Key Points
Apelin plays a key role in maintaining hemostasis through the regulation of platelet function.
Treatment of platelets with apelin inhibits aggregation and thrombus formation.
Abstract
Apelin peptide and its receptor APJ are directly implicated in various physiological processes ranging from cardiovascular homeostasis to immune signaling. Here, we show that apelin is a key player in hemostasis with an ability to inhibit thrombin- and collagen-mediated platelet activation. Mice lacking apelin displayed a shorter bleeding time and a prothrombotic profile. Their platelets exhibited increased adhesion and a reduced occlusion time in venules, and displayed a higher aggregation rate after their activation by thrombin compared with wild-type platelets. Consequently, human and mouse platelets express apelin and its receptor APJ. Apelin directly interferes with thrombin-mediated signaling pathways and platelet activation, secretion, and aggregation, but not with ADP and thromboxane A2-mediated pathways. IV apelin administration induced excessive bleeding and prevented thrombosis in mice. Taken together, these findings suggest that apelin and/or APJ agonists could potentially be useful adducts in antiplatelet therapies and may provide a promising perspective for patients who continue to display adverse thrombotic events with current antiplatelet therapies.
Introduction
To prevent excessive blood loss during vascular injury, platelets form a plug after their interaction with endothelial matrix proteins. However, platelet aggregation also contributes to thrombotic events, causing acute coronary syndrome, heart attacks, and strokes.1-3 After vessel injury, the exposed subendothelial surface induces platelet adhesion. Platelet activation and secretion of soluble mediators, such as adenosine 5′-diphosphate (ADP), thromboxane A2 (TXA2), and thrombin, are all involved in the recruitment of other circulating platelets. At present, several antiplatelet drugs are clinically approved for the treatment and prevention of thrombotic complications. These drugs mainly target cyclooxygenase-1, purinoceptor 12 (P2Y12) receptor, and integrin αIIbβ3.1-3 However, despite the established benefits of these treatments, a large number of patients continue to display adverse thrombotic events. A big part of this is attributed to the variability in individual response to treatments and to sustained platelet activation due to the treatment’s inability to block several platelet signaling pathways. The latter relates to pathways induced by thrombin that continue to activate platelets and thrombus formation and necessitates the development of novel antithrombotic agents that inhibit this pathway.2 Previously, a range of molecules present on the platelet surface and/or stored in their granules was reported to contribute to the cross-talk of platelets with various inflammatory cells. These molecules play an important role in the development and progression of atherosclerosis and the formation of occlusive thrombi.4 Apelin and its cognate receptor APJ were shown to be involved in a number of physiological and pathophysiological conditions,5 and their levels are altered in atherosclerotic coronary arteries,6 in aortic valve stenosis,7 and during acute myocardial infarction and angina.8-10 All these observations raise the possibility that apelin signaling pathways play a role in the physiopathology of vascular disease. Apelin, originally isolated from bovine stomach,11 is produced as a 77-amino acid precursor. This prepropeptide contains sites with a number of basic amino acid residues (Arg-Arg and Arg-Lys) that undergo proteolytic cleavage to generate active apelin peptides of 36, 17, or 13 amino acids and the posttranslationally modified (Pyr1)apelin-13.4 All the different apelin isoforms are expressed in various tissues and found circulating in plasma.11-13 Nevertheless, their expression levels seem to vary significantly depending on tissues and cell types. Indeed, whereas apelin-13, apelin-17, and (Pyr1)apelin-13 are the predominant isoforms in plasma,14-16 apelin-36 is the major isoform in colostrum.17
In the present study, we show that apelin plays a key role in the regulation of platelet activation mainly induced by collagen and thrombin. Apelin-deficient (apelin−/−) mice that were previously reported to develop progressive heart failure after pressure overload18 display a prothrombotic profile characterized by reduced tail-bleeding time and increased thrombus formation. Apelin-13 was found to inhibit hemostatic functions, as shown by the inhibition of platelet aggregation induced by thrombin and collagen. These findings provide new insight into the physiology of the apelinergic system, with potential impact on the pathophysiology of thrombotic disorders such as cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.
Materials and methods
Details for materials and methods are available in the supplemental Material, available on the Blood Web site.
Mouse strains
Wild-type (WT) mice were derived from Janvier Laboratories. Apelin−/− mice used in the experiments have been previously described.18 All mouse strains were reared on a C57BL/6 background.
Preparation of washed platelets
Platelet dense granule secretion
Dense granule secretion was quantified by measuring adenosine triphosphate (ATP) release after platelet aggregation by an ATP Determination Kit (Molecular Probes).20
Apelin quantification assay
Apelin was quantified with the nonselective Apelin-12 Enzyme Immunoassay Kit (Phoenix Pharmaceuticals).
Immunoblotting assay
Washed platelets were used for western blot analysis.20
Hematologic analysis and bleeding time
Complete blood counts and hematocrit were determined with an automatic cell counter. Mice bleeding-time assays were performed.20
Standard electron microscopy
Standard electron microscopy for platelet morphology of was performed according to the standard procedure.20
Platelet aggregation assay
Aggregation of washed platelets was determined using a Chrono-log aggregometer, as previously described.20 Where mentioned, platelets were first incubated with apelin-13, apelin-36, unprocessed double-mutant apelin-36 peptide (apelin-DM), apelin-F13A (F13A), or MM54 for 3 minutes at 37°C.
Static platelet adhesion assay and flow cytometry analysis
See supplemental Methods.
In vitro thrombus formation
Thrombus formation was evaluated in a whole-blood perfusion assay under different shear conditions.
Ferric chloride–induced thrombosis model
Ferric chloride (FeCl3) injury was induced in mice as previously described,21 with slight modifications.
Measurement of intracellular calcium concentration and TXA2, cAMP, and cGMP generation
Intracellular calcium mobilization and generation of thromboxane B2 (a stable metabolite of TXA2), cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), and guanosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate (cGMP) were measured as described in supplemental Methods.
Immunofluorescence analysis
Immunofluorescence assay was used for apelin and APJ, as described in supplemental Methods.
Statistical analysis
Statistical significance was evaluated with Student t tests, 2-tailed Mann-Whitney U tests, or 1-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey or Dunnett test as indicated, using GraphPad Prism (San Diego, CA).
Results
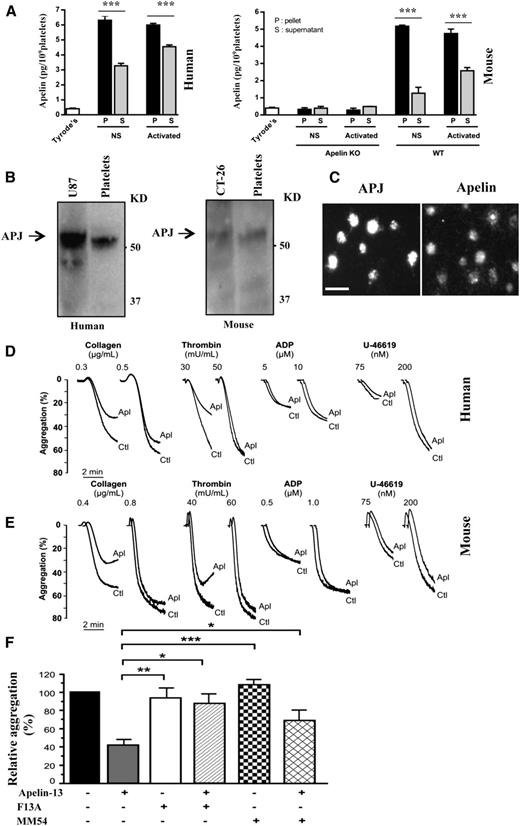
Expression of apelin and APJ receptor in human and mouse platelets: role in platelet aggregation
Altered platelet function1-3 and apelin levels4,11-14 are associated with various cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, we investigated whether apelin could act on platelet function. First, we analyzed the expression of apelin and APJ in platelets. As illustrated in Figure 1A, the use of enzyme immunoassay revealed that although apelin was absent in platelets derived from mice lacking apelin (apelin−/− mice), apelin was detected in resting and thrombin-activated human and mice platelets. Similarly, the expression of APJ was detected in platelets by immunoblot (Figure 1B), and immunostaining analyses (Figure 1C) revealed that both apelin and APJ are expressed in platelets. To investigate the role of apelin in the regulation of platelet activation, we evaluated the effect of apelin-13 on platelet aggregation in response to various platelet agonists, including thrombin and collagen, previously reported as 2 potent activators of platelets.22 Platelet aggregation induced by a low concentration of thrombin or collagen was inhibited by apelin-13 in human (Figure 1D) and mouse (Figure 1E) platelets. However, there was no effect of apelin-13 in the presence of high concentrations of these agonists, and apelin-13 failed to inhibit platelet aggregation induced by ADP and the TXA2 analog U-46619. These finding suggest that apelin-13 seems to act on platelet aggregation by interfering with mechanisms mainly mediated by collagen and thrombin.
Apelin-13 inhibits platelet aggregation that expresses apelin and APJ receptor. (A) Quantity of apelin determined by enzyme immunoassay in cell lysates and media of resting “none-stimulated” (NS) human (left) and mouse (right) platelets and after activation by thrombin (1 U/mL). The quantity of apelin was expressed in picograms per 109 platelets ± standard deviation of at least 3 independent platelet samples. ***P < .001, Student t test. (B) Representative immunoblot of APJ in human (left) and mouse (right) cells. The molecular weight and the APJ-expressing human U87 and murine CT-26 cells (positive controls) are indicated. (C) Immunofluorescence analysis of APJ and apelin expression in platelets. Controls were stained using specific APJ or apelin antibody with the secondary antibodies only and were negative. Original magnification ×100. (D-E) Aggregation of washed human (D) and mouse (E) platelets induced by indicated concentration of collagen, thrombin, ADP plus fibrinogen (100 μg/mL), or U-46619, with or without incubation with apelin-13 (10 μM; Apl). Traces are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. Results are expressed as the percentage change in light transmission with respect to the blank (buffer without platelets; Ctl), set at 100%. (F) Thrombin-induced aggregation of human platelets preincubated with PBS; apelin-13 (10 μM), F13A (100 μM), F13A (100 μM) plus apelin-13 (10 μM), MM54 (100 μM), or MM54 (100 μM) plus apelin-13 (10 μM). The relative percentage ± SEM of 3 independent experiments is expressed and statistical significance was determined by 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test (*P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001). KD, KDa; KO, knockout; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; SEM, standard error of the mean.
Apelin-13 inhibits platelet aggregation that expresses apelin and APJ receptor. (A) Quantity of apelin determined by enzyme immunoassay in cell lysates and media of resting “none-stimulated” (NS) human (left) and mouse (right) platelets and after activation by thrombin (1 U/mL). The quantity of apelin was expressed in picograms per 109 platelets ± standard deviation of at least 3 independent platelet samples. ***P < .001, Student t test. (B) Representative immunoblot of APJ in human (left) and mouse (right) cells. The molecular weight and the APJ-expressing human U87 and murine CT-26 cells (positive controls) are indicated. (C) Immunofluorescence analysis of APJ and apelin expression in platelets. Controls were stained using specific APJ or apelin antibody with the secondary antibodies only and were negative. Original magnification ×100. (D-E) Aggregation of washed human (D) and mouse (E) platelets induced by indicated concentration of collagen, thrombin, ADP plus fibrinogen (100 μg/mL), or U-46619, with or without incubation with apelin-13 (10 μM; Apl). Traces are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. Results are expressed as the percentage change in light transmission with respect to the blank (buffer without platelets; Ctl), set at 100%. (F) Thrombin-induced aggregation of human platelets preincubated with PBS; apelin-13 (10 μM), F13A (100 μM), F13A (100 μM) plus apelin-13 (10 μM), MM54 (100 μM), or MM54 (100 μM) plus apelin-13 (10 μM). The relative percentage ± SEM of 3 independent experiments is expressed and statistical significance was determined by 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test (*P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001). KD, KDa; KO, knockout; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; SEM, standard error of the mean.
The inhibitory effect of apelin on platelet aggregation involves the APJ receptor
Apelin-13 prevents αIIbβ3 activation
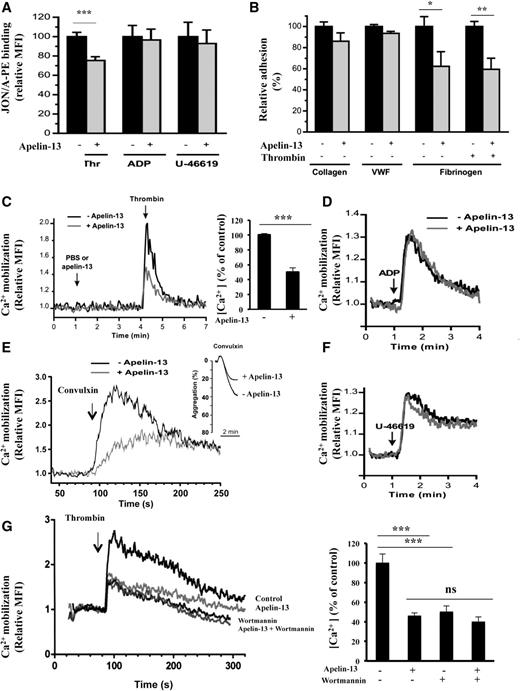
Platelet stimulation by agonists results in transient activation of integrins, including the integrins αIIbβ3 and α2β1 that regulate the adhesiveness of platelets for fibrin(ogen) and collagen, respectively. However, integrin α2β1 is activated by a mechanism that is directly linked to αIIbβ3 activation.22 We therefore evaluated the effect of apelin-13 on the activation of αIIbβ3 integrin through the detection of its activated conformation by the antibody JON/A. As illustrated in Figure 2A, platelet activation by thrombin was significantly inhibited by apelin-13. Under the same conditions, apelin-13 failed to inhibit platelet activation mediated by ADP or U-46619. Similarly, using a platelet adhesion assay under static conditions (Figure 2B), no effect of apelin-13 was noticed on platelet adhesion to collagen or von Willebrand factor, indicating that apelin-13 did not directly act on the platelet adhesive receptors, glycoprotein (GP)VI and GPIb. In contrast, apelin-13 inhibited the adhesion of resting and thrombin-activated platelets to fibrinogen, indicating that apelin-13 prevents the adhesion dependent on integrin αIIbβ3.
Regulation of platelet αIIbβ3 activation and Ca2+ mobilization by apelin-13. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of the integrin αIIbβ3 activation detected by the recognition by the antibody JON/A of the activated conformation of mouse αIIbβ3 integrin after stimulation by thrombin (Thr), ADP, or U-46619 of washed mouse platelets treated with 10 μM apelin-13 (+) or not (−). Results are expressed as relative mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) ± SEM, in arbitrary units, from at least 3 experiments. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (***P < .001). (B) Platelet adhesion of washed human platelets (107) in presence of apyrase (2 U/mL) and preincubated with or without apelin-13 (10 μM) to immobilized collagen (50 μg/mL), von Willebrand factor (VWF; 50 μg/mL), or fibrinogen (100 μg/mL). Platelet adhesion to VWF was performed in the presence of botrocetin (5 μg/mL) and to fibrinogen with and without the activation by thrombin (100 mU/mL). Data are expressed as mean relative adhesion ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments, and statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (*P < .05; **P < .01). (C) Effect of apelin-13 (10 μM) on intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in platelets activated by thrombin (100 mU/mL) (left). Bar graph denotes the corresponding percentages of Ca2+ mobilization (right). (D) Effect of apelin-13 on intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in ADP (10 μM)-activated platelets. (E) Effect of apelin-13 (10 μM) on intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in convulxin (500 pM)-activated platelets. Platelet aggregation induced by convulxin (200 pM) is also indicated. (F) Effect of apelin-13 on intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in U-46619 (200 nM)-activated platelets. (G) Effect of apelin-13 (10 μM) on intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in the absence or presence of wortmannin (10 nM) in platelets activated by thrombin (100 mU/mL). Results are representative of 4 experiments and expressed as the relative MFI, in arbitrary units (left). Bar graph denotes the corresponding percentages of Ca2+ mobilization (right). Values are mean ± SEM (n = 4 per group). Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (***P < .001). Ca2+, calcium ion; ns, not significant.
Regulation of platelet αIIbβ3 activation and Ca2+ mobilization by apelin-13. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of the integrin αIIbβ3 activation detected by the recognition by the antibody JON/A of the activated conformation of mouse αIIbβ3 integrin after stimulation by thrombin (Thr), ADP, or U-46619 of washed mouse platelets treated with 10 μM apelin-13 (+) or not (−). Results are expressed as relative mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) ± SEM, in arbitrary units, from at least 3 experiments. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (***P < .001). (B) Platelet adhesion of washed human platelets (107) in presence of apyrase (2 U/mL) and preincubated with or without apelin-13 (10 μM) to immobilized collagen (50 μg/mL), von Willebrand factor (VWF; 50 μg/mL), or fibrinogen (100 μg/mL). Platelet adhesion to VWF was performed in the presence of botrocetin (5 μg/mL) and to fibrinogen with and without the activation by thrombin (100 mU/mL). Data are expressed as mean relative adhesion ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments, and statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (*P < .05; **P < .01). (C) Effect of apelin-13 (10 μM) on intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in platelets activated by thrombin (100 mU/mL) (left). Bar graph denotes the corresponding percentages of Ca2+ mobilization (right). (D) Effect of apelin-13 on intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in ADP (10 μM)-activated platelets. (E) Effect of apelin-13 (10 μM) on intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in convulxin (500 pM)-activated platelets. Platelet aggregation induced by convulxin (200 pM) is also indicated. (F) Effect of apelin-13 on intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in U-46619 (200 nM)-activated platelets. (G) Effect of apelin-13 (10 μM) on intracellular Ca2+ mobilization in the absence or presence of wortmannin (10 nM) in platelets activated by thrombin (100 mU/mL). Results are representative of 4 experiments and expressed as the relative MFI, in arbitrary units (left). Bar graph denotes the corresponding percentages of Ca2+ mobilization (right). Values are mean ± SEM (n = 4 per group). Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (***P < .001). Ca2+, calcium ion; ns, not significant.
Effect of apelin-13 on calcium mobilization
Elevation in calcium is an immediate consequence of agonist stimulation and represents a crucial event in platelet activation. As illustrated in Figure 2C, although thrombin caused an increase in calcium mobilization, apelin inhibited this effect. Using convulxin, an activator of the collagen receptor GPVI, revealed that although this agonist stimulated intracellular calcium mobilization, pretreatment with apelin-13 inhibited also this process. Accordingly, apelin-13 was found to also inhibit platelet aggregation induced by convulxin (Figure 2E). No effect of apelin-13 on the intracellular calcium mobilization induced by low doses of ADP (Figure 2D) or U-46619 (Figure 2F) was detectable. Previously, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling mechanisms were reported to play an important role in regulating the adhesive function of integrin αIIbβ3, and wortmannin, an inhibitor of PI3K and various PI3K-related proteins,25 was found to interfere with thrombin-induced redistribution and entry of cytosolic calcium, which in turn results in incomplete platelet activation.26 As illustrated in Figure 2G (supplemental Figure 2), although thrombin caused an increased calcium mobilization, wortmannin blocked this effect and failed to interfere with apelin-induced calcium mobilization.
Effect of apelin on cAMP and cGMP production
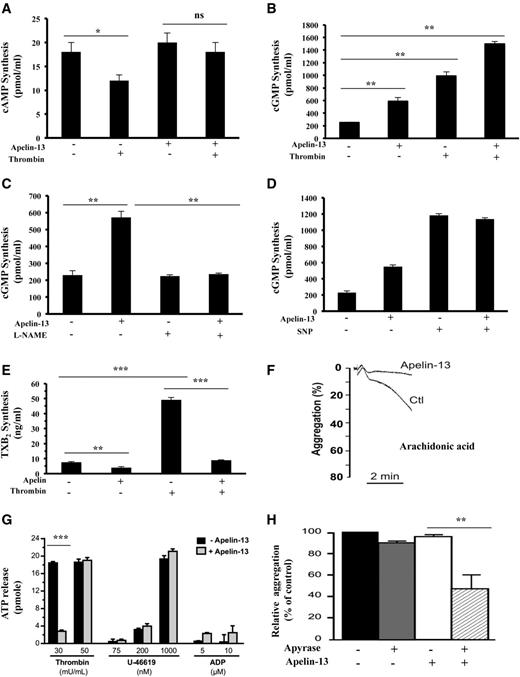
In addition to intracellular calcium mobilization, platelet activation involves other signaling mechanisms, including cAMP, cGMP, and TXA2 synthesis. We therefore assessed the effect of apelin-13 on these signaling pathways in resting and thrombin-activated platelets. Analysis of cAMP production revealed that although thrombin inhibited cAMP accumulation in platelets, under these conditions, apelin-13 failed to alter cAMP accumulation in resting and thrombin-activated platelets (Figure 3A). Under the same conditions, analysis of cGMP production revealed that both apelin and thrombin induced cGMP production (2.5-fold and fourfold, respectively, vs control levels; Figure 3B). In the presence of thrombin, apelin further increased cGMP in these cells (sixfold vs control levels). Previously, nitric oxide (NO) synthesized from L-arginine through NO synthase (NOS) was reported to inhibit platelet adhesion and aggregation by increasing the intracellular level of cGMP through the activation of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC).27 Incubation of platelets with the NOS inhibitor NG-monomethyl- L-arginine (1 mM) blocked the rise of cGMP in platelets exposed to apelin (Figure 3C), suggesting the involvement of NO in cGMP production induced by apelin in platelets. Compared with sodium nitroprusside (10 μM), an NO donor reported to inhibit platelet aggregation,28 the use of similar concentration of apelin (10 μM) was twofold-less efficient in the induction of cGMP (Figure 3D).
Effect of apelin-13 on cAMP, cGMP, and thromboxane B2 synthesis and platelet secretion. Accumulation of cAMP (A) and cGMP (B) was determined in resting and thrombin-activated platelets (5 minutes) in the absence or presence of apelin-13 (10 μM). Results represent the mean ± SEM of at least 4 separate experiments, each performed in triplicate. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (*P < .05; **P < .001). (C) cGMP content in platelets in the presence or absence of the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor NG-methyl-L-arginine (L-NAME) (1 mM) for 5 minutes was measured in untreated or apelin (10 μM)-treated platelets. Results are the mean ± SEM of at least 3 separate experiments, each performed in triplicate (Student t test; **P < .001). (D) Accumulation of cGMP was determined in untreated or apelin-treated platelets (5 minutes) in the absence or presence of sodium nitroprusside (SNP; 10 μM). Results represent the mean ± SEM of 3 separate experiments, each performed in triplicate. (E) Thromboxane B2 (TXB2) content was determined in resting and thrombin-activated platelets after their incubation in the absence or presence of apelin-13 (10 μM) for 5 minutes. Results represent the mean ± SEM of 3 separate experiments, each performed in triplicate (Student t test, **P < .01; ***P < .001). (F) Aggregation of washed mouse platelets induced by arachidonic acid (39 μM) with or without incubation with apelin-13 (10 μM). Traces are representative of at least 3 independent experiments (supplemental Figure 3). Results are expressed as the percentage change in light transmission with respect to the blank (buffer without platelets; Ctl), set at 100%. (G) Dense granule secretion was evaluated by measuring the ATP release after the aggregation induced by the indicated concentration of thrombin, U-46619, and ADP of human platelets preincubated with or without apelin-13 (10 μM). Results were expressed as the amount of ATP release by platelets from at least 3 independent experiments, and statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (***P < .001). (H) Aggregation of washed human platelets induced by thrombin (100 mU/mL) with or without incubation with apyrase (5 U/mL) and apelin-13 (10 μM). The relative percentage ± SEM of 3 independent experiments is expressed, and statistical significance was determined by 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test (**P < .01).
Effect of apelin-13 on cAMP, cGMP, and thromboxane B2 synthesis and platelet secretion. Accumulation of cAMP (A) and cGMP (B) was determined in resting and thrombin-activated platelets (5 minutes) in the absence or presence of apelin-13 (10 μM). Results represent the mean ± SEM of at least 4 separate experiments, each performed in triplicate. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (*P < .05; **P < .001). (C) cGMP content in platelets in the presence or absence of the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor NG-methyl-L-arginine (L-NAME) (1 mM) for 5 minutes was measured in untreated or apelin (10 μM)-treated platelets. Results are the mean ± SEM of at least 3 separate experiments, each performed in triplicate (Student t test; **P < .001). (D) Accumulation of cGMP was determined in untreated or apelin-treated platelets (5 minutes) in the absence or presence of sodium nitroprusside (SNP; 10 μM). Results represent the mean ± SEM of 3 separate experiments, each performed in triplicate. (E) Thromboxane B2 (TXB2) content was determined in resting and thrombin-activated platelets after their incubation in the absence or presence of apelin-13 (10 μM) for 5 minutes. Results represent the mean ± SEM of 3 separate experiments, each performed in triplicate (Student t test, **P < .01; ***P < .001). (F) Aggregation of washed mouse platelets induced by arachidonic acid (39 μM) with or without incubation with apelin-13 (10 μM). Traces are representative of at least 3 independent experiments (supplemental Figure 3). Results are expressed as the percentage change in light transmission with respect to the blank (buffer without platelets; Ctl), set at 100%. (G) Dense granule secretion was evaluated by measuring the ATP release after the aggregation induced by the indicated concentration of thrombin, U-46619, and ADP of human platelets preincubated with or without apelin-13 (10 μM). Results were expressed as the amount of ATP release by platelets from at least 3 independent experiments, and statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (***P < .001). (H) Aggregation of washed human platelets induced by thrombin (100 mU/mL) with or without incubation with apyrase (5 U/mL) and apelin-13 (10 μM). The relative percentage ± SEM of 3 independent experiments is expressed, and statistical significance was determined by 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test (**P < .01).
Effect of apelin on TXA2 synthesis and AA–induced aggregation
As shown in Figure 3E, thrombin induced TXA2 synthesis in platelets, whereas apelin inhibited its accumulation in resting and thrombin-activated platelets. TXA2 is a bioactive metabolite of arachidonic acid (AA), and inhibitors of cyclooxygenase prevent platelet aggregation induced by AA.29 Therefore, we evaluated the effect of apelin-13 on AA-induced platelet aggregation. As shown in Figure 3F (supplemental Figure 3), the presence of apelin-13 (10 μM) inhibited platelet aggregation induced by AA. This finding suggests that the inhibitory effect of apelin-13 occurs directly on TXA2 synthesis and not after alteration of the TXA2 receptor–mediated TXA2 signaling pathway. Indeed, platelet aggregation induced by U-46619 is not affected by apelin (Figure 1D-E).
Apelin inhibits platelet secretion
We next assessed the effect of apelin-13 on the secretion of dense granules by measuring the release of ATP by platelets induced by thrombin, U-46619, and ADP. The presence of apelin-13 inhibited ATP release by 85% after platelet activation by a low dose of thrombin. No effect of apelin-13 was observed after U-46619 and ADP stimulation and in the presence of increased concentration of thrombin (Figure 3G). Because ADP is secreted after platelet activation, we subsequently assessed whether apelin-13 could inhibit platelet function independent of secretion. To address this question, platelet aggregation was performed at a high dose of thrombin in the presence of apyrase, an ADP/ATP-degrading enzyme.30 As illustrated in Figure 3G, apelin-13 inhibited thrombin-induced platelet aggregation in the presence of apyrase, suggesting that apelin-13 is able to block platelet aggregation independent of granule secretion. Platelet aggregation induced by increased concentration of thrombin (Figure 1D-E) seemed to be inhibited by apelin-13 only after inhibition of ADP-induced platelet aggregation by apyrase (Figure 3H).
Mice lacking apelin have reduced tail-bleeding times
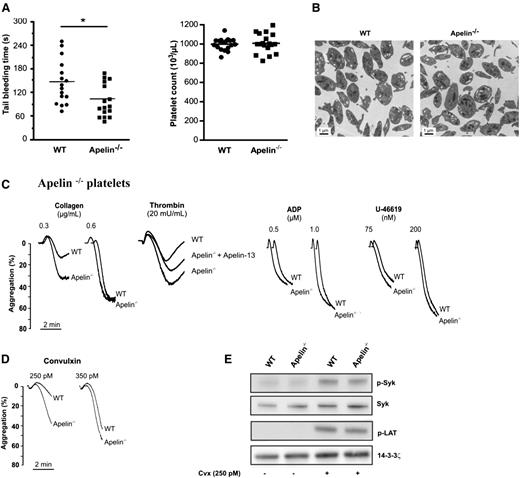
We first compared responses of WT mice to those lacking apelin in a tail-bleeding-time model. Bleeding times for apelin−/− mice were significantly shorter (99 ± 10 seconds vs 145 ± 14 seconds in WT mice; Figure 4A). Further analysis revealed that these differences were not linked to alterations in several hematologic parameters because apelin−/− and WT mice did not show any difference in number of platelets (Figure 4A), hematocrit, hemoglobin concentration, or in white blood cells (supplemental Table 1). Similarly, electron microscopy showed that resting apelin−/− platelets had a normal discoid morphology and a normal count of granules (Figure 4B). In addition, the expression of integrin αIIbβ3, GPIbα, GPVI, and integrin α2 was normal in apelin−/− platelets (supplemental Figure 4).
Reduced bleeding times in apelin−/− mice and aggregation of apelin−/− platelets. (A) Tail-bleeding times (left) and platelet count (right) in WT and apelin−/− mice. (B) Images of WT and apelin−/− platelet ultrastructure obtained by electron microscopy. Bar represents 1 μm. (C) Aggregation of washed WT and apelin−/− platelets induced by indicated concentration of collagen, thrombin, ADP, or U-46619. In several experiments, apelin−/− platelets were challenged with apelin-13 (10 μM). Traces are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. Results are expressed as the percentage change in light transmission with respect to the blank (buffer without platelets), set at 100%. (D) Aggregation of WT and apelin−/− platelets induced by convulxin (250 and 350 pM). Traces are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. Results are expressed as the percentage change in light transmission with respect to the blank (buffer without platelets), set at 100%. (E) Immunoblot of GPVI signaling by analysis of tyrosine phosphorylation of Syk (p-Syk) and LAT (p-LAT) in WT and apelin−/− platelets after activation for 2 min by 250 pM of convulxin (Cvx) in the presence of Leo.H4 (20 μg/mL) to prevent outside-in signaling induced by αIIbβ3 engagement, and in the presence of apyrase (5 U/mL) plus indomethacin (5 μM) to prevent platelet secretion. The expression of 14.3.3ζ was used as loading control. Results are representative of 3 experiments.
Reduced bleeding times in apelin−/− mice and aggregation of apelin−/− platelets. (A) Tail-bleeding times (left) and platelet count (right) in WT and apelin−/− mice. (B) Images of WT and apelin−/− platelet ultrastructure obtained by electron microscopy. Bar represents 1 μm. (C) Aggregation of washed WT and apelin−/− platelets induced by indicated concentration of collagen, thrombin, ADP, or U-46619. In several experiments, apelin−/− platelets were challenged with apelin-13 (10 μM). Traces are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. Results are expressed as the percentage change in light transmission with respect to the blank (buffer without platelets), set at 100%. (D) Aggregation of WT and apelin−/− platelets induced by convulxin (250 and 350 pM). Traces are representative of at least 3 independent experiments. Results are expressed as the percentage change in light transmission with respect to the blank (buffer without platelets), set at 100%. (E) Immunoblot of GPVI signaling by analysis of tyrosine phosphorylation of Syk (p-Syk) and LAT (p-LAT) in WT and apelin−/− platelets after activation for 2 min by 250 pM of convulxin (Cvx) in the presence of Leo.H4 (20 μg/mL) to prevent outside-in signaling induced by αIIbβ3 engagement, and in the presence of apyrase (5 U/mL) plus indomethacin (5 μM) to prevent platelet secretion. The expression of 14.3.3ζ was used as loading control. Results are representative of 3 experiments.
Aggregation capacity of apelin−/− platelets
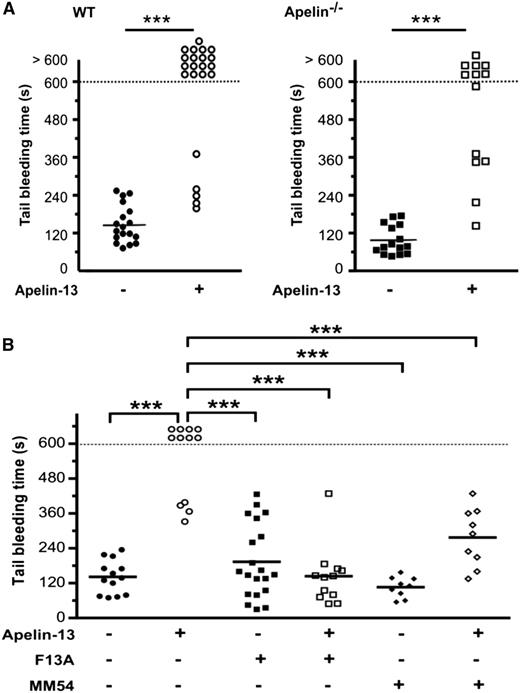
As illustrated in Figure 4C, apelin−/− platelets displayed increased aggregation after stimulation by low thrombin or collagen concentrations compared with WT platelets. In the presence of exogenous apelin-13, the aggregation of apelin−/− platelets induced by thrombin was reduced, indicating functional APJ receptors in apelin−/− platelets (Figure 4C). Under the same conditions, no difference in aggregation was observed between WT and apelin−/− platelets after ADP or U-46619 stimulation. Similar to the aggregations induced by thrombin or collagen, apelin−/− platelets exhibited an increase of aggregation after activation by convulxin, an agonist of the collagen receptor GPVI (Figure 4D). Analysis by western blotting of the phosphorylation of Syk and LAT, the first molecules involved in the signaling pathway of GPVI, did not show any differences in WT and apelin−/− platelets in response to convulxin (Figure 4E). The injection of WT mice with apelin-13 (50 nmol/kg) induced an increase in the bleeding time (Figure 5A), and 77% of mice that received an IV injection of apelin-13 exhibited a bleeding time of >10 minutes. Furthermore, the injection of apelin-13 in apelin−/− mice also led to a significant increase in bleeding time (Figure 5A), confirming functional APJ in these mice. Indeed, using F13A and MM54, it was revealed that IV injection of these inhibitors prevented the increased bleeding time induced by apelin-13 (Figure 5B).
Effect of apelin on bleeding time in apelin−/− mice and the role of APJ. (A) Tail-bleeding time in WT or apelin−/− mice receiving an IV injection of PBS (control; ●, ▪) or apelin-13 (50 nmol/kg; ○, □). (B) Tail bleeding-time in WT mice injected with PBS (●), apelin-13 (50 nmol/kg; ○), F13A (500 nmol/kg; ▪), F13A (500 nmol/kg) plus apelin-13 (50 nmol/kg; □), MM54 (500 nmol/kg; ♦), or MM54 (500 nmol/kg) plus apelin-13 (50 nmol/kg; ♢). Each symbol represents 1 individual, and horizontal lines indicate the mean. Statistical significance was determined by 2-tailed Mann-Whitney test (***P < .0001).
Effect of apelin on bleeding time in apelin−/− mice and the role of APJ. (A) Tail-bleeding time in WT or apelin−/− mice receiving an IV injection of PBS (control; ●, ▪) or apelin-13 (50 nmol/kg; ○, □). (B) Tail bleeding-time in WT mice injected with PBS (●), apelin-13 (50 nmol/kg; ○), F13A (500 nmol/kg; ▪), F13A (500 nmol/kg) plus apelin-13 (50 nmol/kg; □), MM54 (500 nmol/kg; ♦), or MM54 (500 nmol/kg) plus apelin-13 (50 nmol/kg; ♢). Each symbol represents 1 individual, and horizontal lines indicate the mean. Statistical significance was determined by 2-tailed Mann-Whitney test (***P < .0001).
Thrombus formation in apelin−/− mice
In vitro thrombus formation by apelin−/− platelets was studied by performing a whole-blood perfusion assay over a collagen matrix under various shear rates. Following perfusion at low shear rate (150 seconds−1), similar to hemodynamic conditions in venules, apelin−/− platelets exhibited a significantly increased adhesion to collagen (23.1 ± 5.8%) compared with WT platelets (4.5 ± 0.4%). Under these conditions, large thrombi formed that were not detected in WT platelets (Figure 6A). In contrast, under arterial shear rate (1200 seconds−1), the adhesion of WT and apelin−/− platelets was similar (11.4 ± 1.1% and 11.0 ± 1.3%, respectively). We next assessed the role of apelin in vivo in a FeCl3-induced thrombosis model by intravital microscopy (Figure 6B). We found that although occlusion time of arterioles was similar in WT and apelin−/− mice (27.0 ± 1.6 and 25.9 ± 1.0 minutes, respectively), in the venules of apelin−/− mice, the occlusion was significantly reduced (21.4 ± 2.0 minutes) compared with the venules of WT mice (29.1 ± 1.3 minutes).
Regulation of thrombus formation by apelin. (A) In vitro thrombus formation performed in a whole-blood perfusion assay of WT or apelin−/− mice over a fibrillar collagen matrix at a venous (150 seconds−1) or an arterial (1200 seconds−1) shear rate (left). Thrombus formation was quantitated by assessment of the mean percentage of the total area covered by thrombi ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments (right). Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (***P < .001). (B) In vivo thrombosis model in mesenteric vessels (venules [V] and arterioles [A]) of WT or apelin−/− mice after FeCl3-induced injury. Adhesion and thrombus formation of fluorescently labeled platelets were monitored by intravital video microscopy. Representative images of mesenteric vessels after 0, 20, and 30 minutes are shown (left). Occlusion times of the venules and arterioles in WT and apelin−/− mice are shown, with means indicated by horizontal lines (right). Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (**P < .01). (C) In vitro thrombus formation performed in a whole-blood perfusion assay of WT mice over a fibrillar collagen matrix at an arterial shear rate of 1200 seconds−1 in the presence of PBS (control) or apelin-13 (10 μM) (left). Results are expressed as the relative percentage ± SEM of the mean immunofluorescence intensity (IFI) of WT mice (right). Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (***P < .001). Adhesion and thrombus formation of fluorescently labeled platelets were monitored by intravital video microscopy after injection of PBS or apelin-13 (50 nmol/kg). (D) In vivo thrombosis model in mouse mesenteric vessels after FeCl3-induced injury. Representative images of mesenteric vessels after 0 and 30 minutes are shown (left). Occlusion times of the venules and arterioles are shown, with means indicated by horizontal lines (right). Statistical significance was determined by 1-way ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett test (***P < .001).
Regulation of thrombus formation by apelin. (A) In vitro thrombus formation performed in a whole-blood perfusion assay of WT or apelin−/− mice over a fibrillar collagen matrix at a venous (150 seconds−1) or an arterial (1200 seconds−1) shear rate (left). Thrombus formation was quantitated by assessment of the mean percentage of the total area covered by thrombi ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments (right). Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (***P < .001). (B) In vivo thrombosis model in mesenteric vessels (venules [V] and arterioles [A]) of WT or apelin−/− mice after FeCl3-induced injury. Adhesion and thrombus formation of fluorescently labeled platelets were monitored by intravital video microscopy. Representative images of mesenteric vessels after 0, 20, and 30 minutes are shown (left). Occlusion times of the venules and arterioles in WT and apelin−/− mice are shown, with means indicated by horizontal lines (right). Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (**P < .01). (C) In vitro thrombus formation performed in a whole-blood perfusion assay of WT mice over a fibrillar collagen matrix at an arterial shear rate of 1200 seconds−1 in the presence of PBS (control) or apelin-13 (10 μM) (left). Results are expressed as the relative percentage ± SEM of the mean immunofluorescence intensity (IFI) of WT mice (right). Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (***P < .001). Adhesion and thrombus formation of fluorescently labeled platelets were monitored by intravital video microscopy after injection of PBS or apelin-13 (50 nmol/kg). (D) In vivo thrombosis model in mouse mesenteric vessels after FeCl3-induced injury. Representative images of mesenteric vessels after 0 and 30 minutes are shown (left). Occlusion times of the venules and arterioles are shown, with means indicated by horizontal lines (right). Statistical significance was determined by 1-way ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett test (***P < .001).
Inhibition of thrombus formation by apelin
Inhibition of thrombus formation by apelin-13 was assessed in a whole-blood perfusion assay over a collagen matrix under arterial shear rate of 1200 seconds−1 (Figure 6C). Controls adhered to collagen matrix and rapidly built stable platelet aggregates. In contrast, apelin-13 induced a decrease in the size of thrombi by 59 ± 13% (P < .001). Using an FeCl3-induced mesenteric vessel injury thrombosis model (Figure 6D), we found that the injection of apelin-13 provoked a significant time delay of vessel occlusion, and sometimes largely prevented the complete vessel occlusion, due to the presence of unstable thrombi, whereas in control mice injected with PBS, the occlusion time was 30 ± 4 minutes for venules and 25 ± 5 minutes for arterioles.
The inhibitory effects of apelin-13 require apelin precursor processing
Human apelin exists in 36–, 17–, and 13–amino acid forms that are generated by proteolytic processing.8,11 The amino acid sequence of apelin-36 has 2 dibasic motifs (RRK and FRRQR) that are recognized by the proprotein convertases, suggesting the involvement of these proteases in the maturation of the different forms of apelin.31 Using cell transfection experiments, we revealed that apelin is a proprotein convertase substrate and mainly processed by furin (supplemental Figure 5). To evaluate the importance of apelin-36 processing in the mediation of its action on platelet function, we generated synthetic apelin-DM (supplemental Materials). We found that IV injection of apelin-36, apelin-13, or apelin-36 in the presence of apelin-13 induced a significant increase in the bleeding times, whereas apelin-DM injected alone had no effect. When apelin-DM was co-injected with apelin-13, it prevented the increase in bleeding time induced by apelin-13, suggesting an antagonistic effect of apelin-DM. (Figure 7A). Similarly, although apelin-13 and apelin-36 inhibited thrombin-induced platelet aggregation (Figure 7B) and thrombin-induced calcium mobilization (Figure 7C), apelin-DM abolished theses effects. These observations suggest that apelin’s effect on platelet function requires the processing of apelin-36 into apelin-13. In addition, we revealed that the unprocessed apelin-DM is able to antagonize the effects of apelin-13.
The inhibitory effects of apelin are dependent on apelin-13, but not on apelin-36. (A) Tail-bleeding time in WT mice injected with PBS (●), apelin-13 (50 nmol/kg; ○), apelin-36 (500 nmol/kg; △), apelin-DM (500 nmol/kg; ▪), apelin-36 plus apelin-13 (▲), or apelin-DM plus apelin-13 (□). Each symbol represents 1 individual, and statistical significance was determined by 2-tailed Mann-Whitney test (**P < .001). (B) Thrombin-induced aggregation of human platelets preincubated with PBS (black), apelin-13 (10 μM; white), apelin-36 (10 μM; dark gray), apelin-DM (100 μM; light gray), apelin-36 plus apelin-13 (angled lines), or apelin-DM plus apelin-13 (vertical lines). (C) [Ca2+] in human platelets preincubated with PBS (black), apelin-13 (10 μM; white), apelin-36 (100 μM; dark gray), apelin-DM (100 μM; light gray), apelin-36 plus apelin-13 (angled lines), or apelin-DM plus apelin-13 (vertical lines). In panels B and C, the relative percentage ± SEM of 3 independent experiments is expressed, and statistical significance was determined by 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test (*P < .05; **P < .001). (D) Schematic representation of the proposed mechanism regulating platelet activity by apelin in the presence of agonists. After interaction of apelin with its platelet APJ receptor, the latter mediates cGMP production through an NO-dependent mechanism that increased the level of cGMP produced in thrombin-activated platelets, which in turn inhibits platelet activation/aggregation. Apelin also inhibits Ca2+ mobilization induced by thrombin and collagen receptor activation. The inhibition of TXA2 synthesis by apelin is also involved in the inhibition of platelet activity because U-46619, an analog of TXA2, mediated platelet activity in the presence of apelin. ADP-induced platelet activation is not affected by apelin. GTP, guanosine triphosphate; PARs, protease-activated receptors; TPα, TXA2 receptor α isoform; P2Y1, P2Y purinoceptor 1.
The inhibitory effects of apelin are dependent on apelin-13, but not on apelin-36. (A) Tail-bleeding time in WT mice injected with PBS (●), apelin-13 (50 nmol/kg; ○), apelin-36 (500 nmol/kg; △), apelin-DM (500 nmol/kg; ▪), apelin-36 plus apelin-13 (▲), or apelin-DM plus apelin-13 (□). Each symbol represents 1 individual, and statistical significance was determined by 2-tailed Mann-Whitney test (**P < .001). (B) Thrombin-induced aggregation of human platelets preincubated with PBS (black), apelin-13 (10 μM; white), apelin-36 (10 μM; dark gray), apelin-DM (100 μM; light gray), apelin-36 plus apelin-13 (angled lines), or apelin-DM plus apelin-13 (vertical lines). (C) [Ca2+] in human platelets preincubated with PBS (black), apelin-13 (10 μM; white), apelin-36 (100 μM; dark gray), apelin-DM (100 μM; light gray), apelin-36 plus apelin-13 (angled lines), or apelin-DM plus apelin-13 (vertical lines). In panels B and C, the relative percentage ± SEM of 3 independent experiments is expressed, and statistical significance was determined by 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test (*P < .05; **P < .001). (D) Schematic representation of the proposed mechanism regulating platelet activity by apelin in the presence of agonists. After interaction of apelin with its platelet APJ receptor, the latter mediates cGMP production through an NO-dependent mechanism that increased the level of cGMP produced in thrombin-activated platelets, which in turn inhibits platelet activation/aggregation. Apelin also inhibits Ca2+ mobilization induced by thrombin and collagen receptor activation. The inhibition of TXA2 synthesis by apelin is also involved in the inhibition of platelet activity because U-46619, an analog of TXA2, mediated platelet activity in the presence of apelin. ADP-induced platelet activation is not affected by apelin. GTP, guanosine triphosphate; PARs, protease-activated receptors; TPα, TXA2 receptor α isoform; P2Y1, P2Y purinoceptor 1.
Discussion
In this study, we provide evidence for apelin’s role in the maintenance of normal hemostasis. Apelin−/− mice displayed unstable hemostasis and had shorter bleeding times and a prothrombotic phenotype, with predominant effects under venular shear conditions (Figure 4). Accordingly, IV-injected apelin-13 prolonged bleeding time and prevented thrombosis in mice (Figures 5 and 6). In vitro experiments revealed that exposure of platelets to apelin inhibits their activation mediated by thrombin and collagen but not by ADP and TXA2 (Figure 7D).
Previously, apelin was reported to be expressed by various cell types and found in plasma.5 Therefore, in our experiments, we cannot exclude that plasmatic apelin or that derived from endothelial cells activated near the thrombus formation may participate in platelet function. Because apelin is expressed in platelets and purified platelets from apelin−/− mice show increased aggregation, it suggests that platelet apelin is directly involved in platelet activation regulation. Similarly, exposure of platelets to apelin inhibits their activation and function by interfering with integrin αIIbβ3 activation and platelet secretion (Figure 2A-B). Accordingly, IV-injected apelin-13 prolonged bleeding time and prevented thrombosis, likely by acting on thrombus stabilization (Figures 5 and 6).
Platelet activation is achieved through various surface receptors that include G protein–coupled receptors, integrins, and GP receptors.30 Activation of these receptors is mainly mediated by the strong agonists thrombin and collagen, whereas other mediators released from activated platelets, such ADP and TXA2, potentiate the activation cascade by recruiting other platelets.32,33 In our model, apelin was found to inhibit activation of platelets induced by thrombin and collagen but not by ADP or U-46619 (Figure 7D). Of interest, at high thrombin doses, apelin inhibited the thrombin effect only after apyrase-mediated ADP pathway inhibition, suggesting the potential combined action of ADP pathway inhibition and apelin in the blockade of thrombin-induced platelet aggregation (Figures 1D-E and 3H). Analysis of elevation in calcium, understood as the immediate consequence of thrombin stimulation and a crucial event in platelet activation, revealed that apelin inhibited calcium mobilization mediated by collagen and thrombin receptor activation (Figure 2C,E). The use of wortmannin, a nonspecific PI3K inhibitor reported to cross-react with various PI3K-related proteins25 and able to inhibit platelet activation, failed to alter apelin-mediated calcium mobilization blockade. Further analysis revealed that apelin reduced TXA2 synthesis, induced cGMP production, and failed to induce cAMP in resting and activated platelets (Figure 3B). Of interest, although the stimulatory effect of apelin on cGMP was reported for various cell types,34,35 apelin was found to induce or inhibit cAMP.36,37 In the presence of thrombin, platelets increased their cGMP accumulation, which further increased in the presence of apelin (Figure 3B). Previously, cGMP was reported to have a biphasic response in platelets: an initial, transient effect associated with the activation/aggregation of platelets, and a delayed mechanism associated with platelet inhibition.38 This biphasic role of cGMP in platelet activation depended on the level of cGMP induced in platelets. Although cGMP promotes platelet activation at low concentrations, it becomes inhibitory at high concentrations.38,39 Indeed, in our model, platelet activation blockade was found to associate with increased cGMP level, as compared with untreated or apelin-treated cells. Recently, this biphasic role was linked to sGC, an intracellular receptor for NO.38 Apelin was also reported to induce the NO-cGMP cascade,40 suggesting cGMP involvement in the apelin-mediated platelet activation blockade. Indeed, using the NOS inhibitor NG-methyl-L-arginine, we inhibited the cGMP accumulation induced by apelin (Figure 3C). In our model, this biphasic response of cGMP may serve as a mechanism to adjust platelet activation, whereby cGMP plays a stimulatory role at physiologic concentration (produced by platelets) and an inhibitory role at higher concentrations induced by apelin in thrombin-activated platelets. Several agents that activate sGC were suggested to prevent thrombotic diseases.41 The reasons for the variation in the observed effect of apelin in the presence of thrombin and ADP/TXA2 are not clear, but several mechanisms may be postulated. Differences in the chronological implication of these platelet activators and their intracellular signaling may be contributing factors, because platelet aggregation is a sequential process, with reversible and irreversible steps.42-44 Therefore, inhibition of thrombin by apelin may affect all potential thrombin downstream effectors involved in platelet activation. Furthermore, the inability of apelin to inhibit platelet activation in the presence of TXA2 or ADP may be related to ADP/TXA2 intracellular signaling pathways that are not regulated by apelin or to those that may interfere with the apelin signaling. A likely scenario may involve the inability of apelin to inhibit calcium mobilization induced in ADP- or U-46619–activated platelets (Figures 2D,F and 7D). In addition, the inhibition of TXA2 production by apelin after collagen and thrombin receptor activation seems to be also involved in platelet activation blockade by apelin, because U-46619 is able to activate platelets in the presence of apelin (Figures 1C,E and 7D). To date, the inhibition of platelet activation induced by TXA2 and P2Y12 (ADP receptor) with aspirin and clopidogrel, respectively, is the main treatment of recurrent thrombotic complications in patients.45,46 However, these complications may continue to occur despite the use of these antiplatelet treatments. The reason for this can be explained by the existence of multiple pathways contributing to platelet activation and aggregation that are not inhibited by aspirin or P2Y12 antagonists, as in the case of thrombin-mediated pathways. In addition, a large number of patients have shown inadequate response to aspirin and clopidogrel therapy.45,46 Therefore, targeting the thrombin-mediated platelet activation pathway was recently proposed not only as an alternative but also as an additional therapy. In several preclinical studies, blocking of the thrombin receptor protease-activated receptor 1 by several compounds such as vorapaxar and atopaxar was suggested as a promising adjunct therapy.46-49 In our study, apelin was found to mainly inhibit thrombin- and collagen-mediated platelet activation (Figure 7D), suggesting the potential use of this naturally occurring inhibitor (and/or its derivatives) of platelet activation in therapy. In conclusion, we demonstrate in the present work a new biological function of apelin peptide that inhibits platelet activation and aggregation mainly induced by thrombin and collagen. This opens new avenues in the pathophysiology of thrombotic or hemorrhagic diseases and for the development of novel antiaggregant therapies. In addition, apelin or its derivatives may serve for the prevention of thrombin-mediated platelet activation side effects common to various currently used antiplatelet therapies.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank R. Glen (Cambridge, United Kingdom) for providing MM54; J. C. Bordet (Hôpital Herriot, Lyon, France) for standard electron microscopy; C. Denis (INSERM U1176, Le Kremlin-Bicêtre, France) for providing murine von Willebrand factor; and R. Nookala (Institut Bergonié, Bordeaux, France) for reading the manuscript.
This work was supported by INSERM, University of Bordeaux, Région Aquitaine, and Institut National pour la Recherche contre le cancer (2009-1-PL BIO-09); a postdoctoral fellowship from Société Francophone du Diabète (F.A.); a Junta de la Cerva Program (JCI_2012-12934) (J.J.L.); Région Ile de France (C.V.); and by La Ligue Contre le Cancer Region Aquitaine.
Authorship
Contribution: F.A., A.-M.K., B.F., and G.S. designed the research, performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper; J.J.L., C.V., S.T., A.M., F.S., A.A., R.B., C.D., P.V., and I.J. performed the experiments and analyzed the data; P.V. provided the apelin−/− mice; and A.S., D.d.P., and J.A.R. participated in the research.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Geraldine Siegfried, University of Bordeaux, INSERM U1029, Bat B2 Rdc Cote Ouest, Allée Geoffroy St Hilaire, 33615 Pessac Cedex, France; e-mail: geraldine.siegfried@inserm.fr.
References
Author notes
F.A. and A.-M.K. contributed equally to this study.

![Figure 6. Regulation of thrombus formation by apelin. (A) In vitro thrombus formation performed in a whole-blood perfusion assay of WT or apelin−/− mice over a fibrillar collagen matrix at a venous (150 seconds−1) or an arterial (1200 seconds−1) shear rate (left). Thrombus formation was quantitated by assessment of the mean percentage of the total area covered by thrombi ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments (right). Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (***P < .001). (B) In vivo thrombosis model in mesenteric vessels (venules [V] and arterioles [A]) of WT or apelin−/− mice after FeCl3-induced injury. Adhesion and thrombus formation of fluorescently labeled platelets were monitored by intravital video microscopy. Representative images of mesenteric vessels after 0, 20, and 30 minutes are shown (left). Occlusion times of the venules and arterioles in WT and apelin−/− mice are shown, with means indicated by horizontal lines (right). Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (**P < .01). (C) In vitro thrombus formation performed in a whole-blood perfusion assay of WT mice over a fibrillar collagen matrix at an arterial shear rate of 1200 seconds−1 in the presence of PBS (control) or apelin-13 (10 μM) (left). Results are expressed as the relative percentage ± SEM of the mean immunofluorescence intensity (IFI) of WT mice (right). Statistical significance was determined by unpaired Student t test (***P < .001). Adhesion and thrombus formation of fluorescently labeled platelets were monitored by intravital video microscopy after injection of PBS or apelin-13 (50 nmol/kg). (D) In vivo thrombosis model in mouse mesenteric vessels after FeCl3-induced injury. Representative images of mesenteric vessels after 0 and 30 minutes are shown (left). Occlusion times of the venules and arterioles are shown, with means indicated by horizontal lines (right). Statistical significance was determined by 1-way ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett test (***P < .001).](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/127/7/10.1182_blood-2014-05-578781/4/m_908f6.jpeg?Expires=1769525251&Signature=c~ctCp7Y1CrX4d7gYnrmJqsT0cAILcoXmKqHofGN7d2tIMDVNGBUnrurScqodCEUYXQpxGOUttipIqqUsnQ2fCWZVa86vpiHxCGCKsyS0~RFre960pQYqWzHrOAy7Oxir1RwsXBSdvxfnmMLynfQGKktgBm1CzH55-NB5MaeQv2uSA26kDreQ2WnwntKdJRds~P7tHx-Ia65-18sYMlYBikwRWmtOwarTlH4ruUbLQBZ-1IMp5IOne~uwJRwVQrZDSbWKAOGA8w2gecMy6eQV8kyVGH8zfRYrkZA3NaP9tf0I~Y7jiS-VT~LgKx33iE2IpHBTONaKW~A218nP2WW6Q__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
![Figure 7. The inhibitory effects of apelin are dependent on apelin-13, but not on apelin-36. (A) Tail-bleeding time in WT mice injected with PBS (●), apelin-13 (50 nmol/kg; ○), apelin-36 (500 nmol/kg; △), apelin-DM (500 nmol/kg; ▪), apelin-36 plus apelin-13 (▲), or apelin-DM plus apelin-13 (□). Each symbol represents 1 individual, and statistical significance was determined by 2-tailed Mann-Whitney test (**P < .001). (B) Thrombin-induced aggregation of human platelets preincubated with PBS (black), apelin-13 (10 μM; white), apelin-36 (10 μM; dark gray), apelin-DM (100 μM; light gray), apelin-36 plus apelin-13 (angled lines), or apelin-DM plus apelin-13 (vertical lines). (C) [Ca2+] in human platelets preincubated with PBS (black), apelin-13 (10 μM; white), apelin-36 (100 μM; dark gray), apelin-DM (100 μM; light gray), apelin-36 plus apelin-13 (angled lines), or apelin-DM plus apelin-13 (vertical lines). In panels B and C, the relative percentage ± SEM of 3 independent experiments is expressed, and statistical significance was determined by 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test (*P < .05; **P < .001). (D) Schematic representation of the proposed mechanism regulating platelet activity by apelin in the presence of agonists. After interaction of apelin with its platelet APJ receptor, the latter mediates cGMP production through an NO-dependent mechanism that increased the level of cGMP produced in thrombin-activated platelets, which in turn inhibits platelet activation/aggregation. Apelin also inhibits Ca2+ mobilization induced by thrombin and collagen receptor activation. The inhibition of TXA2 synthesis by apelin is also involved in the inhibition of platelet activity because U-46619, an analog of TXA2, mediated platelet activity in the presence of apelin. ADP-induced platelet activation is not affected by apelin. GTP, guanosine triphosphate; PARs, protease-activated receptors; TPα, TXA2 receptor α isoform; P2Y1, P2Y purinoceptor 1.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/127/7/10.1182_blood-2014-05-578781/4/m_908f7.jpeg?Expires=1769525251&Signature=sJkH4hlZUfI8KfW~Y1HYiP5BI-VDdepUqLJzzYQiLSwSJUuTdYOFy~DaGrOntbYcir4IJgG5gxLyZn4GMBr~yPDKF~vQT81u3~-y08ChfvUpEkxliaJtNslDtUlWnpOR5dRf7GW0IcxjwzEwx5~8Gex2O3rE~Fv8JMnfDMj8U085tEGE7o8Fvnl27nQiKvy316JkcUAXmgaec7Em5tjjhTdYk65tWN7C3EghqjAfxPWgePCOlyZWZf~Z7Q4dm7Bn34IbQiYPaAyLRijYNwmZpqovuwyg5pA9d9sNF8~adZ6a5xHXnWBOWDa0YB3S~FUPbr6bF12Y9DpfS6u0WDel5Q__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)