To the editor:
Based on the results of the PARMA and CORAL studies, high-dose chemotherapy (HDT) followed by autologous stem cell rescue has become the standard of care for patients with relapsed, chemosensitive aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL).1,2 Moreover, HDT/autologous stem cell rescue is considered the therapy of choice for Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) patients in chemosensitive relapse.3 However, HDT/autologous stem cell rescue is hampered by several major pitfalls, namely the toxicity related to the procedure and the lack of efficacy in chemoresistant patients.
We previously demonstrated the safety of a new HDT regimen with bendamustine, etoposide, cytarabine, and melphalan (BeEAM) prior to autologous stem cell rescue in 43 patients with resistant/relapsed lymphoma.4 The characteristics of patients are reported in the previously published paper.4 The study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, Good Clinical Practice (ICH-GCP), and the current national guidelines for conducting clinical studies. The protocol was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee. All subjects gave written informed consent. The study was registered at the European Medicines Agency with the European Clinical Trials Database number 2008-002736-15. Transplant-related mortality was 0%. The cumulative incidence of infectious complications was approximately 60%, without any serious adverse events (grades 3-4). Furthermore, this regimen showed significant antilymphoma activity, with 80% of patients being in complete remission after transplant.5 Disease type (NHL vs HL) and disease status at transplant (chemosensitive vs chemoresistant) were the only statistically significant variables influencing progression-free survival (PFS), whereas disease status at transplant was the only variable affecting overall survival (OS) at the time of writing.4 However, the primary objective of the study was to determine the 36-month PFS rate, according to Fleming’s method ([p0] = 40%, [p1] = 60%, α = 0.05, and 1-β = 0.80). At the time of publication, the median follow-up for surviving patients was short (18 months), and therefore, it was not possible either to establish if we had met the primary end point of the study or to draw final conclusions on the efficacy of this regimen.
With this in mind, we updated the follow-up at 41 months after transplant in order to evaluate the midtime efficacy of the BeEAM regimen in terms of PFS and OS. Responses were again evaluated according to the criteria reported elsewhere by Cheson et al.5 At present, 31/43 patients are still in complete remission (72%), as documented by both PET and CT scans. Two patients (4.6%) were refractory to the HDT regimen and rapidly died after HDT/autologous stem cell rescue, whereas 10/43 patients achieving at least a partial response (23%) relapsed after a median time of 7.5 months (range, 4-23 months) after HDT/autologous stem cell rescue. Five of those 10 patients died (3 NHL, 2 HL), and 5 patients are still alive after relapse.
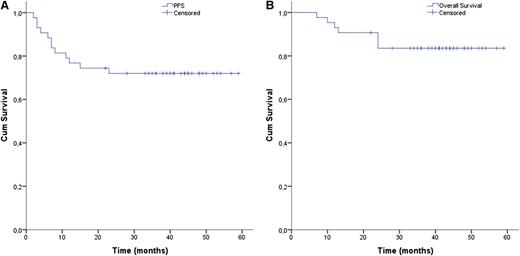
Median PFS and OS were still not reached (Figure 1A-B). Conversely, 3-year PFS was 72%, allowing our study to meet its primary end point (p[1]=60%). Interestingly, disease type (HL vs NHL) at transplant is no longer influencing PFS, and still does not influence OS. On the other hand, disease status at transplant (chemosensitive vs chemoresistant) is confirmed as a strong predictor of both PFS and OS (P = .002 and P = .009, respectively). However, the study was not designed to have the statistical power to compare disease entities, and therefore, the possible effect of HDT/autologous stem cell rescue regimen on disease type should be interpreted with caution, and needs additional confirmation in further trials. At present, 1 patient developed myelodysplasia after transplant. No other late effects were observed up to now.
Cumulative survival rates for Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin resistant/relapsed lymphoma patients treated with bendamustine, etoposide, cytarabine and melphalan followed by autologous stem cell rescue. (A) Progression-free and (B) overall survival of all patients.
Cumulative survival rates for Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin resistant/relapsed lymphoma patients treated with bendamustine, etoposide, cytarabine and melphalan followed by autologous stem cell rescue. (A) Progression-free and (B) overall survival of all patients.
Following the publication of the randomized CORAL study, whose results were less favorable than those reported in nonrandomized studies,6 it has become critical to evaluate novel and effective HDT schedules in order to increase the number of clinical responses among relapsed/refractory lymphoma patients.7 In this regard, by meeting the primary end point of our BeEAM study, we showed that well-designed clinical trials incorporating new drugs in well-established HDT regimens may increase the number of lymphoma patients who become long-term survivors. This study provides the proof of principle for testing the BeEAM regimen in randomized phase 2-3 studies.
Authorship
Acknowledgments: The authors thank Mundipharma (Italy) for providing bendamustine free of charge. This study was supported in part by AIL Pesaro Onlus.
Contribution: G.V. and A.I. equally proposed, designed, and supervised the study and wrote the manuscript; L.M., P.M.S., S.C., P.G., F.G., G.S., G.M., F.G., R.G., M.G., A.S., and F.F. treated the patients, collected the data, and commented on the manuscript; M.R., F.L., and A.I. were responsible for statistical analysis; and E.M.O. and M.D.C. commented on the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Giuseppe Visani, Hematology and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Center, San Salvatore Hospital, Via Lombroso, 61100 Pesaro, Italy; e-mail: pesarohematology@yahoo.it.
References
Author notes
G.V. and A.I. contributed equally to this study.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal