVEM expression intermediate between patients with WT and dual aberrations (Figure 1A-B). In contrast, molecules associated with antigen-presenting capacity (including MHC class I, MHC class II, CD80, CD86, and CD58 [LFA-3]) were expressed at similar levels on TNFRSF14 WT FL B cells and those with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations both before and after in vitro activation which models the proinflammatory posttransplant in vivo environment.11 Importantly, in vitro activation had no significant effect on HVEM expression levels (Figure 1C).
Cell surface expression of HVEM is reduced on FL B cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations but expression of other molecules involved in antigen presentation is maintained. (A) Cell surface expression of HVEM (filled histograms) and isotype controls (open histograms) on FL B cells. Representative data are shown from patients with TNFRSF14 WT (left panel), single TNFRSF14 aberrations (middle panel), and dual TNFRSF14 aberrations (right panel). (B) Mean (± standard deviation) frequencies of HVEM+ cells, expressed as a percentage of FL B cells, for WT (n = 5), single aberration (n = 3), and dual TNFRSF14 aberration cases (n = 5). P value is for 2-tailed unpaired Student t test. (C) Surface expression of molecules involved in antigen presentation on FL B cells shown pre- and postactivation. The mean values are shown for 5 WT cases and 5 cases with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations. Error bars show standard deviation. There were no significant differences in the level of expression of CD58, MHC class I and II, CD80 or CD86 in WT FL B cells and FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations either before or after in vitro activation (P > .05 in 2-tailed unpaired Student t test). MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; ns, not significant.
Cell surface expression of HVEM is reduced on FL B cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations but expression of other molecules involved in antigen presentation is maintained. (A) Cell surface expression of HVEM (filled histograms) and isotype controls (open histograms) on FL B cells. Representative data are shown from patients with TNFRSF14 WT (left panel), single TNFRSF14 aberrations (middle panel), and dual TNFRSF14 aberrations (right panel). (B) Mean (± standard deviation) frequencies of HVEM+ cells, expressed as a percentage of FL B cells, for WT (n = 5), single aberration (n = 3), and dual TNFRSF14 aberration cases (n = 5). P value is for 2-tailed unpaired Student t test. (C) Surface expression of molecules involved in antigen presentation on FL B cells shown pre- and postactivation. The mean values are shown for 5 WT cases and 5 cases with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations. Error bars show standard deviation. There were no significant differences in the level of expression of CD58, MHC class I and II, CD80 or CD86 in WT FL B cells and FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations either before or after in vitro activation (P > .05 in 2-tailed unpaired Student t test). MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; ns, not significant.
FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations stimulated greater frequencies of alloreactive effector T cells
After confirming that aberrations in TNFRSF14 FL B cells resulted in a significant reduction in expression of HVEM, we chose to investigate whether this impacted upon the ability of FL B cells to stimulate allogeneic T-cell responses in vitro. As HVEM expression was more markedly and consistently reduced in FL B cells with dual rather than single TNFRSF14 aberrations, we compared TNFRSF14 WT FL B cells to those with dual aberrations in subsequent functional experiments.
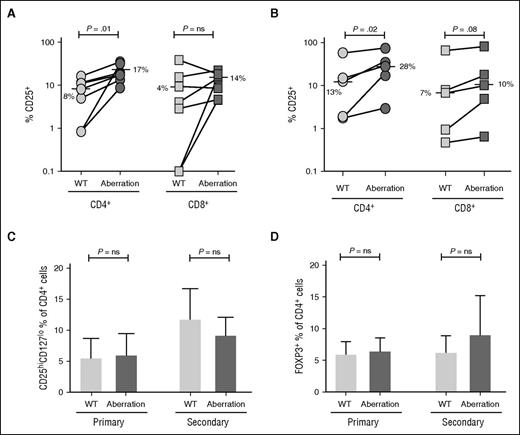
Allostimulation with FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations resulted in significantly higher frequencies of alloreactive responder CD4+ T cells identified by upregulation of the activation marker CD25 when compared with TNFRSF14 WT FL B cells (median 17% vs 8%, P = .01 [primary allostimulation] and 28% vs 13%, P = .02 [secondary allostimulation]). A smaller and less consistent increase of activated alloreactive CD8+ T cells was seen after allostimulation with FL B cells with dual aberrations when compared with TNFRSF14 WT FL B cells with a trend toward significance after secondary allostimulation (median 10% vs 7%, P = .08, Figure 2A-B). The increase in the proportion of activated CD4+ T cells after allostimulation with FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations was not due to an increase in CD4+ T cells with a regulatory T-cell phenotype identified either by surface CD25+CD127lo expression pattern or by expression of intracellular FOXP3 (Figure 2C-D). These data are consistent with an increase in the frequency of activated alloreactive effector T cells after allostimulation with FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations when compared with stimulation with WT FL B cells.
FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations stimulate allogeneic T-cell activation more effectively than WT FL B cells. (A-B) Proportion of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells expressing the activation marker CD25 after primary (A; n = 7) and secondary (B; n = 5) allogeneic cocultures with WT FL B cells or FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations. Horizontal bars and adjacent numbers represent median values and P values are for 2-tailed paired Student t tests. (C) Proportion of CD4+ T cells expressing the CD25hiCD127lo regulatory T-cell surface phenotype or (D) FOXP3 after primary (n = 4) and secondary (n = 4) allogeneic cocultures with WT FL B cells or FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations. Mean values are shown and error bars represent standard deviation. P values are for 2-tailed paired Student t tests.
FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations stimulate allogeneic T-cell activation more effectively than WT FL B cells. (A-B) Proportion of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells expressing the activation marker CD25 after primary (A; n = 7) and secondary (B; n = 5) allogeneic cocultures with WT FL B cells or FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations. Horizontal bars and adjacent numbers represent median values and P values are for 2-tailed paired Student t tests. (C) Proportion of CD4+ T cells expressing the CD25hiCD127lo regulatory T-cell surface phenotype or (D) FOXP3 after primary (n = 4) and secondary (n = 4) allogeneic cocultures with WT FL B cells or FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations. Mean values are shown and error bars represent standard deviation. P values are for 2-tailed paired Student t tests.
Frequencies of polyfunctional alloreactive T cells are increased after stimulation with FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations
We next measured the generation of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-2, IFN-γ, and TNF-α in allogeneic coculture supernatants. When analyzed individually, there was a trend toward significantly increased IL-2 and IFN-γ levels in culture supernatants after allostimulation with FL B cells with dual aberrations compared with TNFRSF14 WT FL B cells. However, allostimulation with FL B cells with dual aberrations resulted in significantly higher combined levels of all 3 proinflammatory cytokines when compared with allostimulation with WT FL B cells (Figure 3A).
Frequencies of polyfunctional alloreactive T cells are increased after stimulation with FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations. (A) Proinflammatory cytokines generated from allogeneic T cells after primary (n = 9) and secondary (n = 7) coculture with TNFRSF14 WT or dual TNFRSF14 aberration FL B cells. (B) Intracellular cytokine accumulation in allogeneic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after primary (n = 8) and secondary (n = 7) coculture with FL B cells. Cytokine-positive cell frequencies are expressed as a percentage of T-cell subsets. (C) Surface CD107a+ cell frequencies (expressed as a percentage of T-cell subsets) in allogeneic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after primary (n = 8) and secondary (n = 7) coculture with FL B cells. (A-C) Mean values ± standard deviation are shown. (D) Frequencies of allogeneic bifunctional T cells (CD107a+ and cytokine+) after primary allogeneic coculture with FL B cells. Horizontal lines depict median values. (E) Multifunctional allogeneic T-cell effectors after primary coculture with FL B cells. Cytokine-secreting populations within the alloreactive CD107a+ T-cell compartment are shown. Arcs show frequencies of T cells positive for CD107a, IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2, and slices show effector populations with combined expression patterns of CD107a, IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2. Mean frequencies from 7 independent experiments are shown. P values are for 2-tailed Student t tests throughout.
Frequencies of polyfunctional alloreactive T cells are increased after stimulation with FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations. (A) Proinflammatory cytokines generated from allogeneic T cells after primary (n = 9) and secondary (n = 7) coculture with TNFRSF14 WT or dual TNFRSF14 aberration FL B cells. (B) Intracellular cytokine accumulation in allogeneic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after primary (n = 8) and secondary (n = 7) coculture with FL B cells. Cytokine-positive cell frequencies are expressed as a percentage of T-cell subsets. (C) Surface CD107a+ cell frequencies (expressed as a percentage of T-cell subsets) in allogeneic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after primary (n = 8) and secondary (n = 7) coculture with FL B cells. (A-C) Mean values ± standard deviation are shown. (D) Frequencies of allogeneic bifunctional T cells (CD107a+ and cytokine+) after primary allogeneic coculture with FL B cells. Horizontal lines depict median values. (E) Multifunctional allogeneic T-cell effectors after primary coculture with FL B cells. Cytokine-secreting populations within the alloreactive CD107a+ T-cell compartment are shown. Arcs show frequencies of T cells positive for CD107a, IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2, and slices show effector populations with combined expression patterns of CD107a, IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2. Mean frequencies from 7 independent experiments are shown. P values are for 2-tailed Student t tests throughout.
We next used intracellular cytokine cytometry to measure allospecific cytokine production at a cellular level. Primary allostimulation with FL B cells with dual aberrations resulted in significantly greater frequencies of CD4+ T cells accumulating IL-2 and a trend to greater frequencies of CD8+ T cells accumulating IL-2 and IFN-γ. In contrast, allostimulation with FL B cells with dual aberrations did not significantly increase frequencies of T cells accumulating TNF-α consistent with our ELISA data (Figure 3B).
As lytic function of alloreactive T cells is associated with clinically significant acute GVHD,26 we also measured surface CD107a expression on alloreactive T cells stimulated with FL B cells as a surrogate marker of degranulation and lytic capacity.27 We observed significantly higher frequencies of CD4+ T cells and a trend toward higher frequencies of CD8+ T cells expressing CD107a following primary allostimulation with FL B cells with dual aberrations compared with TNFRSF14 WT FL B cells (Figure 3C).
Polyfunctional T-cell responses in vitro have been shown to correlate with clinical immunity.28 Therefore, we next used multiparameter flow cytometry combining intracellular measurement of IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α accumulation and surface expression of CD107a to assess the frequencies of polyfunctional alloreactive T cells after stimulation with FL B cells. We observed significantly higher frequencies of dual-function T cells expressing CD107a and accumulating IFN-γ, IL-2, or TNF-α after allostimulation with FL B cells with dual aberrations compared with TNFRSF14 WT FL B cells (Figure 3D). Finally, we used SPICE software to compare the proportion of alloreactive T cells with a polyfunctional phenotype (those positive for 2 or more of surface CD107a, and intracellular IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α) after stimulation with allogeneic FL B cells (Figure 3E). We observed significantly higher frequencies of polyfunctional alloreactive T cells after allostimulation with FL B cells with dual aberrations compared with WT TNFRSF14 FL B cells (9.1% vs 3.7%, P = .03).
FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations stimulate greater allogeneic T-cell proliferation than WT FL B cells
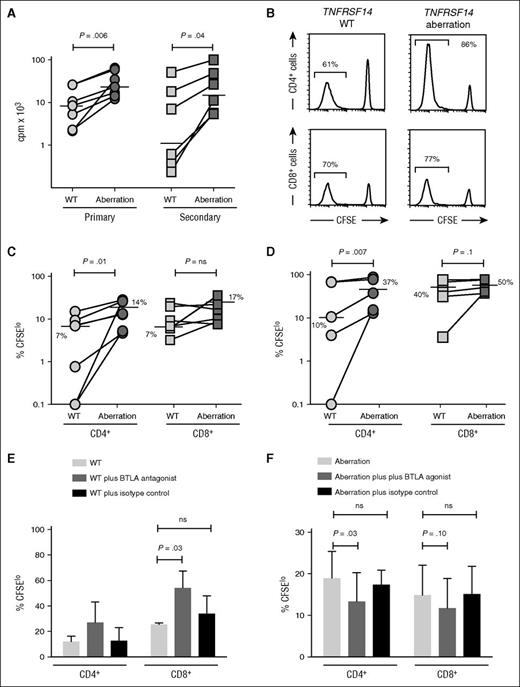
As alloreactive effector T cells must expand in vivo to exert clinically effects, we measured allospecific T-cell proliferation after stimulation with FL B cells. Proliferative responses of allogeneic responder T cells measured by thymidine incorporation were significantly greater after allostimulation with FL B cells with dual aberrations when compared with TNFRSF14 WT FL B cells after both primary and secondary allostimulation (Figure 4A). We next used CFSE dye dilution to determine whether this difference was due to a selective effect on proliferation of either CD4+ or CD8+ responder T cells. The proportion of responder CD4+ T cells proliferating after allostimulation with FL B cells with dual aberrations was consistently and significantly greater than after allostimulation with TNFRSF14 WT FL B cells (median 14% vs 7%, P = .01 [primary allostimulation] and 37% vs 10%, P = .007 [secondary allostimulation]). Consistent with our data for activation marker expression, we also saw a smaller and less consistent increase in proliferation of allogeneic CD8+ T cells after allostimulation with FL B cells with dual aberrations compared with TNFRSF14 WT FL B cells with a trend toward significance after secondary allostimulation (median 50% vs 40%, P = .10, Figure 4B-D).
FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations stimulate greater allogeneic T-cell proliferation than WT FL B cells. (A) Proliferation of allogeneic T cells measured by thymidine incorporation after primary (n = 7) and secondary (n = 6) coculture with TNFRSF14 WT or dual TNFRSF14 aberration FL B cells. Horizontal lines show median values. (B) Representative histograms of CFSE dye dilution in allogeneic T cells in secondary coculture with FL B cells. Numbers are proportions of proliferating cells. (C-D) Proportion of proliferating allogeneic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after primary (C; n = 7) and secondary (D; n = 5) coculture with FL B cells. Horizontal lines show median values. (E) Proportion of proliferating CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after primary allogeneic coculture with TNFRSF14 WT FL B cells without and with exogenous BTLA antagonist or isotype control antibody. (F) Proportion of proliferating CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after primary allogeneic coculture (n = 3) with FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations without and with exogenous BTLA agonist or isotype control antibody. Mean values ± standard deviation for 3 independent experiments are shown in panels E-F. P values are for 2-tailed Student t tests throughout. cpm, counts per minute.
FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations stimulate greater allogeneic T-cell proliferation than WT FL B cells. (A) Proliferation of allogeneic T cells measured by thymidine incorporation after primary (n = 7) and secondary (n = 6) coculture with TNFRSF14 WT or dual TNFRSF14 aberration FL B cells. Horizontal lines show median values. (B) Representative histograms of CFSE dye dilution in allogeneic T cells in secondary coculture with FL B cells. Numbers are proportions of proliferating cells. (C-D) Proportion of proliferating allogeneic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after primary (C; n = 7) and secondary (D; n = 5) coculture with FL B cells. Horizontal lines show median values. (E) Proportion of proliferating CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after primary allogeneic coculture with TNFRSF14 WT FL B cells without and with exogenous BTLA antagonist or isotype control antibody. (F) Proportion of proliferating CD4+ and CD8+ T cells after primary allogeneic coculture (n = 3) with FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations without and with exogenous BTLA agonist or isotype control antibody. Mean values ± standard deviation for 3 independent experiments are shown in panels E-F. P values are for 2-tailed Student t tests throughout. cpm, counts per minute.
Collectively, these data demonstrate that the capacity of FL B cells with dual TNFRSF14 aberrations to stimulate T-cell alloresponses in vitro is both quantitatively and qualitatively enhanced when compared with TNFRSF14 WT FL B cells.
BTLA ligation reduces T-cell alloresponses stimulated by FL B cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations
To provide further evidence that the presence of TNFRSF14 aberrations increases the capacity of FL B cells to stimulate T-cell alloresponses via a reduction in HVEM-BTLA signaling, we next examined the effect of antibody-mediated modulation of BTLA signaling on B-cell–stimulated T-cell alloresponses in vitro. BTLA blockade increased T-cell alloresponses stimulated with TNFRSF14 WT FL B cells demonstrating that interaction of HVEM and BTLA regulates the magnitude of T-cell alloresponses stimulated by FL B cells, as has previously been shown with dendritic cell–stimulated T-cell alloresponses.29 Importantly, addition of agonistic BTLA antibody to cocultures of FL B cells with TNFRSF14 dual aberrations and allogeneic T cells reduced the proportion of alloproliferative CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (Figure 4E-F). Taken together, these results are consistent with BTLA signaling contributing to control of proliferation of alloreactive T cells after stimulation with TNFRSF14 WT FL B cells, and reduced BTLA signaling contributing to increased proliferation of alloreactive T cells after stimulation with FL B cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations.
TNFRSF14 aberrations are associated with increased acute GVHD in FL patients undergoing AHSCT
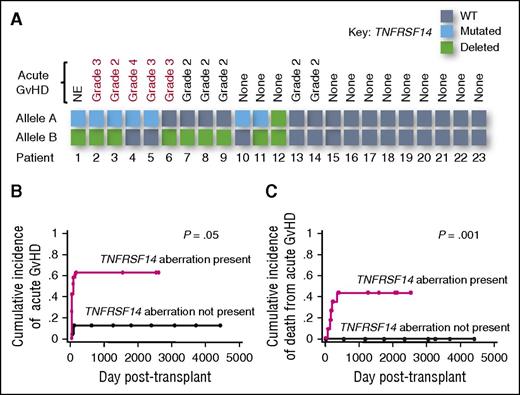
Finally, we sought to assess whether the increased alloantigen-presenting capacity we had observed in FL B cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations had clinical impact after allogeneic transplantation. We assessed the TNFRSF14 status in lymph node biopsies performed prior to transplantation in a cohort of patients with FL (Table 1). We observed a similar frequency of TNFRSF14 aberrations to previously published studies4,5 with aberrations detected in 12 of 23 patients (52%). Seven patients had mutations (all within the region encoding the extracellular domain, supplemental Figure 2), 9 had deletions (with 4 patients possessing both a mutation and a deletion), and 1 had a homozygous deletion of both TNFRSF14 alleles.
To assess the impact of TNFRSF14 aberrations on clinical alloreactivity after transplantation, we determined the incidence of acute GVHD in evaluable patients who engrafted. Ten of 22 evaluable patients developed significant acute GVHD (grades 2-4). Using a categorical approach, the only pretransplant risk factor associated with significantly increased incidence of acute GVHD was tumor TNFRSF14 status (8 of 11 patients with TNFRSF14 aberrations developed acute GVHD compared with only 2 of 11 TNFRSF14 WT patients (P = .03, Figure 5A). There was no significant difference in the incidence of acute GVHD in patients grouped by age, prior histological transformation, prior rituximab therapy, prior lines of therapy, prior autologous transplantation, remission status pretransplant, or donor type, despite there being a higher frequency of unrelated donors in patients with TNFRSF14 aberrations (Table 2). We also analyzed the impact of pretransplant factors on acute GVHD using the time-dependent approach of cumulative incidence (CI) with competing risks. Confirming our categorical analysis, TNFRSF14 status was also the only variable associated with significantly increased CI of acute GVHD (Figure 5B; Table 2).
TNFRSF14 aberrations in FL are associated with severe acute GVHD after AHSCT. (A) Schematic representation denoting TNFRSF14 status of purified FL B cells from lymph node biopsies from patients prior to allogeneic transplantation and occurrence of clinically significant acute GVHD (grades 2-4). Red text denotes patients whose acute GVHD was refractory to steroid therapy. (B) Cumulative incidence analysis of acute GVHD (grades 2-4) after allogeneic transplantation in FL patients with relapse/progression of lymphoma and death from other causes as competing risks. P value is for the Gray test. (C) Cumulative incidence analysis of death from acute GVHD (grades 2-4) after allogeneic transplantation in FL patients with relapse/progression of lymphoma and death from other causes as competing risks. P value is for the Gray test. NE, not evaluable.
TNFRSF14 aberrations in FL are associated with severe acute GVHD after AHSCT. (A) Schematic representation denoting TNFRSF14 status of purified FL B cells from lymph node biopsies from patients prior to allogeneic transplantation and occurrence of clinically significant acute GVHD (grades 2-4). Red text denotes patients whose acute GVHD was refractory to steroid therapy. (B) Cumulative incidence analysis of acute GVHD (grades 2-4) after allogeneic transplantation in FL patients with relapse/progression of lymphoma and death from other causes as competing risks. P value is for the Gray test. (C) Cumulative incidence analysis of death from acute GVHD (grades 2-4) after allogeneic transplantation in FL patients with relapse/progression of lymphoma and death from other causes as competing risks. P value is for the Gray test. NE, not evaluable.
Effect of pretransplant variables on incidence of acute GVHD
| Pretransplant factor . | Incidence of acute GVHD . | |
|---|---|---|
| Categorical . | Cumulative . | |
| P (FET) . | P (Gray) . | |
| Recipient TNFRSF14 status (any aberration vs none) | .03 | .05 |
| Recipient age (above vs below median) | .20 | .14 |
| Prior history of histological transformation (yes vs no) | .35 | .24 |
| Prior rituximab therapy (yes vs no) | 1.00 | .89 |
| Prior lines of therapy (above 5 vs not) | 1.00 | .89 |
| Prior autologous transplant (yes vs no) | .42 | .51 |
| Remission status pretransplant (CR vs not CR) | .23 | .25 |
| Donor (matched sibling vs matched unrelated) | .19 | .15 |
| Pretransplant factor . | Incidence of acute GVHD . | |
|---|---|---|
| Categorical . | Cumulative . | |
| P (FET) . | P (Gray) . | |
| Recipient TNFRSF14 status (any aberration vs none) | .03 | .05 |
| Recipient age (above vs below median) | .20 | .14 |
| Prior history of histological transformation (yes vs no) | .35 | .24 |
| Prior rituximab therapy (yes vs no) | 1.00 | .89 |
| Prior lines of therapy (above 5 vs not) | 1.00 | .89 |
| Prior autologous transplant (yes vs no) | .42 | .51 |
| Remission status pretransplant (CR vs not CR) | .23 | .25 |
| Donor (matched sibling vs matched unrelated) | .19 | .15 |
CR, complete remission; FET, Fisher exact test.
We took a similar approach to determine the impact of pretransplant factors on the incidence of death from acute GVHD. Death from acute GVHD was limited to patients with TNFRSF14 aberrations, occurring in 5 of 11 patients compared with 0 of 11 TNFRSF14 WT patients and TNFRSF14 status was a statistically significant risk factor for death from acute GVHD in using both categorical and CI approaches (Figure 5C). However, death from acute GVHD was also significantly associated with pretransplant remission status (supplemental Table 3) and all patients who died of acute GVHD had both TNFRSF14 aberrations and residual nodal lymphoma at the time of transplantation. Although we cannot separate the effects of TNFRSF14 aberrations and pretransplant remission status on death from acute GVHD in this small cohort, this observation is consistent with the hypothesis that FL B cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations increase clinically significant alloresponses that result in acute GVHD after AHSCT.
In contrast to acute GVHD, the incidence of chronic GVHD was not significantly associated with TNFRSF14 status, or any other pretransplant factor using both categorical and CI approaches (supplemental Table 4). The overall incidence of relapse/progression of lymphoma posttransplant was low in our cohort with only 4 patients relapsing/progressing, precluding an assessment of the impact of TNFRSF14 status on GVL effects, which needs to be addressed prospectively in a larger cohort of patients.
Discussion
We have shown that aberrations in the TNFRSF14 gene, which occur in up to half of FL patients, increase the capacity of tumor cells to stimulate clinically significant allogeneic donor T-cell immune responses. These findings have implications for AHSCT strategies for FL patients. The study also has wider significance in demonstrating for the first time that genetic alterations in tumor cells may impact the outcome of allogeneic immunotherapy.
Although we had demonstrated that FL B cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations stimulate allogeneic T-cell responses more effectively than WT FL B cells in vitro, our finding that this tumor-specific genetic lesion was associated with severe acute GVHD after AHSCT was somewhat unexpected. We anticipated TNFRSF14 lesions would have little effect on allogeneic T-cell responses that initiate GVHD early posttransplant where alloantigen might be presented predominantly by nonmalignant tissue antigen-presenting cells, but would result in increased alloantigen presentation by small numbers of residual tumor cells resulting in increases GVL effects and less lymphoma relapse posttransplant. The increase in acute GVHD in patients with TNFRSF14 aberrations may have reflected 2 different mechanisms. FL B cells present in the early posttransplant period could contribute to direct alloantigen presentation, with tumor cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations priming alloresponses more efficiently than their WT counterparts. This is supported both by our observation that steroid-refractoriness and death from acute GVHD was restricted to patients with TNFRSF14 aberrations with persistent nodal lymphoma pretransplant and by our in vitro experiments. Alternatively, TNFRSF14 aberrations in lymphoma cells might modulate the recipient microenvironment, establishing proinflammatory conditions which increase alloantigen presentation by nonmalignant host antigen-presenting cells thereby increasing donor T-cell alloresponses. Because reduced BTLA ligation on dendritic cells and tissue macrophages increases proinflammatory cytokine release,30,31 this mechanism could further amplify alloresponses in patients with TNFRSF14 aberrations to increase severe acute GVHD.
It is likely that increased T-cell alloresponses stimulated by lymphoma cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations occurred predominantly as a result of reduced ligation of BTLA on donor T cells. FL B cells with TNFRSF14 aberrations induced greater alloproliferation in CD4+ T cells than in CD8+ T cells in vitro, consistent with retention of high levels of BTLA expression on both naive and memory CD4+ T cells, whereas BTLA expression is progressively lost with CD8+ T-cell differentiation.29 Although HVEM also ligates a second coinhibitory T-cell receptor, CD160, it is unlikely that this receptor plays a significant role in this setting, as CD160 is expressed at very low levels on human CD4+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment.32
However, we need to take into account the limitations of our study. The functional in vitro experiments were restricted to FL B cells with dual rather than single TNFRSF14 aberrations. Although further studies are required to accurately define comparative effects of single TNFRSF14 lesions, and the differential impact of specific mutations, our clinical data suggest single TNFRSF14 lesions may also be clinically relevant in this setting as severe acute GVHD was observed in both patients with single and dual TNFRSF14 aberrations. Additionally, other potentially immune-modulating genetic lesions have been identified in lymphoma, including mutations in genes encoding β2-microglobulin and CD58 which could result in reduction of antigen-presenting capacity.33 Although our present study does not directly examine such mutations, it is unlikely they impacted on our results as we demonstrated similar expression of HLA class I and CD58 on FL B cells with and without TNFRSF14 aberrations. Finally, in the current study, we measured the effect of TNFRSF14 aberrations on HLA-mismatched alloresponses which are driven predominantly by direct alloantigen presentation by recipient rather than donor antigen-presenting cells. BTLA ligation is known to also limit human minor histocompatibility antigen (mHag)-specific T-cell responses that mediate acute GVHD in the HLA-matched setting34 and our clinical data are consistent with TNFRSF14 aberrations impacting on the capacity of FL B cells to present mHags leading to increased acute GVHD after HLA-matched AHSCT. Although we have not extended our functional assays to measure mHag-specific HLA-matched alloresponses, this will be a focus of future work. The impact of TNFRSF14 aberrations in FL on alloreactivity in other immunotherapy platforms such as T-depleted approaches or cord blood transplants will need to be further explored.
Given our findings in the allogeneic setting, TNFRSF14 aberrations which reduce expression of HVEM on FL B cells might also be expected to potentiate autologous T-cell antitumor immunity via reduced BTLA-mediated suppression. However, as previous studies suggest that TNFRSF14 aberrations may confer a poor prognosis in patients treated with chemoimmunotherapy,4 it is likely that additional or alternative HVEM-mediated mechanisms impact on FL B-cell survival in the autologous setting. As BTLA is also expressed on B cells, and negatively regulates B-lymphocyte transformation and malignant B-cell survival,35-37 reduction of HVEM ligation of BTLA on FL B cells either in cis or trans (from neighboring tumor cells) could potentiate tumor growth and survival in this setting.
In summary, these data support the development of risk-adapted allogeneic transplant strategies in FL patients with TNFRSF14 aberrations to reduce harmful acute GVHD, which could include pretransplant purging of recipient B cells or augmented posttransplant immunosuppression. Genetic lesions in tumor cells that modulate allogeneic immune responses may have wider significance, impacting the outcome of allogeneic cellular immunotherapy not only for lymphoma but also for other hematologic cancers.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Kay Kendall Leukaemia Fund (Junior Clinical Research Fellowship 557 [J.O.]), Cancer Research UK (Programme Grant 15968 [J.F.] and Centre Grant C16420/A18066), the Medical Research Council (Clinician Scientist Fellowship G0902269 [J.K.D.]), and Barts Cancer Institute Bridge to the Future Fellowship (E.K.).
Authorship
Contribution: E.K. designed and performed experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript; J.O. performed genetic analysis; C.B. performed experiments; S.I. collated patient samples; J.M. provided clinical data; J.F. contributed to the genetic analysis and critically reviewed the manuscript; J.G.G. contributed to experimental design and wrote the manuscript; and J.K.D. conceptualized the study, designed and analyzed experiments and clinical data, and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Jeffrey K. Davies, Centre for Haemato-oncology, Barts Cancer Institute, Charterhouse Square, London EC1M 6BQ, United Kingdom; e-mail: j.k.davies@qmul.ac.uk.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal