Abstract
Abstract 1864
In addition to determining the efficacy and safety of different treatment options for MM, the impact of treatment and associated toxicities on patient-reported QoL should be evaluated. The US community-based phase 3b UPFRONT study compares the efficacy and safety of three bortezomib (VELCADE®, Vc)-based regimens, Vc-dexamethasone (VcD), Vc-thalidomide-dexamethasone (VcTD), and Vc-melphalan-prednisone (VcMP), followed by weekly Vc maintenance, in elderly, newly diagnosed, transplant-ineligible MM patients. Updated efficacy and safety data are reported elsewhere at this meeting; here we present patient-reported QoL results – a secondary endpoint of the trial – from all 502 randomized patients, who received up to a maximum of 13 treatment cycles.
Patients with symptomatic MM were randomized (1:1:1) to receive eight 21-day cycles of VcD (Vc 1.3 mg/m2, days 1, 4, 8, 11; D 20 mg, days 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 9, 11, 12 [cycles 1–4]), days 1, 2, 4, 5 [cycles 5–8]), VcTD (Vc as before; T 100 mg/day, days 1–21; D as before), or VcMP (Vc as before; M 9 mg/m2, and P 60 mg/m2, days 1–4, every other cycle) induction, followed by five 35-day cycles of maintenance with Vc 1.6 mg/m2, days 1, 8, 15, 22. QoL was assessed using the EORTC QLQ-C30 questionnaire, which includes global health status, physical, role, cognitive, emotional, and social functioning, and symptom scales of fatigue, nausea/vomiting, pain, dyspnea, insomnia, appetite loss, constipation, diarrhea, and financial difficulties. Global health status scores combine overall health and QoL scores, with higher scores reflecting better health status. Questionnaires were completed prior to dosing on day 1 of cycle 1 (baseline), prior to dosing on day 1 of every odd-numbered cycle, at the end-of-treatment visit, and every 12 weeks until progressive disease. Patient-reported QoL scores presented herein represent data collected within 1 year of randomization regardless of discontinuation status; for patients who died, missing assessments were assigned the worst possible score of 0. A linear mixed effect model was used to assess QoL changes over time, both within and between treatment arms. Sensitivity analyses were conducted to test the robustness of the primary analysis.
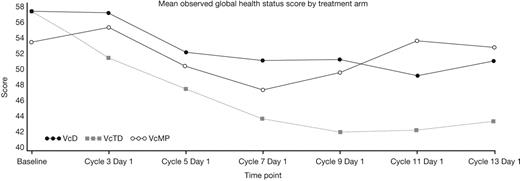
Patient baseline characteristics were well balanced across the VcD (n=168), VcTD (n=167), and VcMP (n=167) arms as reported previously (Niesvizky et al, EHA 2011). Median age was 74.5 (VcD), 73.0 (VcTD), and 72.0 (VcMP) years, and 71%, 62%, and 72% of patients had ISS stage II/III disease. QoL assessments were available at baseline and ≥1 post-baseline time point for 78% (VcD), 69% (VcTD), and 78% (VcMP) of patients. Observed data showed a downward trend in mean global health status score until cycle 7 (VcD, VcMP) or 9 (VcTD), followed by a trend to stabilizing/improving score thereafter (Figure). Symptom scores changed very little during induction in all arms, except for nausea/vomiting and diarrhea, with moderate improvements seen during maintenance. After fitting observed data with a linear mixed effect model, a significant decrease in mean global health status score from baseline to cycle 7 (induction period) was evident in all arms (VcD, p=0.0127; VcTD, p<0.0001; VcMP, p=0.0157), but there were no significant inter-arm differences. During cycles 9–13 (maintenance period), mean global health status scores remained decreased from baseline in the VcD and VcTD arms, and there were significant differences between VcTD and VcMP, with lower scores in the VcTD arm. Sensitivity analyses incorporating patients' QoL data collected after discontinuation of treatment (for patients who discontinued within 1 year) and utilizing a last observation carried forward approach, gave similar results to the linear mixed effect model.
The observed data, linear mixed model estimates, and sensitivity analyses all show a common trend to a transient decrease in QoL during VcD, VcTD, and VcMP induction followed by a subsequent trend to improvement/stabilization in QoL during single-agent Vc maintenance. The trend to decreasing QoL seen during Vc-based induction may reflect the onset of treatment-related toxicities (particularly for VcTD, which was associated with somewhat higher toxicity rates). Post-induction improvements/stabilization in QoL may reflect the beneficial impact of achieving a response and the limited toxicity profile associated with weekly Vc maintenance.
Niesvizky:Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Onyx: Research Funding. Flinn:Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Research Funding. Rifkin:Onyx: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau. Charu:Pfizer: Equity Ownership; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Equity Ownership; Roche: Research Funding; GSK: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Equity Ownership, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Neuwirth:Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Employment. Huang:Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc: Employment. Choi:Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Employment. Corzo:Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal