Abstract
Infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is an orphan disease with unmet need for safe effective therapies. This is an urgent problem because conventional chemotherapies are ineffective and have life-threatening toxicities in infants. Although the MLL rearrangements occurring in 75% of cases are associated with poor outcome, survival is inferior whether MLL is rearranged or not. We recently reported that infant ALL proved sensitive to obatoclax mesylate (GeminX Pharmaceuticals; now an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.) in vitro regardless of poor prognostic features including MLL gene rearrangement. Moreover, we showed that the leukemia cell killing by obatoclax involved apoptosis, necroptosis and autophagy (Urtishak et al., Blood 2013). Therefore, the recent pharmaceutical abandonment of obatoclax led us to search for similarly acting drugs, the Results of which identified the well-known antipsychotic thioridazine as a candidate for potential repurposing.
Correlative analyses were performed between basal gene expression profiles at leukemia diagnosis and single agent obatoclax EC50 values from MTT assays in 47 cases of infant ALL from the Children's Oncology Group P9407 trial (25 MLL-AF4; 8 MLL-ENL; 7 other MLL-rearranged; 7 MLL-germline) in order to find a priori determinants of obatoclax sensitivity; significant genes were further studied by Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA). A search for similarly acting compounds was conducted by Connectivity Map analysis of gene expression profiles of MLL-AF4 ALL cell lines after obatoclax treatment. MTT assays without and with cell death pathway inhibition, Western blot and flow cytometric cell death assays, and phosphoflow cytometric signaling analyses were utilized to investigate activity and target modulation by potential candidates.
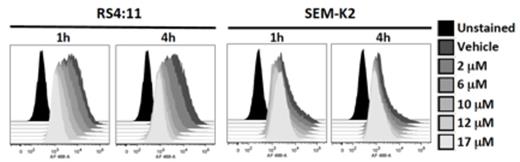
IPA identified significant correlations between basal gene expression of the mTOR and downstream intersecting eIF4/p70S6K signaling programs and obatoclax EC50 in all 47 primary cases of infant ALL, as well as in the subset of the 25 cases with MLL-AF4 rearrangements. Consistent with the relevance of this pathway in leukemia cell killing that was suggested by the basal gene expression profiles in the primary cases, the Connectivity Map analysis of obatoclax-treated cell lines for compound matching returned a number of highly ranked PI3K/AKT/mTOR signal transduction inhibitors as potential obatoclax substitutes. Three of the compounds (LY294002, wortmannin, thioridazine) were not only cytotoxic in MLL-AF4 ALL cell lines, but also they abrogated PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling as indicated by robust inhibition of phosphorylated S6. Of these compounds, the phenothiazine derivative thioridazine, which has been used clinically for decades as a neuroleptic, was of high interest because of potential advantages of drug repurposing for more rapid drug advancement. Moreover, detailed flow cytometric and Western blot analyses, and MTT assays of thioridazine in the presence of cell death pathway inhibitors validated activation of all three cell death mechanisms in the MLL-AF4 ALL cell lines similarly to obatoclax.
Thioridazine is a well-known antipsychotic drug that also has recently recognized properties as a PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling inhibitor and as an inhibitor of other pathways relevant to cancer. In MLL-AF4 ALL cell lines characterized by the most common chromosomal translocation in infant ALL, single-agent thioridazine is highly cytotoxic, robustly inhibits PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling and, moreover, like obatoclax, demonstrates activity as a multi-cell-death pathway agonist. Further preclinical studies now are warranted to determine the extent to which thioridazine inhibits PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling and causes leukemia cell killing in primary infant ALL cells in vitro and in vivo. The repurposing strategy that this drug may allow could have promise to streamline drug development in infant ALL where the need for new therapies is so urgent.
Phospho-S6 inhibition by thioridazine in MLL-AF4 cell lines.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal